Expecting mothers often wonder when they will get their gestational diabetes test results. They also want to know what these results mean for their pregnancy. It’s important for every pregnant woman to understand the timeline and process of gestational diabetes screening.
Receiving test results can be a big worry for pregnant women. Testing for gestational diabetes is key to finding high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. These levels can impact both the mother and the baby.
Most test results come back in one or two days. But, the path from the first screening to the final diagnosis has its own steps. Healthcare providers use these steps to keep both the mother and the baby safe.
Key Takeaways
- Pregnant women usually get tested for gestational diabetes between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy.
- Women with known risk factors might get tested earlier.
- Testing for gestational diabetes is a big part of prenatal care.
- Getting test results can take one to two days.
- Knowing how the testing works can ease worries for pregnant women.
Understanding Gestational Diabetes During Pregnancy

Gestational diabetes is a big deal for pregnant women. It affects their health and the baby’s well-being. It’s a condition where blood sugar levels get too high.
What is Gestational Diabetes?
Gestational diabetes happens only during pregnancy. It’s caused by hormonal changes and insulin resistance. This leads to high blood sugar levels.
The placenta makes hormones to help the baby grow. But these hormones can block insulin. This makes blood glucose levels go up. If the body can’t make enough insulin, gestational diabetes develops.
How It Affects Mother and Baby
Gestational diabetes can be tough for both mom and baby. It raises the risk of pregnancy and delivery problems for mom. It also raises the risk of type 2 diabetes later on.
For the baby, it can cause too much weight. This makes delivery harder. It also raises the risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes later in life.
Risk Factors for Developing Gestational Diabetes
Some things can make a woman more likely to get gestational diabetes. Being overweight or obese before pregnancy is one. Having a family history of diabetes is another. Having had it before is also a risk factor.
Risk Factor | Description |
Being Overweight/Obese | Excess weight before pregnancy increases insulin resistance. |
Family History | Having a parent or sibling with diabetes increases risk. |
Previous Gestational Diabetes | Having had gestational diabetes in an earlier pregnancy. |
Knowing these risk factors helps pregnant women and their doctors. They can take steps to manage gestational diabetes well.
Overview of the Gestational Diabetes Test Process
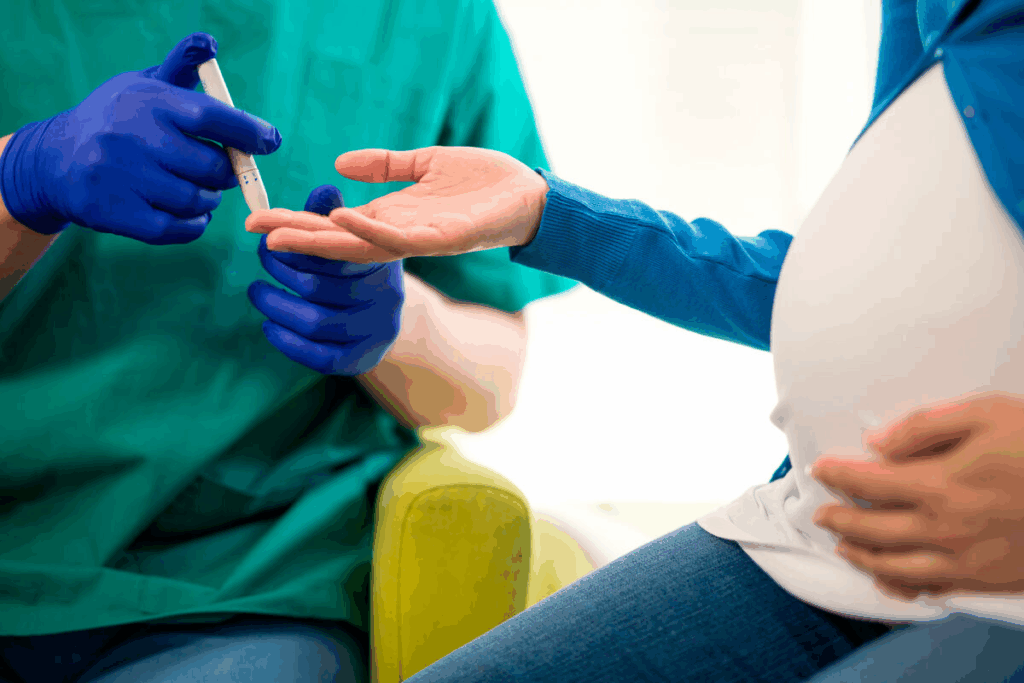
Pregnant women usually get a gestational diabetes test between 24 and 28 weeks. This is when diabetes often starts. We know this test can worry many moms-to-be. So, let’s explain what it’s about and why it’s key.
