High cholesterol is a silent condition that can lead to serious heart problems if left undetected. It is characterized by elevated levels of lipids in the bloodstream, often without noticeable symptoms how do you know if u have high cholesterol.
Cholesterol is a waxy substance found in the blood, necessary for building healthy cells. But, elevated cholesterol levels can increase the risk of heart disease. The only definitive way to identify high cholesterol is through a blood test called a lipid panel.
At Liv Hospital, we emphasize the importance of preventive healthcare and early detection. Regular screening can dramatically reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke. Understanding the risks and taking proactive steps can help manage this condition.
Key Takeaways
- High cholesterol often develops silently without noticeable symptoms.
- A lipid panel blood test is required to identify high cholesterol.
- Elevated cholesterol levels can increase the risk of heart disease.
- Regular screening can reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke.
- Preventive healthcare is key in managing high cholesterol.
Understanding Cholesterol: The Silent Health Threat
Cholesterol is a vital part of our bodies. It can be good or bad, depending on its type and amount. Knowing about cholesterol helps us take care of our health.
What Is Cholesterol and Why It Matters
Cholesterol is a fat in our blood that helps with many body functions. It makes cell membranes, hormones, and vitamin D. But, too much cholesterol can cause heart disease and stroke.
Many things can lead to high cholesterol. These include dietary choices rich in saturated fats, genetics, not being active, being overweight, and some medical conditions. Knowing these factors helps us manage cholesterol levels.
Good vs. Bad Cholesterol: HDL and LDL Explained
There are two main types of cholesterol: HDL and LDL. LDL, or “bad” cholesterol, can clog arteries and raise heart disease risk. HDL, or “good” cholesterol, helps clear cholesterol from the blood, lowering heart disease risk.
- HDL (Good Cholesterol): Helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream.
- LDL (Bad Cholesterol): Contributes to plaque buildup in the arteries.
Triglycerides and Their Role in Blood Lipid Profiles
Triglycerides are fats in the blood. High triglycerides can harden arteries and increase heart disease risk. A blood lipid profile test shows HDL, LDL, and triglyceride levels, giving a full picture of cholesterol health.
Keeping these levels balanced is key for heart health. We’ll look at how to do this in the next sections.
The Silent Nature of High Cholesterol
High cholesterol is a silent threat because it often doesn’t show symptoms. Many people find out they have it when they face serious health problems like heart attacks or strokes.
It’s called a “silent killer” because it doesn’t cause symptoms until it’s too late. The American Heart Association says many adults have high cholesterol without knowing it. This shows how important regular check-ups are.
Why High Cholesterol Often Has No Symptoms
High cholesterol is usually silent because it develops slowly. Cholesterol builds up in arteries, called plaque, over time. This buildup doesn’t cause symptoms until the arteries are blocked a lot.
Because it develops slowly, many people with high cholesterol feel fine. But, about 93 million American adults have cholesterol levels over 200 mg/dL, which is too high.
When Symptoms May First Appear
High cholesterol itself might not show symptoms, but the problems it can cause might. For example, atherosclerosis can lead to chest pain, shortness of breath, or leg pain during exercise.
In rare cases, high cholesterol can cause visible fat deposits under the skin or a grayish-white ring around the cornea. But these signs are not common and usually happen in people with very high cholesterol.
The Prevalence of High Cholesterol in America
High cholesterol is a big health issue in the United States. The CDC says over 94 million adults have cholesterol levels above 200 mg/dL. Almost 30 million have levels above 240 mg/dL.
The CDC also notes that some groups are more at risk. Older adults and those with other health issues are more likely to have high cholesterol. This makes regular cholesterol tests very important, even more so for these groups.
Key Statistics:
- Approximately 93 million American adults have total cholesterol counts exceeding 200 mg/dL.
- Nearly 1 in 3 adults in the United States has high cholesterol.
- High cholesterol is a major risk factor for heart disease, the leading cause of death in the United States.
How Do You Know If You Have High Cholesterol?
High cholesterol usually doesn’t show symptoms. So, the only sure way to find out is with a blood test. This test, called a lipid panel, shows your cholesterol levels.
The Only Definitive Method: Blood Testing
The only sure way to find high cholesterol is through blood testing. A lipid panel checks your cholesterol levels. This helps doctors see how healthy your heart is. It’s smart to get tested often, if you’re at risk.
What a Lipid Panel Measures
A lipid panel checks total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides. Knowing these numbers is key to knowing your heart risk. Total cholesterol shows the big picture. LDL and HDL tell you about “bad” and “good” cholesterol. Triglycerides are another important fat in your blood.
