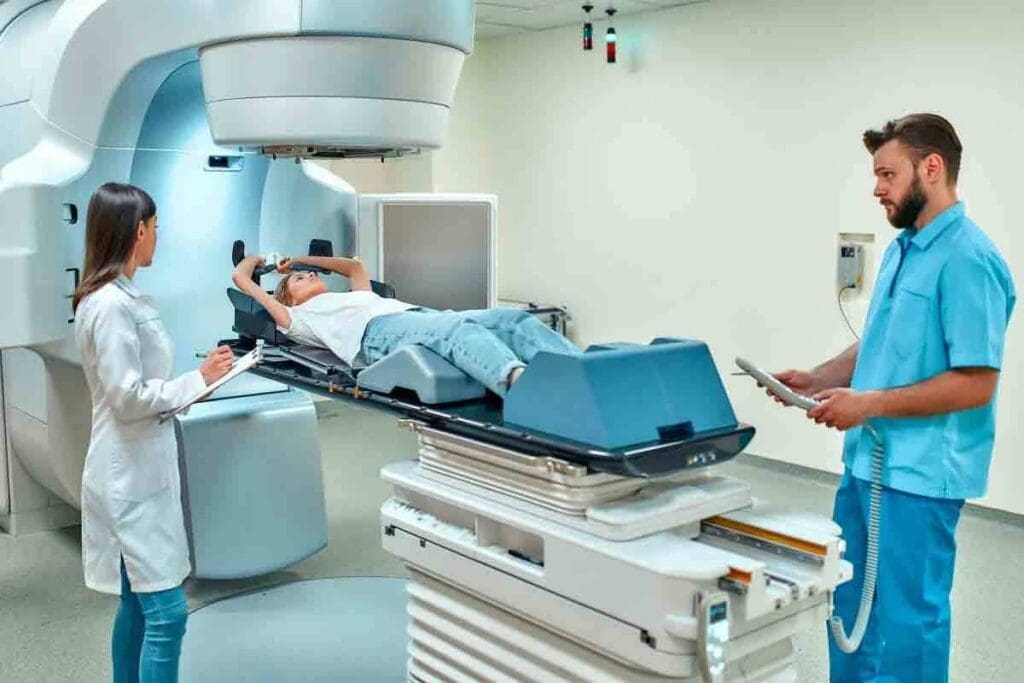
Cancer treatment has changed a lot with new radiation therapy. External beam radiation therapy is a big part of it. It uses high-energy beams to target and destroy tumors. About 50% of cancer patients worldwide use it, making it key in cancer care.
Today’s radiation machines are much better. They can hit tumors more accurately and harm less of the healthy tissue. So, external beam radiotherapy is now a trusted and reliable choice for cancer patients.
Key Takeaways
- Cancer radiation therapy is a local treatment that targets specific parts of the body.
- External beam radiation therapy is used by about 50% of cancer patients globally.
- Modern radiation machines have improved precision and effectiveness.
- External beam radiotherapy is a trusted and reliable treatment option.
- High-energy beams are used to target and destroy tumors.
What Is External Beam Radiotherapy and How Does It Work
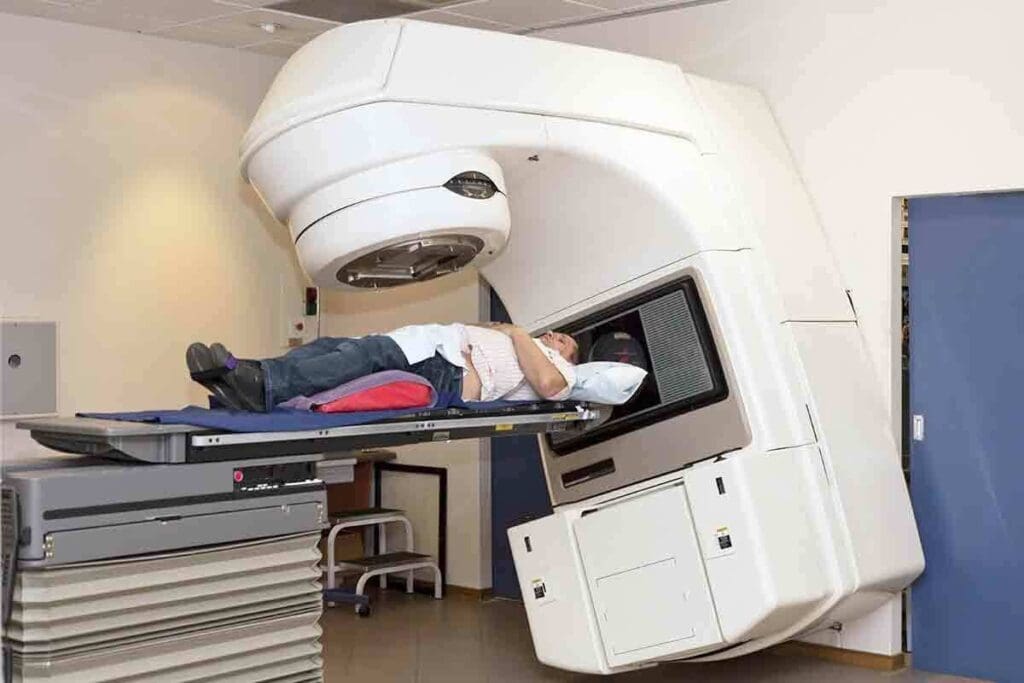
External beam radiotherapy uses high-energy beams to treat cancer. It sends beams from outside the body to kill cancer cells. This method is a key treatment for many cancer patients.
