Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir

Radiation is everywhere, affecting our daily lives and the fields of medicine and technology. At Liv Hospital, we understand how vital it is to grasp radiation and its many uses. There are many examples of radiation, including electromagnetic radiation, which we often see in science and everyday life.
It’s the release of energy as moving waves or streams of particles. We see radiation in many ways, from visible light and radio waves to X-rays and gamma rays. Knowing about these types and sources helps us use them wisely and avoid risks.
Key Takeaways
- Radiation is everywhere and comes in many forms.
- Electromagnetic radiation is the most common type.
- Examples include visible light, X-rays, and gamma rays.
- Understanding radiation is key to medical and technological progress.
- Liv Hospital leads in innovative care related to radiation.
The Fundamentals of Radiation

Radiation is the energy that moves through space. It can be in the form of electromagnetic waves or high-energy particles. Knowing about radiation helps us understand how energy affects matter.
Definition and Basic Principles
Radiation can travel through air or a vacuum. It comes in two main types: non-ionizing and ionizing. Non-ionizing radiation has low energy and doesn’t remove electrons from atoms. This includes radio waves, microwaves, and visible light.
Ionizing radiation, on the other hand, has enough energy to remove electrons. This can damage living tissues. Examples are X-rays, gamma rays, and some ultraviolet radiation.
The Electromagnetic Spectrum Explained
The electromagnetic spectrum covers a wide range of energy frequencies. It goes from low-frequency, long-wavelength forms like radio waves to high-frequency, short-wavelength forms like gamma rays.
| Type of Radiation | Frequency Range | Examples |
| Radio Waves | Low Frequency | Broadcasting, Telecommunications |
| Microwaves | Medium Frequency | Heating, Wireless Communications |
| Visible Light | Medium Frequency | Illumination, Vision |
| X-rays | High Frequency | Medical Imaging |
| Gamma Rays | Very High Frequency | Cancer Treatment, Scientific Research |
Knowing the electromagnetic spectrum helps us see how radiation affects our lives. It’s from the visible light we see to the X-rays used in medical tests.
The Science Behind Radiation Phenomena
Understanding radiation is key to knowing how energy moves. We’ll dive into the science of radiation. This includes how energy travels and the difference between ionizing and non-ionizing radiation.
How Energy Travels Through Space
Energy moves through space as electromagnetic waves. These waves can go through a vacuum. They carry energy from one place to another.
The speed of these waves changes based on the medium. They move fastest in a vacuum.
Ionizing vs. Non-Ionizing Radiation
Ionizing radiation has enough energy to remove electrons from atoms. This creates ions. Examples are X-rays and gamma rays.
Non-ionizing radiation has less energy. It can make atoms vibrate or rotate. Examples include radio waves and microwaves.
| Type of Radiation | Examples | Energy Level |
| Ionizing | X-rays, Gamma Rays | High |
| Non-Ionizing | Radio Waves, Microwaves | Low to Moderate |
In summary, knowing about radiation science means understanding energy travel and the difference between types. Each type has unique properties and uses.
Visible Light: The Radiation We See Daily
Visible light is a key part of our daily lives. It’s a form of electromagnetic radiation we can see. It’s part of the electromagnetic spectrum, which includes many types of radiation,
Properties and Characteristics of Light Waves
Visible light acts like both waves and particles. It has a wavelength and frequency. It can be described by its amplitude, wavelength, and speed. The wavelength of visible light ranges from about 380 nanometers (violet) to 740 nanometers (red).
“Light is the most subtle, the most mysterious, and the most essential of all the forces that surround us,” an expert said. This highlights the importance of knowing about light’s properties.
Natural and Artificial Light Sources
Visible light comes from both natural and artificial sources. The Sun is our main natural source. Other natural sources include stars, lightning, and some chemical reactions. Artificial sources include incandescent bulbs, fluorescent lamps, and LEDs, which are key to our daily lives.
- Natural Sources: Sun, stars, lightning
- Artificial Sources: Incandescent bulbs, fluorescent lamps, LEDs
How Visible Light Enables Vision
Visible light is essential for vision. When light from an object hits our eyes, it’s focused on the retina. There, it’s turned into electrical signals that our brain understands. This complex process lets us see and understand our world.
