Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
Radiation therapy is a key treatment for many types of cancer. It works by damaging the DNA of cancer cells, stopping them from growing or spreading. At Liv Hospital, we focus on global excellence and compassionate care that puts patients first. Our team monitors every step of your treatment to ensure the best results.
Many patients wonder, “how do you know if radiation therapy is working?” The success of radiation therapy is checked in several ways — including follow-up scans, blood tests, and physical exams. Doctors also consider how symptoms improve and how the patient feels over time.
Understanding how you know if radiation therapy is working helps patients feel more confident and informed during their recovery journey.
Key Takeaways
- Radiation therapy damages cancer cells’ DNA, preventing growth.
- Effectiveness is assessed through clinical assessments and imaging scans.
- Patient-reported outcomes play a critical role in evaluating therapy success.
- Liv Hospital provides advanced, patient-centered care.
- Treatment outcomes are closely monitored and evaluated.
Understanding Radiation Therapy and Its Purpose
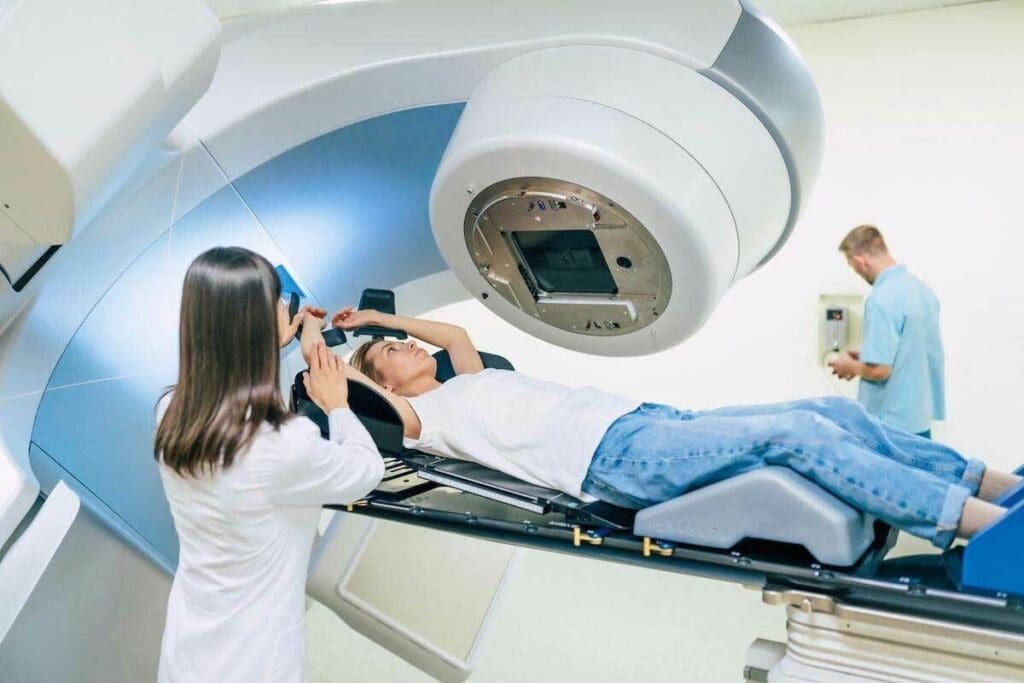
Radiation therapy is a key treatment for many cancers. It’s important for patients and their families to know about it. This treatment targets cancer cells in a specific area of the body.
Radiation therapy uses high-energy particles or waves to kill cancer cells. It damages the DNA of these cells, stopping them from growing and dividing.
What Radiation Therapy Does to Cancer Cells
Radiation therapy damages cancer cells’ DNA, causing them to die or stop growing. This helps shrink tumors and control cancer growth. The goal is to hit the tumor with the right amount of radiation, while keeping healthy tissues safe.
The effects of radiation therapy on cancer cells can happen right away or later. Some cells die quickly, while others may take weeks or months to die as they try to divide.
Types of Radiation Therapy Treatments
There are two main types of radiation therapy: external beam and internal radiation therapy. The choice depends on the cancer type and stage.
