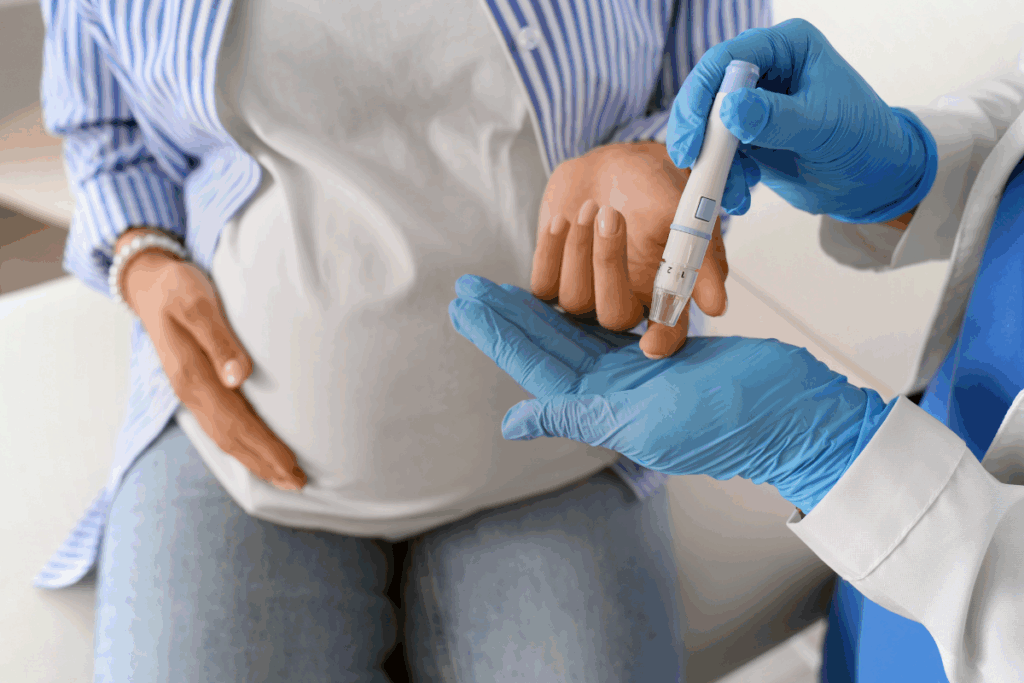
At Liv Hospital, we focus on clear communication and evidence-based care for mothers. Gestational diabetes mellitus affects about 10 percent of pregnant women. This makes glucose testing key in prenatal care.glucose test during pregnancyDoes a Nuclear Stress Test Show Blockages?
Gestational diabetes is when blood sugar levels rise during pregnancy. Our approach puts the mother and baby’s health first. We’ll help you understand if you need to fast before the test.
The glucose screening test checks a pregnant woman’s blood glucose level. Knowing the rules and needs for this test is important for expectant mothers.
Key Takeaways
- Gestational diabetes affects approximately 10% of pregnant women.
- Glucose testing is a critical component of prenatal care.
- The glucose screening test checks a pregnant woman’s blood glucose level.
- Clear communication and evidence-based protocol are essential in maternal healthcare.
- Fasting requirements for the glucose test will be explained by healthcare providers.
Understanding Gestational Diabetes and Why Testing Matters
Gestational diabetes is a big health issue during pregnancy. It’s when blood sugar levels get too high in women who didn’t have diabetes before. This condition is different from other types of diabetes. It happens because of hormonal changes and insulin resistance during pregnancy.
What is Gestational Diabetes Mellitus?
Gestational diabetes is linked to hormonal changes in pregnancy. The placenta makes hormones that help the baby grow. But these hormones can also block insulin, making it hard for the body to use it.
Prevalence and Risk Factors
Gestational diabetes is common in many pregnancies. It can run in families, and being overweight or obese increases the risk. Knowing these risk factors early can help doctors decide when to test for glucose.
Risk Factor | Description |
Family History | Having a first-degree relative (parent or sibling) with diabetes |
Previous GDM | Having had gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy |
Obesity | Being overweight or obese before pregnancy |
Potential Complications for Mother and Baby
Gestational diabetes can cause problems for both mom and baby if not managed. These include a higher chance of cesarean delivery and preeclampsia. Managing it well and testing on time are key to avoiding these risks.
