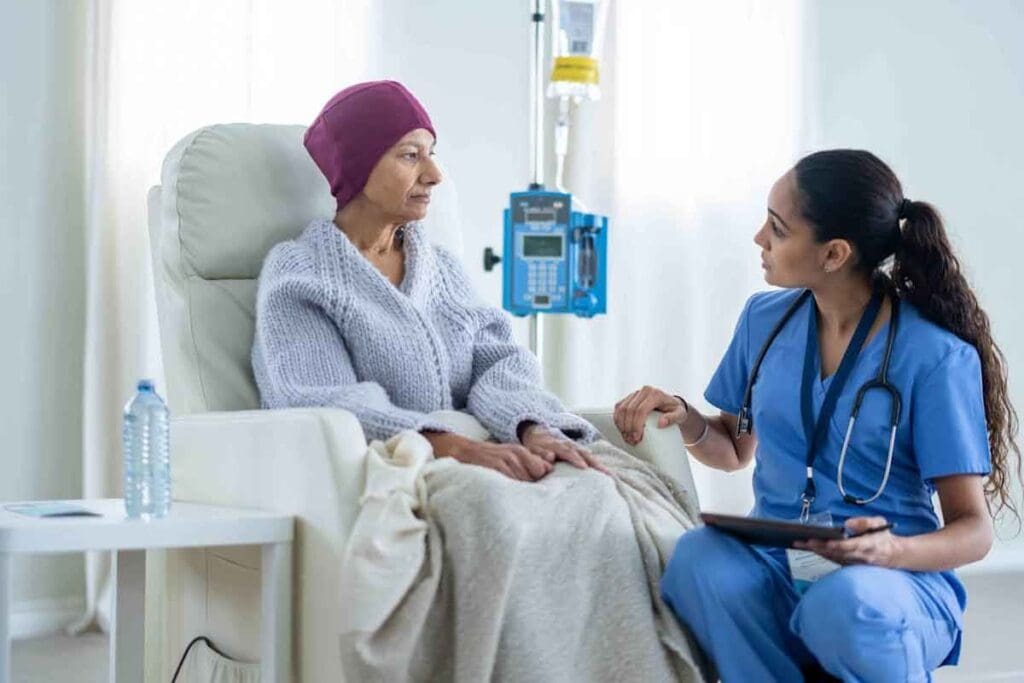
For those with sickle cell disease, knowing how long they might live is key. Thanks to better care and a focus on the patient, the future looks brighter.Find out how long can you live with sickle cell disease. Get key facts on lifespan, prognosis, and serious survival rates.
In the U.S., people with sickle cell anemia usually live about 52 to 54 years. How long you live depends on many things. These include the quality of your healthcare, how well you manage health problems, and your overall health.
Key Takeaways
- Current life expectancy for individuals with SCD is approximately 52 to 54 years.
- Access to quality healthcare significantly influences life expectancy.
- Effective management of complications is key to better survival rates.
- Your overall health and lifestyle greatly affect your prognosis.
- Medical care is getting better, which helps SCD patients more than ever.
Understanding Sickle Cell Disease

Sickle Cell Disease is a genetic disorder that affects how the body makes hemoglobin. This leads to red blood cells that are shaped like sickles. These abnormal cells can cause many health problems.
What Is Sickle Cell Disease?
Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is a genetic disorder that changes the hemoglobin in red blood cells. Normally, these cells are flexible and round. But in SCD, they become stiff and crescent-shaped.
This shape change can cause the cells to break down early. It can also block blood flow, leading to serious complications.
The genetic cause of SCD is a mutation in the HBB gene. This gene codes for a part of hemoglobin. People with two mutated copies of this gene have SCD. Those with one mutated copy are carriers.
Types of Sickle Cell Disease
There are several types of SCD, each caused by different genetic mutations. The most common is Sickle Cell Anemia (HbSS). This happens when someone inherits two sickle hemoglobin genes.
Other types include:
- HbSC Disease: This is when someone has one sickle hemoglobin gene and one hemoglobin C gene.
