Last Updated on November 24, 2025 by Ilayda Cengizhan
Infertility in women is a major health issue worldwide, affecting about 13.4% of women of reproductive age. In the U.S., around 1 in 8 couples struggle with infertility, and women account for roughly one-third of these cases. Understanding infertility in women and its causes is essential for making informed reproductive health decisions.
Infertility in women is a big issue worldwide. We need to understand its causes and effects. It affects many people and families deeply.
Infertility is defined as the inability to conceive after 12 months of unprotected intercourse. Diagnosis involves:
Accurate diagnosis of infertility in women helps guide proper treatment.

Studies show that many women of childbearing age struggle with infertility. About 13.4% of women in this age group face these challenges. This shows we need to help and support them more.
“Infertility is a big health problem,” experts say. It affects not just the person but also society. The issue is more common in some areas, making local health care key.
Infertility means not getting pregnant after a year of trying. Doctors use tests to find out why. They check if the woman is ovulating, if the tubes are open, and if the uterus is healthy.
Finding out what’s wrong can take time and many doctors. Knowing the cause helps find the right treatment.
Infertility in women is not just physical it also affects emotional well-being. Stress, anxiety, and sadness often accompany fertility challenges. Treatments may involve hormone therapy, surgery, or assisted reproductive technologies, all of which can be physically and emotionally demanding.
Knowing what causes infertility is key to finding a solution. Women can face infertility due to health issues, lifestyle choices, and medical problems.
Understanding the main causes of infertility in women helps identify the right solutions.
Primary infertility means a woman can’t get pregnant after a year of trying. Secondary infertility is when a woman who has had a baby before can’t conceive again.
The CDC says tubal problems cause 20–25% of infertility in women. This shows why knowing the difference between primary and secondary infertility matters.
Reproductive health is very important for fertility. Issues like ovulation problems, endometriosis, and uterine issues can make it hard to get pregnant.
“Reproductive health is fundamental to the overall health and well-being of individuals and couples.”
Many things can lead to Infertility in Women. Age, lifestyle, and medical conditions are big factors. As women get older, their eggs quality and number go down, making it harder to conceive.
Ovulatory disorders account for about 40% of infertility in women. They include:
Treating hormonal imbalances is key to restoring ovulation and improving fertility.
Ovulation is a complex process that needs hormones working together. It starts with the hypothalamus telling the pituitary gland to send out hormones. These hormones make the ovaries produce eggs.
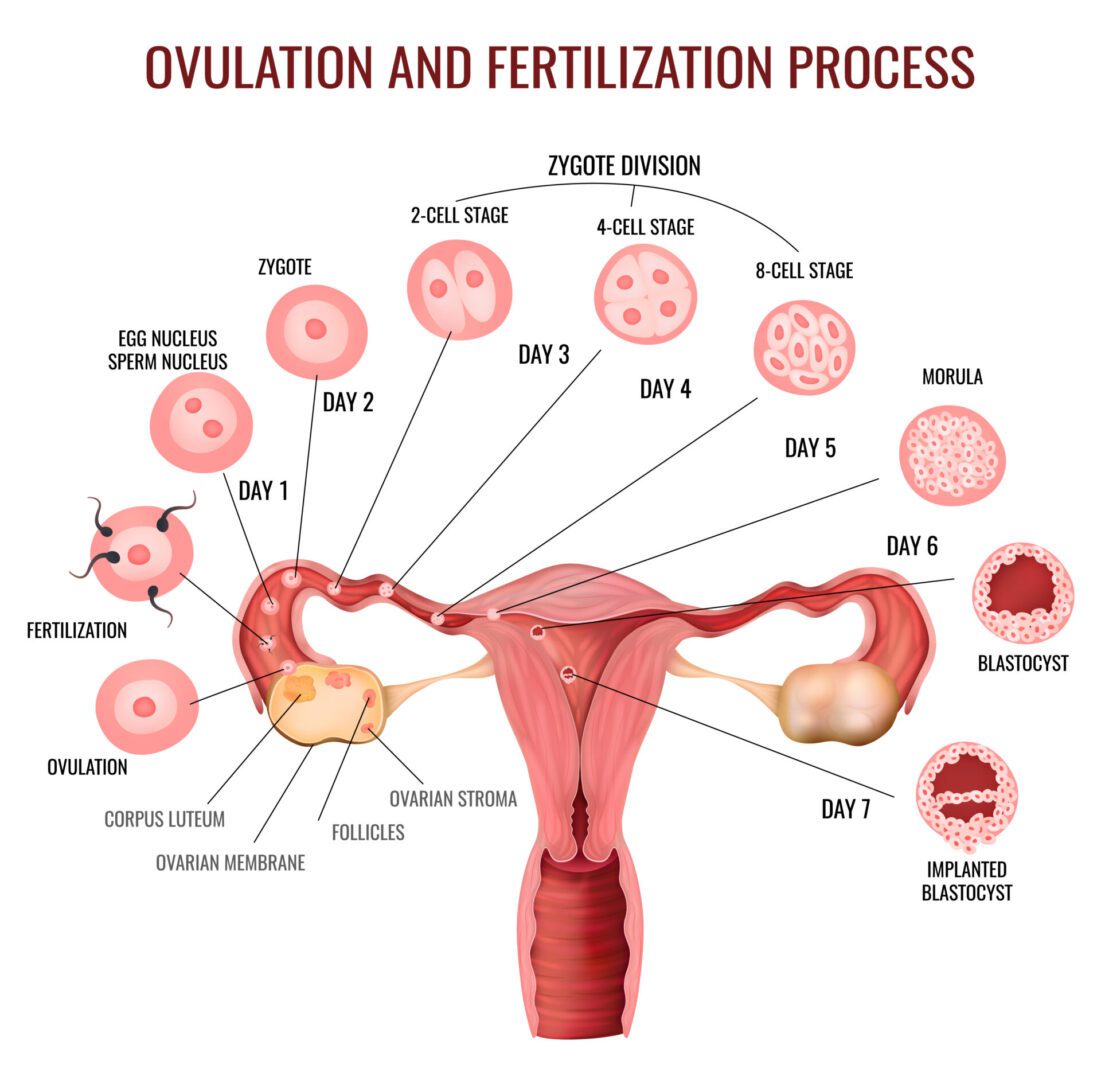
As the egg gets ready, a hormone surge makes it leave the ovary. This egg then moves through the fallopian tube. There, it can meet sperm and get fertilized.
Ovulatory dysfunction affects about 40% of infertility in women. There are several types, including:
