
Glue ear, also known as otitis media with effusion (OME), is when fluid builds up in the middle ear. This can make hearing harder and cause discomfort. For adults, dealing with ongoing hearing problems or discomfort can be really tough.
We’ll look into what causes glue ear in adults, its symptoms, and how to treat it. This guide aims to help you manage this condition. Knowing the best treatments is key to keeping your hearing and quality of life good.
If you have earache tinnitus, learn how to treat glue ear (otitis media with effusion) in adults to relieve these symptoms.

Glue ear, also known as otitis media with effusion, affects adults too. It’s when fluid builds up in the middle ear, behind the eardrum, without an infection. This can really impact an adult’s life.
Glue ear, or otitis media with effusion (OME), happens when fluid gathers in the middle ear. This fluid can be thin or thick, like glue. It can affect one or both ears and cause hearing loss.
The Eustachian tube is key in glue ear. It connects the middle ear to the back of the nose and throat. When it’s blocked, fluid builds up, causing glue ear.
About one-third of people with glue ear are adults. This shows it’s a big issue for grown-ups too. Adults get glue ear from things like colds, allergies, or Eustachian tube problems.
Glue ear can really hurt an adult’s life. It can cause hearing loss, ear fullness, and discomfort. If not treated, it can lead to serious problems like permanent hearing loss or chronic infections.
It’s important for adults to know about glue ear. Recognizing symptoms and causes is the first step to dealing with it. This can help manage the condition and improve life quality.
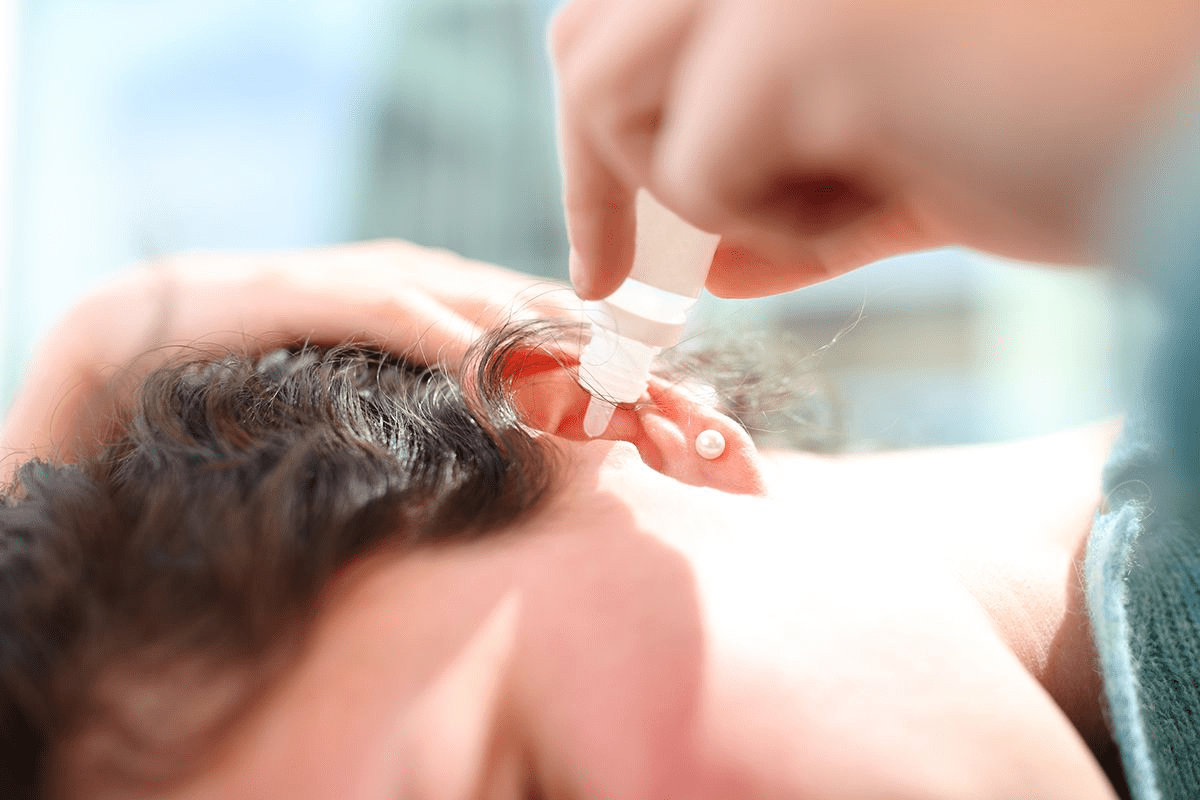
Knowing the signs of glue ear in adults is key to treating it. Glue ear, or otitis media with effusion, happens when fluid builds up in the middle ear. This can cause a range of uncomfortable symptoms.
