Do you wake up with stiff, tight knees or find knee pain limits your day? You’re not alone. Knee stiffness is common, affecting athletes and seniors alike.Explaining the common causes of tight knee pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion.
At Liv Hospital, we know how knee stiffness affects your life. Our team uses advanced tests, proven treatments, and expert orthopedic care. We find the cause of your problem.
Knee stiffness comes from many sources. It can be from injuries, diseases, or how we live. Knowing why is key to getting better and moving freely again.
Key Takeaways
- Knee stiffness affects millions worldwide, impacting daily life.
- Causes range from injuries and arthritis to muscle weakness and lifestyle factors.
- A patient-centered approach is key for effective diagnosis and treatment.
- Advanced diagnostic imaging and orthopedic expertise are vital for finding the cause.
- Evidence-based treatments can help ease knee stiffness and boost mobility.
Understanding Knee Stiffness and Its Prevalence

Knee stiffness is a common symptom linked to many conditions. It affects people of all ages, from young athletes to older adults. It can greatly reduce one’s quality of life.
How Common Is Knee Stiffness?
Knee stiffness is a main symptom of osteoarthritis, affecting millions globally. It’s not just common in older adults but also in younger people, like athletes. This is because sports and activities that stress the knee joint can cause it.
Recent data shows knee stiffness is widespread, with more cases as people get older. It can come from joint wear and tear, injuries, or inflammatory conditions.
Demographics Affected by Knee Stiffness
Knee stiffness can hit anyone, no matter their age or how active they are. But some groups face a higher risk due to certain factors.
Demographic | Risk Factors | Prevalence |
Older Adults | Osteoarthritis, wear and tear | High |
Young Athletes | Sports injuries, overuse | Moderate to High |
Individuals with Obesity | Excess weight on joints | Moderate |
Impact on Daily Activities
Knee stiffness can make everyday tasks hard, from walking to climbing stairs. It can also affect sports or exercise. The impact depends on how severe the stiffness is and its cause.
For many, knee stiffness lowers their quality of life. They might need to change their lifestyle or find ways to manage their symptoms. Knowing the causes and effects of knee stiffness is key to finding good treatments.
Anatomy of the Knee: Why It’s Prone to Stiffness
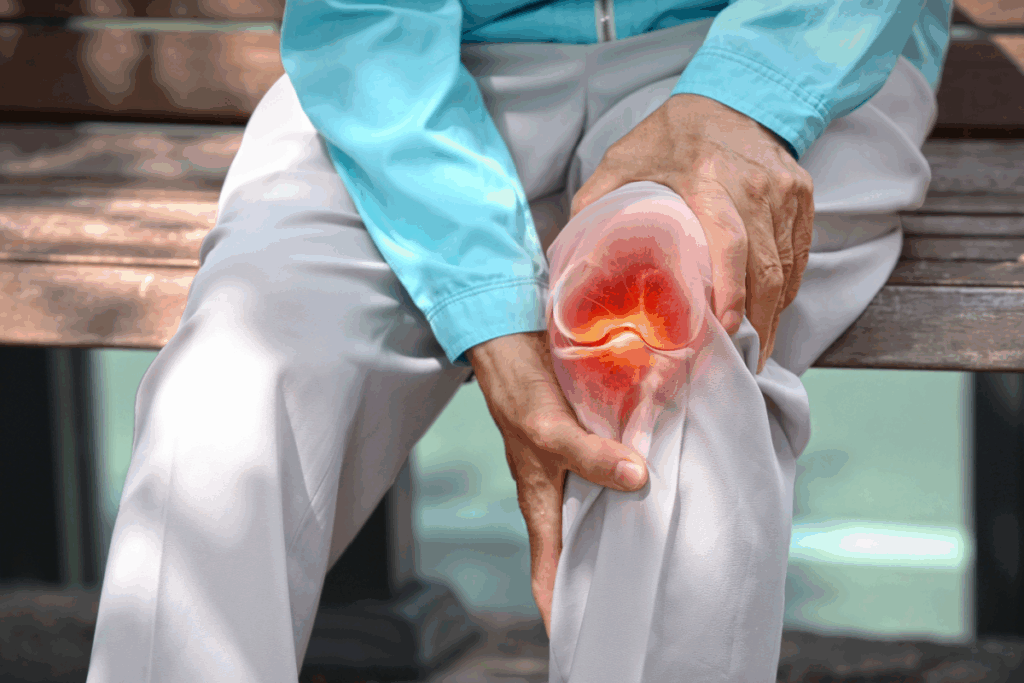
Knowing how the knee works is key to understanding why it can feel stiff. The knee is made up of bones, ligaments, tendons, and cartilage. These parts work together to help us move.
