Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Saadet Demir
Living with a bad hip can really limit what you can do every day. But, evidence-based physiotherapy exercises can help ease pain and improve how you move. Safe hip exercises and modifications for individuals with hip pain are essential, and understanding hip health makes this process even more effective. Instead of thinking you have to live with hip pain or rush to surgery, try structured exercise programs. These are made by physiotherapy experts to boost strength, mobility, and life quality. At Liv Hospital, we use the latest research and tailor care to each person, always keeping hip health in focus.
We know that gentle exercises and stretches can ease pain and help you move better. Our guide shows how to exercise with bad hips using physiotherapy. It highlights the role of gentle exercises and stretches in easing pain and boosting mobility. By improving hip health through consistent movement and expert guidance, many people can regain comfort and maintain an active lifestyle.

Hip pain and mobility issues can really affect someone’s life. The way our hips move is complex, and problems can cause pain and make it hard to move. Knowing what causes hip pain and how it affects movement is key to feeling better.
Hip pain can come from muscle strains, injuries, arthritis, and inflammatory diseases. Hip impingement often causes pain when sitting, bending, or climbing stairs. Studies show that exercises can greatly improve hip movement and strength.
Other reasons for hip pain include tendinitis, bursitis, and fractures. Finding out why you have hip pain is the first step to treating it. We’ll look at how these issues affect how we move.
Hip mechanics are vital for movement, and problems can cause pain and stiffness. The hip joint allows for a lot of movement. But, if it’s not working right, it can wear out and hurt.
Movement and exercise are important for managing symptoms and improving mobility. Knowing how hip mechanics impact movement helps in creating an effective exercise plan to ease pain.
Some signs mean you should see a physiotherapist, like constant pain, stiffness, and trouble moving. If you notice these, seeing a physiotherapist is a good idea. They can create a plan just for you.
Physiotherapy can fix the root of hip pain and boost mobility. Recognizing when you need physiotherapy can help prevent more problems.
If you have ongoing hip pain, trouble moving, or find daily tasks hard, see a physiotherapist. They can tailor exercises to fit your needs and improve your hip health.
Physiotherapy for hip conditions is backed by scientific research. It shows that specific exercises can help a lot. Hip pain and mobility issues can really affect someone’s life, making simple tasks hard.
Studies have shown that good physiotherapy programs can greatly improve hip function and reduce pain. Targeted strengthening exercise programs for at least 3 months are best. They help a lot with hip range of motion and muscle strength.
Many studies have looked into how exercise helps with hip conditions, like osteoarthritis. They found that tailored exercise programs are very helpful. Each program is made to fit the needs of each patient.
Research also shows that stronger hip adductor muscles lead to better quality of life after hip treatments. This is why exercises for these muscles are important in physiotherapy.
Being consistent and lasting at least 3 months is key for physiotherapy success. Longer programs usually lead to better and lasting results.
We stress the need to stick to the exercise plan. Being consistent is essential for good results. Patients should commit to their physiotherapy and work with their healthcare team to make any needed changes.
Physiotherapy for hip conditions aims to reduce pain, improve mobility, and enhance quality of life. By focusing on the root causes of hip pain and using specific exercises, people can see big improvements in their hip function.
Exercise therapy offers moderate to meaningful effects for hip pain. It’s a great option for those with hip issues. With education, exercise, and other physiotherapy methods, patients can get better and do their daily activities more easily.
Before you start any exercise, it’s key to check your hip health. Hip pain can really hurt, and exercising without checking can make it worse.
Start by checking your hip health yourself. Simple movements like walking or squatting can show how bad your pain is. See how your hip feels with different activities and note any pain.
Keeping a pain journal is a good idea. It helps track when and why your hip hurts. This info can guide your exercise choices.
If your hip pain doesn’t go away or is very bad, see a doctor. They can give a detailed check-up and find out why you’re in pain. Don’t wait to get help if your pain is severe, you can’t move well, or it gets worse.
