Last Updated on November 26, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
Becoming an interventional radiologist is a challenging journey. At places like Liv Hospital, we focus on giving deep training in this field. Learn how to become a interventional radiology expert. Our simple guide covers the essential education, residency, and fellowship steps.
The first step is getting a bachelor’s degree in a science or pre-med field. Then, you spend four years in medical school to get an MD or DO. After that, you need a year-long internship to get real-world experience.
Our students follow a traditional path. This includes a four-year radiology residency and a one- to two-year interventional radiology fellowship. Or, they can choose the integrated six-year program that combines these steps.
Key Takeaways
- Becoming an interventional radiologist takes 13-15 years after high school.
- The path starts with a bachelor’s degree, four years of medical school, and a year-long internship.
- Students can pick between a traditional path or an integrated six-year program.
- Board certification comes from the American Board of Radiology.
- The integrated path leads to dual certification in both diagnostic and interventional radiology.
The Field of Interventional Radiology: An Overview
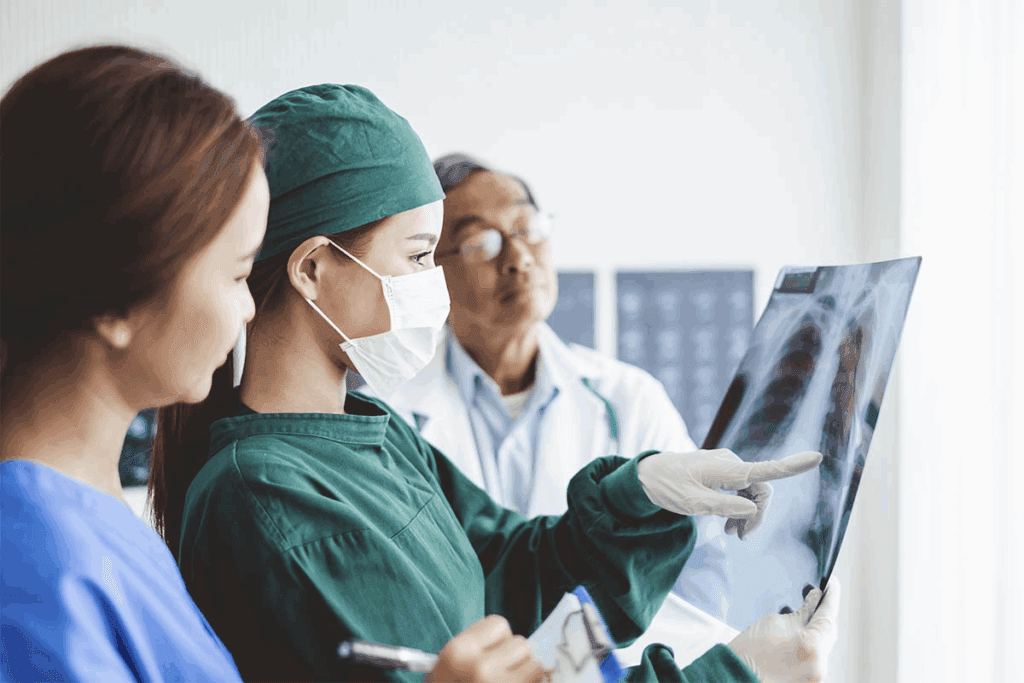

Interventional radiologists are key in diagnosing and treating complex health issues. They use advanced imaging to do minimally invasive procedures. This makes treatments safer and less invasive than traditional surgery.
What Interventional Radiologists Do
Interventional radiologists use imaging to find and treat many health problems. This includes heart diseases, cancers, and stomach issues. They do things like angioplasty and tumor removal.
They use X-rays, CT scans, MRI, and ultrasound to guide their work. This makes treatments more precise and effective.
Thanks to these imaging tools, interventional radiologists can offer targeted treatments. These treatments are safer, have shorter recovery times, and cause less pain than surgery.
Career Outlook and Compensation
The need for minimally invasive procedures is growing. This means interventional radiologists are in high demand. They get good pay for their work.
Their career outlook is bright, with lots of chances for growth. They make a big difference in patient care. Their job is challenging but very rewarding.
Essential Skills and Attributes for Success
To do well in interventional radiology, you need technical skills. This includes knowing how to use imaging tools and perform complex procedures. You also need to be good at solving problems and reading images.
Good patient care skills are also key. They work with patients and other doctors to give the best care. Being detail-oriented, able to handle stress, and good at communicating are important too.
Educational Prerequisites for Interventional Radiology

The journey to becoming an interventional radiologist begins with undergraduate studies. These studies are usually in science-related fields. This lays the groundwork for a future career in this specialized area of medicine.
