Last Updated on November 4, 2025 by mcelik

Achilles tendonitis is a common issue for athletes and non-athletes. It causes pain and discomfort that can affect daily life. Interestingly, nearly 1 in 5 people with Achilles tendon pain may wait over a year to get help.
The recovery time for Achilles tendonitis varies a lot. It depends on how bad the condition is and how well the treatment works. Knowing how long Achilles tendonitis usually lasts is key. It helps set realistic goals and make better care choices.
Achilles tendonitis is a condition that affects the Achilles tendon. This tendon connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. It causes inflammation and irritation.
The Achilles tendon is a strong, fibrous cord. It helps us walk, run, and jump. It’s made of collagen fibers and can handle a lot of stress. But, it can also get injured or inflamed, often in people who do repetitive activities or suddenly start exercising more.
Many things can lead to Achilles tendonitis. These include:
Knowing these risk factors helps prevent and manage chronic Achilles tendonitis. It also helps avoid Achilles tendonitis complications.

Knowing how long Achilles tendonitis takes to heal is key. This condition causes pain and inflammation in the Achilles tendon. It can really affect your life and sports performance.
The time it takes to heal depends on several things. These include how bad the condition is, the treatment, and your overall health. Acute cases usually have a clearer recovery time than chronic ones.
Acute Achilles tendonitis happens suddenly, often from a strain or injury. The first healing phase is 2 to 4 weeks. During this time, rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) are very important.
The total recovery time for acute cases can be 6 to 12 weeks. This depends on how well the treatment works and if you follow the rehab plan.
The healing process for Achilles tendonitis has several stages:
Proper healing means less pain and better function. A good rehab plan includes rest, physical therapy, and slowly getting back to activities. This is essential for the best recovery.
| Recovery Phase | Timeline | Key Interventions |
| Acute | 0-2 weeks | Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation (RICE) |
| Sub-acute | 2-6 weeks | Stretching, Strengthening Exercises |
| Remodeling | 6-12 weeks | Progressive Loading, Functional Training |
Understanding the healing process of Achilles tendonitis helps you manage your treatment. This way, you can achieve a better recovery outcome.
It’s important to know the difference between acute and chronic Achilles tendonitis. This knowledge helps in treating and managing the condition. Achilles tendonitis can really affect someone’s life, and knowing if it’s acute or chronic is key to getting better.
Acute Achilles tendonitis happens when the tendon gets inflamed and painful right away. It’s usually caused by a sudden injury or too much use. Quick treatment is needed to stop it from becoming chronic.
Chronic Achilles tendonitis happens when acute tendonitis isn’t treated right. It leads to long-term inflammation and damage to the tendon. This stage has ongoing pain, stiffness, and less function. Turning chronic can make treatment harder.
The 6 to 8 week mark is very important for Achilles tendonitis. If it lasts longer, it’s likely becoming chronic. Acting fast in this time is key to avoiding lasting harm.
Knowing the signs of chronic tendonitis and the 6-8 week mark is vital. It helps people get medical help early. This can stop the condition from lasting a long time.
The time it takes to recover from Achilles tendonitis depends on several factors. Knowing these can help manage the condition better and shorten recovery time.
Age is a big factor in how long it takes to heal from Achilles tendonitis. Older people often take longer to recover because their tendons are less flexible and blood flow is reduced. Older adults may need more time to heal and might need gentler treatments.
What you do and how often you do it also matters. Jobs or hobbies that stress the Achilles tendon a lot, like running or construction work, can make symptoms last longer. Changing how much you do and taking breaks can help shorten recovery time.
Health issues like diabetes or arthritis can slow down healing. These conditions can mess with blood flow, collagen making, and tendon health, making recovery take longer. It’s important to manage these conditions well for faster healing.
Following the treatment plan is key to getting better. Not sticking to the treatment, like physical therapy or orthotics, can make symptoms last longer. Sticking to the treatment plan can greatly improve recovery chances.
In summary, how long Achilles tendonitis lasts depends on age, activity level, job, health conditions, and following treatment. By understanding and tackling these factors, people can manage their condition better and recover faster.
