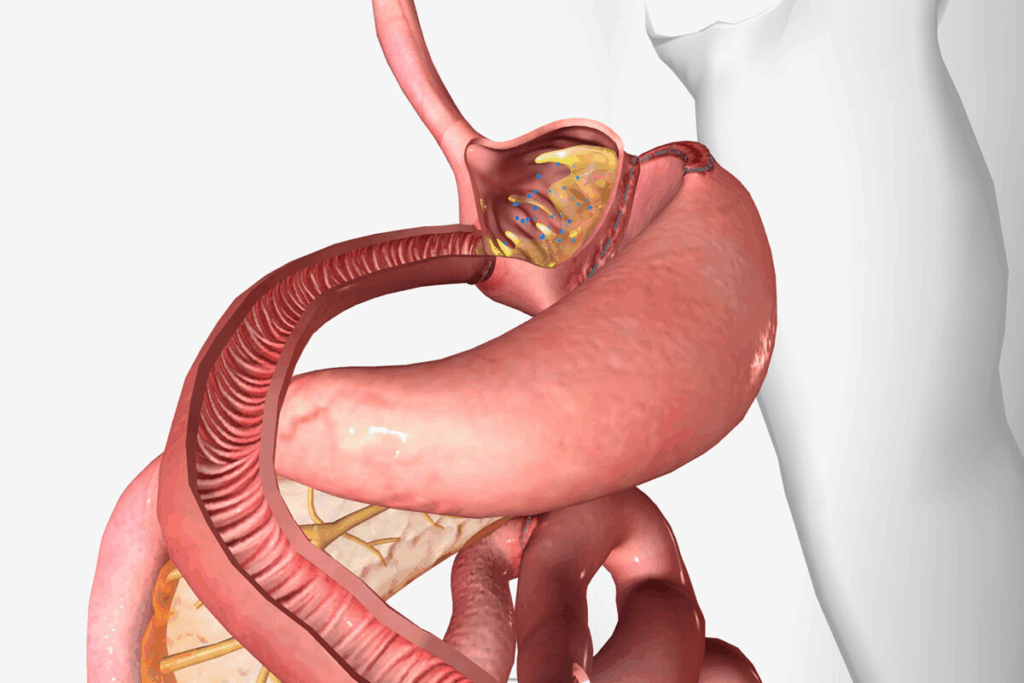
Gastrojejunostomy, or GJ bypass, is a surgery that links the stomach to the jejunum. It skips the duodenum. This method helps with weight loss and fixing stomach blockages.
Explaining the procedure and purpose of a g j bypass (Gastrojejunostomy Bypass).
At Liv Hospital, we offer a detailed guide on GJ bypass. It covers what it is, why it’s done, how it’s done, and its results. We focus on our patients, making sure they get top-notch care. Our services are designed for international patients, with both traditional and endoscopic approaches like EUS-GJ.
Key Takeaways
- GJ bypass is a surgical procedure that connects the stomach to the jejunum.
- It is used to treat gastric obstructions and support weight loss.
- The procedure can be performed through open surgery, laparoscopic techniques, or endoscopic approaches.
- EUS-GJ is a cutting-edge endoscopic method with minimal recovery time.
- Liv Hospital provides complete care and support for international patients undergoing GJ bypass.
What is a G J Bypass: Definition and Medical Purpose
GJ bypass is a key surgery for treating gastric outlet obstruction and helping with weight loss. It connects the stomach directly to the jejunum, skipping the pylorus. This surgery is vital in the field of gastrointestinal surgery.
The Gastrojejunostomy Procedure Explained
The GJ bypass surgery involves an incision in the stomach. It creates a direct link between the stomach and the jejunum. This lets food go straight into the small intestine, bypassing the pylorus.
It can be done in several ways, like open surgery, laparoscopic surgery, or endoscopic ultrasound-guided gastrojejunostomy (EUS-GJ).
Anatomical Changes After GJ Bypass
After a GJ bypass, food’s path through the stomach changes. It now goes directly to the jejunum. This can help with gastric emptying and reduce symptoms of gastric outlet obstruction.
Understanding stomach anatomy and physiology is key to grasping these changes, as noted by the NCBI Bookshelf.
Historical Development of the Procedure
The GJ bypass has a long history, starting in the early 20th century. It was first used for gastric outlet obstruction due to ulcers or cancer. Over time, it has evolved with new surgical technologies and a deeper understanding of the stomach.
Today, it’s used not just for gastric outlet obstruction but also for weight loss and after gastric resection. Knowing its history and purpose helps healthcare providers manage patient expectations and outcomes.