Knowing what’s wrong with your hip is key for a good workout plan. Your doctor will explain your diagnosis and what to do next. Make sure to ask questions if you don’t get something.
A proper diagnosis helps tailor your workout. With the right plan, you can improve your hip health safely and effectively.
Assessing your hip and understanding your diagnosis is important. It makes sure your workout is safe and effective. We’re here to help you get your hip in the best shape with personalized care.
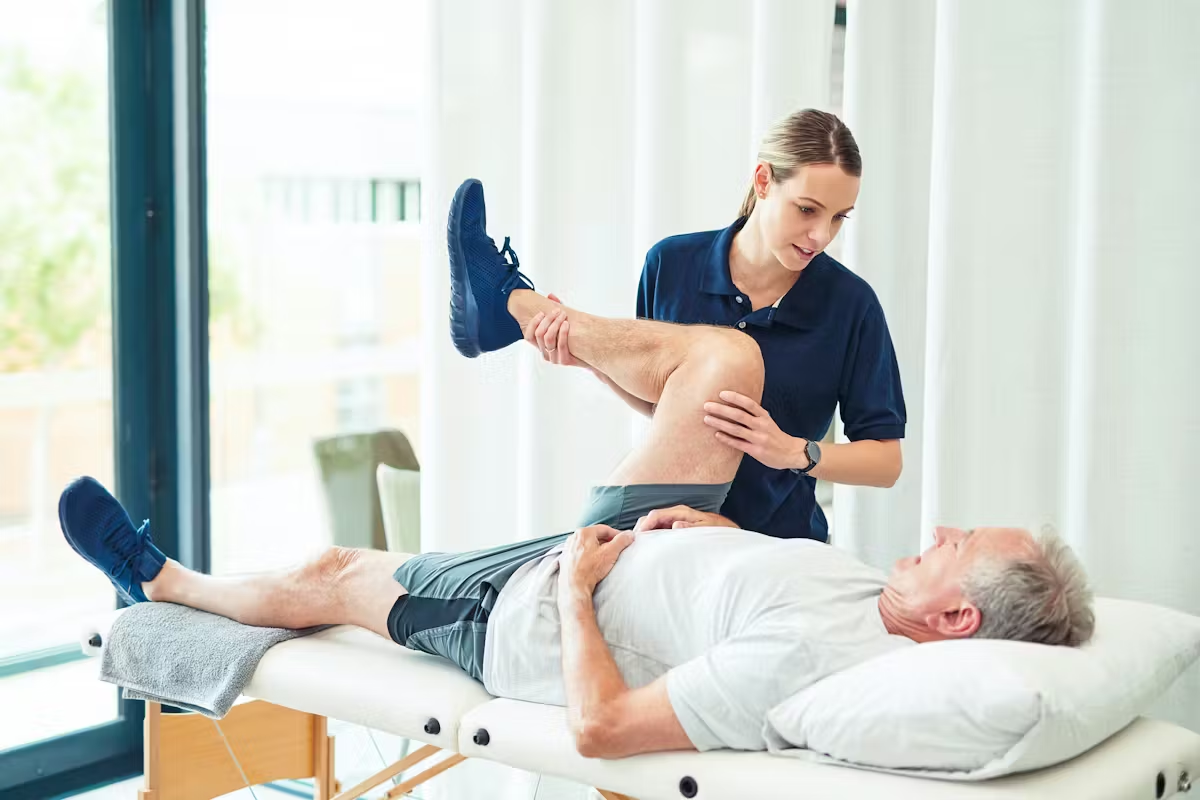
To manage hip pain, you need gentle mobility exercises, strengthening, and resistance training. These help ease pain, improve hip function, and boost mobility.
Keeping your hips flexible is key. Gentle exercises help a lot. Here are some:
Isometric exercises strengthen muscles without moving the joint. They’re great for those with severe pain. Try these:
Progressive resistance exercises build muscle strength around the hip. You can use:
It’s important to manage pain while exercising. Always:
“Listen to your body and stop if you feel sharp pain. Gentle exercises should not hurt too much, but some discomfort is okay.”