Bachelor’s Degree Requirements
Getting a bachelor’s degree is the first step towards becoming an interventional radiologist. Most students major in biology, chemistry, or physics. These subjects give a strong science foundation. Coursework should include pre-medical requirements like anatomy, physiology, and biochemistry to get ready for medical school.
Pre-Medical Coursework and MCAT Preparation
After a bachelor’s degree, preparing for and taking the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT) is key. The MCAT tests knowledge in biology, chemistry, physics, and critical thinking. A competitive MCAT score is essential for medical school admission. Students should prepare well for the exam by practicing and taking MCAT courses if needed.
Building a Competitive Application Profile
While grades are important, they’re not the only thing medical schools look at. They also value clinical experience, research, and a commitment to medicine. Gaining experience through internships or volunteer work in healthcare settings can boost an application. Research projects and presenting at conferences also show a candidate’s expertise and dedication.
By focusing on these educational steps, aspiring interventional radiologists can lay a strong foundation for their careers. Knowing the ir residency length and the path to becoming an interventional radiologist helps guide their early education choices.
Medical School Education and Training
Medical school is key for a career in interventional radiology. It’s a four-year journey. The first two years cover basic sciences, and the last two are for clinical rotations.
In the first two years, students dive into anatomy, biochemistry, pharmacology, and pathology. These subjects are the base of medical knowledge. They help understand radiology and interventional radiology.
Medical School Curriculum Relevant to Radiology
The curriculum includes courses vital for radiology. Key areas include:
- Radiographic anatomy and interpretation
- Principles of imaging modalities (X-ray, CT, MRI, Ultrasound)
- Radiation safety and physics
Knowing these concepts is essential. They lay the groundwork for more specialized knowledge.
Elective Rotations in Radiology
Students get hands-on experience in radiology during clinical years. These rotations offer practical skills and insight into radiologists’ daily work.
Benefits of these rotations include:
- Gaining experience in interpreting imaging studies
- Understanding radiology’s role in patient care
- Developing skills in performing and assisting in radiologic procedures
Research Opportunities and Mentorship
Research projects in medical school boost understanding and preparation for interventional radiology. They allow students to explore interests, develop critical thinking, and contribute to the field.
Mentorship is also vital. Experienced professionals offer guidance, support, and insights. They help students navigate their career paths and make informed decisions.
By combining a strong medical school education with rotations and research, aspiring interventional radiologists can build a solid foundation for their careers.
Internship Year (PGY-1) Requirements
The PGY-1 year is a hands-on experience for future interventional radiologists. It’s a key time between medical school and residency. It helps build a strong patient care foundation and prepares for radiology residency demands.
Types of Acceptable Internships
Several internships can help aspiring interventional radiologists gain needed experience. These include:
- Internal Medicine Internship
- Surgery Internship
- Transitional Year Internship
Each internship offers unique experiences and skills for interventional radiology. For example, an internal medicine internship broadens understanding of medical conditions. A surgery internship provides hands-on surgical procedure experience.
Building a Foundation for Radiology Training
During the internship year, future interventional radiologists gain practical experience. They learn about patient care, medical procedures, and clinical decision-making. This foundation is key for success in radiology residency and fellowship training.
Key skills developed include:
| Skill | Description | Relevance to IR |
| Patient Assessment | Evaluating patient conditions and developing care plans | High |
| Clinical Decision-Making | Making informed decisions about patient care | High |
| Procedural Skills | Performing medical procedures with precision | Medium |
Transitioning from Internship to Residency
The internship year is about gaining clinical experience and preparing for residency. Aspiring interventional radiologists must navigate the application and matching process. This is to secure a spot in a competitive program.
Key steps in transitioning to residency include:
- Preparing a strong application package
- Securing strong letters of recommendation
- Performing well in interviews
- Strategically ranking residency programs
By focusing on these areas, individuals can improve their chances of matching into a diagnostic radiology residency program. This is a step toward becoming an interventional radiologist.
How to Become a Interventional Radiology Specialist: Training Pathways
There are two main ways to become an interventional radiologist. Each path has its own benefits and things to consider. We’ll look at these options to help you decide on your training.
Traditional Pathway: Diagnostic Residency + Fellowship
To become an interventional radiologist, you can take a traditional route. This involves a four-year diagnostic radiology residency followed by a one- to two-year fellowship in interventional radiology. This path gives you a broad base in diagnostic radiology before you specialize in interventional procedures.
In the diagnostic radiology residency, you’ll learn about many imaging methods and diagnostic techniques. This knowledge is key to understanding interventional radiology.