- HbS Beta-Thalassemia: This involves one sickle hemoglobin gene and one beta-thalassemia gene.
- HbSE Disease: This results from one sickle hemoglobin gene and one hemoglobin E gene.
Prevalence and Demographics
SCD is more common in certain areas and among certain groups. It’s most common in sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle East, and parts of India. In the United States, it affects about 100,000 people, mostly those of African descent.
It also affects people of Hispanic, Middle Eastern, and South Asian ancestry.
Knowing who is most affected by SCD helps in creating better healthcare plans. This can improve the lives of those with the disease.
Current Life Expectancy Statistics for Sickle Cell Disease
It’s important to know the life expectancy for sickle cell disease. This info helps patients and doctors. Recent data shows the average life span and what affects it.
Average Lifespan in the United States
In the United States, people with sickle cell disease live about 52 to 54 years. Studies have tracked how long SCD patients live. Advances in medical care have helped, but SCD patients face big health challenges.
Comparison to General Population
People with SCD live much shorter lives than the average American. The general population lives about 78 years. This big difference is due to chronic pain, acute chest syndrome, and increased risk of infections.
Global Variations in Life Expectancy
Worldwide, life expectancy for SCD patients varies a lot. In some places, like sub-Saharan Africa, it’s much lower. This is because of less healthcare and other issues. But, in countries with better healthcare, SCD patients live longer.
- In the US and other developed countries, life expectancy ranges from 52 to 54 years.
- In regions with limited healthcare access, life expectancy can be as low as 30-40 years.
- Global disparities in healthcare access and quality significantly impact SCD life expectancy.
The life expectancy for SCD patients shows we need to keep improving medical care. We also need to make healthcare more accessible. By knowing these facts, doctors can help patients live better lives.
Historical Perspective: How Survival Rates Have Improved
Over the years, life expectancy for people with Sickle Cell Disease has greatly improved. This change is thanks to advances in medical care.
Life Expectancy in the 20th Century
In the early 20th century, Sickle Cell Disease often led to death in early childhood. The life expectancy was much lower than today. Medical advancements have been key in changing this outlook.
By the mid-20th century, understanding SCD started to grow. This led to better ways to manage the disease. But, it wasn’t until the late 20th century that life expectancy really started to improve.
Medical Advancements That Extended Lifespan
Several medical breakthroughs have helped SCD patients live longer. One major development is hydroxyurea. This medicine reduces painful crises and may help patients live longer.
Other important advancements include better blood transfusion techniques and managing complications like acute chest syndrome. A report by the American Society of Hematology shows these improvements have greatly increased life expectancy.
Trends in Mortality Rates Over Time
Mortality rates for SCD have been falling over the years. This shows better healthcare and disease management. The table below shows the trend in mortality rates for SCD patients in the United States over several decades.
| Decade | Mortality Rate per 100,000 |
| 1970s | 15.6 |
| 1980s | 12.3 |
| 1990s | 9.5 |
| 2000s | 7.1 |
| 2010s | 5.4 |
The data shows a steady drop in mortality rates. This highlights the positive effect of medical advancements on SCD patient survival.
Age-Related Survival Rates: From Childhood to Adulthood
Age is key in figuring out how long people with Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) can live. As they grow older, many things can affect how long they live.
Infant and Childhood Survival
Thanks to better medical care, kids with SCD are living longer. Early diagnosis and good care have made a big difference.
A study in the Journal of Pediatrics shows kids with SCD can often grow up. But moving from child to adult care is tough and needs careful planning.
Adolescent and Young Adult Outcomes
When kids with SCD grow into teens and young adults, they face new challenges. Sticking to treatment and managing problems are very important.
“The transition from pediatric to adult care is a critical period for individuals with SCD, requiring coordinated efforts from healthcare providers to ensure continuity of care.”
Young adults with SCD do well with specialized care that meets their needs. This includes help with mental health and learning to manage their disease.
