Last Updated on November 25, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir
Coronary heart disease, also known as coronary artery disease (CAD), affects the heart’s blood supply. At Liv Hospital, we focus on helping patients understand their life expectancy and prognosis. This knowledge is key to managing the disease effectively.Discover how long can you live with coronary heart disease and manage symptoms.
The outlook for coronary heart disease depends on several factors. These include age, sex, disease severity, and when treatment starts. The American Heart Association says CAD can cut life expectancy by about 10 years. We will look at what affects life expectancy with CAD and how early treatment can help.
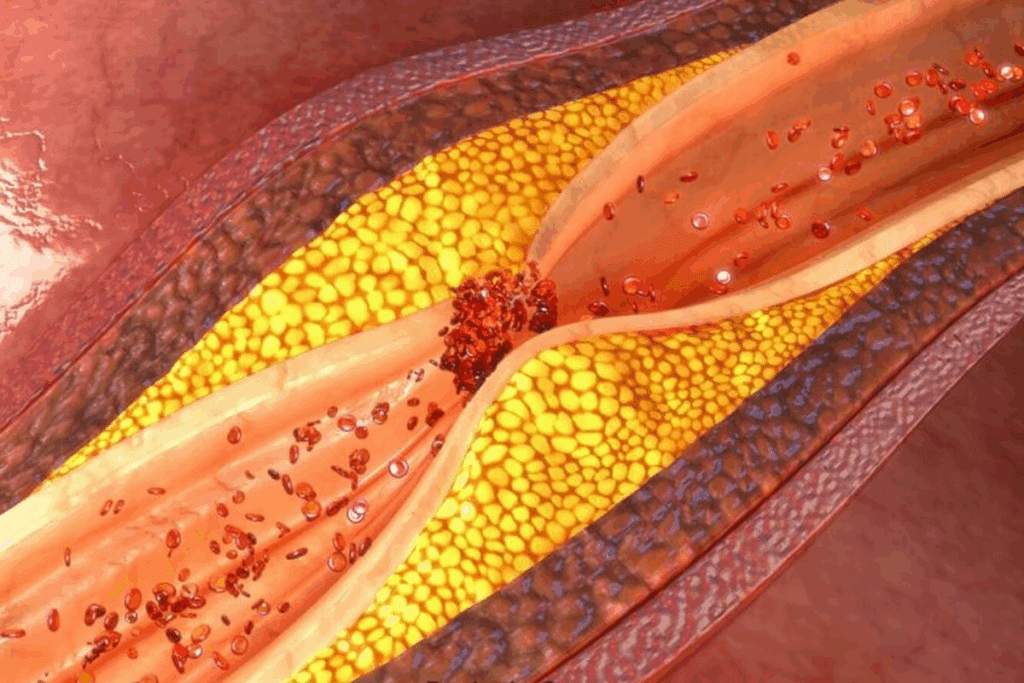
Coronary heart disease, also known as coronary artery disease, is a major health problem worldwide. It needs to be understood and prevented. We will dive into this condition to grasp its impact on global health.
Coronary heart disease (CHD) happens when the coronary arteries narrow or get blocked. This is due to a buildup of plaque made of fat, cholesterol, and other substances. This buildup limits blood flow to the heart, which can cause angina, heart attacks, and more. The process involves complex interactions between vascular biology, lipid metabolism, and inflammation.
As plaque builds up, it can burst, causing a blood clot. This clot can block the artery completely, leading to a heart attack. Knowing how it works is key to finding effective treatments.
Coronary heart disease is a big problem worldwide. In the United States, about 20.5 million adults have CAD, making it the most common heart disease. The World Health Organization (WHO) says it’s one of the top killers globally.
Many factors affect how common CHD is, like lifestyle, genetics, and wealth. As more people get older and lead less active lives, CHD’s impact is expected to grow.
“The global burden of cardiovascular disease is enormous, with coronary heart disease being a major contributor. Efforts to prevent and manage CHD are critical to reducing this burden.”