Standard Testing Timeline (24-28 Weeks)
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists says all pregnant women should get tested for gestational diabetes between 24 and 28 weeks. This is because the placenta starts making more hormones that can block insulin. This can lead to diabetes. The test is done during a routine visit, making it easy for moms.
“Gestational diabetes screening is a routine part of prenatal care that helps us identify and manage possible complications early on,” says Medical Expert, a leading obstetrician. “By finding gestational diabetes during this important time, we can protect the health of both mom and baby.”
Early Screening for High-Risk Pregnancies
Women at high risk for gestational diabetes might get tested earlier. This includes those with a history of diabetes in a previous pregnancy, obesity, a family history of diabetes, or being over 35. Early testing helps catch and manage diabetes sooner, lowering the risk of problems.
Why the 28 Week Glucose Test is Critical
The glucose test at 28 weeks is key because it spots women who might have gestational diabetes. It’s not a sign of poor health but a call for extra care to keep blood sugar in check. Finding diabetes early lets doctors help manage it, ensuring the best health for mom and baby.
Managing gestational diabetes means making diet changes, checking blood sugar, and sometimes taking medicine. With the right care, women with gestational diabetes can have healthy pregnancies and babies.
The Initial Screening: 1-Hour Glucose Challenge Test
For many pregnant women, the 1-hour glucose challenge test is the first step in assessing their risk for gestational diabetes. This test is a key initial screening that helps identify issues early on.
Step-by-Step Process of the Test
The 1-hour glucose challenge test is straightforward. First, you’ll drink a 50-gram glucose solution. This sweet drink tests your body’s glucose processing ability.
One hour later, your blood will be drawn to measure glucose levels. This test doesn’t require fasting beforehand, making it easy to schedule.
The 50-Gram Glucose Solution Experience
The 50-gram glucose solution is a sweet, non-carbonated drink. It contains 50 grams of glucose and is meant to be drunk quickly.
Some women find the drink too sweet. But it’s a necessary part of the test. Your healthcare provider or laboratory will provide the solution.
1-Hour Glucose Test Fasting Requirements
The 1-hour glucose challenge test doesn’t require fasting. You can eat and drink normally before the test. This makes it convenient to schedule at any time.
But, it’s important to follow any specific instructions from your healthcare provider. They may have particular requirements or recommendations.
What to Expect During and After the Test
During the test, you’ll drink the glucose solution and wait for one hour before your blood is drawn. You might feel some discomfort or anxiety during the blood draw. But this is usually minimal.
After the test, you can go back to your normal activities. The laboratory will process your results. You’ll be notified of the outcome.
To better understand glucose levels during pregnancy, let’s look at normal values:
Test | Normal Value |
Fasting Glucose | < 95 mg/dL |
1-Hour Glucose | < 180 mg/dL |
2-Hour Glucose | < 155 mg/dL |
3-Hour Glucose | < 140 mg/dL |
Knowing these values helps you understand your test results. It shows how they relate to your health during pregnancy.
When Do You Get Results of the Glucose Challenge Test?
Waiting for glucose challenge test results can be stressful. But knowing what to expect can ease the wait. This time is important for both the mother and the baby’s health.
Typical Laboratory Processing Times
How long it takes to get results varies. It depends on the lab’s workload and how they test. Usually, women get their results in one or two days.
How Long Does It Take for Glucose Test Results?
Results times can vary by doctor. But, most women get theirs in 24 to 48 hours. Always ask your doctor about their specific time frame.