Hearing loss is a main symptom of glue ear in adults. It can be mild or more serious. The fluid in the middle ear stops the eardrum from vibrating properly.
This makes it hard to hear clearly. Sounds might seem muffled or far away. It can affect daily life, making it tough to talk, work, and socialize.
Hearing loss from glue ear can really impact your life. It’s important to notice these signs and get checked by a doctor if they don’t go away.
Adults with glue ear often feel ear pressure or fullness. This is usually because of the fluid in the middle ear. It can feel like your ears are plugged, like during a flight.
“The feeling of ear fullness is a common complaint among adults with glue ear, and it can be quite distressing,” says Medical Expert, an audiologist specializing in adult hearing disorders. “It’s vital to tackle this symptom to enhance the patient’s quality of life.”
Adults with glue ear may also have ear aching and tinnitus. Tinnitus is when you hear sounds in your ear that aren’t there. These sounds can be ringing, buzzing, or other noises.
Tinnitus management techniques can help. These include sound therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), and relaxation methods. Treating the glue ear can also help reduce tinnitus.
By knowing these symptoms, adults can get the right medical care. This can help manage glue ear and prevent further problems.
Knowing what causes glue ear is key to managing it. Glue ear, or otitis media with effusion, happens when fluid builds up in the middle ear. This can really affect someone’s life if not treated.
Upper respiratory infections often cause glue ear in adults. These infections can block the Eustachian tube. This tube helps keep air pressure in the ears balanced. When it’s blocked, fluid can build up, causing glue ear.
Upper respiratory infections usually come before glue ear. The inflammation from these infections can stop the Eustachian tube from working right. This leads to fluid building up in the middle ear.
Eustachian tube dysfunction is another big factor in glue ear. The Eustachian tube is important for ear pressure and drainage. If it doesn’t work right, it can cause ear problems, like glue ear.
Many things can cause Eustachian tube dysfunction. These include allergies, anatomical issues, or previous ear infections. When it doesn’t work, it can’t keep ear pressure right, leading to fluid buildup.
Other things can also lead to glue ear in adults. These include:
Knowing these risk factors helps in preventing and managing glue ear. Understanding the causes is key to finding the right treatment.
