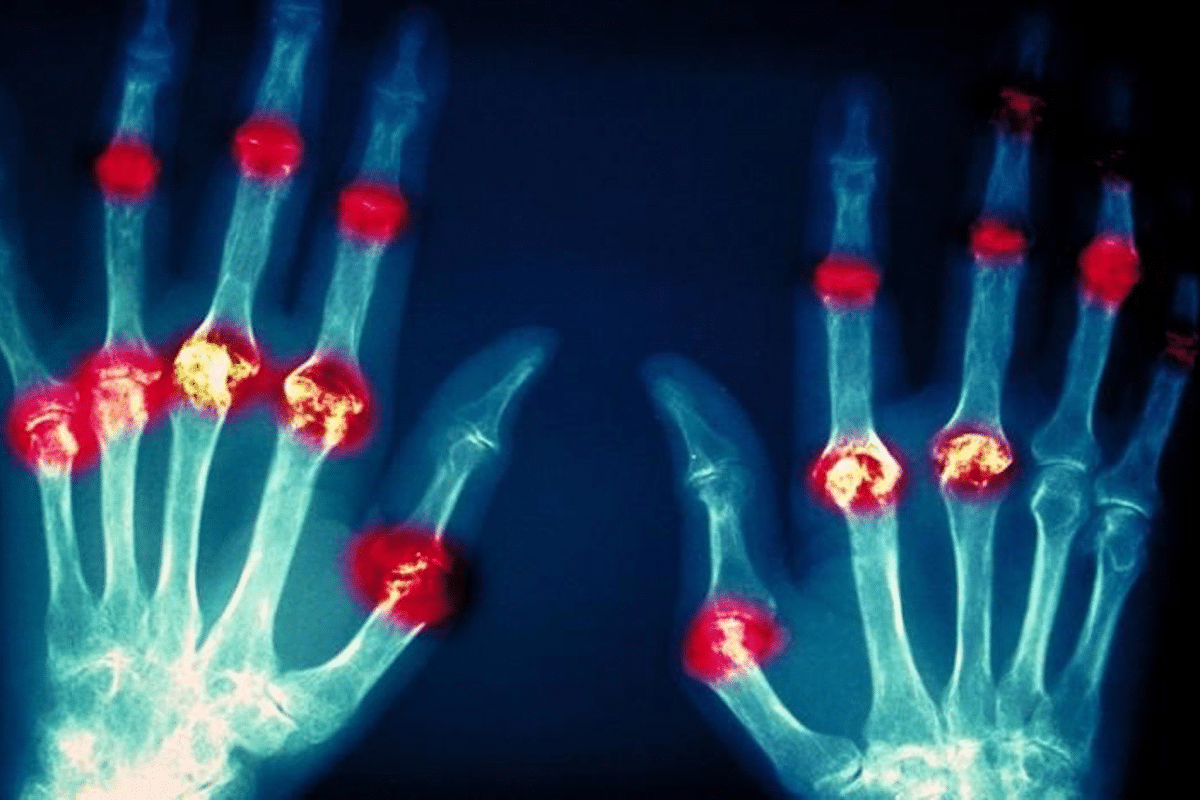
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease that attacks joints and can severely impact your life. If not treated, it can lead to serious disability. But, early treatment with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologic therapies, and JAK inhibitors can manage the disease and prevent damage. Explaining what methods for treating rheumatoid arthritis focus on (reducing inflammation, preventing joint damage, pain management).
At Liv Hospital, we combine international medical knowledge with care focused on the patient. We use treatment strategies that not only ease symptoms but also help patients stay in remission. Our goal is to control inflammation and keep joints working well, leading to better health outcomes for our patients.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic disease that mainly affects the joints. It causes inflammation and can lead to serious damage if not treated. Knowing the early signs is key to catching it early.
RA’s pathophysiology involves immune cells and cytokines causing joint inflammation. This leads to immune cells in the synovial tissue, causing it to grow and produce inflammatory cytokines. This results in progressive joint damage and can lead to disability.
The disease starts with a trigger that sets off an immune response. This leads to the production of autoantibodies like rheumatoid factor. These autoantibodies form immune complexes in the joints, making inflammation worse.
It’s important to tell RA apart from other arthritis types. RA affects joints symmetrically, often in the hands and feet. It’s an autoimmune disease that can affect more than just the joints.
RA is also marked by morning stiffness lasting over an hour and systemic symptoms like fatigue and fever. Tests like rheumatoid factor and anti-CCP antibodies help confirm the diagnosis.
The early signs of RA include rheumatoid arthritis symptoms like joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. Symptoms may start in a few joints but can spread if not treated. Pain lasting three months or more is a sign it won’t go away on its own.
Spotting these signs early is critical for timely treatment. This can change the disease’s course and prevent serious complications with rheumatoid arthritis. Early treatment helps manage symptoms, reduces damage, and improves life quality for those with RA.