Key Structures of the Knee Joint
The knee has four bones: the femur, tibia, patella, and fibula. The femur and tibia carry our weight. The patella (kneecap) protects the joint and helps muscles work better. The fibula helps muscles and ligaments attach.
Ligaments and tendons are vital for knee stability and movement. Ligaments link bones together, while tendons connect muscles to bones, allowing us to move.
How the Knee Functions
The knee acts as a hinge joint, allowing us to bend and straighten it. It also moves slightly when bent. This movement is thanks to the knee’s parts, like the menisci, which cushion and reduce friction.
The knee does more than move; it also supports our body’s weight and absorbs shock. This is important for activities like walking, running, or jumping.
Vulnerable Points in Knee Mechanics
Despite its complexity, the knee can get injured and feel stiff. The menisci and ligaments are often hurt by sudden twists or impacts. The patellofemoral joint can also cause pain and stiffness, mainly in those who run or jump a lot.
Knowing where the knee can get hurt helps us prevent and manage stiffness. By understanding the knee’s mechanics and why it’s prone to stiffness, we can take better care of it. This is important for keeping our knees healthy.
Common Symptoms Associated with Tight Knee Pain
Knee pain and stiffness are common problems affecting millions. Tightness or stiffness in the knee often comes with other symptoms. These symptoms can help find the cause.
Recognizing Different Types of Knee Discomfort
Knee stiffness can feel different for everyone. Some might feel a dull ache, while others might have sharp pain or stiffness. Inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis often cause knee stiffness.
People may also experience pain, swelling, and trouble moving. It’s important to notice these symptoms for the right diagnosis and treatment. For example, swelling and redness might mean an inflammatory condition.
When Stiffness Indicates Serious Problems
In some cases, knee stiffness can mean a serious problem that needs a doctor. If stiffness is with locking or catching in the knee, it might be a meniscus tear or other damage.
Seeking medical help is key if stiffness is severe, lasts a long time, or comes with other scary symptoms. This includes instability, a lot of pain, or noticeable deformity.
Tracking Symptom Patterns
Writing down when knee stiffness happens, how long it lasts, and what makes it better or worse is helpful. This info helps doctors find the best treatment.
Understanding knee stiffness patterns and symptoms helps tackle the main cause. This could be mechanical issues, inflammatory conditions, or other problems.
Mechanical Injuries Causing Knee Stiffness
Mechanical injuries, like those to ligaments and menisci, often cause knee stiffness. These can happen during sports, over time, or from trauma. Knowing what’s wrong with your knee is key to treating it right and avoiding more harm.
Meniscus Tears and Degeneration
The meniscus is a cartilage in the knee that can tear. Meniscus tears are common in athletes or those with repetitive knee strain. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and stiffness, mainly after exercise.
As we get older, the meniscus can degenerate, making it more likely to tear. This can cause long-term stiffness and pain, making everyday tasks hard.
Ligament Injuries (ACL, MCL, PCL)
Ligament injuries also lead to knee stiffness. The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), medial collateral ligament (MCL), and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) keep the knee stable. These injuries can happen from sports, falls, or direct hits to the knee.
ACL injuries are common in sports that require quick stops or changes in direction. MCL injuries usually come from a direct hit to the knee. PCL injuries can happen from falling onto a bent knee. All these injuries cause pain, instability, and stiffness.