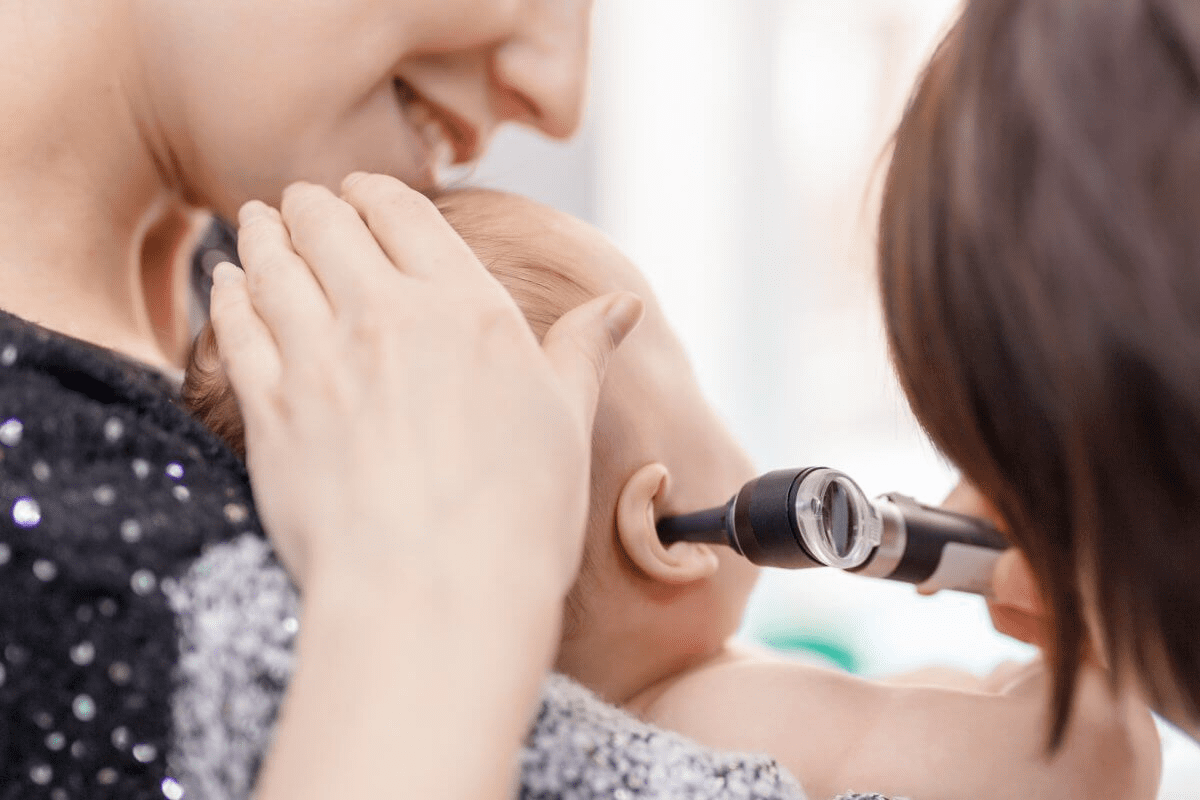
To find out if an adult has glue ear, doctors use a few methods. They do a physical check and use special tools. This way, they can give the right treatment.
The first step is a detailed physical examination of the ear. A doctor looks into the ear canal and at the eardrum. They check for signs of infection or fluid buildup.
Hearing tests are very important for diagnosing glue ear. Pure-tone audiometry checks how well you can hear sounds. Speech audiometry tests how well you understand speech at different volumes. These tests show if glue ear has caused hearing loss.
Tympanometry is another important tool. It checks how well the middle ear works. It does this by changing air pressure in the ear canal. This test can spot fluid buildup or problems with the Eustachian tube, signs of glue ear.
Doctors might also suggest more tests like tympanoplasty or imaging studies. These help them understand the middle ear better. With all these tests, doctors can accurately diagnose glue ear and create a treatment plan.
The watchful waiting approach is a common first step for managing glue ear in adults. It means keeping a close eye on symptoms without rushing to treat them. Glue ear can sometimes clear up on its own in a few months.
Watchful waiting is suggested for mild symptoms that might clear up on their own. If you’ve just been told you have glue ear and symptoms aren’t bad, this might be for you.
Remember, watchful waiting doesn’t mean ignoring your condition. It means regular visits to your doctor to check on your ear health and adjust treatment if needed.
To keep track of your symptoms, it’s a good idea to log any changes in hearing, ear pressure, or discomfort. This helps you and your doctor see how your condition is doing.
Key symptoms to monitor include:
If symptoms get worse or new ones appear, reach out to your doctor right away.
By watching your symptoms closely and working with your doctor, you can find the best way to manage glue ear.