Medical Indications for GJ Bypass Surgery
It’s important to know when GJ bypass surgery is needed. This surgery helps many people with certain stomach problems. It makes their lives better by fixing these issues.
Gastric Outlet Obstruction Management
Gastric outlet obstruction is a big problem. It can happen for many reasons, like cancer or strictures. GJ bypass surgery helps by making a new way for food to go around the blockage.
Studies show GJ bypass works well for this issue. It’s a good choice when other treatments don’t work.
Weight Loss Surgery Applications
GJ bypass is also used for weight loss. It’s a big help for people who are very overweight. According to StatPearls, it’s a key part of treating severe obesity.
Post-Gastric Resection Reconstruction
After removing part of the stomach, patients need to have it fixed. GJ bypass helps fix this by making sure food can move through the stomach again. This lets patients eat normally and get the nutrients they need.
Other Clinical Scenarios
GJ bypass is also used in other situations. This includes patients with special body shapes or those needing care for advanced cancer.
Indication | Description | Benefits |
Gastric Outlet Obstruction | Bypass obstruction caused by malignancies or strictures | Relief from nausea, vomiting, and pain |
Weight Loss Surgery | Part of bariatric surgery for severe obesity | Significant weight loss and improvement in comorbidities |
Post-Gastric Resection | Reconstruction after gastric resection | Restoration of gastrointestinal continuity and nutritional improvement |
Knowing when to use GJ bypass surgery helps doctors help their patients more. This makes sure patients get the best care possible.
Types of GJ Bypass Procedures
GJ bypass surgery comes in different forms, each with its own benefits and considerations. The right procedure depends on the patient’s health, the reason for the surgery, and the surgeon’s skills.
Traditional Open Surgery Approach
The traditional method involves a big incision in the belly to reach the stomach and small intestine. This way, the surgeon can see and work on the tissues directly.
Benefits: It’s a clear and straightforward method.
Limitations: It takes longer to recover, leaves a bigger scar, and can cause more pain after surgery.
Laparoscopic GJ Bypass Techniques
Laparoscopic GJ bypass uses small cuts and a camera to see inside. This method causes less damage and heals faster.
Advantages: It leads to less pain, smaller scars, and quicker healing.
Challenges: It needs special skills and tools, and not everyone can have it.
Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Gastrojejunostomy (EUS-GJ)
EUS-GJ is a new, less invasive method. It uses ultrasound to guide the creation of a gastrojejunostomy. It’s great for those who can’t have traditional surgery.
Key Benefits: It avoids big cuts, shortens recovery time, and is safe for some patients who can’t have surgery.
Recent studies show EUS-GJ works better than old surgery methods for some patients. Here’s a summary of recent research on GJ bypass techniques.
Procedure | Recovery Time | Complication Rate |
Traditional Open Surgery | 6-8 weeks | Higher |
Laparoscopic GJ Bypass | 2-4 weeks | Moderate |
EUS-GJ | 1-2 weeks | Lower |
In conclusion, choosing a GJ bypass procedure depends on many factors. EUS-GJ is a big step forward because it’s less invasive and has good results for some patients.
Patient Selection Criteria for GJ Procedures
To get the most from GJ bypass surgery, strict patient selection is key. This careful process is vital for the best results, as studies in bariatric surgery show.
Medical Eligibility Requirements
Patients for GJ bypass need to meet certain health standards. They must have a condition that requires surgery, like gastric outlet obstruction or severe obesity. We check their overall health and any existing health issues like diabetes or high blood pressure.
Condition | Criteria | Evaluation Method |
Gastric Outlet Obstruction | Presence of obstruction | Endoscopy, Imaging Studies |
Severe Obesity | BMI ≥ 40 or BMI ≥ 35 with comorbidities | BMI Calculation, Comorbidity Assessment |
Contraindications for Surgery
Some health issues make GJ bypass surgery not suitable. These include severe heart or lung disease, active cancer, and serious mental health problems. We look closely at each patient’s health history to spot these issues.
Key contraindications include:
- Severe organ dysfunction
- Active substance abuse
- Uncontrolled psychiatric conditions
Age and Health Considerations
Age and health are big factors in choosing patients for GJ bypass. While age isn’t a strict limit, older patients need extra checks due to health concerns. We consider their physical age, health, and ability to follow post-surgery care.
Alternative Treatments to Consider
We look at other treatments before GJ bypass surgery. These might include endoscopic procedures, diet plans, and non-surgical options.