Definition and Basic Principles
External beam radiation therapy is a cancer treatment. It uses a machine to send beams to the tumor. The goal is to hit the tumor with the right amount of radiation, while keeping healthy tissues safe.
It uses advanced radiation oncology machines to focus on the tumor from different angles. This helps in delivering precise radiation.
How It Differs from Internal Radiation Therapy
Internal radiation therapy places the radiation source inside the body. But external beam radiotherapy sends radiation from outside. This makes a big difference in how the treatment works and its side effects.
External beam radiation is often used for tumors that are hard to reach inside the body. It’s also good for treating larger areas.
The Science Behind Radiation’s Cancer-Fighting Effects
External beam radiotherapy works by damaging cancer cells’ DNA. This stops them from growing and dividing. Radiation beams, like photons or electrons, are set up to hit the tumor hard but spare healthy tissue.
This careful targeting helps reduce side effects and improve treatment results.
The Evolution of Cancer Radiation Therapy Machines
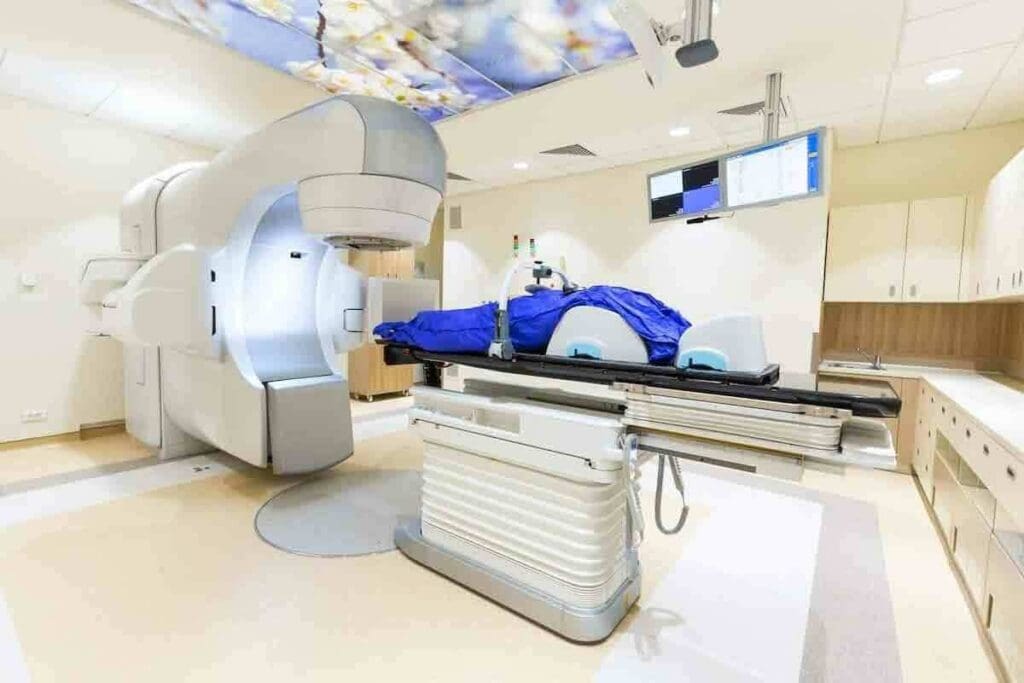
The history of cancer radiation therapy machines is filled with innovation. This has led to better care for patients. These machines have changed a lot over the years, changing how we treat cancer.