Medical treatments are key in easing glue ear symptoms in adults. When simple steps don’t work, doctors have other options. We’ll look at these options, like medicines and therapies.
Antibiotics are used if a bacterial infection is causing glue ear. Amoxicillin is often given for this. It’s important to take the right amount and finish the treatment.
Doctors decide on antibiotics after checking for an infection and how bad the symptoms are.
Decongestants and antihistamines help with nasal stuffiness and Eustachian tube problems. Pseudoephedrine is a decongestant that might be suggested. Diphenhydramine is an antihistamine for allergy symptoms.
But, it’s important to use these with caution. A doctor should guide you, as they can have side effects or interact with other drugs.
Nasal steroids reduce swelling and congestion, helping the Eustachian tube. Fluticasone is a common one. They’re good for allergies or long-term swelling.
Autoinflation techniques are a non-invasive way to manage glue ear. They help open the Eustachian tube. This tube connects the middle ear to the back of the nose and throat. It lets air in and balances the pressure on both sides of the eardrum.
“The principle behind autoinflation is simple yet effective: by inflating the middle ear, we can help to clear any fluid buildup and restore normal hearing,” says Medical Expert, an ENT specialist. This technique can be very helpful for people with glue ear, as it offers a way to manage symptoms.
The Valsalva maneuver is a common autoinflation technique. To do it right:
It’s important to do the Valsalva maneuver gently to avoid hurting your eardrum or Eustachian tube. If done correctly, it can help relieve the pressure and discomfort of glue ear.
For some, using devices like Otovent works better than manual methods. Otovent is a handheld device that helps inflate the middle ear by creating a gentle pressure change in the nasal cavity.
“Using Otovent has been a game-changer for my glue ear management. It’s easy to use and has significantly reduced my symptoms,”
shares Jane Doe, a patient who has benefited from this device.
To get the most out of autoinflation techniques and devices, it’s key to have a regular routine. We suggest:
By adding autoinflation techniques to your daily routine, you can actively manage glue ear and improve your ear health.
When glue ear doesn’t go away in adults, surgery can help. It’s a way to fix the problem and get your ears working right again.
Myringotomy is a surgery where a small cut is made in the eardrum. This lets out the fluid that causes glue ear. Usually, ear tubes are put in too. They help keep the middle ear open and stop fluid from building up again.
The surgery is done under general or local anesthesia with sedation. The ear tubes come out on their own in 6 to 12 months. Sometimes, they need to be taken out.
In some cases, adenoidectomy is suggested. This is when the adenoids are removed. It’s more common in kids, but adults can also benefit if their adenoids are big.
Whether or not to do an adenoidectomy depends on several things. These include your health, how bad your glue ear is, and if you have adenoiditis or keep getting infections.
After surgery for glue ear, it’s important to follow a recovery plan. This means keeping the ear dry, not lifting heavy, and following your doctor’s advice.
Post-surgical care is key to make sure the surgery works. You’ll learn how to handle any pain, when you can start doing normal things again, and how to watch for any problems.
Knowing about surgery and what to expect after can help adults with glue ear make good choices about their treatment.
Glue ear symptoms in adults can be managed with simple home remedies and self-care. By adding these to your daily routine, you can better handle your condition. This improves your ear health overall.
Steam inhalation is a simple way to clear the Eustachian tube and ease glue ear symptoms. Here’s how to do it:
Regular steam inhalation moisturizes the nasal passages and Eustachian tube. This promotes drainage and relief.
Using a warm compress on the affected ear can ease ear pressure and discomfort. Here’s how to apply one:
Good hydration, a balanced diet, and healthy habits are key in managing glue ear symptoms. Drinking lots of water thins out mucus, making it easier to drain. Eating fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can also reduce inflammation.
Avoiding allergens and irritants, like smoke and pollution, can prevent Eustachian tube dysfunction. Regular exercise and stress management, like yoga or meditation, also boost ear health.