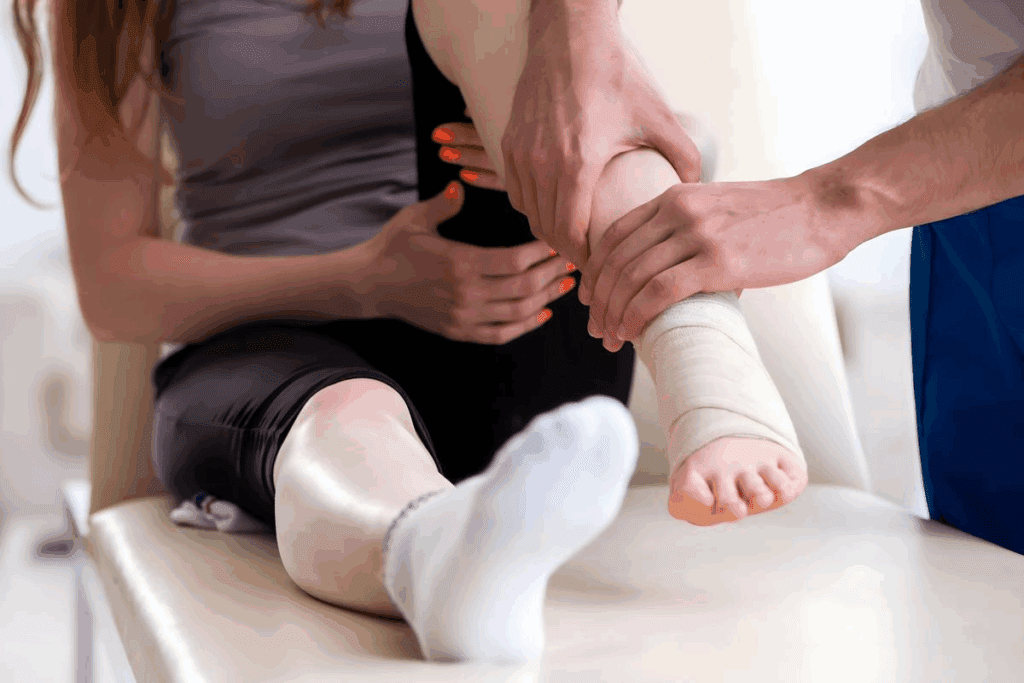
It’s important to know the signs of Achilles tendonitis that won’t heal. If it takes longer than expected, it might mean there’s a bigger problem. You should see a doctor.
Pain that lasts more than 6-8 weeks is a red flag. It could be a sign that your tendonitis is not healing right. You might feel a dull ache or sharp pain, often after you’ve been active or at night.
Watching your pain levels is key. If your pain doesn’t get better or gets worse, don’t ignore it.
Getting worse symptoms like more swelling, redness, or warmth around the tendon is a bad sign. It could mean you’re using it too much, not treating it right, or have another issue.
| Symptom | Description | Potential Implication |
| Increased Swelling | Visible swelling around the Achilles tendon | Inflammation or fluid buildup |
| Redness and Warmth | Redness and warmth to the touch around the tendon | Possible infection or significant inflammation |
| Pain During Activity | Pain or discomfort during or after activity | Tendon strain or overuse |
Changes in the tendon, like thickening or degeneration, can mean chronic tendonitis. These changes can show up on tests like ultrasound or MRI.
If you see any of these signs, see a doctor right away. They can help figure out what’s wrong and how to fix it. Early action can stop things from getting worse and help your tendon heal.
Untreated Achilles tendonitis can lead to serious problems. It can affect the tendon and make moving around harder. This can also lower your quality of life.
At first, untreated tendonitis causes more pain and swelling. Ignoring the condition can make things worse. The tendon might get weaker.
Long-term, untreated tendonitis can cause chronic pain and limited mobility. This can really change your lifestyle. Chronic tendonitis can also make the tendon more prone to damage.
“Neglecting tendonitis can lead to a vicious cycle of pain and decreased function, ultimately affecting an individual’s quality of life.”
Medical Expert
One of the biggest dangers is tendon rupture. This is a serious injury that might need surgery. The risk goes up if the tendon is already weakened.
In conclusion, ignoring Achilles tendonitis is risky. It’s important to treat it early to avoid serious problems. Knowing the risks helps you stay healthy and active.
Knowing when to get help for Achilles tendonitis is important. This condition causes pain and swelling in the tendon. If not treated, it can really affect your life.
Getting help early can really help. It stops the problem from getting worse and keeps you active. Early treatment also means you might avoid more serious surgeries.
Early treatment has many benefits. These include:
Some signs mean you need to see a doctor right away. These include:
If you see these signs, get medical help fast. This can prevent more damage and ensure the right treatment.
Finding the right doctor for Achilles tendonitis is important. You might want to see:
| Specialist | Description |
| Orthopedic Specialist | Expert in musculoskeletal conditions, including tendonitis |
| Sports Medicine Physician | Knowledgeable about treating sports-related injuries |
| Physical Therapist | Specializes in rehabilitation and strengthening exercises |
Choosing a specialist with experience in Achilles tendonitis can greatly improve your recovery.
Diagnosing long-term Achilles tendonitis requires a detailed approach. This includes physical exams and advanced imaging tests. Knowing how long the tendon is inflamed helps choose the best diagnostic method.
A thorough physical exam is the first step in diagnosing Achilles pain. Doctors check for swelling and warmth in the tendon. They also test the ankle’s mobility and pain levels.