External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT) sends radiation from outside the body to the tumor. This is the most common type. It includes subcategories like 3D conformal radiation therapy, intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT), and stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT).
Internal Radiation Therapy, or brachytherapy, places radioactive material inside or near the tumor. This method delivers a high dose of radiation directly to the tumor, reducing damage to nearby tissues.
| Type of Radiation Therapy | Description | Advantages |
| External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT) | Radiation delivered from outside the body | Non-invasive, can treat large areas |
| Internal Radiation Therapy (Brachytherapy) | Radioactive material placed inside or near the tumor | High dose delivered directly to the tumor minimizes damage to surrounding tissues |
Knowing about the different types of radiation therapy helps patients and caregivers make better choices. The choice between external beam and internal radiation therapy depends on the cancer’s type, stage, and location.
The Science Behind Radiation’s Effects on Tumors

It’s important to know how radiation affects tumors to understand its role in cancer treatment. Radiation therapy is a complex treatment that targets cancer cells’ weaknesses, mainly their DNA.
Cellular Damage and DNA Disruption
Radiation therapy damages cancer cells’ DNA. It does this by creating free radicals that mess with DNA’s structure. This stops cancer cells from growing and dividing, leading to their death.
DNA disruption is key to radiation’s success. When DNA is harmed, cells can’t fix themselves, which is a big problem for cancer cells. This is why radiation is so good at fighting cancer cells that grow fast.
Immediate vs. Delayed Effects on Cancer Cells
Radiation’s impact on cancer cells happens right away and later on. Immediate effects happen during or right after treatment, as it damages cancer cells’ DNA. Delayed effects show up weeks, months, or years later, as the body keeps fighting off damaged cells.
A study in a top oncology journal found, “Radiation therapy’s delayed effects can be big, with some patients seeing tumors shrink long after treatment ends.” This shows how complex and varied radiation therapy’s effects on cancer can be.
“Radiation therapy is not just about killing cancer cells; it’s about creating an environment that is not conducive to their survival and proliferation.” – Expert in Radiation Oncology
When you see the effects of radiation therapy can differ a lot between patients. This depends on the cancer type, how much and how often radiation is given, and the patient’s health.
| Effect Type | Timeline | Description |
| Immediate | During or shortly after treatment | Direct DNA damage leading to cell death |
| Delayed | Weeks, months, or years after treatment | Continued immune response and tumor shrinkage |
Key Indicators That Radiation Therapy Is Working
To know if radiation therapy is working, doctors look at many things. They check how the patient is doing and use special tests. These signs help doctors see if the treatment is helping.
Clinical Signs of Effectiveness
Doctors watch for certain signs to see if radiation therapy is working. One key sign is tumor shrinkage. This means the tumor is getting smaller, as seen on scans like CT or MRI.
Other signs include changes in tumor markers and better organ function. For lung cancer, breathing better is a good sign. For liver cancer, normal liver tests mean the treatment is working.
Symptom Improvement as an Indicator
Getting better symptoms is also a big sign that treatment is working. Patients might feel less pain, eat better, or feel more energetic. These changes make a big difference in their life.
For example, people with bone metastases might feel less pain. Those with head and neck cancers might swallow or speak better.
In short, looking at clinical signs and symptom improvement gives a full picture. Regular checks and talking to doctors are key. This helps track progress and make the right treatment choices.
Medical Imaging: The Primary Tool for Evaluation
Medical imaging is key in checking if radiation therapy is working. Doctors use different imaging tools to see how the treatment is doing. They can then make changes if needed.
CT Scans and MRIs in Treatment Assessment
CT scans and MRIs are top choices for checking radiation therapy. CT scans show detailed body images, helping doctors measure tumor size. MRIs, with their high-resolution images, help see how tumors are shrinking or growing.
