
Coronary angioplasty and stent placement are usually done when the patient is awake. They use sedation to help the patient relax. This is a common way to treat blocked arteries. Answering are you awake when a stent is inserted (usually conscious sedation) and defining a surgical stent procedure.
During the procedure, the area where the catheter is inserted is numbed. This is usually in the leg or arm. Sedation helps the patient stay calm and comfortable. Knowing about angioplasty vs angiogram and the role of a stent in leg or heart helps patients prepare. It also helps them understand their cardiac cath recovery time.
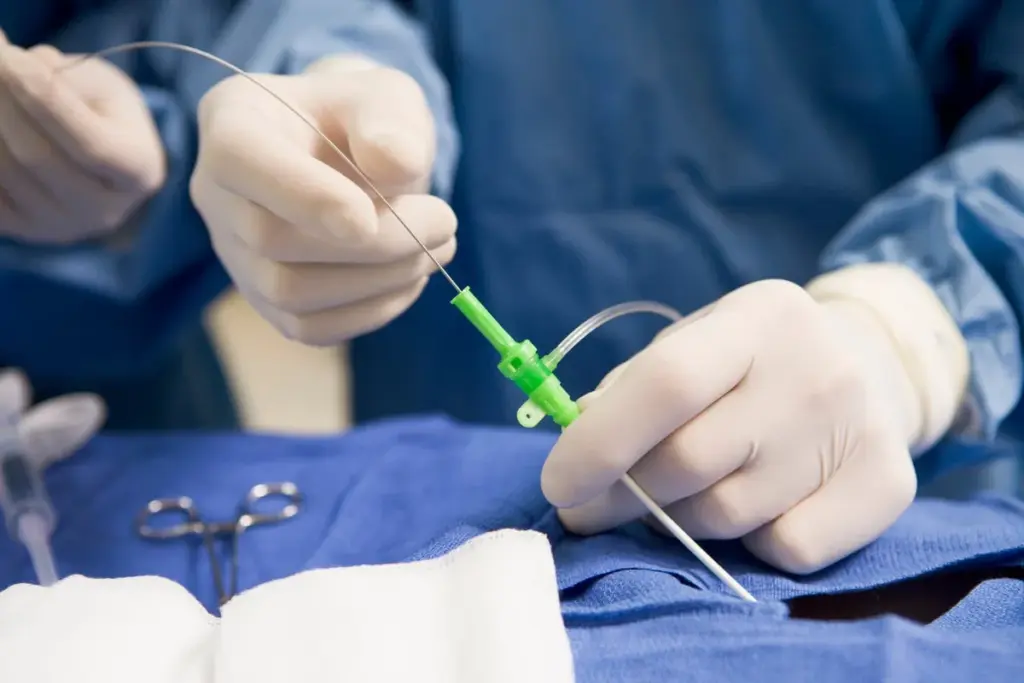
It’s key for patients to know about surgical stents before heart procedures. These stents are devices that keep arteries open. This ensures blood flows well to important organs. Premier Cardiology Consultants say stents help with coronary artery disease, a condition that can cause heart attacks.

A surgical stent is a small, mesh-like tube. It’s made of metal or other materials. It’s put into a narrowed or blocked artery to improve blood flow. Stents are used in the heart, legs, and kidneys to treat various conditions.
Stents are often needed for coronary artery disease, peripheral artery disease, and renal artery stenosis. These conditions cause arteries to narrow or block. If not treated, they can lead to serious health problems.
Stents keep the artery open after an angioplasty. Angioplasty uses a balloon to push aside plaque. The stent stays in the artery, ensuring it remains open. This improves blood flow and lowers the risk of heart attacks and other heart problems.
There are many stent procedures for different vascular issues. Stents are tiny, mesh-like tubes that keep arteries open. They help improve blood flow. The procedure depends on the blockage’s location and severity.
Coronary stents treat blockages in the heart’s arteries. They are often used with angioplasty to keep the artery open. Coronary artery stents are a common treatment for heart disease.
Peripheral stents treat blockages in leg arteries. Stents in leg procedures improve blood flow. They help with pain and cramping in patients with PAD.
Renal stents treat blockages in kidney arteries. Renal stents improve kidney function. They help manage high blood pressure caused by kidney disease.
The way stents are placed changes with the blockage’s location. For example, coronary stents are placed through the wrist or groin. Peripheral stents may need a direct approach to the limb.
|
Stent Type |
Location |
Purpose |
|---|---|---|
|
Coronary Stent |
Coronary Arteries |
Improve blood flow to the heart |
|
Peripheral Stent |
Leg Arteries |
Improve blood flow to the legs |
|
Renal Stent |
Renal Arteries |
Improve blood flow to the kidneys |
Many patients wonder if they’ll be awake during a stent insertion. The answer depends on the anesthesia used. This can change based on the procedure and patient needs.
For stent insertion, you might get conscious sedation or local anesthesia. Some clinics say most patients are awake. They use sedation to help them relax.
