The human nervous system is a complex network. It lets us see, understand, and react to our surroundings. It has billions of neurons that talk to each other through electrical and chemical signals neurological system.
Understanding the nervous system is key for both patients and doctors. At Liv Hospital, we know how important it is to show the nervous system clearly. This helps patients understand their health better.
A simple diagram of the nervous system makes it easier to grasp how it works. The nervous system has two main parts: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).

Understanding the neurological system is key to knowing how our body works. It controls everything from simple movements to complex thoughts. This system is made up of nerve cells and neurons, working together to manage our body’s functions.
We’ll look at the basics of this system, focusing on its structure and role. The human brain has about 100 billion neurons. Each one is important for processing and sending information.
Neurons are the basic units of the nervous system. They have a cell body, axons, and dendrites. These parts help send signals all over the body. Neurons are the building blocks of the neurological system, designed for communication.
The cell body, or soma, is the neuron’s metabolic center. It has the nucleus. Axons carry signals away from the cell body. Dendrites receive signals from other neurons. This setup lets neurons talk to each other, making the nervous system work.
Signal transmission is vital for the neurological system. It lets our body do various things. Neurons send signals through electrical and chemical means. This is fast and accurate.
When a neuron gets a signal, it sends an electrical impulse down its axon. This impulse can reach other neurons, muscles, or glands. It does so through synapses, small gaps between neurons and their targets. Neurotransmitters, chemical messengers, help cross these gaps. This complex process is behind all our body’s functions, from moving on purpose to reacting without thinking.
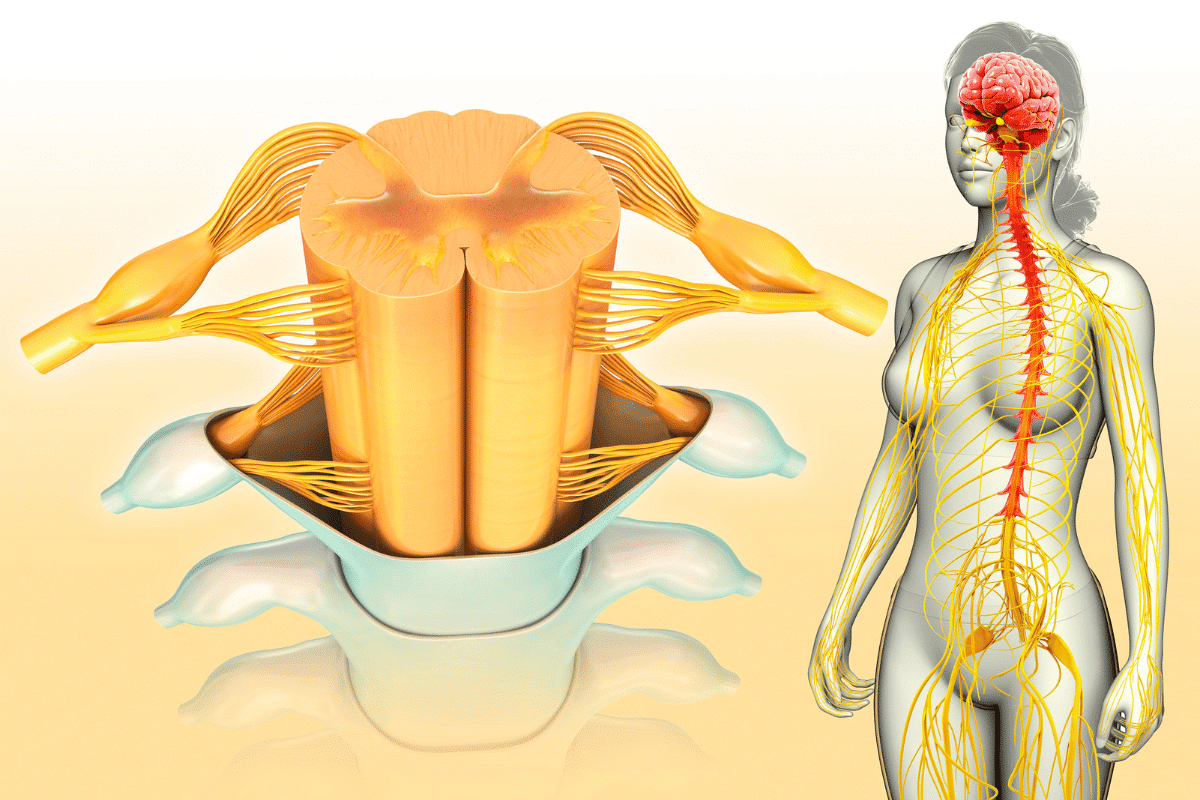
Visual representations make understanding the nervous system easier. They break down complex neural ideas into simple images. These images are key tools for learning about how the nervous system works.
