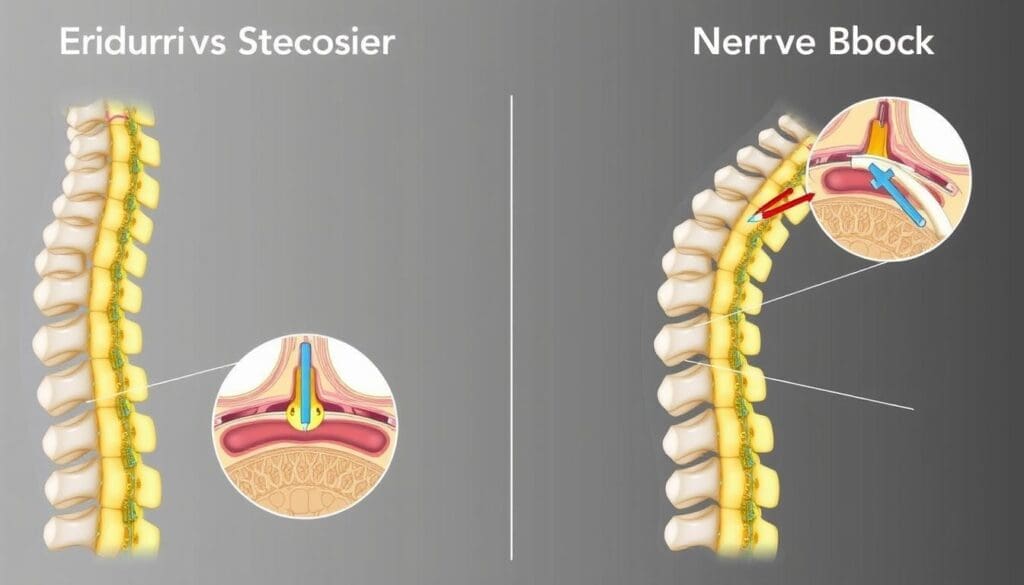
When it comes to managing pain, two common treatments are often considered: epidural steroid injection vs nerve block. At Liv Hospital, we understand the importance of making informed decisions about your care. Both treatments aim to provide relief, but they work in different ways.
Epidural steroid injections deliver medication into the epidural space surrounding the spinal cord and nerve roots. This helps to reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Nerve blocks, on the other hand, involve injecting anesthetic near specific nerves to interrupt pain signals.
Understanding the differences between these two treatments is key for effective pain management. We will explore the main differences, including their uses, benefits, and possible complications. This will help you make an informed decision about your care.
Interventional pain management, including injections, is becoming more common. These methods deliver medicine directly to the pain source. This helps patients with long-term pain conditions find relief.
Interventional pain management is key for chronic pain that doesn’t respond to usual treatments. Injection therapies are a main part of this method. They offer a precise way to ease pain.
We use these techniques to find and treat pain by stopping pain signals to the brain. This method works well for those who haven’t found relief elsewhere.
Injection therapies are chosen for their ability to put anti-inflammatory and/or anesthetic medications right where they’re needed. This targeted method can offer a lot of relief. It often has fewer side effects than medicines taken by mouth.
| Injection Therapy Type | Primary Use | Medication Used |
| Epidural Steroid Injections | Relieving inflammation and pain in the spine | Steroids and local anesthetics |
| Nerve Blocks | Blocking pain signals from specific nerves | Local anesthetics, sometimes steroids |
| Facet Joint Injections | Treating pain in the facet joints of the spine | Steroids and local anesthetics |
Knowing about the different injection therapies helps doctors tailor treatments. This makes pain management more effective for patients.
Epidural steroid injections put corticosteroids and anesthetics into the epidural space around the spinal cord and nerve roots. They help manage pain from spinal issues like herniated discs and spinal stenosis.

Epidural steroid injections are a pain management therapy. The corticosteroid part reduces inflammation, and the anesthetic gives quick pain relief. They target the epidural space to ease pain in the neck, back, and limbs.
“Epidural steroid injections are key in managing spinal pain,” say pain management experts. They offer a less invasive option than surgery.
There are different types of epidural injections:
The epidural space is a fat-filled area between the vertebrae and the dura mater. It has nerve roots, blood vessels, and connective tissue. It’s key for delivering treatments directly to pain sources.
