Last Updated on November 26, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
At Liv Hospital, we focus on trustworthy, patient-centered care and lead the way in advanced vascular treatments. One of our key specialties is EVAR vascular surgery — a minimally invasive procedure for treating aortic aneurysms.
What is EVAR? The EVAR vascular procedure, or Endovascular Aneurysm Repair, uses stent-grafts to reinforce the aorta. This approach offers a safer alternative to traditional open surgery. Patients benefit from smaller incisions, less pain, and faster recovery, all while meeting the highest international healthcare standards.
We are committed to excellence in vascular care, supporting our patients through every stage of their treatment to ensure the best outcomes and lasting health.
Key Takeaways
- EVAR surgery is a minimally invasive procedure for treating aortic aneurysms.
- It involves reinforcing the weakened aorta with stent-grafts.
- EVAR offers a safer alternative to traditional open surgery.
- Patients benefit from smaller incisions, less pain, and quicker recovery.
- Liv Hospital provides complete support and care for patients undergoing EVAR surgery.
Understanding Aortic Aneurysms and Their Risks
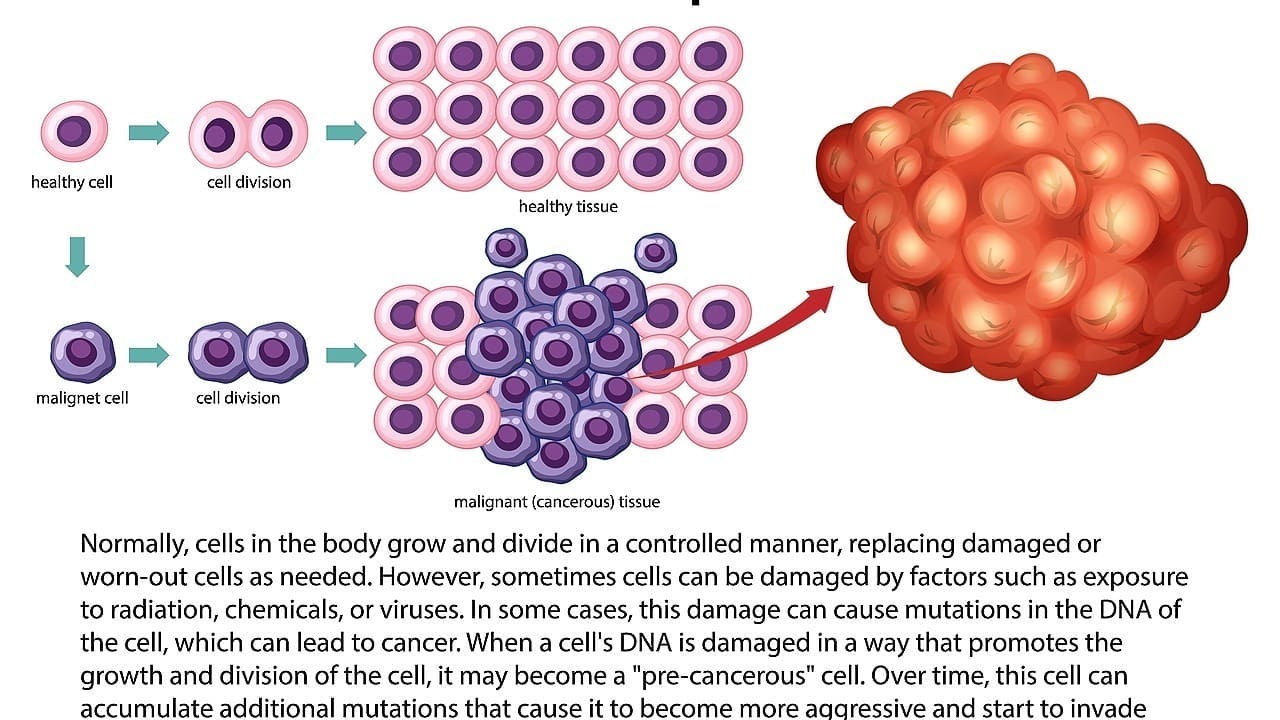
It’s important to know about aortic aneurysms to understand the risks they pose. Aortic aneurysms happen when the aorta, the main blood vessel, bulges or gets bigger. This can be very dangerous.