Key components of the traditional pathway include:
- Four years of diagnostic radiology residency
- One to two years of interventional radiology fellowship
- Broad exposure to diagnostic imaging techniques
Integrated IR Residency Pathway
The integrated IR residency is a newer, six-year program. It combines diagnostic radiology and interventional radiology training into one curriculum. This path aims to make training in interventional radiology more streamlined.
This program lets you start learning IR skills early. It also helps you understand how diagnostic and interventional radiology work together.
Key features of the integrated IR residency pathway include:
- Six-year combined program
- Early exposure to IR principles and techniques
- Integrated curriculum combining diagnostic and interventional radiology
Comparing the Two Pathways: Pros and Cons
Both paths have their good and bad sides. Your choice depends on what you want to achieve in your career and how you learn best.
Pros of the traditional pathway:
- Broad foundation in diagnostic radiology
- Opportunity to explore different areas of radiology before committing to IR
Cons of the traditional pathway:
- Longer overall training period (5-6 years)
- Potential for redundancy in training as some skills may overlap between diagnostic and IR training
Pros of the integrated IR residency pathway:
- Streamlined training with a focus on IR from the outset
- Potential for more efficient skill development in IR
Cons of the integrated IR residency pathway:
- Limited availability of programs
- May require a stronger commitment to IR early in training
Choosing between these paths should be based on your career goals and what kind of training environment you prefer.
Applying to Residency Programs
Applying to residency programs is a detailed process. It needs careful planning and preparation for those aiming to be interventional radiologists. This includes submitting applications through ERAS, going to interviews, and ranking programs through the NRMP Match.
Application Timeline and Requirements
The application timeline for residency programs usually begins in the summer before the residency starts. Applicants must check if they meet the eligibility criteria and follow the application instructions closely.
Key Application Components:
- Academic records
- Letters of recommendation
- Personal statement
- USMLE scores
Interview Preparation Strategies
Interviews are key to making a good impression on the selection committee. It’s important to research the program well, practice common interview questions, and be ready to talk about your experiences and career goals.
Effective Interview Techniques:
- Show enthusiasm for the program
- Highlight relevant skills and experiences
- Demonstrate knowledge of the field
Matching into Competitive Programs
The NRMP Match is a key part of the residency application process. To boost their chances of matching into a competitive program, applicants should rank programs based on their preferences and the program’s competitiveness.
| Factors Influencing Match Success | Description |
| Program competitiveness | The level of competition for spots in the program |
| Applicant’s academic record | The strength of the applicant’s academic achievements |
| Relevance of research experience | The relevance of the applicant’s research to the field of radiology |
By understanding the application process, preparing well for interviews, and strategically ranking programs, applicants can improve their chances of success in the NRMP Match.
Diagnostic Radiology Residency Experience
The diagnostic radiology residency is a key step to becoming an interventional radiologist. It offers a deep dive into radiology. Over four years, residents explore different areas, learning to read images and do procedures.
Core Competencies and Rotations
Diagnostic radiology residency includes rotations in various fields. These include:
- Neuroradiology: Studying brain and spine images.
- Musculoskeletal Radiology: Finding issues with muscles, bones, and joints.
- Cardiovascular Radiology: Looking at heart and blood vessel images and treatments.
Residents hone skills in reading images, caring for patients, and knowing medicine. They also get better at talking to patients and doctors.
Preparing for IR While in Diagnostic Training
Those aiming to be interventional radiologists can start preparing early. They can:
- Look for chances to learn about interventional radiology.
- Join IR-related rotations.
- Work on research projects about interventional radiology.
By being proactive in diagnostic radiology, future interventional radiologists can set a strong base for their fellowship and career.
We stress the value of a broad education in diagnostic radiology. It’s essential for a smooth transition into interventional radiology fellowship training.
Interventional Radiology Fellowship Training
The interventional radiology fellowship program is designed to equip trainees with the skills and knowledge required for a successful career in this field. It provides advanced specialized training in minimally invasive, image-guided procedures.
Fellowship Application Process
Applying for an interventional radiology fellowship is a competitive process. Applicants must show a strong background in radiology and a commitment to interventional radiology. The application process involves submitting a portfolio of work, letters of recommendation, and a personal statement.
To increase their chances, applicants should ensure their application is thorough. It should highlight their relevant experience and skills. We recommend researching each fellowship program’s specific requirements and tailoring applications.
Specialized Skills Development
During the fellowship, trainees develop specialized skills in performing complex interventions and managing complications. The training is typically one to two years and includes hands-on experience with various image-guided procedures.