Historical Development
The first machines were made in the early 1900s, after X-rays were discovered in 1895. These early machines were simple and often caused a lot of side effects. They couldn’t target tumors well.
Then, in the 1950s, Cobalt-60 units were introduced. They were more reliable and powerful. Later, linear accelerators (LINACs) became key in modern radiation therapy.
Major Technological Breakthroughs
New technologies like computerized treatment planning and imaging technologies have made a big difference. Now, machines can target tumors better and protect healthy tissues.
“The integration of advanced imaging and delivery technologies has revolutionized radiation oncology, enabling more precise and effective treatments.”
Big steps forward include Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT). These allow for even more precise and flexible treatments of complex tumors.
Impact on Treatment Outcomes
The new machines have greatly improved treatment results. Patients live longer and have fewer side effects. This is because treatments are now more precise and effective.
- Improved local control of tumors
- Enhanced patient survival rates
- Reduced side effects due to more precise targeting
The ongoing evolution of radiation treatment machines keeps improving cancer care. It offers new hope to patients all over the world.
Types of Radiation Beams in External Beam Therapy
External beam radiotherapy uses different types of radiation beams to fight cancer cells. The choice depends on the tumor’s type, size, and location, and the patient’s health.
There are three main types of radiation beams: photon beams, electron beams, and particle beams. Each has its own properties and uses in cancer treatment.
Photon Beams: The Most Common Approach
Photon beams are the most commonly used in external beam radiotherapy. They are high-energy X-rays that can go deep into the body to hit tumors. These beams are made by a linear accelerator (LINAC) and can be shaped to fit the tumor using IMRT.
Photon beams are good for treating deep tumors and can be precise. But they can also harm healthy tissues around the tumor.
Electron Beams: For Surface Tumors
Electron beams are used for superficial tumors near the skin’s surface. They have a short range in tissue, making them safe for surface lesions without harming deeper areas.
Electron beams quickly drop off in dose beyond the target, protecting deeper tissues. This makes them great for tumors near important structures or in sensitive areas.
Particle Beams: Protons and Heavy Ions
Particle beams, like protons and heavy ions, are advanced radiation therapy options. Proton therapy uses protons to kill cancer cells. Protons have a Bragg peak, delivering a high dose to the tumor while sparing healthy tissues.
- Proton therapy is great for tumors near important areas, like brain tumors or pediatric cancers.
- Heavy ion therapy, though rarer, has similar benefits with possibly better effectiveness for some tumors.
In conclusion, the radiation beam type in external beam therapy depends on the patient’s needs and the tumor’s characteristics. Knowing about the different radiation beams and their uses is key to effective cancer treatment.
Key Machines Used in External Beam Radiotherapy
Modern radiation oncology uses many machines for external beam radiation therapy. These machines are key to giving precise doses of radiation to tumors. They also help protect healthy tissue around the tumor.
Linear Accelerators (LINAC): The Workhorses of Radiation Oncology
Linear accelerators, or LINACs, are the main machines used in external beam radiation therapy. They speed up electrons to make high-energy X-rays or electrons. These machines can do many treatment techniques, like Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT).
- Can deliver high-energy radiation beams
- Flexible in treatment options, including IMRT and SBRT
- Common in radiation oncology departments
Particle Accelerators: Cyclotrons and Synchrotrons
Particle accelerators, like cyclotrons and synchrotrons, speed up protons or heavy ions for cancer treatment. Proton therapy is known for its precise radiation delivery. It’s great for tumors near important structures.
- Cyclotrons accelerate protons for proton therapy
- Synchrotrons can speed up both protons and heavy ions
- These machines provide precise radiation delivery
Specialized Delivery Systems
There are also special delivery systems for certain types of radiation therapy. These include systems for Total Body Irradiation (TBI) and Intraoperative Radiation Therapy (IORT). These systems are made for specific treatment needs. They help radiation oncology departments be more flexible.
- TBI systems for treating large areas of the body
- IORT systems for radiation during surgery
- These systems improve treatment results in certain cases
The Treatment Planning Process for Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy treatment planning is a detailed, multi-step process. It’s key for effective cancer treatment. The goal is to target the tumor precisely, using radiation that’s effective yet safe for healthy tissue.
Initial Consultation and Assessment
The process starts with an initial consultation between the patient and the radiation oncologist. They discuss the patient’s health, medical history, and treatment goals. This step is vital for choosing the right treatment.