What Are Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms (AAA)?
Abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA) occur in the belly area. They happen when the aortic wall weakens. This can lead to a serious rupture if not treated quickly. AAA is a serious condition that requires timely diagnosis and treatment to prevent severe complications.
AAA can be caused by several things, like atherosclerosis, high blood pressure, smoking, and genetics. Knowing these risk factors helps find people who need to be screened.
Risk Factors and Prevalence
There are several risk factors for abdominal aortic aneurysms. These include:
- Age: The risk of developing AAA increases with age, after 65.
- Smoking: Smoking damages the aortic wall and increases the risk of aneurysm.
- Family History: People with a family history of AAA are at higher risk.
- High Blood Pressure: Hypertension strains the aortic wall, raising the risk of aneurysm.
- Atherosclerosis: Hardening of the arteries can also contribute to AAA.
AAA is more common in men over 65. Screening programs help find AAA in high-risk groups. Early detection greatly improves outcomes.
| Risk Factor | Description | Impact on AAA Risk |
| Age | Increased risk after 65 | High |
| Smoking | Damages aortic wall | Very High |
| Family History | Genetic predisposition | Moderate to High |
| High Blood Pressure | Increases strain on aortic wall | Moderate |
| Atherosclerosis | Hardening of arteries | Moderate |
Knowing about these risk factors and AAA’s prevalence is key to preventing and treating it. By identifying at-risk individuals and providing the right care, we can lower the risks of AAA.
The Evolution of Aortic Aneurysm Treatment
The treatment of aortic aneurysms has seen big changes, thanks to new technologies. Before, doctors mainly used surgery to fix these problems. Now, thanks to science, we have less invasive ways to treat them. This has made recovery times shorter and outcomes better.
Traditional Open Surgical Repair
Older treatments for aortic aneurysms were big surgeries. Doctors would make a big cut in the belly to reach the aorta. Then, they would replace the bad part with a man-made tube. This method was good but had many downsides, like long recovery times and risks.
Key aspects of traditional open surgical repair include:
- Major abdominal surgery with a significant risk of complications
- Longer hospital stays and recovery times
- Higher risk of mortality compared to some newer techniques
Development of Minimally Invasive Approaches
Doctors started looking for better ways to treat aortic aneurysms. They wanted to make surgery less invasive. This led to new methods that were less damaging and faster to recover from.
These new techniques were a big step forward. They use smaller cuts and cause less damage. This means patients can get back to their lives faster and with fewer problems.
The Emergence of EVAR Technology
EVAR technology has been a game-changer for treating aortic aneurysms. EVAR uses a stent-graft inserted through the femoral arteries. This keeps the aneurysm from getting worse.
Benefits of EVAR technology include:
| Benefit | Description |
| Minimally Invasive | EVAR is done through small cuts, which means less damage and faster healing. |
| Reduced Recovery Time | Patients usually stay in the hospital less and get back to normal sooner. |
| Lower Risk of Complications | EVAR has fewer risks and better survival rates than old surgery methods. |
EVAR has changed how we treat aortic aneurysms for the better. It’s safer and less invasive than old surgery. As technology keeps getting better, we’ll see even more improvements in treating this condition.
What Is EVAR Vascular Surgery?
EVAR stands for Endovascular Aneurysm Repair. It’s a new way to treat aortic aneurysms without big surgery. This method fixes the aneurysm from inside the aorta, stopping it from getting worse or bursting.
EVAR is a big change in treating aortic aneurysms. It’s less invasive than old surgery methods.