PCOS and hypothalamic amenorrhea are common causes of these problems.
Hormonal imbalances are a big deal in ovulatory disorders. Issues with hormones like estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone can mess up ovulation. For example, in PCOS, hormonal problems cause cysts, irregular periods, and ovulation issues.
Understanding and fixing these hormonal imbalances is key to treating ovulatory disorders and boosting fertility.
Ovulatory disorders are a big hurdle for women trying to get pregnant. By knowing the causes and types, we can tackle the problem and find the right treatments.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a big health problem for women around the world. It’s a common endocrine disorder in women of childbearing age. PCOS causes symptoms that can hurt your quality of life and make it hard to get pregnant.
PCOS affects women in different ways. Symptoms include irregular periods, high male hormone levels, and polycystic ovaries seen on ultrasound. These can lead to infertility, metabolic problems, and mental health issues.
To diagnose PCOS, doctors look for at least two signs. These are infrequent ovulation, high male hormone levels, and polycystic ovaries on ultrasound.
PCOS cases have gone up a lot in recent years. From about 6 million in 1990 to 12.13 million in 2019. This increase is due to lifestyle changes, diet, and better ways to diagnose it.
PCOS is a big deal for women’s health, mainly because it affects fertility. It’s a commonest cause of infertility in women. Knowing about PCOS is key to finding good treatments.
PCOS is a major reason for ovulation problems, which hurts fertility. Women with PCOS often can’t ovulate, making it hard to get pregnant. PCOS also leads to insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome, making fertility issues worse.
Dealing with PCOS-related infertility needs a mix of treatments. This includes changing your lifestyle, hormone therapy, and using advanced fertility technologies. Understanding PCOS and its effects on fertility helps doctors give better care.
It’s important to know how fallopian tubes work to understand female infertility. These tubes are key for getting pregnant. They help the egg move from the ovary to the uterus.
Fallopian tubes are vital for making a baby. They are where the egg meets sperm. After ovulation, the egg goes into the tube. There, it gets fertilized and then goes to the uterus to grow into an embryo.
Many things can harm or block the fallopian tubes, making it hard to get pregnant. These include:
There are several ways to find out if the fallopian tubes are damaged or blocked. These include:
Diagnostic Method | Description |
Hysterosalpingogram (HSG) | An imaging test that uses dye to check if the fallopian tubes are open. |
Laparoscopy | A surgical procedure that allows direct visualization of the fallopian tubes and other pelvic organs. |
Sonohysterography | An ultrasound test that evaluates the uterus and fallopian tubes. |
Knowing the causes and how to diagnose fallopian tube damage is key for women with infertility. By finding the problem, doctors can suggest treatments to help with fertility.
It’s important to understand how endometriosis affects fertility. This condition affects many women, causing pain and possibly making it hard to get pregnant.