Survival Challenges in Middle and Older Age
Even though more people with SCD are living into their 40s and 50s, they face big health problems. Organ damage and chronic pain are common issues.
| Age Group | Common Complications | Survival Challenges |
| Infancy and Childhood | Infections, Acute Chest Syndrome | Access to early diagnosis and treatment |
| Adolescence and Young Adulthood | Stroke, Splenic Sequestration | Transition to adult care, adherence to treatment |
| Middle and Older Age | Organ Damage, Chronic Pain | Managing long-term complications, maintaining quality of life |
The table shows how survival challenges change with age. Knowing this helps us create better care plans.
The image shows how survival rates change with age for people with SCD. It highlights the need for care that fits each age group.
How Long Can You Live With Sickle Cell Disease: Factors Affecting Prognosis
Many factors influence how long someone with Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) can live. It’s important for patients, doctors, and families to understand these factors. This knowledge helps manage the disease better and can increase life expectancy.
Genetic Variants and Their Impact
Genetic variations greatly affect SCD’s severity. Some genetic changes can make the disease worse, while others can help. For example, having alpha-thalassemia can lessen SCD’s impact by reducing hemoglobin S levels.
Table 1: Genetic Variants and Their Effects on SCD Severity
| Genetic Variant | Effect on SCD Severity |
| Alpha-thalassemia | Reduces severity |
| Beta-globin gene haplotypes | Influences disease severity and complications |
| UGT1A1 gene variants | Affects bilirubin metabolism and risk of gallstones |
Access to Specialized Care
Getting regular care from specialists is key to managing SCD. Seeing hematologists and other experts often helps catch and treat problems early. This can greatly improve a patient’s outlook.
Socioeconomic Factors
Socioeconomic status, including income and education, affects SCD outcomes. People from lower-income backgrounds often struggle to get the care they need. This can make managing SCD harder.
- Limited access to healthcare services
- Inadequate health insurance coverage
- Lower adherence to treatment protocols due to lack of education or resources
Comorbidities and Their Effects
Having other health issues like high blood pressure, diabetes, and kidney disease can make SCD harder to manage. It’s important to treat these conditions well to improve survival chances.
Comorbidity Management Strategies:
- Regular monitoring of blood pressure and renal function
- Aggressive management of infections and other complications
- Coordination of care among multiple specialists
Major Complications That Impact Lifespan
People with Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) face many complications that can shorten their life and lower their quality of life. These problems come from the sickle-shaped red blood cells that are a hallmark of the disease.
Acute Chest Syndrome
Acute Chest Syndrome (ACS) is a big problem for SCD patients. It causes new lung problems, fever, breathing issues, or chest pain. ACS can lead to serious breathing problems and is a major reason for death in SCD patients.
Stroke and Neurological Complications
Stroke is a serious problem for SCD patients, mostly in children. It happens when sickled red blood cells block brain blood vessels, causing damage. Other brain problems, like silent cerebral infarcts, can also occur without symptoms but can affect thinking and development.
Organ Damage and Failure
SCD can harm many organs over time. This is because of chronic anemia, blocked blood vessels, and repeated damage. Organs like the kidneys, liver, and heart are often affected. For example, sickle cell nephropathy can cause kidney disease and failure.
Infections and Immune System Challenges
People with SCD are more likely to get infections because their spleen doesn’t work well. This makes their immune system weak. Serious infections, like those from Streptococcus pneumoniae, can be deadly.
| Complication | Impact on Lifespan | Management Strategies |
| Acute Chest Syndrome | High mortality risk | Prompt medical attention, pain management, and respiratory support |
| Stroke | Significant morbidity and mortality | Regular blood transfusions, monitoring for stroke risk |
| Organ Damage | Progressive organ failure | Regular monitoring, management of organ-specific complications |
| Infections | Increased risk of severe infections | Prophylactic antibiotics, vaccinations |
Managing these complications well is key to improving the lives of SCD patients. It requires a full plan that includes regular checks, prevention, and quick action when problems happen.
Treatment Approaches That Improve Survival
The way we manage Sickle Cell Disease has changed, bringing new hope. New treatments help people with SCD live longer and better. These advances aim to improve life quality and life span.
Disease-Modifying Therapies
Disease-modifying therapies are key in managing SCD. They aim to lessen the disease’s impact. Hydroxyurea is a well-known therapy that helps reduce painful crises and acute chest syndrome. This improves survival rates.