Defining EVAR and Its Medical Abbreviation
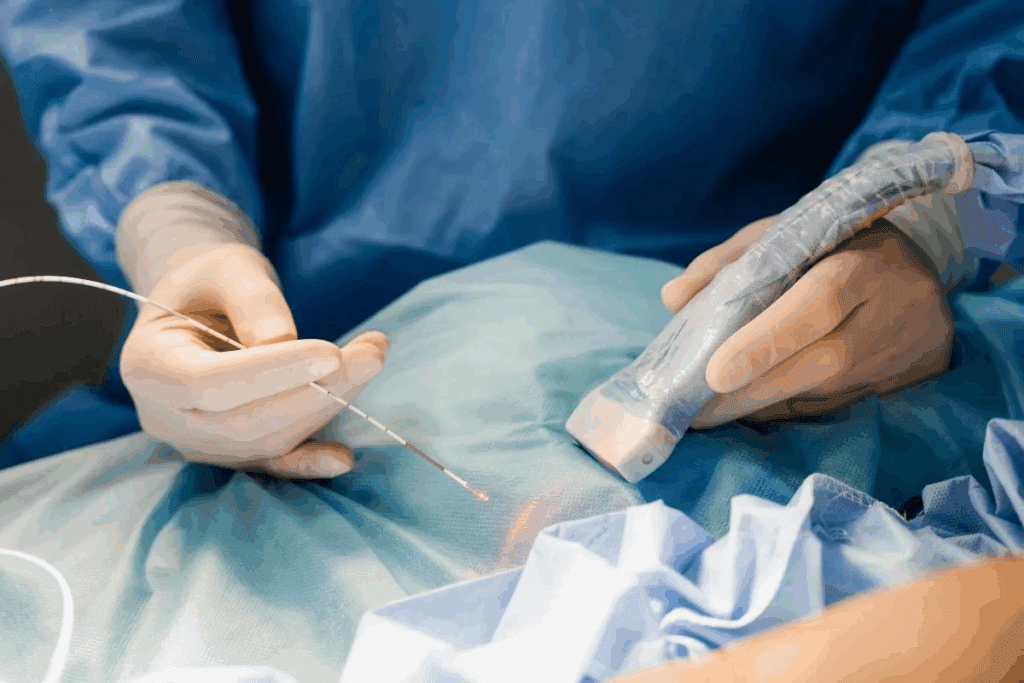
EVAR means Endovascular Aneurysm Repair. It’s a way to treat aortic aneurysms by putting a stent-graft in the aorta. The stent-graft is a fabric tube with metal mesh. It goes in through small cuts in the groin and is guided to the aneurysm.
The Science Behind Endovascular Aneurysm Repair
EVAR uses stent-grafts to block blood flow to the aneurysm. This stops it from getting bigger and bursting. The stent-graft lines the aorta, making sure blood flows through it, not into the aneurysm.
This lowers the pressure on the aneurysm wall. It makes it much less likely to burst.
Types of Stent-Grafts Used in EVAR
There are many stent-grafts for EVAR, each for different needs. The main types are:
- Standard infrarenal stent-grafts for typical abdominal aortic aneurysms.
- Fenestrated and branched stent-grafts for complex aneurysms that involve major branches of the aorta.
- Thoracic stent-grafts for aneurysms located in the thoracic aorta.
| Type of Stent-Graft | Application | Key Features |
| Standard Infrarenal | Typical AAA | Simple design, easy to deploy |
| Fenestrated/Branched | Complex aneurysms | Custom-made, preserves branch vessels |
| Thoracic | Thoracic aortic aneurysms | Longer grafts, flexible design |
Knowing about the different stent-grafts helps us see how EVAR can treat many aortic aneurysms. It shows how versatile and effective EVAR is.
The EVAR Procedure: Step-by-Step
Exploring the EVAR procedure, we see each step is vital. This endovascular treatment needs careful planning and precise execution. It also requires thorough monitoring after the procedure.
Pre-Procedure Assessment and Planning
Before starting the EVAR procedure, patients get a detailed check-up. This includes looking at their medical history and doing CT scans. We assess their health to plan the procedure well, choosing the right stent-graft and access sites.
The EVAR Surgical Technique
The EVAR technique starts with small incisions in the groin. We use imaging to guide the way to the aortic aneurysm. Then, we place a stent-graft to block the aneurysm, lowering the risk of rupture.
Post-Procedure Recovery and Hospital Stay
After the EVAR procedure, patients are watched in the recovery unit for hours. Most go home in a few days, based on their health and any issues. We schedule follow-up visits to check the stent-graft and watch for complications.
| Procedure Step | Description | Key Considerations |
| Pre-Procedure Assessment | Comprehensive evaluation of patient’s medical history and imaging studies | Determining suitability for EVAR, planning stent-graft selection |
| EVAR Surgical Technique | Minimally invasive deployment of stent-graft via femoral artery access | Precision in stent-graft placement, imaging guidance |
| Post-Procedure Recovery | Monitoring in recovery unit, follow-up appointments | Managing possible complications, checking stent-graft function |
Understanding the EVAR procedure helps patients see the care and complexity involved. Our team is dedicated to giving full care throughout the EVAR process.