Visual aids in neuroscience make it clear how sensory information is processed. Diagrams help us see the complex interactions in the nervous system. They let us see how neurons and networks work together.
Neural structures and functions can be hard to grasp. But, visual aids like brain diagrams show how different parts connect and function. This helps us understand how our bodies work.
Visual representations are very helpful for students and healthcare professionals. They make learning about the nervous system easier. By seeing neural pathways and structures, students can remember information better.
Healthcare professionals find visual aids essential for diagnosing and treating neurological disorders. They help understand complex neural structures and functions. This is key for good patient care.
In clinics, visual representations help diagnose and treat many neurological conditions. They help doctors find the cause of symptoms and plan treatments. Visual aids also help explain complex diagnoses to patients.
Visual representations in neuroscience are used in research too. They help show complex neural mechanisms and share research findings with others.
The CNS, which includes the brain and spinal cord, is vital for integrating and processing information throughout the body. As we explore CNS diagrams, we will dive into the brain’s structure and the spinal cord’s organization.
The brain is a complex organ, divided into several distinct regions, each with specific functions. The cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem are the three main parts of the brain. The cerebrum is further divided into hemispheres and lobes, which are responsible for various cognitive and motor functions.
Key regions of the brain include:
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tube-like structure made of nerve tissue, extending from the base of the brain down to the lower back. It plays a critical role in the nervous system, facilitating the transmission of messages between the brain and the rest of the body.
The spinal cord is organized into different segments, corresponding to the vertebrae through which it passes. These segments give rise to nerve roots that branch out to various parts of the body.
When interpreting CNS diagrams, several key features should be identified. These include the different regions of the brain, the structure of the spinal cord, and the various nerve pathways.
Important features to look for:
Understanding these diagrams can provide valuable insights into the functioning of the CNS. It helps in the diagnosis and treatment of neurological disorders.
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is a complex network of nerves. It connects the central nervous system to the rest of the body. It controls various bodily functions by sending information between the central nervous system and other parts of the body.
The PNS includes cranial nerves and spinal nerves. These nerves are key to understanding the PNS.
Cranial nerves start from the brain and control functions like sight and smell. There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves, each with its own role. Spinal nerves, which come from the spinal cord, send signals to the rest of the body.
Mapping these nerves helps us understand their paths and functions. Detailed diagrams make it easier to see how they work together in the PNS.
Nerve plexuses are complex networks from the spinal cord. They control many bodily functions. The main plexuses are the cervical plexus, brachial plexus, lumbar plexus, and sacral plexus. Each plexus has nerves that reach different parts of the body.
Knowing the paths of these nerves is key for diagnosing and treating nerve issues. Diagrams of nerve plexuses and pathways offer insights into the PNS’s complex network.
Understanding PNS diagrams is important. They show how nerves branch and where they go. This helps doctors spot nerve damage or disorders.
To interpret PNS diagrams well, you need to know about different nerves and their roles. You also need to understand how they work with other parts of the nervous system.
Neurons are the basic units of the nervous system. They have several parts that work together to send signals. Knowing how neurons are structured helps us understand our brain’s network.
A neuron has three main parts: the cell body, axons, and dendrites. The cell body has the nucleus and is the neuron’s metabolic center. Axons are long and carry signals away from the cell body. Dendrites receive signals from other neurons.
Neurons can send and receive signals through electrical and chemical means. The axon terminals release neurotransmitters into the synapse. This gap between neurons allows signals to pass through.
Synaptic connections are key for neural communication. When a signal reaches the axon terminals, neurotransmitters are released. These chemicals bind to receptors on other neurons’ dendrites, allowing the signal to spread.
There are many types of neurons, each with its own structure and function. Sensory neurons send information from sensory receptors to the central nervous system. Motor neurons carry signals from the central nervous system to muscles or glands. Interneurons process and integrate information within the neural network.
Visual representations of different neuron types help us understand their roles. Diagrams of sensory, motor, and interneurons provide insights into their functions and interactions.
The autonomic nervous system is a complex network that controls our body’s automatic actions. It has two main parts: the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Knowing about these diagrams helps us understand how our body manages its automatic functions.
The sympathetic nervous system gets our body ready to face stress or danger. It increases heart rate, opens airways, and gets energy ready. Diagrams show how this system works and its connections.
The parasympathetic nervous system helps our body relax and digest food. It slows down heart rate, helps digestion, and saves energy. Its diagrams show how it keeps our body balanced.
Comparing diagrams of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems is very helpful. They show how these systems work together to keep our body in balance. Here are some key differences:
|
Characteristics |
Sympathetic Nervous System |
Parasympathetic Nervous System |
|---|---|---|
|
Primary Function |
Fight-or-Flight Response |
Rest-and-Digest Functions |
|
Heart Rate |
Increases |
Decreases |
|
Digestion |
Slows Down |
Stimulates |
By looking at these diagrams and comparisons, we learn more about the autonomic nervous system. We see how it controls our body’s functions.