Understanding Your Test Results
It’s important to understand your lipid panel results. Your doctor will explain what they mean for your health. High total and LDL cholesterol, and low HDL, mean you might be at risk for heart disease.
Home Testing Options and Their Reliability
Home cholesterol testing kits are out there, but they’re not always reliable. They don’t give the detailed look a lipid panel does. If you use a home test, make sure to check with your doctor to confirm the results.
What Constitutes High Cholesterol Levels?
Knowing what high cholesterol levels are is key to keeping your heart healthy. Cholesterol is measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). These numbers help figure out your risk for heart disease.
Normal vs. Elevated Cholesterol Numbers
Cholesterol levels above 200 mg/dL are too high. Levels below 200 mg/dL are good. Numbers between 200-239 mg/dL are borderline high, and 240 mg/dL or higher is high.
Here’s a breakdown of cholesterol levels:
Cholesterol Level (mg/dL) | Category |
Less than 200 | Desirable |
200-239 | Borderline High |
240 or above | High |
Borderline High vs. High Cholesterol Classifications
It’s important to know the difference between borderline high and high cholesterol. Borderline high means you’re at a higher risk for heart disease. High cholesterol means you’re at a much higher risk.
Target Levels for Different Age Groups
Cholesterol targets change with age and health. Adults should aim for an LDL level under 100 mg/dL. Those at high risk might need an LDL level under 70 mg/dL.
The Importance of LDL/HDL Ratio
The LDL/HDL ratio shows your heart disease risk. LDL is “bad” cholesterol, and HDL is “good” cholesterol. A lower ratio means less heart disease risk. To find this ratio, divide your LDL by your HDL.
For example: With an LDL of 100 mg/dL and an HDL of 60 mg/dL, your ratio is 1.67. That’s good.
Keeping a healthy LDL/HDL ratio is vital for heart health. Changing your lifestyle and, if needed, taking medication can help keep your cholesterol in check.
Risk Factors for Developing High Cholesterol
High cholesterol comes from genetics, lifestyle, and health conditions. Knowing these risks helps us spot who’s at risk. It also guides us on how to prevent it.
Genetic Predisposition and Familial Hypercholesterolemia
Genetics are key in high cholesterol risk. Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a genetic disorder. It causes very high LDL cholesterol levels.
People with FH have a gene problem. This makes it hard for their body to remove LDL cholesterol. This greatly raises the risk of heart disease early on.
Key aspects of genetic predisposition include:
- Inherited conditions like familial hypercholesterolemia
- Family history of high cholesterol or early heart disease
- Genetic variations affecting lipid metabolism
Lifestyle Factors That Increase Risk
Our lifestyle choices affect our cholesterol levels. Diet, exercise, smoking, and weight all play a part in our risk.
Lifestyle factors that increase the risk of high cholesterol include:
- A diet high in saturated fats and cholesterol
- Lack of physical activity or a sedentary lifestyle
- Smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke
- Obesity or being overweight
Lifestyle Factor | Impact on Cholesterol |
Diet high in saturated fats | Increases LDL cholesterol |
Sedentary lifestyle | Lowers HDL cholesterol |
Smoking | Damages blood vessels, increases LDL |
Medical Conditions That Affect Cholesterol Levels
Some health issues can change cholesterol levels. Diabetes, hypothyroidism, and kidney disease can all affect lipid profiles. This increases the risk of high cholesterol.
Medical conditions that impact cholesterol levels:
- Diabetes
- Hypothyroidism
- Kidney disease
- Liver disease
Knowing these risk factors helps us take action. We can make better lifestyle choices and manage health conditions. This reduces the risk of high cholesterol.
How Does Cholesterol Increase in Your Body?
Cholesterol levels in your body come from what you eat and how much your body makes. Knowing these factors helps you manage your cholesterol better.
Dietary Sources of Cholesterol
What you eat affects your cholesterol levels a lot. Foods high in saturated fats, like red meat and full-fat dairy, can raise your cholesterol. Try to eat less of these foods if you want to keep your cholesterol in check.
Also, watch out for trans fats in processed foods. They increase the bad cholesterol and lower the good cholesterol, upsetting the balance.
How Your Body Produces Cholesterol
Your liver makes cholesterol, which then spreads through your blood. This cholesterol is vital for making cell membranes and hormones.
But, too much cholesterol can cause problems. Genetics can affect how much cholesterol your liver makes, making some people more likely to have high cholesterol.