It’s vital for pregnant women and doctors to understand gestational diabetes. Knowing the risks and complications helps stress the need for glucose tests during pregnancy.
Types of Glucose Tests During Pregnancy
Glucose testing during pregnancy is key for catching gestational diabetes early. These tests check how well the body handles blood sugar. There are mainly two types of tests used during pregnancy.
The glucose challenge test and the oral glucose tolerance test are the two main tests. Each has its own purpose and rules.
Glucose Challenge Test (One-Hour Screening)
The glucose challenge test is a first step that doesn’t need fasting. It’s simple: a woman drinks a glucose solution, and her blood sugar is checked after one hour.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (Three-Hour Diagnostic)
If the glucose challenge test shows a problem, an oral glucose tolerance test follows. This test requires fasting for 8 to 14 hours. Blood is taken before drinking a glucose solution and then every three hours to see how the body handles glucose.
Early Glucose Testing for High-Risk Patients
Women at high risk of gestational diabetes may get tested earlier. This early test helps find those who need extra care or quick action.
Key differences between the tests include the duration and fasting requirements. The glucose challenge test is quicker and doesn’t need fasting. The oral glucose tolerance test is more detailed and requires fasting.
- The glucose challenge test is used as an initial screening.
- The oral glucose tolerance test is used for diagnosis if the screening indicates a problem.
Knowing about the different glucose tests and their roles helps expectant mothers get ready for them. It also helps them understand their results.
When Do Glucose Tests Occur in Pregnancy?
Glucose testing is key in prenatal care, happening between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. This time is best for finding gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). It usually shows up in the second half of pregnancy.
Standard Timeline (24-28 Weeks)
Most pregnant women get a glucose screening test between 24 and 28 weeks. This helps doctors spot problems with glucose in the body during pregnancy.
Early Testing Scenarios
Some women need to test for glucose earlier than 24 weeks. This includes those with:
- A history of gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy
- Obesity or other risk factors for diabetes
- A family history of diabetes
- Previous delivery of a macrosomic baby (over 4 kg)
Testing early helps catch and manage gestational diabetes sooner.
Testing in Multiple Pregnancies
Women with twins or multiple pregnancies might have different testing times. Some doctors test at the same time as for single babies. Others might test earlier or more often because of the extra needs of multiple babies.
The Glucose Challenge Test Explained
The glucose challenge test is a key first step for checking for gestational diabetes. It’s a simple test to see how your body handles sugar.
Test Procedure and Duration
You’ll drink a glucose solution during the test. This sweet drink is given in a set amount. Then, you wait one hour before a blood test to check your sugar levels.
The whole process, from drinking the solution to getting your blood drawn, takes about an hour.
What to Expect During the Test
Here’s what happens when you get your glucose challenge test:
- You’ll drink a glucose solution.
- Then, you’ll wait for one hour.
- After waiting, your blood will be drawn.
You don’t need to fast before this test. It’s easy to fit into your day.
As stated by the American Diabetes Association, “The glucose challenge test is used to identify pregnant women who may be at risk for gestational diabetes.”
Understanding Your Results
After your blood is drawn, it’s sent to a lab for testing. Your healthcare provider will get the results. They’ll tell you if your sugar levels are normal.
If your levels are too high, you might need more tests. This could be the oral glucose tolerance test.
It’s very important to follow up on any abnormal results to keep yourself and your baby healthy.
Do You Need to Fast for the Glucose Challenge Test?
Many expectant mothers wonder if they need to fast before a glucose challenge test. The answer is no, unlike some other tests. You don’t have to fast before this test.
You can eat before the test, but choose wisely. Official guidelines suggest eating a normal meal the night before. And have a usual breakfast on the test day.
Official Recommendations on Eating Before the Test
Medical guidelines say you don’t need to fast. You can eat your usual meals. But, try to avoid high-sugar foods or drinks right before the test. This helps prevent false positive results.
Foods to Avoid Before Testing
Even though fasting isn’t required, it’s best to skip high-sugar foods and drinks on test day. Eating too much sugar can cause your blood glucose to spike. This might lead to a false positive screening.
Optimal Meal Planning on Test Day
Eat a balanced meal the night before and have a normal breakfast on test day. Stay away from heavy, high-sugar, or fatty meals. They can mess with your test results.
By following these tips, you’ll be ready for the glucose challenge test. Your results will accurately show your health status.