It’s important to know the symptoms of coronary heart disease to catch it early. Common signs include chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, and feeling tired. Some people might feel pain or discomfort in their arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach. It’s key to remember that some people might not show symptoms until they have a severe event like a heart attack.
Signs that mean you need to get medical help right away include severe chest pain, trouble breathing, and signs of a heart attack. Spotting these signs early can greatly improve your chances of recovery.

Coronary heart disease (CAD) greatly affects life expectancy. It’s important to understand this to manage the disease well. When CAD is diagnosed, patients and doctors look at many factors to predict life expectancy. This helps in making treatment and lifestyle choices.
Research has given us insights into CAD life expectancy. The data shows that life expectancy after diagnosis depends on several things. These include the age at diagnosis and gender.
Key statistical findings include:
Studies show that there are gender differences in CAD life expectancy. For example, women diagnosed with CAD at 50 can live about 7.9 years. Men diagnosed at the same age have an average life expectancy of 6.7 years. These numbers stress the need to consider gender in CAD management.
“Understanding these gender differences is key for customizing treatment and lifestyle advice for each patient.”
The age of CAD diagnosis greatly influences life expectancy. Early detection leads to longer life expectancy because it allows for timely treatment. A later diagnosis often means a shorter life expectancy due to more advanced disease.
It’s vital for people to know their risk factors and get regular check-ups. This helps in early detection and treatment.
It’s important to know what affects life expectancy with coronary heart disease. This knowledge helps both patients and doctors. Several key factors play a big role in how long someone can live with this condition.
The severity and extent of arterial blockage are key in determining life expectancy. Arterial blockage happens when plaque builds up in the coronary arteries, restricting blood flow to the heart. The more severe the blockage, the higher the risk of heart attack and other complications. We will look at how blockage extent affects prognosis and treatment options.
Research shows that patients with more extensive coronary artery disease have a poorer prognosis. The location and severity of blockages also affect treatment decisions and life expectancy.
Comorbidities, or additional health conditions, can greatly impact survival rates for those with coronary heart disease. Conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and kidney disease can make treatment harder and worsen prognosis. Effective management of these comorbidities is essential to improving overall life expectancy. We will examine how various comorbidities affect coronary heart disease outcomes and strategies for managing them.
For example, diabetes can speed up the progression of coronary heart disease, while hypertension can increase the risk of heart attack. Managing these conditions through lifestyle changes and medication can help improve survival.
Early diagnosis and treatment of coronary heart disease can greatly improve life expectancy and quality of life. Timely intervention can help prevent complications and reduce the risk of heart attack. We will discuss the benefits of early diagnosis, including diagnostic tests and effective treatment strategies.
Advances in medical technology and treatment options have improved outcomes for patients with coronary heart disease. Early diagnosis allows for the start of appropriate treatment, which can slow disease progression and improve survival rates.
Thanks to medical progress, people can live longer after a heart attack. But, how long they live can vary a lot. Knowing what affects survival can help both patients and doctors make better choices.
Thanks to new treatments, more people survive heart attacks. Interventions like angioplasty and thrombolysis have cut in-hospital deaths. Now, less than 5% of heart attack patients die in the hospital, studies show.
What’s behind these better survival rates? It’s things like:
People who have a heart attack at 50 can live about 18 years after. This shows how important it is to manage health long-term. Sticking to medication, eating right, and exercising regularly are key.
Many things can affect how well someone does after a heart attack. These include:
By tackling these factors, people can live longer and better after a heart attack.
Coronary artery calcification shows plaque buildup in arteries. It’s a sign of atherosclerosis. This condition can predict heart attacks and strokes.
Arterial calcification is a complex process. It involves calcium and phosphate in artery walls. It’s linked to aging, inflammation, and metabolic disorders.
Key factors contributing to arterial calcification include:
Living long with coronary artery calcification is possible. It needs careful management of heart risk factors. The calcification level shows heart risk.