Advantages of EVAR Over Traditional Open Surgery
EVAR has changed how we treat aortic aneurysms. It’s a minimally invasive method that benefits patients and healthcare systems. This shift has made EVAR a preferred choice over traditional open surgery.
Reduced Mortality and Morbidity Rates
EVAR is safer than open surgery. It has lower mortality and morbidity rates. A study on PMC shows EVAR improves outcomes, reducing death rates.
| Treatment Approach | Mortality Rate | Morbidity Rate |
| EVAR | 1.2% | 5.5% |
| Open Surgery | 3.5% | 10.2% |
Shorter Recovery Times and Hospital Stays
EVAR leads to shorter recovery times and hospital stays. It’s less invasive, causing less tissue damage. This means patients can get back to their lives faster, improving their quality of life.
Quality of Life Considerations
EVAR greatly improves a patient’s quality of life. It reduces pain and speeds up recovery. This allows patients to quickly resume their daily activities, boosting their overall well-being.
Suitability for High-Risk Patients
EVAR is great for high-risk patients. It’s less invasive, making it safer for those with health issues. This opens up treatment options for more people with aortic aneurysms.
EVAR for Different Types of Aortic Aneurysms
EVAR vascular surgery has changed how we treat aortic aneurysms. It offers a flexible solution for many aneurysm types. This technology can handle different aortic aneurysms, improving patient results for all kinds of aneurysm cases.
EVAR for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms
Abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) are common. EVAR is a top choice for treating AAAs because it’s less invasive than open surgery. It uses a stent-graft to block blood flow to the aneurysm, stopping it from growing or rupturing.
Fenestrated and Branched EVAR for Complex Aneurysms
Complex aortic aneurysms need special care because they involve important branch vessels. Fenestrated and branched EVAR is designed for these cases. It uses custom stent-grafts with special features to keep blood flowing to vital organs while sealing off the aneurysm.
Thoracic EVAR (TEVAR) Applications
Thoracic aortic aneurysms (TAAs) are another challenge. Thoracic EVAR, or TEVAR, is a less invasive option compared to open surgery. It places a stent-graft in the thoracic aorta to treat the aneurysm, lowering the risk of rupture. This method is great for patients at high risk for open surgery complications.
In summary, EVAR technology has opened up new ways to treat aortic aneurysms, from abdominal to complex and thoracic types. Its flexibility and minimally invasive approach make it a good choice for many patients.
Potential Complications and Long-Term Outcomes
EVAR is a groundbreaking treatment for aortic aneurysms. Yet, it’s important to know about possible complications. As vascular surgery advances, tackling these issues is vital for better patient care.
Common Complications Following EVAR
EVAR is mostly safe, but it comes with risks. Issues like endoleaks, graft migration, and vascular access problems can happen. These problems usually need quick medical help, sometimes leading to secondary interventions.
Understanding Endoleaks and Their Management
Endoleaks are a big worry after EVAR, where blood leaks into the aneurysm sac. There are various types, each needing different treatments. Type I and Type III endoleaks are high-risk and often need immediate action. Type II endoleaks might be watched unless they cause big problems.
Secondary Interventions and Their Frequency
Secondary interventions after EVAR are common. They’re done to fix issues like endoleaks or graft migration. How often these are needed depends on the aneurysm size, graft type, and patient health. Regular checks are key to catching problems early.
Long-term Surveillance Requirements
Long-term monitoring is vital for EVAR care. Patients get regular scans to watch the aneurysm sac and look for signs of trouble. This early detection helps in fixing problems quickly, leading to better long-term results.
In summary, EVAR is a top choice for treating aortic aneurysms, but knowing and dealing with complications is key. By understanding risks and using the right follow-up and treatment plans, we can keep improving care for EVAR patients.