Exploring the role of visible light in our lives shows its importance. It’s not just for lighting. It’s key to how we interact with and understand our surroundings.
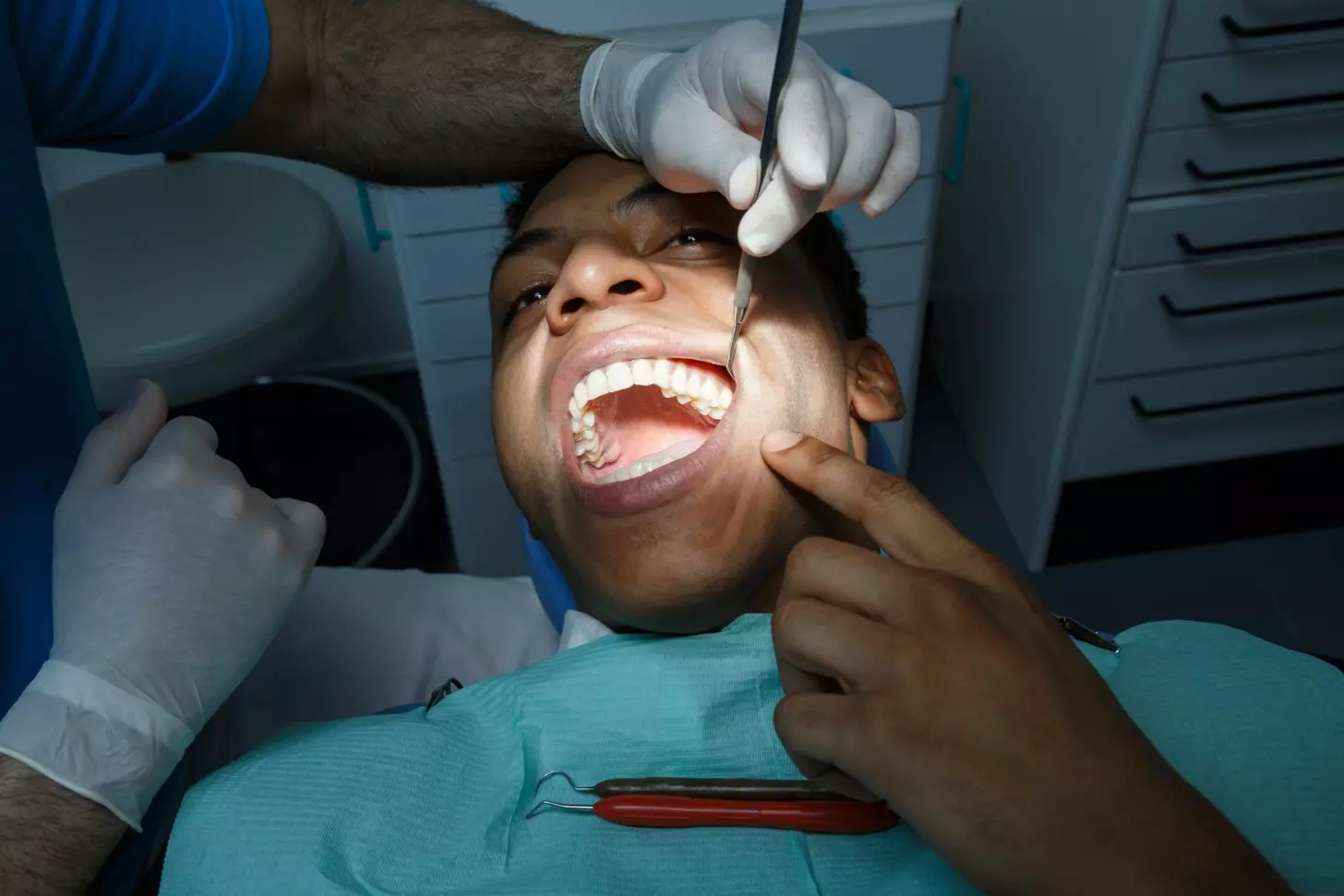
X-rays: Penetrating Radiation for Medical Diagnostics
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation used a lot in medical diagnostics. They are made artificially and can go through many materials. This makes them very useful in both medical and industrial fields.