The prognosis varies based on several factors, including:
| Risk Category | Coronary Artery Calcification Score | Recommended Actions |
| Low Risk | 0-100 | Lifestyle modifications, monitoring |
| Moderate Risk | 101-300 | Lifestyle modifications, possible medication |
| High Risk | >300 | Aggressive risk factor modification, medication |
Several tools detect coronary artery calcification. The most common is the coronary artery calcium (CAC) scan. It’s a non-invasive CT scan that measures calcium in arteries.
Monitoring approaches include:
Understanding coronary artery calcification helps manage heart risk. It can lead to a longer, healthier life.
It’s important to know about coronary artery disease (CAD) death rates and survival chances. Studies and data give us insights into these trends and factors.
Coronary artery disease is a top cause of death worldwide. The World Health Organization (WHO) says it causes about 17.9 million deaths each year. Most of these deaths are from heart attacks and strokes. These numbers highlight the need for better prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.
In countries with good healthcare, survival rates are getting better. In the United States, for example, survival after heart attacks is now over 90%. This is thanks to better treatments like stents and managing risk factors.
Survival rates are improving, but there are big differences in different places and among different people. Things like money, access to healthcare, lifestyle, and genes affect these differences. For example, some groups may face higher death rates because they can’t get good healthcare.
Looking at CAD death rates and survival chances, we see both challenges and hope. Medical science is getting better, and healthcare is improving. By focusing on prevention, early diagnosis, and effective treatment, we can help more people with CAD.
Medical technology has made big strides, helping people with coronary heart disease live longer. We now have many effective treatments. These not only add years to a person’s life but also make life better for those with CAD.
Medicine is key in managing coronary heart disease. Different drugs are used to treat CAD, each with its own benefits:
Using these medicines together can greatly improve CAD management and life expectancy.
| Medication Class th> | Primary Benefit | Example Medications |
| Antiplatelet agents | Prevent blood clots | Aspirin, Clopidogrel |
| Statins | Lower LDL cholesterol | Atorvastatin, Simvastatin |
| Beta-blockers | Reduce heart workload | Metoprolol, Atenolol |
| ACE inhibitors | Relax blood vessels | Lisinopril, Enalapril |
For many CAD patients, surgery or interventional procedures are needed. These include:
These procedures can greatly improve symptoms and survival for those with severe CAD.
Cardiac rehabilitation is a program that includes exercise, education on heart-healthy living, and stress management. It’s designed to help patients recover from heart events and procedures. It also improves overall health and reduces the risk of future heart problems.
By combining medication, surgery, and cardiac rehabilitation, we can greatly extend life and improve quality of life for CAD patients.
Changing your lifestyle can greatly improve your health if you have coronary heart disease. Making smart choices about what you eat, how much you exercise, quitting smoking, and managing stress can help. These actions can make you healthier and might even add years to your life.
Eating right is key to managing heart disease. A heart-healthy diet should include lots of fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean proteins. It’s also important to cut down on bad fats and cholesterol, and eat less sodium.
The Mediterranean-style diet is great for heart health. It focuses on olive oil, nuts, and fatty fish, which are full of omega-3s. This diet can lower bad fats and blood pressure, helping your heart stay healthy.
Staying active is vital for heart disease management. CAD patients should aim for 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly, or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise, or a mix of both. Good activities include brisk walking, cycling, or swimming.
Adding strength training to your routine can also be beneficial. It helps build muscle and strengthen bones. But, always talk to your doctor before starting any new workout plan.
Quitting smoking is a huge step for CAD patients. Stopping smoking can greatly lower your risk of heart attacks and other heart problems. Look into counseling, nicotine replacement, and medications to help you quit.
If you can drink alcohol, it’s okay in moderation. But, talk to your doctor about how much is safe. Too much alcohol can raise blood pressure and harm your heart, so it’s important to know your limits.
Stress can hurt your heart, so managing it is important. Meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can help reduce stress. Try different methods to find what works best for you.
By making these lifestyle changes, people with coronary heart disease can greatly improve their health and quality of life.
Coronary artery disease (CAD) can change your life, but you can live well with it. To manage CAD, you need a plan that includes medical care, lifestyle changes, and emotional support.