Knowing the epidural space’s anatomy is vital for safe injections. It helps healthcare providers target the area well, ensuring the best results with fewer risks.
Nerve blocks have changed how we manage pain in medicine. They help diagnose and treat pain by stopping pain signals to the brain. A nerve block is when we inject medicine near nerves.
A nerve block is a way to inject medicine into or around nerves. It blocks pain signals. This is done with local anesthetics or agents that last longer.
There are many types of nerve blocks. Each targets different areas and conditions. Here are a few:
Saddle blocks are used for lower pelvic area procedures. This includes childbirth and anorectal surgery. They inject local anesthetic into the spinal fluid.
This numbs the perineal area. It gives pain relief without affecting the upper body.
Knowing about nerve blocks helps patients choose their pain management. We aim to give full care and advice during treatment.
Epidural steroid injections and nerve blocks have different injection sites and targets. Knowing these differences helps choose the right pain treatment.
Epidural steroid injections go into the epidural space. This area is outside the sac with spinal fluid and nerves. It’s between the vertebrae and the dura mater, a protective layer around the spinal cord.
By putting steroids here, we can lower inflammation and ease pain around the nerves.
Nerve blocks inject anesthetic or steroid medication around or on specific nerves. The goal is to block pain signals from these nerves. This can help with chronic pain and pain after surgery.
A big difference is how epidural injections and some nerve blocks, like saddle blocks, deal with the dura mater. Epidural injections stay outside this membrane. But, some nerve blocks, like saddle blocks, go through the dura mater to reach the subarachnoid space.
This difference is important because it changes the procedure’s risks, benefits, and the type of medication used.
Understanding the targets and sites of epidural injections and nerve blocks helps doctors pick the best treatment. This way, they can offer the best chance for pain relief.
The ways epidural steroid injections and nerve blocks are given are quite different. This affects how well they work and how patients feel. Let’s dive into the details of these methods to understand their role in managing pain.
The type and size of needles used are key in both epidural steroid injections and nerve blocks. Epidural steroid injections often need bigger needles to get to the epidural space. Nerve blocks might use smaller needles, depending on where the nerve is.
The needle’s size and type can change how much pain a patient feels and how well the injection works. Smaller needles might be less painful but aren’t right for every procedure.
There’s a big difference in using catheters versus single injections. Epidural steroid injections often use a catheter for ongoing pain relief. This allows for more doses or a steady flow of medication. Nerve blocks, on the other hand, usually involve a single injection of anesthetic or steroid.
Which method is chosen depends on the patient’s condition, how bad the pain is, and how long the pain relief is needed.
Both epidural steroid injections and nerve blocks often use imaging guidance for accurate needle placement. Tools like fluoroscopy, ultrasound, or CT scans help guide the needle. This makes the procedure more precise and safer.
Using imaging guidance is now common in pain management. It lowers the risk of problems and boosts success rates.
Medications in epidural steroid injections and nerve blocks work differently. This is key for healthcare providers to choose the right pain management. Understanding these differences is essential.
Epidural steroid injections put corticosteroids near the spinal cord. These steroids cut down inflammation and swelling around nerves. This reduces pain.
The steroids used are strong anti-inflammatory agents. They help lower the production of chemicals that cause inflammation. This leads to less pressure on nerves and less pain.
This method is great for people with herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or degenerative disc disease.
Nerve blocks inject anesthetics onto or near nerves. These anesthetics block pain signals from the nerve to the brain. This stops pain signals, giving relief.
The anesthetics can be short-acting or long-acting. This flexibility helps manage both sudden and ongoing pain. Nerve blocks are used for both diagnosis and pain relief.
At times, a mix of steroid injections and nerve blocks is used. This is good for patients needing both anti-inflammatory effects and quick pain relief. It lets healthcare providers customize treatment for each patient.