The Discovery and Generation of X-rays
Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen discovered X-rays in 1895. He found out they can go through soft tissues but not through denser materials like bones. X-rays are made in an X-ray tube. Here, electrons are sped up and then stopped suddenly when hitting a metal target, creating X-ray photons.
Key characteristics of X-rays include:
- High energy levels
- Ability to penetrate various materials
- Ionizing radiation, capable of altering DNA and potentially causing biological damage
Medical Imaging Applications
X-rays are used a lot in medical imaging to diagnose many conditions. They are great for:
- Imaging bones and detecting fractures or osteoporosis
- Visualizing foreign objects within the body
- Guiding certain medical procedures
| Medical Application | Description |
| Bone Imaging | X-rays are used to diagnose fractures, osteoporosis, and other bone-related conditions. |
| Dental Imaging | Dental X-rays help in diagnosing tooth decay, gum disease, and other oral health issues. |
| Mammography | X-rays are used in mammography to detect breast cancer early. |
Industrial and Security Uses
X-rays are also used in many industrial and security areas, including:
- Inspecting welds and detecting defects in industrial components
- Screening luggage and cargo at airports and border crossings
- Analyzing the internal structure of materials and components
X-rays are a non-destructive way to check the inside of objects. This makes them very useful in quality control and security screening.
Gamma Rays: High-Energy Radiation from Nuclear Processes
We look into gamma rays, a high-energy radiation from nuclear processes. Gamma radiation is very penetrating. It’s emitted during nuclear reactions and is useful in many ways.
Nuclear Origins and Properties
Gamma rays come from nuclear reactions, like radioactive decay and nuclear fission. They have no mass or charge. This lets them travel far through materials, even through human tissue.
Properties of Gamma Rays:
- High energy
- Penetrating power
- No mass or charge
Experts say, “Gamma radiation is used in various fields because of its unique properties.”
“The penetrating power of gamma rays makes them ideal for applications where deep tissue penetration is required,”
Medical Applications in Cancer Treatment
Gamma rays are used in cancer treatment, mainly in radiation therapy. They can target tumors to kill cancer cells or slow their growth.
| Application | Description |
| Cancer Treatment | Gamma rays are used to kill cancer cells |
| Radiation Therapy | Precise targeting of tumors with gamma radiation |
Scientific Research Applications
In scientific research, gamma rays help study nuclear reactions and material properties. They aid in understanding complex phenomena and developing new technologies.
For example, gamma-ray spectroscopy analyzes the energy of gamma rays from nuclei. It gives valuable information about nuclear structure and reactions.
Microwaves: Radiation for Cooking and Telecommunications
Microwaves are everywhere, used for cooking and in telecommunications. We use them every day, but often don’t think about the science behind them.
How Microwave Radiation Functions
Microwave radiation heats food using electromagnetic waves. These waves have a frequency of about 2.45 gigahertz. This frequency is what water molecules in food absorb best.
When microwave energy hits food, it makes water molecules move. This movement creates heat through a process called dielectric heating.
Key characteristics of microwave radiation include:
- Non-ionizing: Microwaves don’t have enough energy to break chemical bonds or cause DNA damage.
- Penetrating: Microwaves can go through food, making it heat evenly.
- Controlled: The frequency and power of microwaves are set to ensure safe and efficient cooking.
Microwave Ovens and Food Preparation
Microwave ovens use microwave radiation to cook food. They are designed to keep the microwave energy inside, keeping users safe.
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
| Quick Cooking | Microwaves heat food fast | Saves time in food preparation |
| Energy Efficiency | Microwaves directly heat the food | Uses less energy than traditional cooking |
| Safety Features | Interlocks prevent accidental exposure | Ensures user safety during use |
Telecommunications Infrastructure
Microwaves are key in telecommunications, mainly in wireless systems. They are used for sending data between cell towers and satellites.
Microwaves in telecommunications have big advantages. They offer high bandwidth and can send data over long distances. They’re used where laying fiber optic cables is hard or too costly.
As we keep improving in telecommunications, microwaves remain important. They help with fast data transmission, making them key in our communication systems today.