Key components of the physical examination include:
These steps help doctors understand how severe the condition is. They guide further diagnostic choices.
Imaging tests are key in diagnosing and assessing Achilles tendonitis. The right imaging test depends on the symptoms and suspected cause.
| Imaging Modality | Advantages | Limitations |
| Ultrasound | Dynamic assessment, cost-effective | Operator-dependent |
| MRI | High-resolution imaging, soft tissue detail | Expensive, not suitable for all patients |
| X-ray | Quick, widely available | Limited soft tissue visualization |
Each imaging test has its own benefits and drawbacks. The choice depends on the patient’s situation.
When diagnosing Achilles pain, other causes must be considered. Possible causes include:
A detailed diagnostic process helps rule out other conditions. This ensures an accurate diagnosis, which is key for effective treatment.
Understanding the tendonitis persistence timeline and inflammation duration achilles tendon is vital. It helps manage patient expectations and guide treatment.
Recovering from Achilles tendonitis means trying different treatments that fit your needs and schedule. These treatments are often the first choice and can really help ease symptoms.
One key step is to let the tendon rest and change how you do activities. This might mean doing less or lighter workouts. Rest is key for healing.
Physical therapy is a big part of getting better. It helps strengthen the Achilles tendon and makes the ankle move better. A physical therapist will create a special plan for you to help you heal and avoid future problems.
Using special devices and wearing supportive shoes can help lessen the stress on the Achilles tendon. Custom orthotics can fix foot problems that might be causing the tendonitis.
There are also things you can do at home to help. Applying ice to reduce pain and swelling, wearing compression bandages, and keeping the leg up are all helpful.
By using these treatments together, people with Achilles tendonitis can manage their symptoms and get better. It’s important to be patient and stick with the treatment plan. Everyone heals at their own pace.
When simple treatments don’t work, doctors may need to step in for long-term Achilles tendon pain. This pain can really hurt your daily life. So, doctors use stronger treatments to help you feel better and recover.
Anti-inflammatory drugs are often the first choice for Achilles tendonitis. These medicines, like ibuprofen or naproxen, cut down pain and swelling. But, it’s important to take them only as your doctor tells you to avoid side effects.
Corticosteroid shots can really help with long-lasting Achilles tendonitis. They work well to reduce inflammation. But, it’s important to think about the risks, like making the tendon weaker or even breaking it.
New treatments like platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy and stem cell therapy are being used. They try to help the tendon heal by using the body’s own repair tools.
Each of these treatments has its own role in treating long-term Achilles tendonitis. The right treatment depends on how bad the condition is, your health, and what you prefer.
When treatments like rest and physical therapy don’t work, surgery might be needed. This is usually for those who haven’t seen improvement after 6 months or have severe tendon damage.
Surgery is considered if the condition makes daily life hard or stops you from doing sports. Doctors look at the tendon’s health, your overall health, and how active you are before deciding.
There are different surgeries for chronic Achilles tendonitis, each with its own benefits.
Recovering from Achilles tendon surgery needs a careful plan to get strength and function back.
Immediate Post-Surgery: Rest, elevate your leg, and use ice to reduce swelling. Managing pain is key during this time.
Rehabilitation Phase: A slow rehab program starts, with exercises to improve movement, strengthen the tendon, and boost function.
“A well-structured rehabilitation program is key for the best recovery after Achilles tendon surgery.”
An Orthopedic Surgeon
Getting back to full activity can take 3 to 6 months or more. This depends on the surgery and how fast you heal.
Knowing how long it takes to recover from Achilles tendonitis treatment is key. It helps manage expectations and ensures a good outcome. The recovery time can vary a lot, depending on the treatment type.
Patients getting conservative treatment usually take weeks to months to recover. At first, they need to rest and avoid activities that make the problem worse. As they get better, they can slowly start doing normal things again.
Key phases in conservative treatment recovery include:
| Treatment Phase | Duration | Key Activities |
| Initial Recovery | 2-4 weeks | Rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE) |
| Strengthening | 4-6 weeks | Physical therapy, strengthening exercises |
| Return to Activity | 6-12 weeks | Gradual return to sports or strenuous activities |
Surgical treatment means a longer and more intense recovery. Post-surgical rehab is very important for the best results.
Post-surgical rehabilitation phases typically include:
Many things can affect how long it takes to recover from Achilles tendonitis. These include age, health, following the treatment plan, and any other health issues.
Common factors that can delay recovery include:
To stop Achilles tendonitis from coming back, it’s key to use a complete plan. This includes the right training, shoes, and exercises. Handling chronic Achilles tendonitis means tackling many factors that cause it.
Starting with a good warm-up is vital before any exercise. It should include gentle stretches and movements to get the tendon ready. Gradual progression in how hard and long you train can prevent injuries.