For example, combining a steroid with a local anesthetic in a nerve block offers both quick pain relief and long-term inflammation reduction. This combo is great for complex pain conditions.
| Characteristics | Epidural Steroid Injections | Nerve Blocks |
| Medication Used | Corticosteroids | Anesthetics (local or regional) |
| Primary Mechanism | Reduces inflammation | Blocks pain signal transmission |
| Onset of Action | Gradual (hours to days) | Immediate |
| Duration of Relief | Variable (weeks to months) | Variable (hours to days or longer with certain types) |
Epidural steroid injections and nerve blocks have different effects. They work at different speeds and for varying lengths of time. Knowing these differences helps patients and doctors choose the best treatment.
Nerve blocks give quick pain relief. They block pain signals right away. Epidural steroid injections take longer, as they reduce inflammation over time.
Immediate Relief with Nerve Blocks: You feel relief right after the procedure. It’s great for sudden pain.
Gradual Relief with Epidural Steroid Injections: Relief starts a few days to weeks later. This is because the steroids take time to work.
The length of pain relief differs between treatments. Nerve blocks can last from days to months. Epidural steroid injections can last weeks to months.
| Treatment | Onset of Relief | Duration of Relief |
| Nerve Blocks | Immediate | Days to Months |
| Epidural Steroid Injections | Gradual (Days to Weeks) | Weeks to Months |
Many things can change how long relief lasts. These include the type of medication, how bad the condition is, and the patient’s health.
Medication Type: What you’re given affects how long relief lasts.
Condition Severity: Severe cases might need more treatments or different therapies.
Patient Factors: Your age, health, and past treatments can also play a role.
It’s important to know how epidural steroid injections and nerve blocks work. They are both used to manage pain but in different ways. This knowledge helps doctors choose the best treatment for each patient.
Epidural steroid injections are best for conditions like spinal stenosis and herniated discs. They help by reducing inflammation and easing pressure on nerves.
These injections are great for radicular pain, which travels along a nerve. For example, sciatica causes pain in the lower back and legs. The injections can help by cutting down inflammation and pain.
Nerve blocks are used for many types of pain. They involve injecting anesthetics or steroids near nerves to block pain signals. They can be used to find or treat pain sources.
They work well for pain in specific areas or nerve paths. For example, they’re used for shingles pain, facial pain, and post-surgery pain.
The success of epidural steroid injections versus nerve blocks depends on the condition. Let’s look at how they compare for different conditions.
| Condition | Epidural Steroid Injections | Nerve Blocks |
| Spinal Stenosis | Effective in reducing inflammation and relieving pressure on nerves | Can be used but less common; more focused on specific nerve roots |
| Sciatica | Frequently used to treat radicular pain | Used in some cases, when specific nerve roots are involved |
| Postherpetic Neuralgia | Not typically used | Effective in managing localized pain |
| Chronic Facial Pain | Rarely used | Commonly used to target specific nerves |
In conclusion, both epidural steroid injections and nerve blocks are important in pain management. But, they work differently for different conditions. Knowing this helps doctors pick the best treatment for each patient.
Both epidural steroid injections and nerve blocks have risks and side effects. It’s important to know these to make good choices about pain relief.
Epidural steroid injections can cause temporary pain relief, headache, and increased blood sugar levels. Nerve blocks might lead to numbness, weakness, and temporary nerve damage. These effects are usually mild but can affect daily life.
Nerve blocks can also cause systemic toxicity if the anesthetic spreads too fast in the blood. Talking about your health history with your doctor can help avoid problems.
Though rare, serious issues can happen with both treatments. Epidural steroid injections might cause spinal cord injury or infection. Nerve blocks can lead to permanent nerve damage or allergic reactions to the anesthetic. It’s key to know these risks and talk to your doctor about them.
Some conditions make it risky to use epidural steroid injections or nerve blocks. For instance, people with bleeding disorders or on anticoagulant medications face a higher risk of bleeding. Also, those with diabetes need to watch their blood sugar levels closely because steroids can change them.
Knowing the risks, side effects, and safety of epidural steroid injections and nerve blocks helps patients make smart choices for pain relief. It’s vital to talk to your doctor about any health concerns to get the best results.
Epidural steroid injections and nerve blocks have different recovery processes and aftercare needs. Patients need to know these differences. This knowledge helps manage expectations and ensures a smooth recovery.
Right after the procedure, patients might feel different levels of discomfort. Epidural steroid injections can cause a temporary increase in pain or discomfort at the injection site. Nerve blocks, on the other hand, can lead to numbness or weakness in the affected area due to the anesthetic.