Alternative treatments may offer:
- Less invasive options
- Reversible procedures
- Complementary therapies
By carefully choosing patients, we make sure GJ bypass surgery helps those who need it most. This approach improves outcomes and reduces risks.
Pre-Surgical Preparation for GJ Bypass
To get the best results from GJ bypass surgery, patients need to prepare well before. This preparation includes several important steps. These steps help make sure the surgery and recovery go smoothly.
Required Medical Evaluations
Before GJ bypass surgery, patients must go through many medical checks. These checks are key to finding any health risks. They make sure the patient is ready for surgery.
Medical evaluations typically include:
- Complete blood count and blood chemistry tests
- Imaging studies such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI
- Cardiovascular evaluation, including ECG and stress test if necessary
- Respiratory function tests
- Nutritional assessment
Dietary Restrictions Before Surgery
Following certain diet rules before GJ bypass surgery is very important. It helps lower the risk of complications and aids in recovery.
Patients are typically advised to:
- Follow a liquid diet for a certain period before surgery
- Avoid certain foods that could complicate the procedure
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water
Medication Management
Managing medications is a key part of pre-surgical prep. Patients must tell their doctor about all medicines they take.
Medications may need to be adjusted or discontinued before surgery, including:
- Blood thinners
- Diabetes medications
- Certain supplements that could interfere with surgery
Mental Preparation and Expectations
Mental prep is as important as physical prep. Knowing what to expect can help reduce anxiety and improve results.
We recommend that patients:
- Discuss their concerns and expectations with their healthcare provider
- Engage in stress-reducing activities such as meditation or yoga
- Build a support network of family and friends
By following these guidelines, patients can greatly help their GJ bypass surgery success and recovery.
Step-by-Step GJ Bypass Procedure Guide
GJ bypass surgery has many important steps. Each step needs to be done with great care for the best results. Knowing each step is key for both doctors and patients.
Anesthesia Administration
The first thing we do is give the patient anesthesia. General anesthesia keeps them comfortable and pain-free. We choose the right amount based on their health and medical history, watching their vital signs closely.
Surgical Access Creation
After the anesthesia, we make the surgical access. This can be done in two ways: traditional open surgery or laparoscopic techniques. The choice depends on the patient’s needs and the doctor’s opinion. Laparoscopic surgery is often better because it’s less invasive and leads to faster recovery.
Stomach and Jejunum Identification
Finding the stomach and jejunum is a key step. We locate these parts carefully to make sure the connection is right. This is very important for how well the patient’s digestive system works after surgery.
Anastomosis Formation Techniques
The last step is making the connection between the stomach and jejunum. We use different surgical techniques to make a strong and working connection. The method we choose depends on the patient’s body and the doctor’s skill. Studies show that EUS-GJ procedures use endoscopic ultrasound for better precision and safety.
We always focus on being precise and keeping the patient safe during the GJ bypass procedure. By carefully following each step, we can get the best results for our patients.
Recovery and Post-Operative Care
Recovery and post-operative care are key parts of GJ bypass treatment. After a GJ bypass, patients need close monitoring and support. This helps them smoothly return to their normal lives.
Immediate Post-Surgical Monitoring
Patients are watched closely in the recovery room after surgery. We check their heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels. This ensures they are stable.
Pain Management Protocols
Managing pain is very important after surgery. We use medicines and other methods to control pain. Our goal is to reduce discomfort and help the patient recover well.
Dietary Progression After GJ Bypass
Diet changes start with clear liquids and move to solid foods slowly. We give patients specific diet advice during recovery.
Day | Dietary Recommendations |
1-2 | Clear liquids |
3-7 | Full liquids, pureed foods |
7+ | Soft foods, gradual introduction to regular diet |
Physical Activity Guidelines
Starting gentle movements helps with healing and prevents problems. We suggest gentle activities first and then increase them.
By following these guidelines, patients can have a successful recovery. This ensures the best results from their GJ bypass surgery.
Clinical Outcomes and Latest Research Findings
Recent studies have greatly improved our understanding of GJ Bypass surgery results. We are learning more about how different GJ methods work. This new research gives us important insights into their effects on patients.
Comparative Analysis of Different GJ Techniques
Studies have shown that different GJ Bypass methods have different success rates. EUS-GJ procedures are getting more attention for their less invasive approach and good results. Now, treatments are more tailored to each patient’s needs and body.
“The introduction of EUS-GJ has changed gastroenterology, providing a less invasive option,” research says. This has cut down on complications and sped up recovery times for patients.