Imaging and Simulation
Imaging and simulation come next. Advanced scans like CT, MRI, or PET help locate the tumor. They also show its size and shape. Simulation then replicates the treatment position for accuracy.
Computer-Assisted Planning
After imaging and simulation, computer-assisted planning starts. Sophisticated software creates a detailed radiation therapy plan. It considers the radiation type, dose, beam angles, and treatment duration.
| Step | Description | Importance |
| Initial Consultation | Assessment of the patient’s health and medical history | Determines treatment approach |
| Imaging and Simulation | Locating the tumor and understanding its dimensions | Ensures accuracy in treatment delivery |
| Computer-Assisted Planning | Creating a detailed plan for radiation therapy | Crucial for effective treatment |
| Treatment Verification | Confirming the accuracy of the treatment plan | Ensures safety and effectiveness |
Treatment Verification Protocols
The last step is treatment verification. It checks if the plan is correct and the radiation will be delivered as planned. Imaging tests before and during treatment help ensure the tumor is targeted correctly.
This careful process helps radiation oncologists deliver effective external beam radiotherapy. It aims to give patients the best possible outcomes in cancer radiation therapy.
Advanced Techniques in External Beam Radiotherapy
Advanced radiation therapy techniques have changed cancer treatment for the better. They offer more precision and better results. This means better outcomes for patients and fewer side effects.
Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT)
Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) is a cutting-edge treatment. It targets tumors with great accuracy. IMRT changes the radiation beam’s intensity to hit the tumor hard while protecting healthy tissue.
This method is great for complex tumors. It uses advanced planning and delivery systems. This ensures the radiation dose fits each patient’s needs perfectly.
3D-Conformal Radiotherapy
3D-Conformal Radiotherapy uses 3D imaging to target tumors. It shapes the radiation dose to fit the tumor, protecting nearby tissues. This is a big step up from older methods.
With 3D imaging, doctors can map the tumor and its surroundings. This makes delivering radiation more accurate.
Image-Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT)
Image-Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT) combines imaging with radiation delivery. It lets doctors watch the tumor in real-time and adjust the treatment as needed.
IGRT ensures the radiation hits the tumor right, even if it moves. This is key for tumors in areas that move, like the lungs or abdomen.
Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT)
Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) is precise for small, well-defined tumors. It gives high doses of radiation in a few sessions. This makes it effective for some cancers.
SBRT is used for tumors that can’t be removed or for those who can’t have surgery. It needs careful planning and precise delivery to hit the tumor right.
The Patient Experience During Radiation Treatment
The experience of patients during radiation treatment is very important. It involves a series of sessions that need careful planning. External beam radiotherapy is a common treatment for many cancers. Knowing about the treatment process can greatly affect a patient’s experience.
What to Expect at Each Session
At each session, patients see a team of experts working together. This team includes radiation oncologists, nurses, and radiographers. The treatment is usually done on an outpatient basis and lasts about 30 minutes. But the actual radiation time is just a few minutes.
Preparation is key to a successful session. Patients lie on a couch and may use immobilization devices for accuracy. The therapists control the machine from another room, using images to check the treatment area.
Managing Side Effects
Managing side effects is very important during radiation treatment. Even though the treatment aims to protect healthy tissues, side effects can happen. Common ones include fatigue, skin irritation, and nausea, depending on the area treated.
Patients should talk openly with their healthcare team about any side effects. Supportive care measures, like skin care and diet changes, can help lessen these effects. This improves the patient’s life during treatment.
Duration and Frequency of Treatments
The length and frequency of treatments depend on the cancer type and stage. Patients usually have treatments five days a week, Monday through Friday, for several weeks.
| Treatment Type | Typical Duration | Frequency |
| Curative Treatment | 6-7 weeks | 5 days a week |
| Palliative Treatment | 1-3 weeks | 5 days a week |
| Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) | 1-5 sessions | Once every other day or daily |
Quality of Life Considerations
Keeping the quality of life high is a big concern for patients. They are encouraged to keep up with their usual activities as much as they can. But they might need to make some changes to manage fatigue and side effects.
Nutritional counseling and psychological support are also key. They help patients deal with the emotional and physical challenges of treatment. By focusing on these areas, healthcare providers aim to make the treatment experience as good as possible for patients.
Precision and Targeting in Modern Radiotherapy
Modern radiotherapy has changed cancer treatment a lot. It uses new ways to target tumors accurately. This is thanks to advanced imaging and computer planning.