Radio Waves: Some Examples of Radiation in Wireless Technology
Radio waves are a key part of wireless communication. They are used in broadcasting, mobile phones, and wireless networks. This makes them essential for our daily communication.
Properties and Transmission of Radio Waves
Radio waves are great for wireless tech because they can travel far. They can go through some materials, but it depends on their frequency. To send radio waves, we turn electrical signals into waves and broadcast them with antennas.
The frequency of radio waves matters a lot. Lower frequencies are good for long distances. Higher frequencies are better for shorter ranges because they carry more data.
Broadcasting and Media Applications
Radio waves are key to broadcasting. They let us send audio and video to many people. AM and FM radios use them to play music and news. TV also uses radio waves to send video and sound.
Some main uses of radio waves in broadcasting are:
- AM and FM radio broadcasting
- Television broadcasting
- Satellite communications
Modern Wireless Communications
In today’s world, radio waves power our mobile phones, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth. These technologies help us communicate quickly and reliably. They make global connections possible.
Radio waves in wireless tech offer many benefits. They include:
- Flexibility and mobility
- High-speed data transfer
- Wide coverage area
As wireless tech gets better, radio waves will keep being important. They will help us with new ways to communicate and improve old ones.
What Are Non-Examples of Radiation? Common Misconceptions
Understanding radiation means knowing what it is and what it’s not. We often get things wrong when talking about radiation. It’s important to clear up these mistakes to really get it.
Sound Waves: Mechanical, Not Electromagnetic
Many think sound waves are a type of radiation. But sound waves are actually mechanical waves, not radiation. They need a medium to move, unlike radiation, which can go through a vacuum.
Sound is made when objects vibrate. This vibration makes air particles move. We hear this movement as sound. The big difference is that sound can’t go through space.
Mechanical Vibrations and Their Properties
Mechanical vibrations, like those that make sound, are different from radiation. They are physical movements that pass energy through a medium.
These vibrations have their own set of properties. They include frequency, amplitude, and how fast they move. But, unlike radiation, their speed changes based on the medium they’re in.