EUS-GJ vs. Traditional Methods: Statistical Data
Studies show EUS-GJ procedures lead to shorter hospital stays and quicker procedures than traditional surgery. For example, a study found EUS-GJ patients stayed in the hospital for 2.5 days, while traditional surgery patients stayed for 5 days.
- EUS-GJ procedures: Average hospital stay of 2.5 days
- Traditional surgical methods: Average hospital stay of 5 days
- Reduced procedural time with EUS-GJ: Average of 45 minutes vs. 2 hours for traditional methods
Complication Rates and Safety Profiles
Complication rates for GJ Bypass vary by method. EUS-GJ has a good safety record, with fewer major complications than open surgery. This suggests EUS-GJ may lower the risk of serious problems.
“The safety profile of EUS-GJ is noteworthy, with fewer complications than traditional surgery.” Recent Study
Quality of Life Improvements
After GJ Bypass surgery, patients often see big improvements in their quality of life. They can eat and digest food better, which greatly improves their well-being.
Looking at long-term results, GJ Bypass surgery, including EUS-GJ, offers big benefits. Our review of recent studies supports EUS-GJ as a good and effective treatment option.
Conclusion
We’ve looked into GJ bypass surgery, which connects the stomach directly to the jejunum. This surgery is used for managing gastric outlet obstruction and for weight loss. It’s a complex procedure with many uses.
Recent studies in StatPearls show that bariatric surgery, like GJ bypass, helps with severe obesity and related health issues. Knowing the different ways to do the surgery helps patients make better choices. This includes open surgery, laparoscopic GJ bypass, and EUS-GJ.
In wrapping up our guide on GJ bypass, it’s clear that choosing the right patient, preparing well before surgery, and using precise techniques are key. We urge patients to talk to doctors to find the best treatment for them.
FAQ
What is a GJ bypass procedure?
A GJ bypass, or gastrojejunostomy, is a surgery that links the stomach to the jejunum. It skips the duodenum. This can be done in several ways, like open surgery or laparoscopic methods. Even endoscopic approaches like endoscopic ultrasound-guided gastrojejunostomy (EUS-GJ) are used.
What are the medical indications for GJ bypass surgery?
GJ bypass surgery helps with many health issues. It’s used for managing gastric outlet obstruction and for weight loss. It’s also for post-gastric resection reconstruction and other cases where a direct stomach-jejunum connection is needed.
What types of GJ bypass procedures are available?
There are different GJ bypass procedures. You can have traditional open surgery or laparoscopic GJ bypass. There’s also endoscopic ultrasound-guided gastrojejunostomy (EUS-GJ). Each method has its own advantages and drawbacks, depending on the patient’s needs.
How is patient selection done for GJ procedures?
Choosing patients for GJ procedures is a careful process. Doctors check if the patient is medically eligible and if surgery is safe. They also look at the patient’s age and health, and consider other treatments. This ensures the best care for each patient.
What is involved in pre-surgical preparation for GJ bypass?
Getting ready for GJ bypass surgery includes several steps. Patients need medical checks, follow dietary rules, manage their medications, and mentally prepare. Good preparation is key for a successful surgery.
What can I expect during the GJ bypass procedure?
The GJ bypass surgery involves several steps. First, anesthesia is given, then the surgeon makes an access point. Next, the stomach and jejunum are found and connected. The exact steps depend on the surgical method used.
What is the recovery process like after GJ bypass surgery?
After GJ bypass surgery, patients need to rest and follow a recovery plan. This includes managing pain, starting with soft foods, and gradually increasing physical activity. Proper care is vital for a smooth recovery.
What are the clinical outcomes and benefits of GJ bypass surgery?
GJ bypass surgery can greatly improve a patient’s life. It can manage certain health conditions and help with weight loss. The results depend on the surgery type and the patient’s health.
How does EUS-GJ compare to traditional GJ bypass methods?
EUS-GJ is a newer, less invasive method. It has shown to have faster recovery times. Studies are ongoing to compare it with traditional methods, looking at outcomes and complications.
Are there any risks or complications associated with GJ bypass surgery?
Like any surgery, GJ bypass carries risks and complications. These can vary based on the surgery type, patient’s health, and other factors. It’s important to talk to a healthcare provider about these risks and benefits.
Reference
National Health Service (NHS). Gastrojejunostomy (GJ) Bypass: Procedure, Weight Loss, and Blockage Relief. Retrieved from https://www.gosh.nhs.uk/conditions-and-treatments/procedures-and-treatments/gastrojejunostomy-transgastric-jejunal-feeding-device-care/