The Role of the Liver in Cholesterol Regulation
The liver is key in keeping cholesterol levels right. It makes and removes cholesterol from your blood. This helps keep cholesterol levels healthy.
- The liver produces cholesterol and releases it into the bloodstream.
- It also removes excess cholesterol from the bloodstream, helping to maintain balance.
- Liver function can be influenced by diet, lifestyle, and genetic factors.
Factors That Disrupt Cholesterol Balance
Many things can upset the balance of cholesterol in your body. Lifestyle choices like eating too much saturated fat, not moving enough, and smoking can all play a part. Medical conditions and genetics can also affect it.
Knowing what affects your cholesterol is important. By making smart choices and working with your doctor, you can keep your cholesterol healthy.
Physical Signs That May Indicate High Cholesterol
High cholesterol often doesn’t show symptoms. But, there are signs that might mean you have it. These signs come from lipids building up in the body. We’ll look at these signs and what they might mean for your cholesterol.
Xanthomas and Visible Fat Deposits
Xanthomas are fat deposits on the skin, often a sign of high cholesterol. They form when too much lipid builds up under the skin. This creates yellowish patches or nodules. You can find them on the hands, feet, elbows, and knees.
Characteristics of Xanthomas:
Location | Description |
Hands, feet, elbows, knees | Yellowish patches or nodules under the skin |
Size | Variable, from small papules to large nodules |
Corneal Arcus and Other Eye Indicators
Corneal arcus is a deposit in the cornea, a sign of high cholesterol. It looks like a white or gray ring around the cornea. In older adults, it’s common. But in younger people, it might mean high cholesterol or other lipid disorders.
Symptoms of Advanced Atherosclerosis
When lipids build up in blood vessels, they form plaque. This narrows arteries and causes atherosclerosis. Symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, and leg pain mean the condition is serious. You need to see a doctor right away.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you see xanthomas, corneal arcus, or have symptoms like chest pain or leg pain, see a doctor. Early treatment of high cholesterol can stop atherosclerosis from getting worse. It also lowers the risk of heart problems.
When Should You Get Tested for High Cholesterol?
Getting regular cholesterol screenings is key to catching high cholesterol early. Knowing when to get tested helps keep your heart healthy. It’s all about being proactive with your health.
Recommended Screening Guidelines by Age
The American Heart Association says adults 20 and up should get their cholesterol checked every 4-6 years. This is a basic rule, but some people might need to get tested more often.
For kids and teens, the rules are different. The American Academy of Pediatrics says kids 9 to 11 should get tested once. Then, they should get checked again between 17 and 21.
Special Considerations for High-Risk Individuals
Some people are at higher risk for high cholesterol. This includes those with a family history, being overweight, or having diabetes or high blood pressure. Lifestyle choices like eating too much saturated fat or smoking also raise your risk.
If you fit into any of these groups, talk to your doctor about how often you should get tested. They’ll help you figure out the best schedule for you.
How Often to Retest Based on Previous Results
If your last cholesterol test showed normal levels, you might not need another for 4-6 years. But if your levels were borderline or high, your doctor might want you to get tested more often. This helps them see if your treatment is working.
People taking medicine for high cholesterol need regular tests too. This ensures the medicine is working right and makes any needed changes to your treatment.
Preparing for Your Cholesterol Test
To get accurate results, you usually need to fast for 9-12 hours before your test. This means no food or drinks except water during that time.
Tell your doctor about any medicines you’re taking. Some can affect your test results. They’ll tell you exactly how to prepare for your test.
What Happens When You Have High Cholesterol?