How Results Are Communicated to Patients
Results are shared in different ways. You might get a call, see them online, or talk about them in person. It depends on your doctor and what you prefer.
Understanding Your Initial Screening Numbers
It’s key to understand your glucose test results. They help decide what to do next in your pregnancy. Here’s a table to help you understand your results.
Result (mg/dL) | Interpretation | Next Steps |
Less than 140 | Normal | No further testing needed |
140 or higher | Abnormal | Further testing required (e.g., 3-hour OGTT) |
Talking to your healthcare provider about your results is important. They can explain what they mean for you.
The Diagnostic Test: 3-Hour Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
If your first glucose screening shows high levels, you might need a more detailed test. The 3-hour oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) is key in figuring out if you have gestational diabetes.
Why You Might Need This Follow-Up Test
If your first test shows high glucose, your doctor might recommend a 3-hour glucose test. This test is needed to confirm or rule out gestational diabetes. The first test is just a start, and the 3-hour OGTT gives a clearer view of how your body handles glucose.
The main reasons for this follow-up test include:
- To confirm or rule out gestational diabetes after an abnormal initial screening
- To see how your body processes glucose over a longer time
- To get a more accurate diagnosis based on your body’s glucose metabolism
How Does a 3-Hour Glucose Test Work?
The 3-hour OGTT involves several steps and requires fasting for 8 to 14 hours before the test. Here’s what you can expect:
- You will arrive at the testing facility after fasting for the required period.
- A baseline blood sample will be taken to measure your fasting glucose level.
- You will then be given a 100-gram glucose solution to drink within a specified time frame.
- Additional blood samples will be taken at one, two, and three-hour intervals after consuming the glucose solution.
It’s essential to follow the instructions provided by your healthcare provider or the testing facility to ensure accurate results.
What to Bring and How to Prepare
To make the 3-hour OGTT as smooth as possible, here are some tips on how to prepare:
- Fasting: Ensure you have fasted for the required 8 to 14 hours before the test. You can drink water during this period.
- Comfort: Wear comfortable clothing and consider bringing a book or other entertainment for the waiting periods.
- Snacks: Bring a snack to eat after the test is completed, as you may feel hungry or lightheaded after fasting and the glucose solution.
- Medications: Inform your healthcare provider about any medications you are taking, as some may need to be adjusted before the test.
By understanding what to expect and how to prepare for the 3-hour OGTT, you can approach the test with confidence and ensure accurate results.
Alternative Testing Protocol: 75-Gram OGTT
In many countries, the 75-gram OGTT is the go-to test for gestational diabetes. It’s simpler and works well. This method is used worldwide because it’s easy and effective.
Differences Between 100g and 75g Tests
The main difference is the glucose dose. The 75-gram test uses less glucose, which pregnant women might find easier. It also needs fewer blood draws, with a two-hour test versus the 100-gram test’s three hours.
Key differences include:
- Glucose dose: 75 grams vs. 100 grams
- Testing duration: 2 hours vs. 3 hours
- Number of blood draws: Fewer draws for the 75-gram test
75-Gram OGTT Normal Values for Pregnancy
Normal values for the 75-gram OGTT in pregnancy are slightly different. Here are the general guidelines:
Time | Normal Value (mg/dL) |
Fasting | 92 |
1 hour | 180 |
2 hours | 153 |
If any of these values are too high, it might mean you have gestational diabetes.
International vs. U.S. Testing Standards
The IADPSG and WHO suggest the 75-gram OGTT for diagnosing gestational diabetes. But in the U.S., the ADA says either test is okay, though the 100-gram test is more common.
“The adoption of the 75-gram OGTT aligns with international standards and provides a more streamlined approach to gestational diabetes screening.” – Dr. [Last Name], Endocrinologist
Two-Hour vs. Three-Hour Testing Protocols
The 75-gram OGTT is a two-hour test, while the 100-gram test takes three hours. The shorter 75-gram test is easier for patients and less work for hospitals.
Comparison of testing protocols:
- 75-gram OGTT: 2 hours, fewer blood draws
- 100-gram OGTT: 3 hours, multiple blood draws
Healthcare providers need to know these differences. They help choose the best test for each patient and their needs.