Patella-Related Problems
The patella, or kneecap, is essential for knee function. Issues like patellofemoral pain syndrome or patellar dislocation can cause a lot of discomfort and stiffness. These problems often stem from overuse, misalignment, or trauma.
Patellofemoral pain syndrome causes pain around or behind the patella, often from activities that stress the knee, like climbing stairs or squatting. Exercises to strengthen and align the knee can help ease these symptoms.
Inflammatory Conditions Leading to Stiff Knees
Understanding how inflammatory conditions affect knee stiffness is key. These diseases can make moving hard and cause pain. This makes simple tasks tough.
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Joint Inflammation
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic disease that attacks the joints. It mainly hits the knees. The immune system mistakenly attacks the joint lining, causing inflammation and pain.
Key aspects of RA include:
- Symmetrical joint involvement
- Morning stiffness lasting more than an hour
- Presence of rheumatoid factor or anti-CCP antibodies in the blood
Getting RA treated early is vital. It helps prevent damage and improves life quality.
Bursitis and Its Effects
Bursitis is when a bursa, a fluid-filled sac, gets inflamed. It cushions joints and reduces friction. Inflammation can cause knee pain and stiffness.
Type of Bursitis | Common Causes | Symptoms |
Prepatellar Bursitis | Direct blow to the knee, repetitive kneeling | Pain and swelling at the front of the knee |
Pes Anserine Bursitis | Overuse, repetitive stress on the knee | Pain on the lower inner aspect of the knee |
Treating bursitis means reducing inflammation. It also means avoiding activities that make it worse.
Gout and Pseudogout
Gout and pseudogout are two types of arthritis that cause sudden knee pain. They are caused by crystals in the joints.
“Gout is characterized by elevated levels of uric acid in the blood, leading to the formation of monosodium urate crystals within the joints.”
Pseudogout is caused by calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals. Both can cause sudden, severe pain and inflammation.
Managing gout and pseudogout means reducing crystals and inflammation. This is often done through medication and lifestyle changes.
Osteoarthritis: The Leading Cause of Knee Stiffness in Older Adults
Knee stiffness in older adults often comes from osteoarthritis. This condition breaks down cartilage. As we get older, our cartilage wears out, causing bone-on-bone contact and stiffness.
Cartilage Deterioration Process
The cartilage breakdown in osteoarthritis happens slowly. At first, the cartilage gets thinner and more damaged. Then, the cartilage can disappear, exposing the bone. This causes pain and leads to bone spurs and cysts.
Cartilage loss is a key sign of osteoarthritis. Without cartilage, joints can’t absorb shock or move smoothly, causing stiffness.
Risk Factors for Developing Knee Osteoarthritis
Several factors can lead to knee osteoarthritis. These include:
- Age: Older age increases the risk due to joint wear and tear.
- Obesity: Extra weight stresses the knee joints, speeding up cartilage loss.
- Previous Knee Injuries: Fractures or ligament tears can raise the risk of osteoarthritis.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some people are more likely to get osteoarthritis due to their genes.
- Repetitive Stress: Doing the same knee movements over and over can lead to osteoarthritis.
A leading orthopedic specialist says, “Knowing these risk factors is key to preventing and managing knee osteoarthritis.”
“The key to managing osteoarthritis lies in early detection and intervention, which can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected.”
Progression and Long-term Outlook
Knee osteoarthritis can progress differently for everyone. Some may see it get worse slowly, while others may experience a faster decline. The rate of progression depends on how well it’s managed and any other health issues.
In the long run, osteoarthritis can cause a lot of disability if not treated right. But, with the right treatment, like lifestyle changes and medical care, it’s possible to slow it down and keep moving well.
Lifestyle Factors Contributing to Tight Knee Pain
Our daily habits and lifestyle choices greatly affect our knee health. Some factors are unavoidable, but many lifestyle choices play a big role in tight knee pain.
Impact of Excess Weight on Knee Joints
Carrying extra weight puts extra stress on the knee joints. This can cause wear and tear on the cartilage and other structures. It leads to inflammation and pain, mainly in the knee.