By doing these exercises regularly and watching your pain, you can lessen hip pain and improve health.
Hip pain can come from many sources. We focus on exercises that target each issue. These exercises help those with osteoarthritis, femoroacetabular impingement, hip dysplasia, and post-dislocation rehabilitation.
Osteoarthritis in the hip can cause a lot of pain and stiffness. It’s important to do exercises that make the joint move better and strengthen the muscles around it, especially when focusing on improving hip health. Range of motion exercises like hip flexion, extension, and rotation are key. For example, lying on your back and bringing one knee toward your chest can help.
Isometric strengthening exercises, like gluteal sets, are also helpful. They strengthen the muscles without putting too much strain on the joint and support better hip health overall.
Femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) needs exercises that reduce pain and improve how the hip moves. Stretching exercises for the hip flexors can help. For example, a kneeling hip flexor stretch is effective.
Doing exercises that strengthen the gluteal muscles, like clamshell exercises, can also help. This improves hip stability and reduces FAI symptoms.
Hip dysplasia is a malformation of the hip joint. It can lead to arthritis and mobility problems. A strengthening program focusing on the hip abductors and external rotators can help stabilize the hip. Side-lying leg lifts are a good exercise for strengthening the hip abductors.
After a hip dislocation, it’s important to do rehabilitation exercises that support hip health during recovery. Start with gentle range of motion exercises. Then, move on to strengthening exercises like straight leg raises to improve hip stability.
By choosing exercises that match your hip condition, you can see big improvements in pain and function while also protecting long-term hip health. Always talk to a healthcare professional to find the right exercises for you.
Studies show that stronger hip adductors lead to a better quality of life. These muscles are key for hip stability and mobility. Strengthening them is essential for hip health.
The adductor muscles keep the hip aligned and help with movement. Weak or imbalanced adductors can cause poor hip mechanics. This may lead to pain or injury. Strengthening these muscles improves hip function and lowers injury risk.
Key functions of the adductor muscles include:
A progressive adductor strengthening series increases exercise intensity. This promotes continuous muscle strength improvement. It helps avoid plateaus and challenges the muscles enough.
Here’s an example of a progressive strengthening series:
Exercise | Week 1-2 | Week 3-4 | Week 5-6 |
Adductor Squeeze | 3 sets of 10 reps | 3 sets of 15 reps | 3 sets of 20 reps |
Side-Lying Leg Lifts | 3 sets of 10 reps | 3 sets of 12 reps | 3 sets of 15 reps |
Cable Adductions | 3 sets of 12 reps | 3 sets of 15 reps | 3 sets of 18 reps |
Tracking adductor strength improvement is key. It helps adjust the strengthening program as needed. This can be done through manual muscle testing and dynamometry.
Key indicators of improved adductor strength include:
When you have hip pain, listening to your body is key to avoid more harm. We stress the need for safety and adjusting exercises to help you heal safely and well.
Knowing when to stop is vital. Look out for increased pain, swelling, or instability in your hip. If you see these signs, stop right away and talk to a doctor.
If your hip pain is bad, changing your exercises is important. You might need to modify the range of motion or reduce the intensity. A physiotherapist can help create a plan that fits your needs and pain level.
Keeping the right form is key to avoid injury and make your rehab work. Good form targets the right muscles and supports hip health without straining your hip. A physiotherapist can teach you how to do it right.
By listening to your body, adjusting exercises, and keeping the right form, you can safely move forward in your hip rehab. This will help you get better results while protecting your hip health throughout recovery.
Using exercise and manual therapy together can really help with hip pain. Manual therapy uses different methods to make tissues healthier, lessen pain, and boost movement. Together with exercises, it offers a full plan to tackle hip issues.
Self-massage is great for handling hip pain. It uses your body weight and tools to ease muscle tension around the hip. You can use your fingers or knuckles for gentle massage.