Adding eccentric training to your routine is also smart. This type of exercise strengthens the tendon by making it longer under load.
Choosing the right shoes is key for chronic Achilles tendonitis. Shoes should support and cushion, mainly in the heel. Orthotic devices can help if you have foot problems.
Look for shoes with good arch support, a proper heel-to-toe drop, and a good fit. Stay away from shoes that might make the problem worse, like those with high heels or too little cushioning.
Other strengthening exercises can also help with chronic Achilles tendonitis. Calf raises, for example, strengthen the muscles around the tendon, giving it more support.
Flexibility exercises are also important. Regular stretching keeps the tendon flexible and reduces stiffness.
Changing your lifestyle can also help manage chronic Achilles tendonitis. Keeping a healthy weight, for example, lessens the tendon’s stress.
Avoiding activities that make it worse and doing low-impact ones like swimming or cycling can help. Dietary changes to eat more anti-inflammatory foods can also support tendon health.
Living with chronic Achilles tendon pain can really get in the way of daily life. It affects how you do everyday things and exercise. Managing pain and changing your lifestyle are key to living with long-term Achilles tendonitis.
One big challenge is changing activities to avoid putting too much strain on the tendon. You might switch from running to cycling or swimming. It’s also important to warm up and cool down properly to avoid making the pain worse.
For people who stay active, finding exercises that don’t hurt the tendon is important. You can try upper body workouts or low-impact aerobic exercises. These keep your heart rate up without stressing the Achilles tendon too much.
Managing pain is key for those with long-term Achilles tendonitis. This might include physical therapy, orthotic devices, and pain relief medications. Physical therapy can make the muscles around the tendon stronger, which helps with stability and pain reduction.
Using heel lifts or orthotic shoe inserts can also help take some pressure off the tendon. Sometimes, doctors might suggest anti-inflammatory medications to help with pain and swelling.
If Achilles tendonitis doesn’t get better, you might need to try other treatments. This could be acupuncture, platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy, or other treatments that help the tendon heal.
Talking to a healthcare professional is important to find the right treatment. They can figure out why you’re in pain and suggest ways to improve your life.
Dealing with Achilles tendonitis pain for a long time is tough, both physically and mentally. The constant pain and limits it brings can really affect how you feel and live your life.
Handling chronic pain from Achilles tendonitis needs a mix of strategies. It’s key to see how pain affects your mind and find ways to manage it well.
Some good ways to cope include:
Keeping your mind healthy while recovering is very important. It means staying positive, setting realistic goals, and staying in touch with loved ones.
Ways to keep your mind well include:
Finding the right support is key for those with Achilles tendonitis. This includes doctors, support groups, and online help.
Some great support options include:
By understanding the mental side of Achilles tendonitis and using available support, people can manage their condition better. This can improve their quality of life a lot.
Achilles tendonitis can really hurt, affecting people of all ages and fitness levels. How long it lasts depends on how bad it is, the treatment, and your overall health.
For acute Achilles tendonitis, recovery can take weeks to months. But, if not treated right, it can turn chronic, lasting years. Knowing what affects its duration is key to managing it well.
Spotting the signs of long-term Achilles tendonitis early and getting medical help is important. This can prevent serious damage and lower the chance of more problems. A good treatment plan, whether it’s non-surgical or surgery, can help ease symptoms and aid in healing.
Knowing about Achilles tendonitis and its treatments gives people the power to manage their recovery. This can shorten the time it takes to get better and help them regain full foot function.
Achilles tendonitis recovery time varies. Acute cases usually heal in 6-8 weeks with proper care.
Chronic Achilles tendonitis lasts more than 6-8 weeks. It needs medical help to avoid more problems.
Causes include overuse and poor training. Risk factors are inadequate shoes and health issues like arthritis.
Signs include persistent pain and tendon thickening. These need medical attention.
Untreated tendonitis can cause tendon rupture. Timely treatment is key to avoid these risks.
Seek treatment if symptoms don’t improve. Early treatment helps avoid complications and speeds recovery.
Options include rest, physical therapy, and orthotics. These can manage symptoms and aid recovery.
Interventions include anti-inflammatory drugs and corticosteroid injections. Newer treatments also help manage symptoms and promote healing.
Surgery is for chronic cases that don’t respond to other treatments. It’s for severe tendon damage.
Prevent recurrence with proper warm-ups and training. Wear good shoes and do exercises to strengthen and stretch the tendon. Lifestyle changes also help.
Manage chronic tendonitis by adapting activities and using pain management. Consider alternative treatments to improve quality of life.
Chronic tendonitis can cause anxiety and depression. It’s important to focus on mental health during recovery and seek support.
Recovery time after surgery varies. It usually takes several months of rehabilitation.
Signs include increasing pain, swelling, and stiffness. Decreased function and mobility also indicate worsening tendonitis, needing prompt medical attention.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!