Conscious sedation keeps you awake but relaxed. It’s different from general anesthesia, which makes you completely unconscious. With conscious sedation, you can breathe on your own and follow your doctor’s instructions.
Patients under conscious sedation often feel very relaxed. They might feel a bit of pressure or discomfort, but this is usually managed with medication.
You might feel a pinch when the local anesthetic is given, or pressure when the stent is placed. But, the procedure is usually not painful. This is thanks to the conscious sedation and local anesthesia.
Conscious sedation during stent insertion makes patients comfortable and relaxed. They can breathe on their own and respond to their healthcare providers as needed.
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) is a non-surgical way to open blocked heart arteries. It’s a big change from older, more invasive surgeries. This method helps treat heart disease in a new way.
The PCI process starts with a cardiac catheterization. This step uses a small incision to reach the blocked artery. A thin tube, or catheter, is guided through the body to the heart’s arteries with X-ray help.
After finding the blockage, a balloon angioplasty is done to widen the artery. Then, a stent is placed to keep it open.
Angioplasty and stenting are key parts of PCI, but they’re different. Angioplasty uses a balloon to open the artery. Stenting involves putting a metal tube (stent) to keep it open.
Using both methods together has greatly improved PCI results for patients.
Patients are usually awake but a bit sleepy during a cardiac catheterization. They might feel a bit of pain when the catheter goes in, but this is usually numbed. The whole time, the procedure is watched closely, and patients can talk to their team.
Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions to follow before your stent procedure. Proper preparation is key to a successful outcome and a smooth recovery.
Before the procedure, you’ll undergo various tests to assess your overall health and the condition of your arteries. These may include blood tests, electrocardiograms, and imaging studies such as angiograms.
Your doctor may instruct you to adjust your medications before the procedure. This could involve stopping certain medications that increase the risk of bleeding or adjusting the dosage of others.
“It’s essential to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions regarding medication adjustments to minimize risks during the procedure.”
On the day of your stent procedure, plan to arrive at the hospital with plenty of time to spare. You’ll need to register, change into a hospital gown, and undergo final preparations.
Upon arrival, you’ll be directed to the catheterization lab or a pre-procedure area where you’ll be prepared for the stent placement. This includes inserting an IV line for medications and monitoring your vital signs.
|
Pre-procedure Task |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Blood Tests |
To assess your overall health and check for any underlying conditions. |
|
Medication Adjustment |
To minimize the risk of bleeding or other complications. |
|
Imaging Studies |
To evaluate the condition of your arteries and plan the stent placement. |
Many patients are curious about the stent insertion process. It’s a detailed and interesting procedure. It involves several steps and uses advanced technology for success.
The catheterization lab has the latest technology. This includes fluoroscopy machines for live X-ray images. Doctors use this to see what they’re doing.
The tools used are:
The stent insertion technique is precise:
The stent insertion procedure can take 30 minutes to several hours. It depends on the case’s complexity. During this time, patients are closely monitored.
Patients may feel a warm sensation or flushing when contrast dye is injected. This is normal and usually goes away quickly. The dye helps doctors see the arteries and stent placement.
The stent insertion process is very effective. It has changed how we treat blocked arteries. Knowing about the equipment, technique, and what to expect helps patients prepare.
Today, there are many stents to meet different needs. They have evolved to help with various health issues. Knowing about their materials and types is key for doctors and patients.
Bare metal stents are simple and made from metals like stainless steel. They are less likely to cause some problems. Drug-eluting stents, on the other hand, release medicine to keep the artery open. Some clinics say most stents today are drug-eluting, showing they work well.
A study found drug-eluting stents are better than bare metal ones. This makes them a top choice for many patients needing stents.
Biodegradable stents are a new type. They dissolve over time, which might help avoid long-term issues. They are a hopeful option for some, but more research is needed.
|
Stent Type |
Material |
Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
|
Bare Metal |
Stainless Steel |
Simple design |
|
Drug-Eluting |
Metal with drug coating |
Reduces artery re-narrowing |
|
Biodegradable |
Biodegradable polymers |
Dissolves over time |
Stent technology has grown a lot, from drug-eluting to biodegradable stents. These updates aim to better patient care and cut down on problems.
New stent designs focus on being easier to use, more effective, and safer. They try to be more flexible and lower the chance of issues. As research goes on, we’ll see even more stent improvements.
Knowing what to expect after stent placement can ease worries and help with healing. Premier Cardiology Consultants tell patients to rest and follow specific recovery steps.
Right after the procedure, patients stay in a recovery area for a few hours. Medical staff watch their vital signs and look for any immediate issues. It’s key to follow the doctor’s advice on rest, medication, and follow-up visits.
The time spent in the hospital varies based on the patient’s health and the procedure’s complexity. Some might go home the same day, while others need to stay overnight for more observation.