For CAD patients, staying active is key. Regular exercise boosts heart health and overall happiness. But, it’s important to choose exercises that fit your health and abilities.
Here are some physical tips:
Living with CAD can affect your mood. Anxiety and depression are common. So, taking care of your mental health is very important.
Here are ways to keep your mind healthy:
Having a strong support system is key for CAD patients. This includes family, friends, support groups, and healthcare teams.
| Support System | Description | Benefits |
| Family and Friends | Emotional support and practical help | Less stress, better mental health |
| Support Groups | Sharing experiences and advice with others who have CAD | Emotional support, tips, and a sense of community |
| Healthcare Professionals | Medical guidance and treatment | Good CAD management, better health outcomes |
By using these strategies, people with CAD can improve their quality of life. It’s about making smart choices and using the resources available to live well with CAD.
Preventive measures are key in managing coronary artery disease. They help improve life expectancy. By being proactive, people can lower the risk of CAD complications.
Primary prevention aims to stop CAD before it starts. It involves making healthy lifestyle choices. This includes eating well, staying active, keeping a healthy weight, and not smoking.
Secondary prevention helps those with CAD avoid further damage. It combines medication, lifestyle changes, and regular check-ups.
| Prevention Strategy | Description | Benefits |
| Medication Therapy | Use of statins, beta-blockers, and antiplatelet drugs | Reduces cholesterol levels, lowers blood pressure, and prevents clot formation |
| Lifestyle Modifications | Dietary changes, increased physical activity, stress management | Improves overall cardiovascular health, enhances quality of life |
| Regular Monitoring | Regular check-ups, diagnostic tests | Early detection of issues, timely intervention |
Regular monitoring is vital for managing CAD. It includes regular doctor visits, diagnostic tests, and tracking risk factors like blood pressure and cholesterol.
People with CAD need to know the warning signs for urgent medical care. These include:
Living with coronary heart disease needs a full approach to management and treatment. Medical science and management strategies have made big improvements. This offers a better future for those with CAD.
The future of CAD management is all about new ideas and care that fits each person. With the latest treatments, lifestyle changes, and prevention, people with CAD can live longer and healthier. Early diagnosis, effective treatment, and regular checks can really improve life expectancy and quality.
As the field keeps growing, we’ll see even better ways to manage CAD. By staying up-to-date and working with healthcare providers, people with CAD can handle their condition well. The future for those with coronary heart disease looks brighter, with better outcomes and a better quality of life ahead.
Living with coronary artery disease (CAD) can vary a lot. It depends on how blocked the arteries are, other health issues, and how well treatment works. With good care, many people can live 10-20 years or more after finding out they have CAD.
Yes, it’s possible to live a long life with coronary heart disease. Early detection and effective treatment are key. Making lifestyle changes and sticking to treatment plans also helps a lot.
After a heart attack at 50, people usually live about 18 years. But, this can change based on how serious the heart attack was and overall health.
Getting diagnosed early is very important. It means you can start treatment and make lifestyle changes sooner. This can lead to better outcomes.
Several things affect how long you can live with coronary heart disease. These include how blocked the arteries are, any other health issues, and how well you get treated early on.
Yes, making healthy choices can really help. Eating right, exercising, quitting smoking, and managing stress can all improve your life and health with coronary heart disease.
There are many ways to treat coronary artery disease. This includes medicines, surgeries like angioplasty and bypass, and programs to help your heart get stronger. All these can help you feel better and live longer.
Coronary artery calcification shows you have atherosclerosis, which means you’re at higher risk. But, with the right care and monitoring, you can live a long life even with it.
Coronary artery disease is a big killer worldwide. But, thanks to better care, more people are surviving it. In the US, for example, survival rates are now over 90%.
To live well with CAD, you need to adapt physically and take care of your mind and heart. Also, having support from friends and family helps a lot in improving your life.
To live longer with CAD, it’s important to prevent it before it starts and manage it well after. Regular check-ups and care are key to improving your chances of a long life.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!