Timeframe for Receiving Your Gestational Diabetes Test Results
Knowing when you’ll get your gestational diabetes test results can ease anxiety during pregnancy. Waiting for test results can be stressful. Knowing what to expect can help a lot.
Processing Time for the 3-Hour Test
The time it takes to get 3-hour glucose test results varies. It depends on the lab and your healthcare provider. Usually, you’ll get your results in a few days.
This time lets labs check your blood sugar levels at different times during the test.
Test Type | Average Processing Time | Notification Method |
1-Hour Glucose Challenge Test | 1-3 days | Email or Patient Portal |
3-Hour Oral Glucose Tolerance Test | 3-5 days | Phone Call or Patient Portal |
When and How You’ll Be Notified
How you get notified can change based on your healthcare provider and what you prefer. You might get email notifications, patient portals, or phone calls. It’s good to talk to your healthcare provider about your preferred method.
What to Do If You Haven’t Received Results
If you haven’t gotten your gestational diabetes test results, contact your healthcare provider. They can tell you when you’ll get your results and why there might be a delay.
Digital Patient Portals and Result Access
Many healthcare providers offer digital patient portals for test results. These portals let you see your results, track your progress, and talk to your healthcare provider. If you want to use a patient portal, ask your healthcare provider about it.
Normal Pregnancy Glucose Levels and Interpreting Your Results
Knowing normal glucose levels during pregnancy is key to understanding test results. Gestational diabetes is when blood sugar levels are too high during pregnancy. It’s important to read test results correctly to diagnose and manage this condition.
How to Read Pregnancy Glucose Test Results
Reading glucose test results means understanding the values from these tests. These tests check how well your body handles blood sugar after drinking a glucose solution. The results are in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L).
Healthcare providers look at specific numbers to see if your glucose levels are normal or if you have gestational diabetes. These numbers are based on guidelines from trusted medical groups.
Normal Values for the 1-Hour Test
The 1-hour glucose challenge test is a first step in checking for gestational diabetes. Normal values are usually below 140 mg/dL, but this can vary. Your healthcare provider’s guidelines might be different.
If your result is below 140 mg/dL, it’s considered normal. But if it’s above, you might need a more detailed test, like the 3-hour OGTT.
OGTT Normal Values During Pregnancy
The 3-hour OGTT is a detailed test for diagnosing gestational diabetes. It checks blood glucose levels after fasting and after drinking a glucose solution at different times.
Time | Normal Values (mg/dL) |
Fasting | Less than 95 |
1 hour | Less than 180 |
2 hours | Less than 155 |
3 hours | Less than 140 |
To diagnose gestational diabetes, you must meet or exceed the thresholds at two or more of these times.
“Understanding your glucose test results is the first step in managing your health during pregnancy. If you have any concerns or questions, it’s always best to consult with your healthcare provider.”
What Constitutes a Gestational Diabetes Diagnosis
A diagnosis of gestational diabetes is based on glucose test results. It’s diagnosed when two or more OGTT values meet or exceed the thresholds.
Key diagnostic criteria include:
- Fasting glucose level of 95 mg/dL or higher
- 1-hour glucose level of 180 mg/dL or higher
- 2-hour glucose level of 155 mg/dL or higher
- 3-hour glucose level of 140 mg/dL or higher
If you’re diagnosed with gestational diabetes, your healthcare provider will help you manage it. This might include changing your diet, monitoring your blood glucose, and possibly using insulin.
What Happens After Your Gestational Diabetes Test Results
After you get your gestational diabetes test results, it’s time to take action. A positive diagnosis can feel scary, but knowing what to do next can make you feel more in control.
Next Steps After a Positive Diagnosis
If you test positive for gestational diabetes, your doctor will create a detailed plan for you. This plan will include regular checks, changes to your lifestyle, and follow-up visits to keep you and your baby healthy.
Key components of the management plan may include:
- Blood glucose monitoring to track your sugar levels
- Dietary changes to manage carbohydrate intake and maintain stable blood glucose levels
- Exercise recommendations to improve insulin sensitivity
- Regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider to review your progress
Meeting with Healthcare Providers
After finding out you have gestational diabetes, talking to your doctors is key. They will explain your condition, go over your management plan, and answer any questions. These talks are a chance to clear up any doubts and make sure you’re okay with your plan.