These tools are vital for:
- Checking tumor size and location
- Seeing changes in tumor characteristics
- Looking at nearby tissue for side effects
PET Scans and Functional Imaging
PET scans are also important for checking radiation therapy. They show how active the tumor is, unlike CT scans and MRIs, which focus on body structure. PET scans are great for:
- Checking if the tumor is alive
- Finding early changes in tumor activity
- Spotting possible cancer return
Frequency of Follow-up Imaging
How often imaging is done varies. It depends on the cancer type, stage, and how well the treatment is working. Imaging is usually done:
- At the start, to set a baseline
- During treatmen,t to see how it’s going
- After treatment to watch for cancer return
Regular imaging is key to catching any tumor changes. By using different imaging types, doctors can fully understand the treatment’s success.
How Do You Know If Radiation Therapy Is Working: Assessment Methods
Healthcare experts use several key methods to check if radiation therapy is working. These strategies help understand how the treatment affects the patient’s health.
Clinical Assessments During Treatment
Clinical assessments are key to seeing if radiation therapy is effective. Patients have regular check-ups with doctors to track their treatment progress. Doctors do physical exams, review medical history, and check for symptom changes.
According to the radiation therapy treatment process, these visits help spot issues early.
Patient-Reported Outcomes
Patient-reported outcomes (PROs) are important in checking radiation therapy’s success. Patients share their experiences, symptoms, and quality of life during treatment. This feedback is key to understanding the treatment’s effects.
By using PROs, doctors get a full picture of how the treatment is working.
Objective Measurement Techniques
Objective measurement techniques are also vital in checking radiation therapy’s success. Tools like CT scans, MRIs, and PET scans show tumor changes. Blood tests and physical assessments offer more insights.
By mixing these methods with clinical assessments and patient feedback, doctors can decide if treatment should continue or change.
Timeline: How Long Does It Take for Radiation to Work?
Radiation therapy doesn’t work right away. It has a timeline with different stages. Knowing this timeline helps patients and doctors track the treatment’s progress.
Initial Response Timeframes
Patients start feeling better in 2-4 weeks after starting treatment. The body starts to react to the radiation. Some people feel less pain or discomfort from the tumor.
But, how fast you feel better depends on your cancer type, its stage, and your health.
Long-Term Effects and Continued Improvement
The full effects of radiation therapy take time. Long-term effects and continued improvement show up months after treatment ends. This is because cancer cells die slowly, and the body heals slowly too.
Patients need to be ready for a long recovery. Regular check-ups with their doctor are key during this time.
Factors Affecting Response Time
Many things can change how fast radiation therapy works. These include the cancer type and stage, how much and how often you get radiation, your age, and your health. Also, if you’re getting radiation with other treatments like chemotherapy can affect how fast it works.
Knowing these factors helps set realistic hopes for treatment results.
In summary, how long radiation therapy takes to work varies a lot. By understanding the initial response, long-term effects, and what affects them, patients can better understand their treatment journey.
Will Radiation Shrink a Tumor? Understanding Tumor Response
Tumor response to radiation therapy varies among individuals. It’s key to understand how radiation can affect tumor size. Radiation therapy is a vital part of cancer treatment, and its ability to shrink tumors is important for patient outcomes.
Patterns of Tumor Shrinkage
Tumors can react differently to radiation therapy, leading to various patterns of shrinkage. Some tumors may shrink quickly, while others may take longer. The rate and extent of shrinkage depend on several factors, including the cancer type and stage, radiation dose and duration, and individual patient characteristics.
Rapid shrinkage is common in tumors highly sensitive to radiation, like certain lymphomas. On the other hand, slow and gradual shrinkage is seen in tumors more resistant to radiation, such as some sarcomas.
Partial vs. Complete Response
Tumor response to radiation therapy can be partial or complete. A partial response means the tumor has shrunk significantly but is not gone. A complete response indicates the tumor has disappeared, confirmed by imaging and clinical assessments.
- A partial response can improve symptoms and quality of life.
- A complete response is often linked to better long-term outcomes.
When Tumors Don’t Shrink: Stable Disease
In some cases, tumors may not shrink despite radiation therapy. This is called stable disease. While it may not be seen as a successful outcome in terms of shrinkage, stable disease can be beneficial if the tumor is not growing.