Minimizing Damage to Healthy Tissue
The main goal of modern radiotherapy is to protect healthy tissue. Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) and Image-Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT) help target tumors well. This way, they don’t harm nearby healthy tissues.
Advanced imaging, like CT scans, MRI, and PET scans, helps. They give detailed information about the tumor’s size and location.
Adapting to Tumor Movement
Tumors can move during treatment. This can be due to breathing or digestion. Modern radiotherapy systems can adjust to this movement in real-time.
Some machines have real-time imaging. This lets them track the tumor’s movement. They then adjust the radiation beam to match.
Dose Calculation and Delivery
Getting the dose right is key in radiotherapy. It ensures the tumor gets the right amount of radiation. This also helps protect healthy tissues.
Advanced algorithms and Monte Carlo simulations help figure out the best dose. Machines like linear accelerators then deliver the radiation. They can change the intensity and shape of the beam.
Treatment Margins and Safety Protocols
Treatment margins are used to cover any uncertainty. They make sure the tumor gets enough radiation. This is important for treatment success.
Safety checks are also in place. These include quality assurance programs and regular machine checks. They help prevent too much or too little radiation.
Statistical Insights: The Reach of External Beam Radiotherapy
External beam radiotherapy is a key part of cancer treatment worldwide. It’s important for both healthcare providers and patients to know about its reach and how well it works.
Global Treatment Statistics
About 50% of cancer patients globally get external beam radiation therapy. This shows how widely used and important it is in fighting cancer. It proves that more people need effective cancer treatments.
Cancer Types Most Commonly Treated
External beam radiotherapy helps with many cancers, like breast, prostate, lung, and brain cancers. It’s chosen often because it works well with different types and locations of tumors.
Effectiveness Rates Across Different Cancers
The success of external beam radiotherapy depends on the cancer type, stage, and patient. For some cancers, like early-stage prostate cancer, it has high cure rates. For others, it helps manage symptoms and improve life quality.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Looking at the cost of external beam radiotherapy, several things matter. These include the cost of the equipment, running it, and each treatment. Research shows it’s worth the initial cost because it helps many patients and can save money in the long run.
Key statistics show it’s cost-effective. It helps lower healthcare costs for advanced cancer symptoms. It also improves patient outcomes, leading to a better life and possibly fewer expensive treatments.
Combining External Beam Radiotherapy with Other Treatments
Using external beam radiotherapy with other treatments is key in fighting cancer. This method, called combined modality treatment, uses different ways to treat cancer better.
Radiotherapy and Surgery: Neoadjuvant and Adjuvant Approaches
External beam radiotherapy often goes hand in hand with surgery. Neoadjuvant radiotherapy is given before surgery to make tumors smaller. Adjuvant radiotherapy is used after surgery to kill any cancer cells left behind.
“The use of neoadjuvant radiotherapy has been shown to improve surgical outcomes by reducing tumor size and increasing the likelihood of complete resection.”
A study in the Journal of Clinical Oncology showed that neoadjuvant radiotherapy boosts survival rates for some cancers.
| Treatment Approach | Purpose | Benefits |
| Neoadjuvant Radiotherapy | Before surgery to shrink tumors | Improves surgical outcomes, increases the chance of complete resection |
| Adjuvant Radiotherapy | After surgery to eliminate the remaining cancer cells | Reduces risk of recurrence, improves overall survival |
Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy: Timing and Synergies
Combining external beam radiotherapy with chemotherapy is common in cancer treatment. Chemotherapy can be given before, during, or after radiotherapy, based on the cancer type and goals.
Concurrent chemoradiotherapy means giving chemotherapy and radiotherapy at the same time. This makes treatment more effective by making cancer cells more sensitive to radiation.
- Chemotherapy before radiotherapy can shrink tumors and address microscopic disease.
- Chemotherapy during radiotherapy can enhance the radiation’s effectiveness.
- Chemotherapy after radiotherapy can help eliminate any remaining cancer cells.
Radiotherapy and Immunotherapy: Emerging Combinations
Using external beam radiotherapy with immunotherapy is a new and promising area in cancer treatment. Immunotherapy boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer. When combined with radiotherapy, it can make the immune response stronger against tumors.
Studies show that radiotherapy and immunotherapy can cause abscopal effects. This means the immune response from localized radiotherapy can target and fight distant, untreated tumors.
Multimodal Treatment Planning
Effective treatment planning needs a team effort from many healthcare professionals. This includes radiation oncologists, surgeons, medical oncologists, and others.