Distinguishing Between Wave Types
To tell waves apart, we look at their characteristics and what they need to move. The table below shows the main differences between radiation and mechanical waves.
| Characteristics | Electromagnetic Radiation | Mechanical Waves |
| Medium Required | No | Yes |
| Wave Type | Transverse | Longitudinal or Transverse |
| Examples | Light, X-rays, Gamma Rays | Sound Waves, Water Waves |
Knowing these differences helps us understand radiation better. It also helps us avoid mistakes about what radiation is.
Advanced Medical Applications of Radiation Science
Radiation science is key in today’s medicine, bringing new ways to diagnose and treat. At Liv Hospital, we use the latest in radiation tech to improve patient care.
Cutting-Edge Diagnostic Imaging Technologies
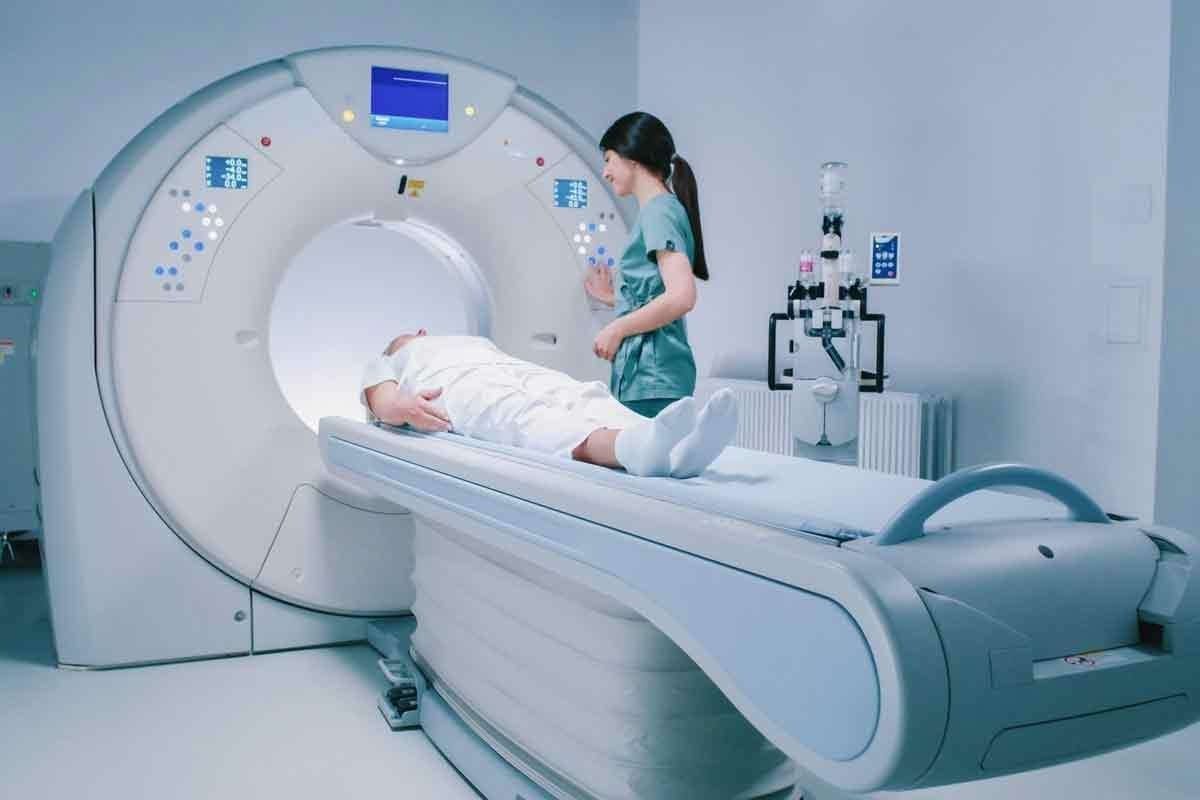
Diagnostic imaging has changed how we find and treat health issues. Tools like CT scans and PET scans use radiation to show us what’s inside the body.
These tools are vital in today’s medicine. They help doctors find problems early and plan treatments that work best.
| Imaging Technology | Application | Benefits |
| CT Scans | Detailed cross-sectional images | Accurate diagnosis of internal injuries and conditions |
| PET Scans | Functional imaging of metabolic processes | Early detection of diseases such as cancer |
Radiation Therapy Innovations
Radiation therapy is a key part of fighting cancer, using high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. New ideas have made it better and safer.
At Liv Hospital, we use advanced methods like Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT). These methods aim at tumors with care, protecting healthy tissues.
Liv Hospital’s Approach to Radiation-Based Treatments
Liv Hospital aims to offer top-notch radiation treatments, following global standards and using a team approach. Our experts in radiation oncology, medical physics, and radiology create custom treatment plans.
We use the latest tech to ensure our patients get the best care. We focus on making treatments effective and safe.
Radiation Safety Measures and Regulatory Standards
Radiation safety is very important for public health and safety. We must follow strict safety rules and standards to reduce radiation exposure.
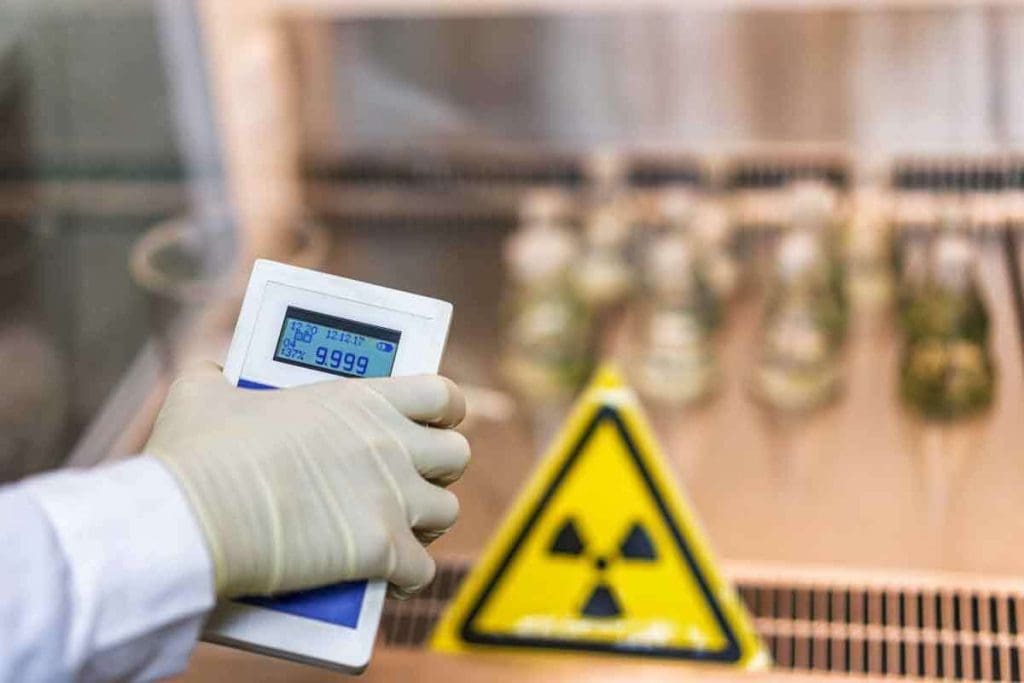
Measuring and Monitoring Radiation Exposure
It’s key to accurately measure and monitor radiation exposure. We use tools like Geiger counters and dosimeters to check radiation levels. Regular checks help spot any dangers early.