Early diagnosis and treatment are key to managing Rheumatoid Arthritis well. This chronic autoimmune disease can cause serious joint damage and disability if not treated early.
Rheumatoid Arthritis is a complex condition. Its diagnosis needs a thorough approach. This includes clinical evaluation, lab tests, and imaging studies.
The diagnosis of RA is based on several criteria. These include clinical signs, lab findings, and imaging results. The American College of Rheumatology (ACR) and the European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) have set these criteria.
|
Diagnostic Criteria |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Joint Involvement |
Number and type of joints involved |
|
Serological Markers |
Rheumatoid Factor (RF) and Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibody (Anti-CCP) |
|
Acute-Phase Reactants |
C-Reactive Protein (CRP) and Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) |
There’s a critical time to start treatment for RA, usually within the first few months. Early treatment can greatly change the disease’s course. It can reduce joint damage and improve long-term results.
Early treatment with Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs), like biologic therapies and JAK inhibitors, is very effective. It controls inflammation and stops disease progression.
Setting realistic treatment goals is vital for managing RA. Goals include achieving clinical remission or low disease activity. They also include improving functional ability and quality of life.
Understanding the importance of early diagnosis and treatment helps us work towards these goals. This improves outcomes for patients with RA.
Rheumatoid Arthritis treatment now focuses on changing the disease. This uses DMARDs, biologics, and JAK inhibitors. The goal is to control inflammation, prevent joint damage, and improve life quality for patients.
DMARDs are key in treating Rheumatoid Arthritis. They change the disease process, reducing inflammation and slowing disease progression. Conventional DMARDs, like methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, sulfasalazine, and leflunomide, are often the first choice.
Biologic therapies are a big step forward in RA treatment. These drugs target specific parts of the immune system involved in inflammation. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) inhibitors, like etanercept and adalimumab, are well-established treatments.
Other biologic agents include:
JAK inhibitors are a newer class of DMARDs that show great promise in treating RA. They work by blocking the Janus kinase pathway, involved in signaling of multiple cytokines. Examples include tofacitinib and baricitinib.
The benefits of JAK inhibitors include:
By understanding and using these disease-modifying therapies, healthcare providers can offer personalized treatment plans. This improves outcomes for patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Managing rheumatoid arthritis (RA) symptoms is key to better health and happiness. RA causes pain, swelling, and inflammation in the joints. This can make everyday tasks hard and affect how we feel.
There are many ways to handle RA symptoms and pain. We’ll look at both medicine and non-medicine methods.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) help with pain and swelling in RA. They block enzymes that cause inflammation. This makes swelling and irritation go down.
NSAIDs have many benefits:
But, NSAIDs can cause stomach problems like ulcers and bleeding. So, it’s important to use them carefully and with a doctor’s help.
Corticosteroids are strong anti-inflammatory medicines for RA. They can be taken by mouth or injected into joints.
The good things about corticosteroids are:
But, corticosteroids have downsides too:
There are also non-medicine ways to manage RA symptoms. These include:
By adding these methods to their treatment, RA patients can manage their symptoms better. This improves their life quality a lot.
The market for RA treatments is growing fast. This is because more people have rheumatoid arthritis worldwide. They are looking for better ways to treat it.
The RA therapies market was worth $28.5 billion in 2024. It’s expected to hit $41.1 billion by 2030. This shows a big increase in the market size.
New drugs and biologic therapies are making a big difference. They have changed how RA patients are treated.
Several things are pushing innovation in RA treatments. Advances in biotechnology have led to better, safer treatments. Also, understanding RA better has opened up new ways to treat it.
Even with the market growing, getting access to treatments is hard. High costs and different insurance rules can block patients from new therapies.
We need to think about the money side of treating RA. Insurance and government policies play big roles. Making sure everyone can get the treatments they need is key to better health outcomes.
The treatment for rheumatoid arthritis is changing. New therapies offer hope for patients and doctors. Researchers are finding new ways to fight the disease.
Filgotinib is a new JAK1 inhibitor. It has shown great promise in studies. It works by targeting JAK1, which could lower heart risks.
Studies show filgotinib can reduce disease activity and improve how patients feel. It also seems safer than some other treatments.
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes are a new treatment for rheumatoid arthritis. They have anti-inflammatory effects and help repair tissues. This makes them a good option for joint damage.
Research shows these exosomes can fight inflammation and help heal in animal studies. They might improve joint health and function in people too.
“The use of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes represents a novel approach to treating rheumatoid arthritis, with the promise of joint repair and inflammation reduction.” Medical Expert, Rheumatology Researcher
Artificial intelligence (AI) is helping create personalized treatments for rheumatoid arthritis. AI looks at big data to find patterns. This helps doctors tailor treatments for each patient.