Understanding different tumor responses is vital for managing patient expectations and making informed treatment decisions. By assessing tumor response to radiation therapy, healthcare providers can adjust treatment plans to improve patient outcomes.
Cancer-Specific Response Patterns
Cancer types react differently to radiation therapy. This helps doctors see how well treatments work. Things like the cancer’s type, where it is, and the patient’s health play a big role.
Breast Cancer Response to Radiation
Breast cancer is often treated with radiation. Radiation is used after a lumpectomy to kill any cancer cells left behind. This helps lower the chance of cancer coming back. Many patients see their tumors shrink a lot.
Studies show that radiation can help patients live longer. It also means some might not need to have their whole breast removed. Doctors check how well the treatment is working with tests like mammograms and MRIs.
Lung Cancer and Radiation Effectiveness
Lung cancer, like non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), often gets radiation therapy. How well radiation works depends on the tumor’s stage and where it is. For early-stage lung cancer, radiation can be very effective on its own or with other treatments.
New ways to give radiation, like SBRT, help lung cancer patients. This method gives high doses of radiation right to the tumor. It helps avoid harming healthy tissue around it.
Brain Tumors and Special Considerations
Brain tumors are tricky to treat with radiation because of the brain’s sensitivity. Radiation is used for different brain tumors, like gliomas and meningiomas. The goal is to stop the tumor from growing without harming the brain too much.
Special radiation methods, like Gamma Knife radiosurgery, are used for brain tumors. These methods allow for precise radiation delivery. This improves results and lessens side effects.
Knowing how different cancers react to radiation is key. It helps doctors make treatment plans that work best for each patient. This increases the chances of a good outcome.
Modern Technologies for Monitoring Radiation Therapy
Modern technologies are changing how we monitor radiation therapy. They make treatments more effective and tailored to each patient. These advancements are transforming cancer treatment, leading to better patient outcomes.
3D Imaging and Real-Time Tracking
3D imaging and real-time tracking are big steps forward. They help doctors pinpoint tumors accurately. This means they can give more radiation to the tumor while protecting healthy tissues.
Using 3D imaging makes radiation therapy more precise. It lowers the chance of side effects.
The table below shows the benefits of 3D imaging in radiation therapy:
| Benefits | Description |
| Precision | Accurate localization of tumors |
| Dose Escalation | Higher doses are delivered to the tumor |
| Sparing Healthy Tissues | Reduced risk of side effects |
Wearable Dosimeters and Patient Monitoring
Wearable dosimeters are another big leap. They track radiation exposure in real-time. This data helps adjust treatment plans for the best results.
Wearable dosimeters improve patient safety and treatment success. They allow for quick adjustments based on real-time data.
Artificial Intelligence in Response Assessment
Artificial intelligence (AI) is now used to assess radiation therapy response. AI analyzes data to predict treatment outcomes. This helps tailor treatments for better results.
AI in response assessment could change radiation therapy. It offers accurate and timely predictions. This leads to better care decisions for patients.
Comparing Radiation and Chemotherapy Effectiveness
To understand how well radiation therapy and chemotherapy work, we need to look at how they treat cancer. Both are key in fighting cancer, but they treat it in different ways. They have different effects on cancer cells.
Similarities in Evaluation Methods
Even though they treat cancer differently, radiation and chemotherapy are evaluated in similar ways. They both use:
- Imaging, like CT scans, MRIs, and PET scans to see how tumors react
- Doctors check patients through physical exams and what patients say
- Lab tests watch for changes in tumor markers and other important signs
Key Differences in Response Patterns
Radiation therapy and chemotherapy have different ways of working. Radiation therapy:
- Directly harms cancer cells’ DNA, causing them to die
- Focuses on a specific area or tumor
Chemotherapy, on the other hand:
- Uses drugs to kill cancer cells all over the body
- Can target both the main tumors and cancer that has spread
Knowing these differences helps doctors see how well each treatment works.
Combined Therapy Assessment Challenges
When radiation and chemotherapy are used together, it’s harder to see how well each works. Challenges include:
- Figuring out how much each treatment helps the overall response
- Watching for how radiation and chemotherapy might affect each other’s safety and effectiveness
- Changing treatment plans based on how they work together
Doctors must think carefully about these issues when using both treatments together.