Every pound of extra weight means the knee joint bears more pressure. This is true for activities like walking or climbing stairs. Losing even a little weight can help reduce this strain.
Muscle Weakness and Imbalances
Muscle weakness and imbalances around the knee are key factors in knee stiffness. The muscles around the knee, like the quadriceps and hamstrings, support and stabilize it.
Weak or imbalanced muscles can affect the knee’s mechanics. This leads to abnormal stress and strain. It causes pain and stiffness, often after sitting or at the end of the day.
Muscle Group | Function | Effect of Weakness |
Quadriceps | Knee extension | Instability, difficulty straightening knee |
Hamstrings | Knee flexion | Instability, difficulty bending knee |
Poor Flexibility and Movement Patterns
Poor flexibility and abnormal movement patterns also contribute to tight knee pain. Limited flexibility reduces range of motion and increases stress on the knee. Abnormal movement patterns add extra strain on the knee structures.
Exercises that involve repetitive knee movements, like running or cycling, need proper warm-up and stretching. This helps maintain flexibility and lowers the risk of knee stiffness.
By focusing on these lifestyle factors, we can take steps to reduce knee stiffness and improve knee health.
Diagnosing the Cause of Your Knee Stiffness
To treat knee stiffness, finding the cause is key. A thorough diagnostic approach is needed. This includes physical exams, imaging tests, and lab tests to find the root of the problem.
Physical Examination Techniques
A physical exam is the first step in diagnosing knee stiffness. A healthcare professional checks the knee’s movement, strength, and stability. They look for signs of inflammation, redness, or swelling.
They might use tests like the Lachman or McMurray test. These tests check ligaments and meniscus for damage.
This exam gives important info about the knee. It helps decide what tests to do next. It helps find out what’s causing the stiffness.
Imaging Tests for Knee Problems
Imaging tests are vital for diagnosing knee stiffness. They show the knee’s inside structures in detail. Tests like X-rays, MRI, and ultrasound are used.
X-rays help find bone problems like fractures or osteoarthritis. MRI is great for soft tissue injuries like ligament sprains or meniscal tears. Ultrasound checks tendons and fluid in the knee.
Choosing the right imaging test helps doctors understand knee stiffness better.
Laboratory Tests for Inflammatory Conditions
Sometimes, lab tests are needed to find inflammatory causes of knee stiffness. Blood tests look for signs of inflammation like CRP or ESR. These tests help diagnose conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
Joint aspiration might also be done. It removes fluid to check for infection or inflammation. Lab tests, along with physical exams and imaging, help doctors find the right treatment.
Treatment Options for Relieving Stiff and Painful Knees
There’s no single treatment for stiff knees. It depends on the cause and how bad it is. Finding the right treatment can be tough. But, by looking at all the options, people can find relief from knee pain and stiffness.
Conservative Approaches
First, we try conservative treatments for knee stiffness. These include:
- Physical therapy to strengthen the muscles around the knee and improve flexibility
- Using assistive devices like canes or walkers to reduce stress on the knee
- Applying heat or cold packs to alleviate pain and stiffness
- Engaging in low-impact exercises such as cycling or swimming
Physical therapy is very helpful. It improves knee function and reduces pain. A physical therapist creates a program that meets your needs. It focuses on exercises that build strength and flexibility.
Medications for Pain and Inflammation
For many, medications are key in managing knee pain and inflammation. Common medications include:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen
- Prescription medications such as corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid injections
Always talk to a healthcare provider before starting any medication. They can discuss the benefits and risks with you.
Surgical Interventions When Necessary
If other treatments don’t work, surgical interventions might be needed. Surgical options include:
- Arthroscopic surgery to repair damaged cartilage or remove bone spurs
- Knee replacement surgery for severe arthritis or significant joint damage
Surgery might seem scary, but it can greatly improve your life. For many, it’s a big step towards less pain and better health.
Prevention Strategies to Maintain Healthy Knee Function
Keeping your knees healthy is easier than you think. By doing certain exercises, warming up right, and changing your lifestyle, you can lower the chance of knee stiffness. These steps are key to keeping your knees in top shape.