The Oral Glucose Tolerance Test in Detail
Expectant mothers need to know about the oral glucose tolerance test. It’s key for spotting gestational diabetes. This test checks how well the body handles glucose, unlike the simpler glucose challenge test.
When This Test Is Necessary
This test is needed if the glucose challenge test shows problems or if there are other signs of gestational diabetes. We’ll explain when it’s required.
It’s vital for diagnosing gestational diabetes, mainly when the first test hints at a problem. It shows how the body handles blood sugar after drinking a glucose drink.
Step-by-Step Test Procedure
The oral glucose tolerance test has several steps:
- Fasting for 8 to 12 hours before the test
- Providing an initial blood sample to measure fasting glucose levels
- Consuming a glucose-rich drink within a specified timeframe
- Having blood drawn at intervals (usually 1, 2, and sometimes 3 hours) after consuming the glucose drink
We’ll walk you through each step of the test.
Understanding the Test’s Duration and Blood Draw Schedule
The test takes 2 to 3 hours, depending on the protocol. The blood draw schedule checks how well the body manages blood sugar over time.
Here’s what the blood draw schedule might look like:
Time | Activity |
0 minutes | Fasting blood glucose measurement |
60 minutes | Blood draw after glucose consumption |
120 minutes | Second blood draw |
180 minutes | Third blood draw (for a 3-hour test) |
Knowing about the oral glucose tolerance test helps pregnant women prepare. They can understand the importance of the test results.
Fasting Requirements for the Glucose Tolerance Test
The glucose tolerance test needs fasting to get good results. It’s key for checking for gestational diabetes in pregnancy. Knowing the fasting rules helps moms-to-be get ready.
Mandatory Fasting Guidelines
For the test, fasting for 8 to 12 hours is required. You can only have water during this time. Following these rules is key for accurate results. The test is usually in the morning, so fasting overnight is needed.
Drink water to stay hydrated during fasting. But, avoid coffee, tea, or juice as they can mess with the test. Also, don’t chew gum or eat anything with sugar.
What Constitutes Breaking a Fast
Breaking a fast can ruin the test’s accuracy. Eating or drinking anything with calories, like gum or candy, can change blood sugar levels. Even a little bit of food or drink can affect the test.
Managing Medications During Fasting
If you’re pregnant and on meds, talk to your doctor about fasting. Some meds need food, while others don’t. Getting advice from your doctor is important for safe fasting. Tell your doctor about all meds, including vitamins.
By following fasting rules, pregnant women can get accurate test results. This helps doctors make better care plans for them.
Preparing for Your Glucose Test During Pregnancy
Getting ready for your glucose test during pregnancy is key. Knowing how to prepare can greatly affect your test results. It’s all about making sure you’re ready.
Carbohydrate Loading Before the Tolerance Test
Carbohydrate loading is a big part of getting ready. Eat at least 150 grams of carbs for three days before your test. This gets your body ready for the test, giving you better results.
To get enough carbs, eat foods like whole grains, fruits, and veggies. Here’s a daily meal plan:
Meal | Food | Carbohydrate Content (grams) |
Breakfast | Oatmeal with banana and honey | 60 |
Lunch | Whole wheat bread sandwich with fruit salad | 80 |
Dinner | Pasta with marinara sauce and vegetables | 90 |
Snacks | Fruit and yogurt | 40 |
Total | 270 |
Hydration Guidelines
Drinking water is also important. Drink at least eight glasses a day. Stay away from sugary drinks that can mess with your blood sugar.
Physical Activity Considerations
It’s okay to be active during pregnancy, but not too much before your test. Avoid hard workouts the day before and the day of your test. They can mess with your blood sugar, affecting your test.
What to Expect on Test Day
On the day of your glucose test, being ready can really help. The test might take a while and could be a bit uncomfortable. But, with the right steps, you can handle it better.
Comfort Items for Extended Testing
Having comfort items can make the wait easier. Bring a book, magazine, or your favorite podcast to keep you busy for the 1-hour wait after drinking the glucose solution. Also, bring a snack to eat after the test, as you’ll likely get hungry.
Managing Hunger and Discomfort
It’s key to manage hunger and discomfort during the test. Don’t eat or drink anything except water before the test, as it can mess with the results. If you feel dizzy or uncomfortable, tell the medical staff. They’ll help you out.