It’s a good idea for patients to have someone drive them home after the procedure. They might feel drowsy or uncoordinated. Having someone stay with them for a few hours is also recommended to monitor their condition.
Activity restrictions differ between the two procedures. For epidural steroid injections, patients should avoid heavy lifting, bending, or strenuous activities for a few days. Sometimes, they might be advised to limit their activities for up to a week.
Nerve blocks require more caution. Patients are usually told to avoid driving or operating heavy machinery until the numbness or weakness goes away. This can take several hours.
Follow-up care is key to the recovery process. Both procedures require patients to follow up with their healthcare provider. This is to assess the treatment’s effectiveness and address any concerns.
The follow-up schedule varies, but patients usually need to return within a few weeks to a few months after the procedure. Keeping a pain diary can help patients track their symptoms. This information is useful during follow-up visits.
| Aspect | Epidural Steroid Injections | Nerve Blocks |
| Immediate Post-Procedure Experience | Temporary increase in pain or discomfort | Numbness or weakness in the affected area |
| Activity Restrictions | Avoid heavy lifting, bending, or strenuous activities for a few days to a week | Avoid driving or operating heavy machinery until numbness or weakness resolves |
| Follow-up Care | Follow-up within a few weeks to a few months | Follow-up within a few weeks to a few months |
Understanding how patients feel is key when managing pain. Both epidural steroid injections and nerve blocks help with pain, but patients see them differently.
Pain during the procedure worries patients a lot. Epidural steroid injections put steroids near the spinal cord. This might hurt a bit, but local anesthesia helps.
Nerve blocks put anesthetic around nerves. The pain from this can change based on where and how it’s done.
How patients feel during the procedure is also important. Most stay awake for both epidural steroid injections and nerve blocks.
But, how awake they are can differ. For example, nerve blocks might make patients more aware, while epidural injections might need more sedation.
What patients say about their experience is vital. Studies show both methods can really help with pain.
Choosing between epidural steroid injections and nerve blocks depends on what each patient needs. Knowing the differences helps doctors guide patients better.
Understanding the difference between epidural steroid injections and nerve blocks is key for pain management. We’ve looked at how each procedure works, from where they target pain to how they deliver medicine.
What procedure you choose depends on your health, medical history, and what you prefer. Epidural steroid injections are good for issues like herniated discs and spinal stenosis. Nerve blocks are better for diagnosing or treating pain from specific nerves.
Talking to a doctor is the first step in deciding between these options. Discuss your health and pain with your doctor to find the best treatment. This way, you can start managing your pain effectively.
Epidural steroid injections target the area around the spinal cord. They use steroids to reduce inflammation. Nerve blocks, on the other hand, target specific nerves. They use anesthetics or steroids to block pain signals.
No, they are not used for the same conditions. Epidural steroid injections are for back pain, sciatica, and spinal stenosis. Nerve blocks are for chronic pain, surgical pain, and headaches.
The techniques are different. Epidural injections need precise placement with fluoroscopy. Nerve blocks use ultrasound or other imaging to target nerves.
Epidural injections take days to start working and last weeks to months. Nerve blocks can start working right away. Their effects can last from hours to months, depending on the medication.
No, they are not the same. Both are used for pain, but they target different areas and use different medications. They are distinct procedures for different needs.
Yes, you can get both treatments. They can be given separately or together, depending on your condition and your doctor’s advice.
Both can cause pain at the injection site, numbness, or weakness. Serious problems like infection, nerve damage, or allergic reactions are rare but possible.
Your choice depends on your pain, medical history, and your doctor’s advice. Talking to a pain management specialist is key to finding the right treatment for you.
Repeated injections can lead to nerve damage or hormonal changes. Your doctor will weigh the risks and benefits for your situation.
These treatments are considered on a case-by-case basis during pregnancy. Epidural analgesia is used during labor. But steroid injections or nerve blocks for chronic pain need careful thought and doctor’s advice.
A spinal block injects anesthetic into the spinal fluid for quick, strong anesthesia. An epidural injects medication outside the spinal fluid for a broader, less intense effect.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!