Hydroxyurea and Other Medications
Hydroxyurea is not the only treatment for SCD. Drugs like voxelotor and crizanlizumab also show promise. They target different parts of the disease, like reducing hemolysis or preventing vaso-occlusive crises.
Blood Transfusions
Blood transfusions are a key treatment for SCD. They help lower the risk of stroke and acute chest syndrome by reducing sickled red blood cells. But, transfusions can lead to iron overload, which needs careful management.
Stem Cell Transplantation
Stem cell transplantation is the only cure for SCD. It replaces the patient’s bone marrow with healthy stem cells from a donor. While it offers a cure, it comes with risks like graft-versus-host disease. It’s usually for severe cases.
In conclusion, many treatments have made life better for people with Sickle Cell Disease. Understanding each treatment’s benefits and challenges helps healthcare providers create better plans. This improves patients’ quality of life and life span.
Preventive Care and Management Strategies
Managing Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) well means using preventive care to improve life quality and length. People with SCD need a care plan that covers all parts of the disease.
Regular Screening and Monitoring
Checking and watching closely are key in SCD care. This means regular blood tests to check hemoglobin, liver, and kidney health. Spotting problems early helps fix them fast, which can greatly help.
Seeing doctors often lets them track how the disease is doing and change treatment plans if needed. This active approach helps manage symptoms and avoid serious problems.
Pain Management Protocols
Pain is a big problem in SCD, and managing it well is key to a good life. Treatment plans mix medicines and other methods. Each person’s pain plan is made just for them, using things like medicine, physical therapy, and acupuncture.
Knowing and dealing with what causes pain crises is also key. By finding and avoiding these causes, people with SCD can have fewer and less severe pain episodes.
Infection Prevention
Infections are a big risk for people with SCD, more so for kids. Vaccines and antibiotics help lower infection risk. Keeping clean and avoiding germs is also very important.
Learning about preventing infections and getting medical help right away when sick is part of good care.
Nutritional Considerations
What you eat is very important for your health if you have SCD. Eating a balanced diet full of nutrients helps your health and can ease some symptoms. Getting advice on what to eat helps make good food choices.
Drinking enough water is also key, as not drinking enough can lead to sickling crises. Making sure to drink enough fluids and electrolytes is a big part of managing SCD.
Quality of Life Considerations
Living with Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) affects many aspects of life. It impacts not just physical health but also mental and emotional well-being. Managing chronic pain and getting psychological support are key to a better life.
Managing Chronic Pain
Chronic pain is a big challenge for SCD patients. It makes everyday life tough. The Sickle Cell Disease Association of America says managing pain is vital. It involves using medicine, trying other therapies, and making lifestyle changes.
Pain management strategies include:
- Pharmacological interventions, such as hydroxyurea and pain relievers
- Non-pharmacological approaches, including physical therapy, acupuncture, and cognitive-behavioral therapy
- Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and avoiding triggers
Psychological and Social Impacts
SCD can lead to anxiety and depression. The disease’s chronic nature and its effects on daily life are big contributors. A study in the Journal of Clinical Psychology shows SCD patients face higher mental health risks. This highlights the need for psychological support.
“The psychological burden of SCD cannot be overstated. It affects not just the patients but also their families and caregivers.”
Educational and Occupational Challenges
SCD can hinder education and work. Frequent hospital stays and health issues cause missed school or work. Supportive measures like special education plans and work adjustments can help.
Healthcare providers play a big role in improving SCD patients’ lives. They must focus on pain management, psychological support, and help with education and work. A leading expert says, “Comprehensive care is essential for better lives for SCD patients.”
Advanced Care Models and Specialized Treatment Centers
The way we manage sickle cell disease has changed a lot. Now, we have advanced care models. These models aim to give patients the best care possible.
Multidisciplinary Care Approaches
Multidisciplinary care is key in treating sickle cell disease. It brings together many healthcare experts. This way, patients get care that covers all their needs.
Comprehensive care teams include doctors, nurses, and more. They work together to handle the complex issues of SCD patients.