The somatic nervous system is key for voluntary movements and sensory input. It sends info between the CNS and skeletal muscles. This lets us do many actions, from simple to complex.
Voluntary actions start in the brain’s motor cortex. Signals go through the spinal cord to muscles. The somatic nervous system diagrams show these paths. They highlight how motor neurons send signals to muscles for precise movements.
These diagrams focus on the corticospinal tract, a key for motor control. They help healthcare pros understand voluntary movement and find problems.
The somatic nervous system also handles sensory input. Sensory receptors pick up touch, pressure, and temperature. They send this info to the CNS through sensory neurons.
Diagrams show how sensory info is processed. They include the role of dorsal root ganglia and the spinal cord. Knowing these paths is key for diagnosing sensory disorders.
Reflex arcs are a big part of the somatic nervous system. They involve sensory, motor, and sometimes interneurons. Together, they create quick responses to stimuli.
Diagrams of reflex arcs explain how these circuits work. They show how sensory input leads to a motor response without thinking. This knowledge is vital for checking neurological function.
Looking at somatic nervous system diagrams, like those of reflex arcs, helps healthcare pros. They can see how the nervous system works and find problems.
Neurological system diagrams are key in neuroscience education. Yet, they can be overwhelming due to the vast amount of information they show. To understand these diagrams, we need to tackle the complexity of neurological structures and the terms used to describe them.
One big challenge is dealing with complex terms. Words like “dendrite,” “axon,” and “synapse” are essential in neuroscience but can be tough for beginners. Learning the meanings of these terms can make a big difference. For example, knowing “dendrite” means “tree” in Greek helps remember its role in neurons.
The brain’s regions and the nervous system’s pathways are also complex. Visual aids and diagrams are very helpful because they show these structures clearly.
Another challenge is turning two-dimensional diagrams into three-dimensional thinking. Neurological structures are three-dimensional, and seeing them in this way is key to understanding their functions. Using 3D models or interactive diagrams can help a lot.
It’s also important to know the different planes of section (sagittal, coronal, transverse). Practicing to mentally put these sections together into a 3D model improves understanding and memory.
To tackle the challenges of neurological system diagrams, several strategies can help. First, start with the basics and then add complexity gradually. Begin with simple diagrams and move to more complex ones as you get better.
By using these strategies and keeping at it, learners can gain a strong grasp of neurological system diagrams. Being patient and persistent is essential, as mastering these diagrams takes time.
Diagrams of the nervous system are key in learning about neural structure and function. They help us understand the complex nervous system better. By using the five types of diagrams mentioned, we can dive deeper into the neurological system.
Visual aids are vital for grasping complex neurological ideas. They make learning easier. By using visual learning, we can understand neural structure better. This leads to better results in education and healthcare.
Learning neural structure through visuals helps both healthcare workers and students. It makes it easier to understand the nervous system’s details. This skill helps us diagnose and treat neurological issues better. It leads to better care for our patients.
The nervous system is a complex network that helps us understand and react to our surroundings. It has billions of neurons that send and receive signals. These signals help us move, feel sensations, and control our body’s functions.
There are five main types of nervous system diagrams. These include the Central Nervous System (CNS), Peripheral Nervous System (PNS), Neuron Structure, Autonomic Nervous System (ANS), and Somatic Nervous System diagrams. Each type offers a unique view of how the nervous system works.
Visual representations, like diagrams, are key in neuroscience. They make complex ideas simple and help us see how the brain works. They are very useful in teaching and treating neurological problems.
Neurons talk to each other through electrical and chemical signals. They have special parts like cell bodies, axons, and dendrites. These parts help them send and get information. Connections between neurons let them share signals, enabling complex brain functions.
The sympathetic nervous system gets us ready to act when we’re stressed or in danger. The parasympathetic nervous system helps us relax and recover. Both systems work together to keep our body balanced and functioning right.
To get better at understanding nervous system diagrams, start with the basics. Learn important terms and practice reading diagrams. Thinking in three dimensions and using visual tools can also help. Getting help from teachers or doctors can be very useful too.
The somatic nervous system controls our voluntary movements and handles sensory input. It lets the brain and muscles talk to each other and receive information from the world.
A basic diagram of the nervous system shows the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. It might also highlight different brain areas and the spinal cord’s layout. This gives a simple overview of the nervous system’s structure.
The nervous system is divided into several types. These include the central nervous system (CNS), peripheral nervous system (PNS), autonomic nervous system (ANS), and somatic nervous system. Each type has its own role and works together to keep the nervous system functioning well.
Nerve system diagrams are very helpful in medical settings. They help doctors diagnose and treat neurological issues. By showing how the nervous system works, they help doctors understand and treat complex conditions effectively.
World Health Organization. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241563367
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!