Endometriosis happens when tissue like the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus. This tissue bleeds and thickens with each menstrual cycle. It can cause a lot of pain and problems.
Key aspects of endometriosis include:
Research shows that up to 50% of women with infertility have endometriosis. This condition can make it hard to get pregnant. It can cause inflammation, scarring, and adhesions that block the fallopian tubes.
Endometriosis doesn’t make someone completely infertile, but it can lower chances of getting pregnant. The extent of the condition, other fertility issues, and overall health are important factors.
Endometriosis is staged based on how widespread and deep the implants are. The stages range from minimal to severe. The stage doesn’t always match the severity of symptoms or infertility.
Knowing the stage of endometriosis helps tailor treatments. Treatments include surgery, hormonal therapies, and IVF. These options aim to reduce symptoms and improve fertility.
It’s important to focus on treating the condition, not trying to make yourself infertile. Understanding and managing factors that affect fertility is key.
The uterus is key to fertility. Problems with its structure can stop conception. These issues can make it hard for a fertilized egg to implant or raise the risk of miscarriage.
Uterine issues affecting infertility in women include:
These issues can be present at birth or develop later due to surgery, infection, or trauma.
Fibroids are non-cancerous growths in or around the uterus. They can make it hard to get pregnant by:
Research shows women with fibroids have a lower chance of getting pregnant than those without.
Other issues like polyps and adhesions can also impact fertility. Polyps grow on the uterine lining, while adhesions are scar tissues inside the uterus.
Structural Abnormality | Effect on Fertility |
Fibroids | Distorts uterine cavity, interferes with implantation |
Polyps | Interferes with implantation, affects endometrial function |
Adhesions | Can cause Asherman’s syndrome, leading to menstrual abnormalities and infertility |
It’s important to understand and address these uterine issues for women facing infertility. Identifying and treating these problems can help improve the chances of getting pregnant.
Fertility declines with age due to:
Early intervention is essential for age-related infertility in women.
Fertility starts to drop in the early 30s and falls faster after 35. This is because the ovaries age, reducing egg number and quality. This makes it harder to get pregnant and raises the risk of miscarriage and genetic problems.
Fertility specialists stress that egg quality is key for getting pregnant. Older eggs are more likely to have genetic issues. This makes it harder to conceive and increases pregnancy risks.
Diminished ovarian reserve means the ovaries don’t work well, leading to fewer and lower quality eggs. This can be due to age or other factors like genetics, medical treatments, or lifestyle.
Women with this condition may find it hard to get pregnant because of fewer eggs. IVF can help, but success depends on age and egg quality.
Reproductive tract infections, like PID, can harm fertility. These infections can damage reproductive organs, leading to infertility or ectopic pregnancy risks.
It’s important to treat these infections quickly to avoid lasting damage. Women should watch for symptoms like pelvic pain or unusual discharge and see a doctor.
In summary, age and infections are big factors in female infertility. Knowing about these and getting medical help early can help women make smart choices about their reproductive health.
Understanding what causes infertility in women is key for early action and effective treatment. Many factors can lead to infertility, such as ovulation problems, PCOS, and fallopian tube damage. Other causes include endometriosis, uterine issues, and age-related egg quality decline.
Getting a diagnosis and treatment early can greatly improve a woman’s chances of getting pregnant. If you’re having trouble getting pregnant, it’s important to see a doctor. They can help find the best treatment for you, which might include medication, surgery, or IVF.
By tackling the main causes of infertility and getting the right treatment, many women can overcome their fertility issues. Early action is essential for success. We urge those facing infertility to talk to healthcare experts to find their best options.
Common causes include ovulatory disorders and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Fallopian tube damage, endometriosis, and uterine abnormalities also play a role. Age is another factor.
Yes, they can. Medications like clomiphene citrate or gonadotropins help. Lifestyle changes, such as losing weight and reducing stress, are also beneficial.
PCOS disrupts ovulation, causing irregular cycles and reduced fertility. It also leads to insulin resistance, affecting fertility further.
Symptoms include pelvic pain and heavy or irregular bleeding. Infertility and bowel or urinary issues are also common.
Yes, some can. Surgery can fix issues like fibroids or a septate uterus. This improves fertility and reduces miscarriage risk.
Age significantly impacts fertility. Egg quality and quantity decline with age. Women over 35 face reduced fertility and higher chromosomal risk.
Yes, they can. Infections like PID damage the fallopian tubes and other organs, leading to infertility.
Primary infertility is the inability to conceive after a year of trying. Secondary infertility is when a woman can’t conceive again after a previous pregnancy.
Yes, they can. Smoking, excessive alcohol, and obesity affect fertility in both men and women.
A healthy weight, balanced diet, and regular exercise help. Managing stress and avoiding smoking and alcohol also reduce risk.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!