One big plus of this care is better handling of complications. For example, regular checks and prevention can lower the chance of serious problems like acute chest syndrome.
Liv Hospital’s Academic Protocols
Liv Hospital is a leader in SCD treatment. They use advanced academic protocols to improve patient care. Their method includes evidence-based treatment plans and continuous monitoring for the best results.
| Protocol | Description | Benefits |
| Disease-Modifying Therapies | Treatments aimed at reducing the frequency of SCD crises | Reduces pain episodes and improves quality of life |
| Regular Blood Transfusions | Transfusions to reduce the number of red blood cells that can sickle | Decreases the risk of stroke and other complications |
| Pain Management Protocols | Comprehensive plans for managing pain associated with SCD | Improves patient comfort and reduces hospitalizations |
Preventive and Curative Healthcare Strategies
Preventive and curative healthcare strategies are essential for SCD management. They include regular screenings, vaccinations, and medications like hydroxyurea. These steps help reduce disease severity.
By being proactive in care, SCD patients can see better health and a better life. Advanced care models and places like Liv Hospital are setting the standard for care.
Conclusion: Living Well With Sickle Cell Disease
Living with Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is tough, but medical care has improved a lot. Now, people with SCD can live longer and feel better. Knowing how to manage SCD is key to living a longer life.
Managing SCD means using special treatments, checking health often, and taking steps to prevent problems. These actions help people with SCD stay healthy and active. Thanks to new research, the future for SCD patients looks bright.
Dealing with SCD needs a team effort. This includes special care models and treatment centers. With the right care, people with SCD can live better and longer lives.
As doctors learn more and treatments get better, living well with SCD is becoming more possible. By staying informed and taking action, people with SCD can handle their condition better. This improves their life quality.
FAQ
What is the average lifespan of someone with sickle cell disease?
The lifespan of someone with sickle cell disease varies. It depends on healthcare access, social status, and other health issues. In the U.S., people with sickle cell disease usually live between 40 to 60 years. But, this number can change a lot.
How has the life expectancy for sickle cell disease patients changed over time?
Life expectancy for sickle cell disease patients has gotten better. This is thanks to better medical care. Now, we have hydroxyurea, blood transfusions, and better ways to fight infections.
What factors affect the prognosis of individuals with sickle cell disease?
Several things affect how well someone with sickle cell disease will do. These include their genes, access to care, social status, and other health problems. These factors can change how long they live and how well they feel.
What are the major complications of sickle cell disease that impact lifespan?
Big problems for sickle cell disease patients include acute chest syndrome, stroke, and organ damage. Infections and immune system issues also matter. Managing these problems is key to living longer.
How can preventive care and management strategies improve outcomes for individuals with sickle cell disease?
Preventive care and management can really help. Regular check-ups, pain management, fighting infections, and good nutrition are important. They can lower the risk of serious problems and make life better.
What role do disease-modifying therapies play in improving survival for individuals with sickle cell disease?
Therapies like hydroxyurea are very important. They help by making sickle cell disease less severe. This can lead to a longer, healthier life.
How does access to specialized care impact the life expectancy of individuals with sickle cell disease?
Getting the right care is very important. It helps manage the disease better. This can prevent serious problems and improve life expectancy.
What are the benefits of advanced care models and specialized treatment centers for individuals with sickle cell disease?
Places like Liv Hospital offer top-notch care. They provide a team approach to managing sickle cell disease. This can greatly improve life quality and outcomes.
Can individuals with sickle cell disease lead active and fulfilling lives?
Yes, with the right care, people with sickle cell disease can live full lives. They can manage their condition and avoid serious problems.
What is the survival rate for individuals with sickle cell disease?
Survival rates have gotten much better. Many people with sickle cell disease now live into their 40s and beyond. But, survival rates can vary based on many factors.
References
- Afranie-Sakyi, J. A., et al. (2025). The mortality of adults with sickle cell disease at a comprehensive sickle cell center. American Journal of Hematology. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39748504




