When Radiation Therapy Isn’t Working: Warning Signs
When radiation therapy isn’t effective, there are clear signs to watch for. Both patients and doctors need to know these signs. They help decide what to do next.
Tumor Growth Despite Treatment
Tumor growth despite treatment is a big warning sign. If CT scans or MRIs show the tumor is getting bigger, it means the therapy isn’t working. Sometimes, the tumor might not grow, but if it does, it’s a bad sign.
Persistent or Worsening Symptoms
Persistent or worsening symptoms are another sign that treatment isn’t working. If you’re feeling pain, tired, or having trouble swallowing, it could mean the treatment isn’t helping.
Next Steps When Treatment Is Ineffective
If radiation therapy isn’t working, talking to your doctor about next steps is key. You might look into other treatments like chemotherapy or immunotherapy. Or, you might consider joining a clinical trial for new treatments. It’s also important to manage any persistent symptoms or side effects.
In short, knowing the signs that radiation therapy isn’t working is important. By watching for tumor growth and symptoms, you can work with your healthcare team to find the best way forward.
Conclusion
Checking if radiation therapy works is key in finding the best cancer treatment. Doctors use many ways to see their impact. These include clinical checks, scans, and what patients say.
In this article, we looked at how to tell if radiation therapy is effective. We covered the science behind it and how new tech helps track treatment.
Figuring out if radiation therapy is working is complex. It involves looking at how tumors react, if symptoms get better, and the patient’s overall health.
Knowing how to check if radiation therapy is effective helps both patients and doctors. It leads to better cancer treatment results.
FAQ
How do you know if radiation therapy is working?
To check if radiation therapy is working, doctors use several methods. They look at medical images, do clinical checks, and listen to what patients say. Seeing the tumor get smaller, feeling better, and changes in tumor markers are signs it’s working.
How long does it take for radiotherapy to work?
Radiotherapy’s effects can be seen in 2-4 weeks. But, it might take months to see the full effect. How fast it works depends on the cancer type, tumor size, and the dose of radiation.
Will radiation shrink a tumor?
Yes, radiation can make tumors smaller. But, how much it shrinks can vary. Seeing the tumor get smaller is a good sign, but it’s not the only way to know if treatment is working.
How do you know if chemo is working?
Chemotherapy’s success is checked the same way as radiation. Doctors look at medical images, do clinical checks, and listen to patients. Seeing the tumor shrink, feeling better, and changes in tumor markers show it’s working.
Is radiation or chemo worse?
Both treatments have their own side effects. The choice between them depends on the cancer type and stage, and the patient’s situation. Some cancers respond better to one treatment than the other.
How does radiation treatment work?
Radiation therapy damages cancer cells’ DNA, stopping them from growing. This can cause cell death and tumor shrinkage. There are different ways to deliver radiation, like external beam and internal radiation therapy.
Is tumor shrinking a good sign?
Tumor shrinkage is a good sign that treatment is working. But, it’s not the only sign. Feeling better and changes in tumor markers are also important.
How can you tell if chemotherapy is working?
Chemotherapy’s success is checked through medical images, clinical assessments, and patient reports. Seeing the tumor shrink, feeling better, and changes in tumor markers show it’s working.
What are the warning signs that radiation therapy isn’t working?
Signs that radiation therapy isn’t working include the tumor growing, symptoms getting worse, and no change in tumor markers. If these happen, it’s time to re-evaluate and possibly change the treatment plan.
How is radiation therapy effectiveness evaluated?
Doctors use medical images, clinical assessments, and patient reports to check radiation therapy’s success. These methods help understand how well the treatment is working and guide further decisions.
References
- Stieb, S., Kelly, C., & Deasy, J. O. (2019). Imaging for response assessment in radiation oncology. Frontiers in Oncology / PMC. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7253297/
- Kwon, J. Y., et al. (2022). Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement in Radiation Therapy. PMC. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9139498/