During these meetings, you can expect to discuss:
- The importance of blood glucose monitoring and how to perform it effectively
- Dietary recommendations tailored to your needs and preferences
- Safe exercise options during pregnancy
- How to recognize and manage possible complications
Blood Glucose Monitoring Requirements
Monitoring your blood sugar is a big part of managing gestational diabetes. You’ll need to check your levels often to keep them in the right range. Your doctor will tell you how often to check and what levels to aim for.
Tips for effective blood glucose monitoring:
- Use a reliable glucose meter and follow the manufacturer’s instructions
- Keep a log of your readings to track patterns and identify areas for improvement
- Adjust your diet and exercise routine based on your readings
- Consult your healthcare provider if you have consistently high or low readings
Dietary and Exercise Recommendations
Making healthy food choices and staying active are key to managing gestational diabetes. A healthcare provider or dietitian can help you create a meal plan that meets your needs and helps control your blood sugar.
Consider the following dietary tips:
- Choose complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables
- Incorporate lean proteins and healthy fats into your meals
- Avoid sugary drinks and foods high in added sugars
- Spread your carbohydrate intake throughout the day to maintain stable blood glucose levels
By following these steps and working with your healthcare team, you can manage gestational diabetes well and have a healthy pregnancy.
Conclusion: Managing Your Health Throughout Pregnancy
Managing gestational diabetes is key for a healthy pregnancy. We’ve talked about tests like the glucose challenge test and the oral glucose tolerance test. Knowing about these can really help your pregnancy journey.
Handling gestational diabetes means medical care, lifestyle changes, and keeping an eye on your health. Working with your doctor and following their advice is important. This includes eating well and staying active.
Gestational diabetes care is more than just managing the condition. It’s about being proactive for a healthy pregnancy. We urge you to stay informed, ask questions, and get help when you need it. With the right care, you can have a successful pregnancy.
By focusing on your health and teaming up with your healthcare team, you can manage gestational diabetes well. We’re here to give you the resources and support you need for a healthy pregnancy.
FAQ
What is gestational diabetes and how is it diagnosed?
Gestational diabetes is when blood sugar levels are too high during pregnancy. It’s found through a glucose screening test. This test is usually done between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy.
What is the standard testing timeline for gestational diabetes?
The usual time for testing is between 24 and 28 weeks. Women at higher risk might get tested earlier.
How long does it take to get results from the glucose challenge test?
It can take a few days to a week to get the results. This depends on the lab’s processing time.
What are normal glucose levels during pregnancy?
Normal levels vary by test. For the 1-hour test, a normal result is below 140 mg/dL. The 3-hour OGTT has fasting and post-load values.
How does a 3-hour glucose test work?
The 3-hour test, or OGTT, involves drinking a glucose solution. Blood sugar levels are checked at three times over three hours. It shows how well the body handles glucose.
What are the differences between the 100g and 75g OGTT?
The 100g OGTT is common in the U.S., while the 75g is used worldwide. The 75g test is easier for patients because it uses less glucose. Its normal values are also different.
How are gestational diabetes test results communicated to patients?
Results are shared by the healthcare provider. This can be in person or through a patient portal, depending on the system.
What happens after a positive gestational diabetes diagnosis?
After a diagnosis, patients talk with their provider about managing it. This includes monitoring blood sugar, changing diet, and exercising.
How can I access my gestational diabetes test results digitally?
Many providers offer patient portals. Here, patients can see their test results, including gestational diabetes screenings, online.
What are the risk factors for developing gestational diabetes?
Risk factors include a history of gestational diabetes, obesity, and family history of diabetes. Age over 35 and certain ethnic backgrounds also increase risk.
Can I prepare for the glucose challenge test or OGTT?
There’s no special prep for the glucose challenge test. Just eat normally before it. For the OGTT, fasting overnight is usually required.
References
Gestational diabetes mellitus screening is classically recommended between weeks 24 and 28 of pregnancy, the period during which glucose tolerance deteriorates.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21163427/