Strengthening Exercises for Knee Support
Strong muscles around the knee are vital for support and stability. Squats, lunges, and leg presses are great for building strong quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles. Start with low-intensity exercises and slowly increase the intensity to avoid knee strain.
Here are some effective exercises:
- Straight leg raises for the quadriceps
- Hamstring curls for the back of the thigh
- Calf raises for the calf muscles
Proper Warm-up and Stretching Techniques
Warming up is essential before any physical activity. It prepares the muscles and joints. A good warm-up includes light cardio and dynamic stretching.
Good knee stretches include:
- Static stretches for the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles
- Dynamic stretches like leg swings and lunges
Lifestyle Modifications for Joint Health
Changing your lifestyle can greatly improve knee health. Keeping a healthy weight reduces knee pressure. Eating a balanced diet with omega-3s and antioxidants can also help.
Appropriate Footwear and Support
Choosing the right shoes is vital for knee health. Shoes with good arch support and cushioning reduce knee impact. Remember to replace your shoes regularly for ongoing support.
Footwear Feature | Benefit for Knee Health |
Adequate Arch Support | Reduces strain on the knee by aligning the foot properly |
Cushioning | Absorbs shock, reducing the impact on the knee joint |
Proper Fit | Prevents excessive movement that could strain the knee |
Conclusion: Managing and Understanding Your Knee Health
It’s key to understand and manage knee health, mainly for those with knee stiffness. Knowing what causes knee stiffness helps us find ways to treat and prevent it. This way, we can ease tight knee pain and keep our knees healthy.
Managing knee health means making lifestyle changes, doing exercises, and sometimes seeing a doctor. We need to tackle the reasons behind knee stiffness. This could be from injuries, inflammation, or osteoarthritis.
By being proactive, like doing exercises that support the knee, warming up right, and making healthy lifestyle choices, we can lower the chance of knee stiffness. This helps keep our knees in good shape.
Good knee health management helps us stay mobile and enjoy life. We can improve our knee health by using a full approach to handle knee stiffness and pain.
FAQ
What are the main causes of knee stiffness?
Knee stiffness can come from injuries, inflammation, and lifestyle choices. Knowing the cause helps in finding a solution.
How common is knee stiffness?
Many people experience knee stiffness. It can affect anyone, making daily tasks harder.
What are the symptoms associated with tight knee pain?
Symptoms include discomfort, pain, and stiffness. These signs can point to serious issues.
What mechanical injuries can cause knee stiffness?
Injuries like meniscus tears and ligament damage can stiffen the knee. So can problems with the patella.
How do inflammatory conditions contribute to stiff knees?
Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and gout can stiffen the knee. They cause inflammation and damage.
What is the role of osteoarthritis in knee stiffness, specially in older adults?
Osteoarthritis is a big reason for stiff knees in older adults. It wears down cartilage, affecting knee function.
How do lifestyle factors contribute to tight knee pain?
Being overweight, weak muscles, and poor flexibility can stiffen the knee. These factors contribute to pain.
What diagnostic approaches are used to determine the cause of knee stiffness?
Doctors use physical exams, imaging tests, and lab tests. These help find the cause of knee stiffness.
What are the treatment options for relieving stiff and painful knees?
Treatments include pain and inflammation meds, physical therapy, and surgery. The choice depends on the cause and severity.
How can knee stiffness be prevented?
Preventing stiffness involves strengthening exercises, proper warm-ups, and stretching. Making healthy lifestyle choices also helps.
Why is understanding and managing knee health important?
Managing knee health is key to avoiding stiffness. It keeps you mobile and improves your life quality.
What causes stiffness in the knee joint?
Knee stiffness can result from injuries, inflammation, and lifestyle factors. Understanding these causes is essential.
How does excess weight affect knee stiffness?
Extra weight puts more stress on the knee. This can lead to stiffness and pain.
Can muscle weakness lead to knee stiffness?
Yes, weak muscles around the knee can cause stiffness and pain. It leads to imbalances.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3408027/