Radiation Exposure Limits are set by rules to keep people safe from harmful radiation. These limits change based on the radiation type and the job.
| Occupation | Annual Radiation Limit (mSv) |
| Radiation Workers | 20 |
| General Public | 1 |
Protective Equipment and Best Practices
Protective gear is vital for radiation safety. We use lead aprons, thyroid shields, and lead glasses to protect ourselves. We also keep a safe distance from radiation sources and limit our time near them.
Proper training is key for those working with radiation. It teaches how to use protective gear correctly and follow safety rules.
International Safety Guidelines
Groups like the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) create safety guidelines. These are followed by countries to keep radiation safety standards the same worldwide.
We follow these guidelines to keep our safety practices up to date. This means we regularly update our safety rules based on new research and advice.
Conclusion: The Balanced Perspective on Radiation
Radiation comes in many forms, from radio waves to gamma-rays. It’s complex and has both good and bad sides. We use it every day, like visible light to see and X-rays for medical checks.
Understanding radiation is key to seeing its value in science and medicine. Knowing about its types and sources helps us stay safe.
Radiation is everywhere, like microwaves in cooking and radio waves in broadcasts. Learning about it helps us appreciate its role in our lives and the world.
FAQ
What are some examples of radiation?
Radiation is all around us. We see it in visible light, X-rays for medical images, and gamma rays for cancer treatment. Microwaves cook our food, and radio waves help us talk wirelessly.
What is the difference between ionizing and non-ionizing radiation?
Ionizing radiation can knock electrons out of atoms. This includes X-rays and gamma rays. Non-ionizing radiation, like visible light and microwaves, doesn’t have enough energy to do this.
How does visible light enable vision?
Visible light lets us see by reflecting off objects and entering our eyes. This way, we can see the world around us.
What are some applications of X-rays?
X-rays help us see inside the body for medical imaging. They’re also used in industries to check materials and find hidden objects.
What are gamma rays used for?
Gamma rays kill cancer cells in treatment. They’re also used in science to study materials and the universe.
How do microwaves function in cooking?
Microwaves cook food using non-ionizing radiation. This makes microwave ovens quick and easy for cooking meals.
What are some examples of non-ionizing radiation?
Non-ionizing radiation includes visible light, microwaves, and radio waves. These are used in many ways, like in telecommunications and broadcasting.
What are some common misconceptions about radiation?
Some people think radiation is like sound waves. But radiation is electromagnetic, not mechanical like sound.
How is radiation used in medical applications?
In medicine, radiation helps diagnose and treat diseases. This includes using it for imaging and therapy, like in cancer treatment.
What safety measures are taken when handling radiation?
Handling radiation safely is very important. We measure exposure, use protective gear, and follow safety guidelines to keep risks low.
What is LivHospital’s approach to radiation-based treatments?
LivHospital uses the latest radiation treatments. This includes therapy for cancer and other diseases, to give patients the best care.
References
- PubMed. (2014, May 7). Applications of electromagnetic radiation in medicine. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24864099/