The goal is to create a treatment plan that fits the patient’s needs. This considers the cancer type and stage, as well as the patient’s health and preferences.
- Initial assessment and staging to determine the most appropriate treatment modalities.
- Coordination among specialists to develop a complete treatment plan.
- Ongoing monitoring and adjustment of the treatment plan as needed.
Future Innovations in Cancer Radiation Machines
The world of cancer treatment is about to change a lot. New technologies in radiation therapy are leading the way. These changes will make cancer treatment better for everyone.
Emerging Technologies
New technologies are changing radiation oncology. We’re seeing better machine learning, improved imaging, and new ways to deliver radiation.
Advancements in Machine Learning: Machine learning is making treatment planning smarter. It uses lots of data to create the best plans for patients.
Artificial Intelligence Applications
Artificial intelligence (AI) is big in radiation therapy now. AI helps with planning, predicting results, and making treatments fit each patient.
Personalized Medicine: AI helps make treatments just right for each person. It looks at each patient’s unique data to plan the best treatment.
Personalized Treatment Approaches
Personalized treatments are becoming common in radiation oncology. They make plans based on each patient’s cancer.
| Technology | Application | Benefit |
| Machine Learning | Enhanced Treatment Planning | Improved Accuracy |
| Artificial Intelligence | Personalized Treatment | Better Patient Outcomes |
| Advanced Imaging | Precise Tumor Targeting | Reduced Side Effects |
Accessibility and Global Adoption Challenges
These new technologies are exciting, but there are big challenges. Making them available worldwide is hard because of cost and training needs.
As these technologies get better, cancer treatment will improve a lot. We need to work on making them available everywhere to help everyone.
Conclusion: The Evolving Role of External Beam Radiotherapy in Cancer Care
External beam radiotherapy is a key part of cancer treatment, getting better with new tech. It’s a non-invasive way to target tumors with precision, protecting healthy tissue nearby.
This treatment is getting more precise and flexible, working better with other treatments. New methods like intensity modulated radiation therapy make it more accurate. This leads to better results for patients.
New tech and approaches are making radiation therapy even more effective. This means more hope for people fighting cancer all over the world.
The future of cancer treatment is bright, thanks to ongoing innovation in radiation therapy. By improving what we already know, doctors can give patients even better care.
FAQ
What is external beam radiotherapy?
External beam radiotherapy is a cancer treatment. It uses beams like X-rays or protons to kill cancer cells from outside the body. It’s used by about 50% of cancer patients worldwide.
How does external beam radiotherapy differ from internal radiation therapy?
External beam radiotherapy sends radiation from outside the body. Internal radiation therapy puts a radioactive source inside or near the tumor.
What types of radiation beams are used in external beam therapy?
Photon, electron, and particle beams, like protons and heavy ions, are used. Each type has its own use and characteristics.
What machines are used in external beam radiotherapy?
Machines like linear accelerators (LINAC) and particle accelerators are used. Cyclotrons and synchrotrons are also part of the equipment.
What is the treatment planning process for radiation therapy?
The process starts with a consultation and imaging. Then, computer planning and verification protocols are used. This ensures the radiation is delivered precisely.
What are some advanced techniques used in external beam radiotherapy?
Techniques like IMRT, 3D-Conformal Radiotherapy, IGRT, and SBRT are used. They help improve treatment results.
What can patients expect during radiation treatment sessions?
Patients have sessions several times a week, lasting a few minutes. Managing side effects and keeping quality of life is important.
How is precision and targeting achieved in modern radiotherapy?
Precision is achieved by minimizing damage to healthy tissue. It also involves adapting to tumor movement and accurate dose delivery.
Can external beam radiotherapy be combined with other cancer treatments?
Yes, it can be combined with surgery, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. The choice depends on the cancer type, stage, and the patient’s health.
What are the future innovations in cancer radiation machines?
Future innovations include artificial intelligence and personalized treatments. Advances in particle therapy are also expected to improve outcomes.
Is external beam radiotherapy effective across different types of cancer?
Yes, it’s effective for many types of cancer. Effectiveness varies based on the cancer type, stage, and other factors.
What is the cost-effectiveness of external beam radiotherapy?
It’s considered cost-effective compared to other treatments. It treats a wide range of cancers and improves patient outcomes.
References
- Gilbert, F. J. (2022). Diagnostic accuracy systematic review and meta-analysis. National Center for Biotechnology Information. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK578679/


