Modern Approaches to EVAR Vascular Procedures
Modern EVAR procedures lead the way in vascular surgery. They use the latest technology and a team effort. This has greatly improved results and cut down recovery times.
Technological Advancements in EVAR
Technology has been key in making EVAR better. New stent-grafts and imaging tools help doctors treat patients more accurately and effectively.
Key Technological Advancements:
- Advanced stent-graft designs for better fit and durability
- Improved imaging technologies for enhanced visualization
- Minimally invasive techniques for reduced trauma
Multidisciplinary Team Approach
A team effort is vital for EVAR success. Vascular surgeons, radiologists, anesthesiologists, and others work together. This ensures patients get the best care.
| Team Member | Role in EVAR Procedure |
| Vascular Surgeon | Performs the EVAR procedure and oversees patient care |
| Radiologist | Provides imaging guidance during the procedure |
| Anesthesiologist | Manages patient anesthesia and comfort during the procedure |
Liv Hospital’s Protocol for EVAR Procedures
Liv Hospital leads in EVAR treatment. They use the latest tech and a team effort. Their approach focuses on personalized care and thorough follow-up.
Liv Hospital’s EVAR Protocol Highlights:
- Personalized treatment planning based on individual patient needs
- State-of-the-art technology for precise and effective procedures
- Comprehensive post-procedure care and follow-up
Liv Hospital combines modern tech with teamwork. This ensures the best results for patients in EVAR procedures.
Conclusion: The Future of EVAR and Aortic Aneurysm Management
EVAR vascular surgery has changed how we treat aortic aneurysms. It offers a less invasive option compared to open surgery. The future of EVAR is looking good, with new tech and techniques on the horizon.
We expect EVAR to get even safer and more effective. This will help it work for more types of aortic aneurysms. New stent-graft designs and better imaging will be key in this progress.
At Liv Hospital, we take a team approach to care. This means patients get help from start to finish. We’re dedicated to using the latest EVAR and aortic aneurysm management to better patient care.
The outlook for EVAR and aortic aneurysm management is bright. With ongoing tech advancements, we’re hopeful for better treatment options and care for patients. We’re excited to see how medical technology will improve lives.
FAQ
What is EVAR vascular surgery?
EVAR (Endovascular Aneurysm Repair) is a minimally invasive surgery. It treats aortic aneurysms by placing a stent-graft through blood vessels. This blocks blood flow to the aneurysm.
What is an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)?
An abdominal aortic aneurysm is a bulge in the aorta. The aorta is the main blood vessel from the heart to the abdomen. If it ruptures, it can cause severe bleeding.
How is EVAR different from traditional open surgery?
EVAR is less invasive than traditional surgery. It uses smaller incisions and causes less tissue damage. This leads to quicker recovery and fewer complications.
What are the benefits of EVAR over traditional open surgery?
EVAR has many advantages. It lowers the risk of death and complications. Patients also have shorter hospital stays and faster recovery times. This makes EVAR a good choice for those at high risk.
What are the possible complications of EVAR?
EVAR can have complications like endoleaks and stent-graft migration. These issues can be managed with close monitoring and timely action.
What is an endoleak, and how is it managed?
An endoleak is a leak around the stent-graft. It can be treated with additional interventions. This might include embolization or placing more stent-grafts.
Is EVAR suitable for all types of aortic aneurysms?
Yes, EVAR can treat various aortic aneurysms. This includes abdominal, complex, and thoracic aneurysms. It’s used with TEVAR for thoracic aneurysms.
What is the role of a multidisciplinary team in EVAR procedures?
A team of vascular surgeons, radiologists, and anesthesiologists is key in EVAR. They ensure patients receive the best care and have the best outcomes.
How is EVAR performed at Liv Hospital?
At Liv Hospital, EVAR is done with advanced technology and a team approach. This ensures high-quality care and the best results for patients.
What is the future of EVAR and aortic aneurysm management?
The future of EVAR and managing aortic aneurysms looks bright. Advances in technology and techniques will lead to better outcomes and more treatment options for patients.
References:
- England, A. (2012). Endovascular aortic aneurysm repair (EVAR): A randomized controlled trial of EVAR versus open surgery. Journal of Vascular Surgery, 55(3), 691-701. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3632841/