Fellows learn to:
- Perform complex interventions with precision and accuracy
- Manage complications effectively
- Provide high-quality patient care
- Stay up-to-date with the latest advancements in interventional radiology
Fellowship vs. Integrated Residency Experience
There are two main pathways to becoming an interventional radiologist: the traditional fellowship pathway and the integrated residency pathway. Both pathways have their advantages, but the fellowship pathway offers a more focused experience in interventional radiology.
| Training Pathway | Duration | Specialized Training |
| Fellowship Pathway | 1-2 years | Advanced training in IR |
| Integrated Residency Pathway | 5 years | Comprehensive training in IR and DR |
Ultimately, the choice between the two pathways depends on the individual’s career goals and preferences. We recommend researching both options thoroughly to determine which pathway is best for them.
Board Certification and Professional Development
Interventional radiologists need to get board certified to work. The American Board of Radiology (ABR) oversees this process. Getting certified shows they are experts and dedicated to their field.
American Board of Radiology Examinations
The ABR gives out certifications in diagnostic and interventional radiology. To get certified, you must pass exams that check your skills and knowledge. Here’s what you need to do:
- Pass the initial exam in diagnostic radiology
- Get more training in interventional radiology
- Pass the exam for interventional radiology
Preparation is key for passing these exams. It’s important to know the exam format, content, and ABR’s rules well.
Maintaining Certification and Continuing Education
To keep your certification, you need to keep learning. The ABR says you must get a certain number of education credits over time. This keeps you up-to-date with new techniques and practices.
Here are ways to meet these requirements:
- Go to conferences and workshops
- Take online courses and webinars
- Do research and write articles
Professional Societies and Networking
Joining professional societies like the Society of Interventional Radiology (SIR) is important. These groups help you learn, network, and keep up with the latest news.
Being a member of SIR has many benefits. You get:
- Access to annual meetings and conferences
- Learning resources and publications
- Chances to meet other professionals
By joining these societies, interventional radiologists can grow professionally and help the field advance.
Conclusion: Is Interventional Radiology Right for You?
Thinking about a career in interventional radiology is a big step. It’s important to consider your interests, skills, and goals. Becoming an interventional radiologist means a lot of education and training.
This includes getting a degree in interventional radiology, doing residency programs, and getting fellowship training. You need to be dedicated to learning and growing in this field.
If you’re passionate about using new technologies to help patients, interventional radiology might be for you. The field is always changing. It’s key for those interested to keep up with new developments.
FAQ
What is the first step to becoming an interventional radiologist?
First, you need to get a bachelor’s degree. It’s usually in a science like biology, chemistry, or physics. You also need to meet pre-medical requirements.
How long does it take to become an interventional radiologist?
It takes at least 13-14 years after high school. This includes four years of college, four years of medical school, a one-year internship, and four years of radiology residency. You also need a one- to two-year fellowship in interventional radiology.
What are the two main training pathways to become an interventional radiologist?
There are two main paths. The traditional path includes a four-year radiology residency and a one- to two-year fellowship. The integrated IR residency is a six-year program that combines both.
What is the role of the American Board of Radiology in becoming an interventional radiologist?
The American Board of Radiology offers certifications in radiology and interventional radiology. To get certified, you must pass exams that show your knowledge and skills.
How competitive is the application process for diagnostic radiology residency programs?
Applying to radiology residency programs is very competitive. You need to apply through ERAS and prepare for interviews. This is to show your knowledge, skills, and fit for the program.
What skills are essential for success in interventional radiology?
You need technical skill, diagnostic ability, and patient care skills. It’s important to be good at minimally invasive procedures, managing complications, and caring for patients.
What is the difference between a diagnostic radiology residency and an interventional radiology fellowship?
A radiology residency gives a broad foundation in radiology. An interventional radiology fellowship focuses on advanced training in minimally invasive procedures. It helps develop specialized skills in interventional radiology.
How can one stay updated on the latest advancements in interventional radiology?
Joining professional societies like the Society of Interventional Radiology (SIR) is helpful. Also, take part in continuing education and professional development to stay current with new advancements and best practices.
What is the significance of research opportunities and mentorship during medical school for aspiring interventional radiologists?
Research and mentorship in medical school are key. They help deepen your understanding and prepare you for a career in interventional radiology. They offer valuable experience and guidance.
Can you explain the importance of the internship year for aspiring interventional radiologists?
The internship year is vital. It gives you hands-on experience in a clinical setting. It helps build a strong foundation in patient care and prepares you for radiology residency.
Reference
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. (2024). Interventional radiology residency. MedlinePlus. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/007535.htm