Patients might feel some discomfort at the catheter site, which can be managed with over-the-counter pain meds. It’s important to watch for signs of complications like severe pain, swelling, or trouble moving the affected limb.
Most people can get back to normal in a few days to a week after the procedure. But, it’s best to avoid heavy lifting, bending, or hard exercises for a time advised by your doctor.
|
Activity |
Recommended Waiting Period |
|---|---|
|
Light Exercise |
2-3 days |
|
Strenuous Exercise or Heavy Lifting |
7-10 days |
|
Returning to Work |
1-3 days |
As Premier Cardiology Consultants advise, sticking to the post-procedure instructions is key for a good recovery. If you notice anything unusual, reach out to your healthcare provider right away.
“The key to a successful recovery after stent placement is adherence to the post-procedure care instructions and being aware of the signs of possible complications.”
Life after getting a stent means making some big changes. These changes help the stent work right and keep your heart healthy.
Patients often take blood thinners after a stent. These medicines stop blood clots from forming on the stent. You might take aspirin and a P2Y12 inhibitor like clopidogrel. How long you take these medicines depends on your stent type and health risks.
Eating well is key after a stent. Some clinics suggest eating lots of fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean proteins. Try to eat less of foods high in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol.
|
Food Group |
Recommended Foods |
Foods to Limit |
|---|---|---|
|
Fruits and Vegetables |
Apples, berries, broccoli, spinach |
Fried or processed vegetables |
|
Proteins |
Lean meats, fish, beans, lentils |
Processed meats, high-fat meats |
|
Grains |
Whole grains, oats, brown rice |
Refined grains, white bread |
It’s good to stay active after a stent. Start with easy activities like walking. Then, you can do more as you get stronger and your doctor says it’s okay.
Traveling with a stent? Carry your medicines and have a plan for emergencies. Always check with your doctor before you go.
It’s important for patients and doctors to know about the risks and long-term effects of stent insertion. Stents help improve blood flow and treat heart conditions. But, there are possible complications that can happen.
Some common issues with stent placement include bleeding, clotting, and artery narrowing. These problems can happen for different reasons. This includes the type of stent and the patient’s health.
Bleeding can happen because of medicines used during and after the procedure. Clot formation, or thrombosis, is serious and can be deadly if not treated quickly. Restenosis is when the artery gets narrow again, which might need more treatment.
The life of a stent depends on many things. This includes the stent type, where it’s placed, and following care instructions. Drug-eluting stents are made to lower the chance of artery narrowing by releasing medicine.
|
Stent Type |
Characteristics |
Longevity |
|---|---|---|
|
Bare Metal Stents |
Simple metal mesh |
Higher risk of restenosis |
|
Drug-Eluting Stents |
Release medication to prevent cell growth |
Lower risk of restenosis |
|
Biodegradable Stents |
Dissolve over time |
Varies; under research |
It’s key for patients to know the signs of possible problems. These include severe chest pain, trouble breathing, or bleeding signs. Seeing a doctor right away is vital if these symptoms show up.
Regular check-ups are important to watch how the stent is doing. This means taking medicines as told, going to follow-up visits, and making lifestyle changes as advised by doctors.
By knowing the possible complications and following care instructions, patients can have better long-term results after getting a stent.
Understanding stent procedures is key for those with heart conditions. We’ve looked at the purpose, types, and care after stent placement. This helps patients know what to expect.
To make good choices about stents, knowing the benefits and risks is important. Knowing about different stents and what happens during and after the procedure helps. This way, patients can pick the best treatment for them.
Being informed about stent procedures helps patients take charge of their health. It’s vital to talk to a doctor about any worries or questions. This ensures the best care for each patient.
PCI, or Percutaneous Coronary Intervention, is a non-surgical method. It opens blocked heart arteries. This improves blood flow to the heart.
Yes, most patients stay awake during stent insertion. This is because the procedure is done under conscious sedation or local anesthesia.
Angioplasty uses a balloon to widen a blocked artery. Stenting places a metal mesh tube (stent) to keep the artery open.
There are several stent types, like bare metal, drug-eluting, and biodegradable stents. Each has its own benefits and characteristics.
Recovery time varies. But most people can get back to normal activities in a few days to a week after the procedure.
Patients usually need to take antiplatelet therapy and blood thinners. These help prevent clotting and promote healing.
Flying after a stent procedure is generally safe. But it’s best to wait a few days and check with your doctor first.
Complications can include bleeding, clotting, stent failure, and allergic reactions, among others.
Stent longevity varies. But most can last many years, and some may last a lifetime.
Symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, or severe bleeding need immediate medical attention.
Most modern heart stents are safe for MRI. But it’s important to tell your doctor about your stent before undergoing an MRI.
Coronary stents treat heart artery blockages. Peripheral stents treat blockages in other arteries, like those in the legs.
A renal stent is used to treat blockages in the arteries that supply blood to the kidneys.
Stents keep the artery open. This allows for better blood flow to the affected area.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28279314/
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!