AI can predict how patients will react to different treatments. This means doctors can choose the best treatment for each person. It could lead to better results and save money.
|
Therapeutic Approach |
Mechanism of Action |
Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Filgotinib |
JAK1 inhibition |
Reduced disease activity, improved safety profile |
|
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes |
Anti-inflammatory, tissue repair |
Joint repair, reduced inflammation |
|
AI-Powered Personalized Treatment |
Data analysis, pattern identification |
Improved treatment outcomes, reduced healthcare costs |
As research keeps moving forward, these new treatments will likely change rheumatoid arthritis care. They offer more effective and personalized options. This could greatly improve the lives of those with this chronic condition.
It’s important to know the complications of rheumatoid arthritis to manage the disease well. This chronic condition can cause serious problems if not treated right.
Rheumatoid arthritis can damage joints, leading to loss of function and disability. The inflammation in the joints can break down cartilage and erode bones.
Joint damage makes daily life hard. Starting treatment early can help prevent this.
People with rheumatoid arthritis face a higher risk of heart problems. The ongoing inflammation can lead to atherosclerosis.
High blood pressure, high cholesterol, and smoking are major risks. Managing these can lower heart disease risk in RA patients.
|
Cardiovascular Risk Factor |
Management Strategy |
|---|---|
|
Hypertension |
Regular blood pressure monitoring and antihypertensive medication |
|
Hyperlipidemia |
Lipid profile monitoring and statin therapy |
|
Smoking |
Smoking cessation programs and counseling |
Immunosuppressive treatments raise the risk of infections in RA patients. They need close watch and preventive steps.
Vaccination against flu and pneumococcus is advised for those on these treatments. Also, preventive actions may be needed to stop other infections.
Lifestyle changes are key in managing rheumatoid arthritis. They help improve patient outcomes. By adding healthy habits to daily life, people with RA can support their treatment plans and feel better overall.
Eating a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can help manage RA symptoms. Anti-inflammatory diets include foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and fiber.
It’s also important to avoid pro-inflammatory foods. These include processed meats, sugary drinks, and refined carbohydrates.
“Dietary interventions can significantly impact the management of rheumatoid arthritis, providing a complementary approach to traditional treatments.” — Expert in Rheumatology
|
Food Group |
Examples |
Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Fatty Fish |
Salmon, Sardines |
High in Omega-3 fatty acids, reduces inflammation |
|
Fruits |
Berries, Oranges |
Rich in Antioxidants, helps reduce oxidative stress |
|
Leafy Greens |
Spinach, Kale |
Packed with Vitamins and Minerals, supports overall health |
Regular exercise is vital for maintaining joint mobility and strength in individuals with RA. Gentle exercises such as yoga, swimming, and cycling are recommended.
Physical therapy can also play a key role in managing RA symptoms. A physical therapist can help develop a personalized exercise program to improve joint function and reduce pain.
Stress can worsen RA symptoms, making stress management techniques essential. Practices such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness can help reduce stress levels.
Mental health support is also vital. Connecting with support groups, either online or in-person, can provide emotional support and help individuals cope with the challenges of living with RA.
By adopting these lifestyle modifications, individuals with rheumatoid arthritis can better manage their condition and improve their quality of life.
Managing rheumatoid arthritis (RA) well is key to a better life for those with it. Early diagnosis and treatment are vital to avoid long-term damage. This helps prevent serious complications.
Knowing about RA and its treatments is important. This includes medicines like DMARDs and biologic therapies. Working with doctors, patients can create a treatment plan that fits them. Eating right and exercising regularly also help manage the disease.
When symptoms are under control, people can live more active lives. We stress the need for a complete care plan for RA. This plan should include medical treatment and healthy lifestyle choices for overall well-being.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease that causes inflammation in the joints. This leads to pain, stiffness, and can cause long-term damage. It can also affect other parts of the body, like the skin, eyes, lungs, heart, and blood vessels.
Early signs include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and tenderness, often in the hands and feet. Other symptoms are fatigue, fever, and loss of appetite.
Doctors diagnose rheumatoid arthritis by looking at symptoms, medical history, and physical exams. They also use blood tests and imaging tests like X-rays and ultrasound.
Treatments include disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologic therapies, and JAK inhibitors. These help control inflammation, slow disease progression, and preserve joint function.
Complications include joint destruction, cardiovascular issues, infection susceptibility, and osteoporosis.
Eating well, exercising, managing stress, and getting enough sleep can help. These lifestyle changes support treatment and improve health outcomes.
New treatments include filgotinib, mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes, and AI-powered personalized strategies. These are being researched to improve treatment outcomes.
Patients can manage symptoms with medication like NSAIDs and corticosteroids. Non-pharmacological approaches include physical therapy, exercise, and stress management.
DMARDs slow disease progression, control inflammation, and preserve joint function. They are key in treating rheumatoid arthritis.
Biologic therapies target specific immune pathways. This reduces inflammation and slows disease progression.
JAK inhibitors block certain enzymes involved in inflammation. This reduces inflammation and slows disease progression.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Early Treatment to Prevent Complications. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9273041/
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!