Lifestyle Adjustment | Benefit |
Staying Hydrated | Thins out mucus, promoting drainage |
Balanced Diet | Reduces inflammation, supports overall health |
Avoiding Irritants | Minimizes risk of Eustachian tube dysfunction |
Regular Exercise | Enhances overall health, including ear health |
By using these home remedies and self-care strategies, adults with glue ear can find significant relief. This improves their quality of life.
Managing ear aching and tinnitus is key for those with glue ear. We’ll look at ways to ease these symptoms.
For ear aching, try over-the-counter meds like acetaminophen or ibuprofen. Sometimes, you might need a prescription.
Common Pain Relief Options:
Medication | Dosage | Side Effects |
Acetaminophen | 500mg every 4-6 hours | Liver damage (rare) |
Ibuprofen | 400mg every 4-6 hours | Stomach upset, allergic reactions |
Tinnitus, or ringing in the ears, can be managed. Sound therapy is one effective way to reduce it.
Knowing when to get medical help is important. If you have severe ear pain, hearing loss, or worsening tinnitus, seek help right away.
Warning Signs:
Understanding these strategies and knowing when to seek help can help those with glue ear manage their symptoms better.
To prevent glue ear, it’s important to know what causes it and how to avoid it. Making smart lifestyle choices and taking care of your ears can help a lot. This way, adults can lower their chances of getting glue ear again.
Changing your lifestyle can help prevent glue ear from coming back. These changes help keep your ears healthy and lower the risk of getting glue ear.
As “The key to preventing glue ear lies in understanding its causes and making the necessary lifestyle adjustments.” By following these tips, you can greatly lower your risk of getting glue ear again.
Creating a long-term plan for ear health is vital to stop glue ear from coming back. This plan should include regular doctor visits, watching for signs of ear tube problems, and managing colds and flu well.
A study in a well-known medical journal found that
“Regular ear check-ups and quick action on colds and flu can greatly cut down glue ear in adults.”
Being careful and proactive can keep your ears healthy and prevent glue ear from happening again.
By adding these habits to your daily routine, adults can stop glue ear from coming back and keep their ears in top shape.
We’ve looked into glue ear in adults, covering its causes, symptoms, and treatments. Managing glue ear well means using medical treatments, autoinflation, and changing your lifestyle.
Getting a proper diagnosis is key. It’s important to see a doctor to find the best treatment. Knowing your options helps you make better choices for your health.
To wrap it up, treating glue ear needs a mix of medical help and self-care. Adults can feel better and avoid future problems by using these methods. This way, they can keep their ears healthy.
Glue ear, also known as otitis media with effusion, is when fluid builds up in the middle ear. This causes hearing loss and discomfort. It’s more common in kids, but adults can get it too.
Adults with glue ear might hear less, feel ear pressure, or have ringing in their ears. They might also feel ear pain. These symptoms can make daily life hard.
Doctors use a physical exam, hearing tests, and tympanometry to diagnose glue ear. These tests show if you have it and how bad it is.
Glue ear in adults can come from colds, Eustachian tube problems, or other middle ear issues.
Treatment for adults includes waiting it out, using medicine, autoinflation, or surgery. Surgery might include myringotomy and ear tube placement.
Autoinflation uses the Valsalva maneuver or devices like Otovent. It helps open the Eustachian tube and drain fluid.
You can’t prevent glue ear completely. But, making lifestyle changes and taking care of your ears can lower the risk.
For ear pain and tinnitus, try over-the-counter or prescription pain meds. Use tinnitus management techniques. See a doctor if symptoms get worse.
Yes, steam inhalation, warm compresses, and staying hydrated can help. So can changing your diet and lifestyle.
If your symptoms are severe or getting worse, see a doctor. They can check your hearing and treat you properly.
Watchful waiting means watching your symptoms to see if they go away on their own. It’s for mild cases.
Surgery like myringotomy and ear tube placement can help. They can make symptoms better and improve hearing.
MedlinePlus. (n.d.). Tonsillectomy – adult. Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002930.htm
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!
WhatsApp us