Foam rollers and therapy balls are good for self-massage. They help loosen muscle tension and improve blood flow. To use a foam roller, put it under the tight muscle and roll it slowly, applying light pressure.
While self-massage and tools like foam rollers are helpful, sometimes you need a pro. If pain doesn’t go away or is really bad, see a healthcare expert. They can give you a treatment plan made just for you.
Here’s a comparison of different manual therapy techniques:
Therapy Technique | Description | Benefits |
Self-Massage | Using fingers or knuckles to massage affected areas | Reduces muscle tension, improves circulation |
Foam Rolling | Using a foam roller to release muscle tension | Enhances muscle recovery, reduces pain |
Professional Manual Therapy | Personalized therapy provided by a healthcare professional | Tailored treatment, improved mobility, pain relief |
By mixing exercise with manual therapy, you can see big improvements in hip health. Whether it’s self-massage or professional therapy, adding manual therapy to your plan can lead to better results.
To get the best results in hip rehabilitation, a 3-month plan with different stages is key. A well-structured program guides you through a recovery journey. It helps you reach your goals.
The first stage builds a base of mobility and strength. Weeks 1-4 include gentle exercises to boost hip flexibility. You also start basic strengthening to stabilize the hip.
As you get better, the program gets tougher. Weeks 5-8 introduce exercises that push your hip muscles harder. This boosts your strength.
The last stage focuses on using your new strength and mobility in daily tasks. You learn to do more complex movements.
It’s important to keep track of your progress in the 3-month program. Regular checks help adjust the program to fit your changing needs. This keeps it effective and right for you.
Phase | Weeks | Key Focus | Example Exercises |
Foundation | 1-4 | Mobility and initial strength | Gentle mobility exercises, isometric strengthening |
Progressive Loading | 5-8 | Increased intensity and strength | Progressive resistance band exercises, weight-bearing exercises |
Functional Integration | 9-12 | Functional strength and mobility | Functional exercises, agility drills, advanced strengthening |
By sticking to this 3-month hip rehabilitation plan, you can see big improvements in your hip health. Remember, being consistent and patient is key to a successful recovery.
Keeping your hips healthy long-term is very important after rehab. We stress that keeping active is key to keeping your hips strong. Exercise keeps your hips flexible and strong, lowering the chance of injuries or problems later on.
Good posture is also critical for hip health. Being aware of your posture helps avoid putting too much strain on your hips. This can help prevent future issues. Regular visits to healthcare professionals are also important. They help catch and treat any problems early on.
By making these habits part of your daily life, you can greatly improve your hip health over time. We suggest sticking to a routine to keep your hips mobile and pain-free for years to come.
Gentle exercises like knee lifts and butterfly stretches can help. Isometric strengthening and progressive resistance methods also work well.
It takes at least 3 months of consistent effort. You’ll see better hip health, less pain, and more mobility.
Hip pain often comes from muscle strains, injuries, arthritis, and inflammatory disorders. These issues can hurt your hip mechanics and mobility.
Use self-assessment to understand your hip’s current state. Knowing when to see a professional is key for a proper diagnosis and exercise plan.
Strengthening hip adductors is essential for better hip health. It improves stability and mobility, leading to stronger hips and less pain.
It’s important to manage pain while exercising. Adapt exercises for severe pain, keep proper form, and watch for warning signs to avoid injury.
Manual therapy, along with exercise, is very beneficial. Self-massage with foam rollers and therapy balls, and professional manual therapy, can enhance treatment.
A 3-month program has several phases. Start with a foundation phase, then add progressive loading and functional integration. Track progress and adjust as needed.
Keep exercising, maintain good posture, and see healthcare professionals regularly. This will help keep your hips healthy over time.
Look for persistent pain, stiffness, and limited motion. These are signs you need physiotherapy to address with exercises and manual therapy.
Yes, physiotherapy can improve joint mobility and strength in hip dysplasia. A strengthening program can be designed to meet your specific needs.
Physiotherapy can improve joint mobility and strength, reduce pain, and enhance your quality of life. It offers routines tailored to your needs.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!