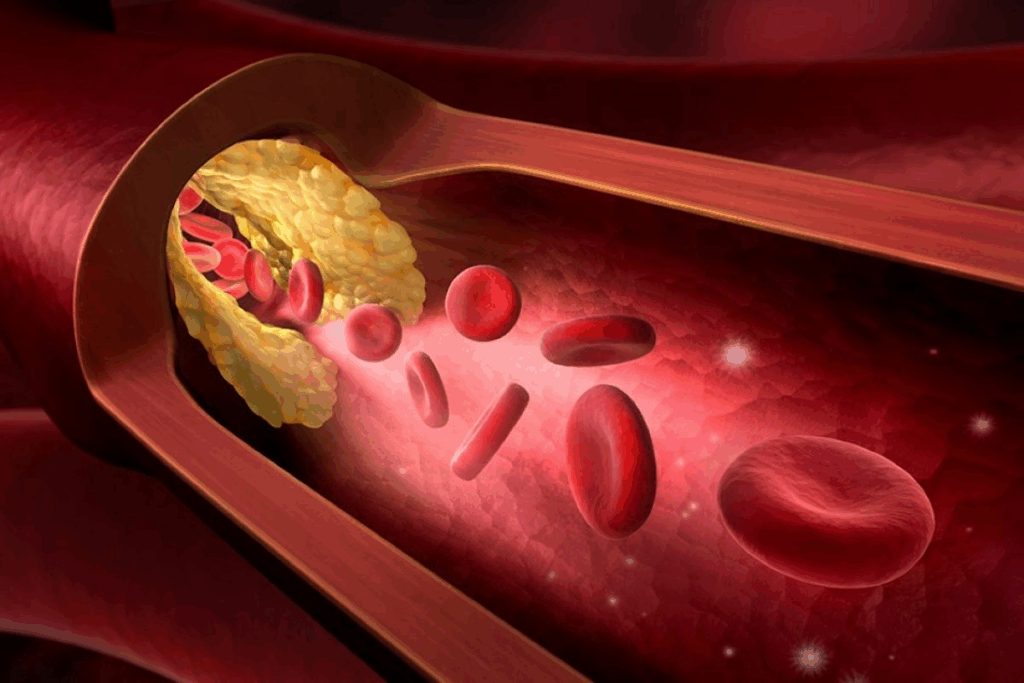
High cholesterol can cause atherosclerosis, a condition that affects the arteries. Atherosclerosis happens when plaque builds up in the arteries. This can lead to heart attacks, strokes, and other heart diseases.
This process takes time and is influenced by diet, genetics, and lifestyle. It’s important to understand these factors.
The Progression of Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis starts when too much lipid builds up in blood vessels. This forms plaque that narrows the arteries. Narrowed arteries reduce blood flow, causing health problems.
For example, if the coronary arteries are narrowed, it can lead to heart issues. The progression of atherosclerosis is often silent, meaning it may not show symptoms until it’s advanced.
High blood pressure, smoking, and diabetes can make it progress faster.
How Plaque Forms in Blood Vessels
Plaque formation in blood vessels is a complex process. It involves cholesterol, fatty substances, and other materials on the inner walls of arteries. This can start as early as childhood and grow over decades.
- The process starts with damage to the arterial wall, often due to high blood pressure or smoking.
- Cholesterol and other lipids then penetrate the damaged area.
- White blood cells are attracted to the site, trying to repair the damage, but they can become trapped, contributing to plaque buildup.
- Over time, the plaque can harden or rupture, potentially blocking the artery or causing a blood clot.
Potential Complications and Health Risks
The complications of untreated high cholesterol and atherosclerosis are severe. They can be life-threatening. These include:
- Heart Attack: Occurs when the blood flow to the heart is blocked, damaging the heart muscle.
- Stroke: Happens when the blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, preventing brain tissue from getting oxygen and nutrients.
- Peripheral Artery Disease: A condition characterized by the narrowing of peripheral arteries, often causing pain and discomfort in the legs.
Understanding these risks and taking proactive steps can help manage cholesterol levels. This reduces the chance of developing these complications.
What To Do If You Have High Cholesterol
Managing high cholesterol needs a mix of lifestyle changes and medical treatments. A good plan can lower cholesterol and cut down heart disease risk.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle changes are key in managing high cholesterol. These changes help lower cholesterol and boost overall health.
Important lifestyle changes include:
- Dietary Changes: Eating more fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean proteins can lower cholesterol. Avoid saturated fats, trans fats, and dietary cholesterol.
- Increased Physical Activity: Regular exercise, like walking or swimming, raises “good” cholesterol and improves heart health.
- Weight Management: Keeping a healthy weight is vital, as extra weight raises cholesterol and heart disease risk.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking greatly improves heart health and lowers cholesterol over time.
- Limiting Alcohol Consumption: Drinking less alcohol helps manage cholesterol better.
These lifestyle changes can make a big difference. A study in the Journal of the American Medical Association showed intensive lifestyle changes can greatly improve cholesterol levels.
Lifestyle Modification | Potential Impact on Cholesterol Levels |
Dietary Changes | Can lower LDL (bad cholesterol) by 10-15% |
Increased Physical Activity | Can raise HDL (good cholesterol) by 5-10% |
Weight Management | Can lower LDL by 5-10% and raise HDL |
Medical Treatments and Medications
For some, lifestyle changes alone may not be enough. Medical treatments and medications are then needed.
Common cholesterol-lowering medications include:
- Statins: Often prescribed, statins reduce liver cholesterol production.
- Bile Acid Sequestrants: These remove bile acids, leading to more cholesterol use by the liver.