Post-Test Recovery Tips
After the test, you can go back to your usual activities. But, if you felt any discomfort, take it easy for the rest of the day. Make sure to eat a meal or snack after the test to keep your blood sugar stable.
Understanding and Managing Glucose Test Results
It’s key to understand your glucose test results to keep your health in check during pregnancy. We’ll help you make sense of these results and what to do next.
Normal Range Values
Good glucose test results mean your body is handling blood sugar well. For a 3-hour 100-gram oral glucose tolerance test, here’s what’s normal: Fasting should be under 95 mg/dL. After eating, levels should be under 180 mg/dL at 1 hour, 155 mg/dL at 2 hours, and 140 mg/dL at 3 hours.
Test Timing | Normal Value (mg/dL) |
Fasting | Less than 95 |
1 Hour | Less than 180 |
2 Hour | Less than 155 |
3 Hour | Less than 140 |
Borderline Results and Follow-Up Testing
If your results are borderline or abnormal, we might suggest more tests or monitoring. Borderline results show some values are a bit high, so we need to keep a close eye on them.
Treatment Options for Gestational Diabetes
If you’re diagnosed with gestational diabetes, we’ll talk about treatment plans. This could include changing your diet, checking your blood sugar, or using insulin. Our aim is to manage your condition well for a healthy pregnancy.
Working together, you and your healthcare provider can manage glucose test results. We’re here to support you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Understanding the importance of glucose testing during pregnancy is key. It helps manage gestational diabetes and reduces risks for both mom and baby. We’ve talked about how glucose tests, like the glucose challenge test and oral glucose tolerance test, are vital.
At our institution, we offer top-notch healthcare to international patients. Our team is here to give personalized prenatal care. We make sure expectant mothers get the help they need to manage gestational diabetes and have a healthy pregnancy.
Early detection and management of gestational diabetes can prevent complications. This ensures the best outcomes for both mom and baby. Our goal is to provide quality care and support. We empower women to take charge of their health and make informed choices about their pregnancy.
FAQ
What is a glucose test during pregnancy?
A glucose test during pregnancy checks for gestational diabetes mellitus. It sees how well your body handles sugar after drinking a sugary drink.
When do I take the glucose test during pregnancy?
We usually do the glucose test between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. But, if you’re at risk for gestational diabetes, we might test you earlier.
Are you supposed to fast before a glucose test?
For the glucose challenge test, you don’t need to fast. But, for the oral glucose tolerance test, you must fast for 8-12 hours.
What is the difference between the glucose challenge test and the oral glucose tolerance test?
The glucose challenge test is a first step to check blood sugar levels after a sugary drink. If it shows abnormal results, we do the oral glucose tolerance test. This test checks blood sugar levels at different times after drinking a sugary drink.
Do I need to fast before a glucose test?
It depends on the test. For the glucose challenge test, you don’t need to fast. But, for the oral glucose tolerance test, fasting is required.
What should I eat before a glucose test?
For the glucose challenge test, eat a normal meal before. But, avoid sugary foods and drinks. For the oral glucose tolerance test, fast for 8-12 hours before.
How much sugar is in a glucose test drink?
The glucose test drink has a set amount of glucose, usually 50-100 grams.
What are the normal range values for a glucose test?
Normal values vary by test. For the glucose challenge test, a normal result is under 140 mg/dL. For the oral glucose tolerance test, normal results are under 95 mg/dL fasting, under 180 mg/dL at 1 hour, and under 155 mg/dL at 2 hours.
What happens if I have abnormal glucose test results?
If your results are abnormal, we’ll talk about treatment options. This might include diet changes, exercise, and insulin therapy to manage your blood sugar.
Can I manage gestational diabetes through diet and exercise alone?
In some cases, yes. We might suggest diet changes and exercise to manage gestational diabetes. But, some women might need insulin therapy or other treatments to control their blood sugar.
How does gestational diabetes affect my baby?
Untreated gestational diabetes can harm your baby. It can lead to macrosomia, birth trauma, and neonatal hypoglycemia. With proper management, we can reduce these risks.
What are the risks associated with gestational diabetes?
Gestational diabetes can lead to complications for both you and your baby. These include preeclampsia, cesarean delivery, and a higher risk of type 2 diabetes later on.
References
Gestational diabetes mellitus screening is classically recommended between weeks 24 and 28 of pregnancy, the period during which glucose tolerance deteriorates.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21163427/