- Cholesterol Absorption Inhibitors: These drugs reduce cholesterol absorption, lowering blood cholesterol.
- Fibrates: Fibrates lower triglycerides and raise HDL cholesterol.
- PCSK9 Inhibitors: Newer drugs target PCSK9 to lower LDL cholesterol.
Working with a healthcare provider is key to finding the right treatment. Medications work differently for everyone.
Combining lifestyle changes with medical treatments is effective in managing high cholesterol. This approach reduces cardiovascular disease risk.
Monitoring and Managing Cholesterol Over Time
To keep cholesterol levels in check, it’s key to have a good plan. This plan should include lifestyle changes, regular checks, and sometimes medicine.
Creating a Cholesterol Management Plan
A cholesterol plan is made just for you. It sets target cholesterol levels, suggests lifestyle changes, and decides if you need medicine. We work with doctors to make this plan.
Key parts of a cholesterol plan are:
- Changing your diet to lower cholesterol
- Being more active
- Managing your weight
- Stopping smoking, if you do
- Taking medicine as told, if needed
Tracking Progress and Adjusting Treatment
Checking your cholesterol regularly is key. This means blood tests to see your cholesterol and heart health. Changes to your plan are made based on these tests.
Tracking your progress helps in:
- Seeing if your plan is working
- Making changes to your lifestyle or medicine
- Keeping you motivated to stick with your plan
Working With Healthcare Providers
It’s important to work with your healthcare team for a good cholesterol plan. They help choose the best treatments and check how you’re doing.
“Collaboration between patients and healthcare providers is key to successful cholesterol management.”
Medical Expert, Cardiologist
Special Considerations for Different Life Stages
Cholesterol plans can change as you get older. For example, older adults might need more treatment because of higher heart risks. Younger people might focus on lifestyle changes.
Things to think about at different ages include:
Life Stage | Considerations |
Young Adults | Lifestyle changes, catching risk factors early |
Adults | Regular checks, medicine if needed |
Older Adults | More treatment, managing other health issues |
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Cholesterol Health
Managing high cholesterol needs a full plan. This includes changing your lifestyle, getting medical help when needed, and keeping an eye on your levels. By making smart choices, you can control your cholesterol and lower your heart disease risk.
A healthy lifestyle is key to managing cholesterol. Eating right, staying active, and not smoking are important. These habits can boost your heart health.
It’s vital to work with your doctor to make a plan for your cholesterol. Tracking your progress and changing your treatment as needed helps keep your levels in check. This way, you can avoid serious heart problems.
Being proactive about your health can make a big difference. Knowing the dangers of high cholesterol and taking charge of your health can lead to a better life.
FAQ
What is high cholesterol, and how does it affect my health?
High cholesterol means your blood has too much fat. This can lead to heart disease. It’s often silent, so getting checked regularly is key.
How do I know if I have high cholesterol?
The only way to know for sure is with a blood test called a lipid panel. It checks your HDL, LDL, and triglycerides.
What constitutes high cholesterol levels?
High cholesterol is when your LDL is 160 mg/dL or higher. Or if your HDL is too low, below 40 mg/dL for men or 50 mg/dL for women.
What are the risk factors for developing high cholesterol?
Risk factors include your genes, diet, and lack of exercise. Certain health issues like diabetes or hypothyroidism also play a part.
How does cholesterol increase in the body?
Cholesterol levels are affected by what you eat and how much your body makes. Your liver controls this balance. Diet, genes, and health conditions can upset this balance.
Are there any physical signs that may indicate high cholesterol?
High cholesterol might not show symptoms. But, signs like xanthomas or corneal arcus could indicate it.
When should I get tested for high cholesterol?
Adults should get tested every 4-6 years. If you have risk factors or a family history, you might need to go more often.
What happens if I have high cholesterol?
If left untreated, high cholesterol can cause heart disease. This increases the risk of heart attacks or strokes.
What can I do if I have high cholesterol?
To manage it, change your diet and exercise more. You might also need medication.
How can I monitor and manage my cholesterol over time?
Work with your doctor to make a plan. Track your progress and adjust as needed. Consider your age and health.
What is the importance of the LDL/HDL ratio in managing cholesterol?
The LDL/HDL ratio shows your heart risk. A lower ratio means less risk. A higher ratio means more risk, so it’s key to manage it.
How often should I retest my cholesterol levels based on previous results?
How often you need to retest depends on your results and risk factors. If you have high cholesterol, you might need to test every 6-12 months.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. High Cholesterol: Silent Condition, Serious Heart Problems. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279318/