
At Liv Hospital, we aim to give top-notch healthcare. We offer full support and guidance to international patients. Brachytherapy is a key cancer treatment. It uses radioactive materials placed directly into or near tumors. This method targets cancer cells while protecting healthy cells nearby.
Finding the right cancer treatment can be tough. That’s why we’re here to help. Brachytherapy, or sealed radiation therapy implant, is a precise and effective internal radiation therapy. It’s trusted by people all over the world.
Key Takeaways
- Brachytherapy is a type of internal radiation therapy that targets cancer cells directly.
- It involves placing radioactive materials into or near tumors.
- This treatment allows for a high dose of radiation with minimal impact on healthy cells.
- Brachytherapy is a trusted treatment option worldwide.
- Liv Hospital provides full care and guidance throughout the treatment process.
The Precision of Internal Radiation: How Brachytherapy Targets Cancer Cells
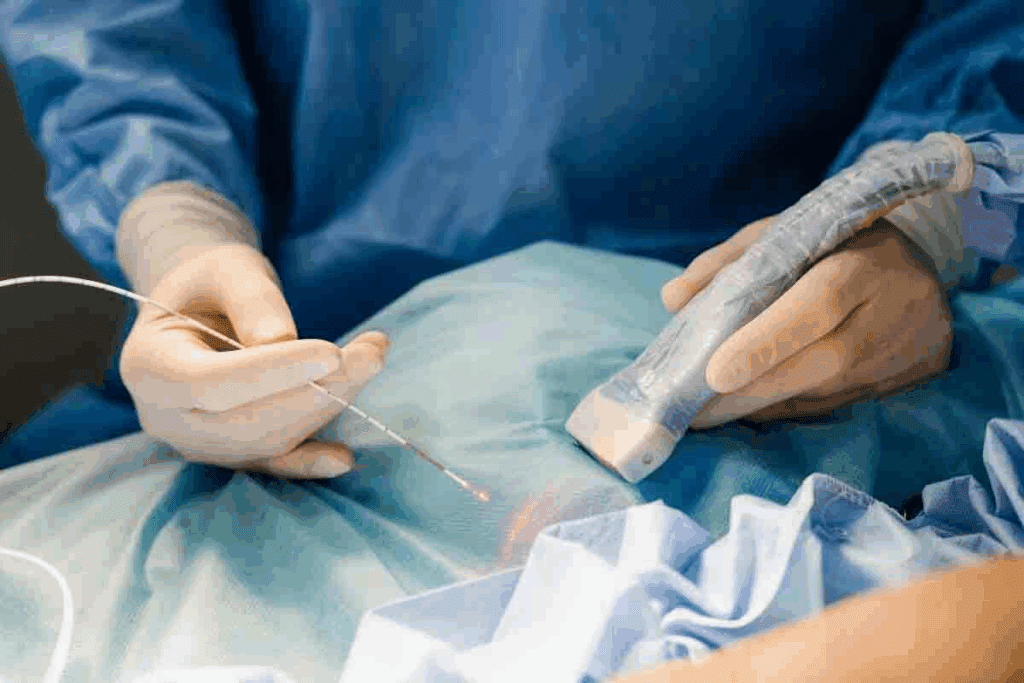
Brachytherapy uses radioactive materials placed directly into or near tumors. This method delivers a high dose of radiation right to the cancer cells. It makes the treatment more effective.
Radioactive Sources Placed Directly Into or Near Tumors
Brachytherapy uses small, encapsulated sources of radiation. These radioactive sources are implanted into the body. They are placed directly into or near the tumor site for precise radiation delivery.
- Radioactive seeds or pellets are used for permanent implants.
- Temporary implants use removable applicators or catheters.
- The choice between temporary and permanent implants depends on the type of cancer, its location, and the patient’s overall health.
Minimizing Exposure to Healthy Surrounding Tissues
Brachytherapy’s big advantage is it minimizes radiation to healthy tissues. It delivers radiation directly to cancer cells. This reduces damage to nearby healthy tissues and lowers side effects.
Advanced imaging technologies help place radioactive sources accurately. This ensures radiation is delivered exactly where needed. It maximizes treatment effectiveness while protecting patients from unnecessary radiation.
Types of Radioactive Materials Used in Brachytherapy
Brachytherapy uses different radioactive materials to fight cancer. The right material is key for a good treatment. It affects how much radiation the tumor gets and how it’s delivered.
Common Isotopes: Iodine-125, Cesium-137, and Iridium-192
Isotopes like iodine-125, cesium-137, and iridium-192 are often used. Each is chosen for its special qualities, fitting different cancer treatments.
Iodine-125 is great for prostate cancer. It has low energy gamma radiation. This helps target the tumor well without harming nearby healthy tissues.
Cesium-137 is used for gynecological cancers. It has a longer half-life and higher energy gamma radiation.
Iridium-192 is used in high-dose rate brachytherapy. It’s good for cancers like breast, prostate, and head and neck. It has high energy and a short half-life.
How Radioactive Seeds, Pellets, and Wires Work
Radioactive materials come in seeds, pellets, and wires. They’re placed directly in or near the tumor. This allows for targeted radiation delivery.
Seeds are tiny and contain a small amount of radioactive material. They’re placed carefully in the tumor using special techniques.
Half-Life Considerations in Treatment Planning
The half-life of a radioactive isotope is very important. It shows how long the isotope stays radioactive and how fast it decays. For example, iodine-125 has a half-life of about 59.4 days. This means it can deliver radiation for a longer time.
Knowing the half-life helps plan the treatment. It’s used to figure out the total radiation dose and how long the treatment will last. It also helps with safety measures for patients, caregivers, and family.
Temporary vs. Permanent Radiation Implants: Delivery Methods Explained
Choosing between temporary and permanent implants in brachytherapy depends on many things. These include the cancer type, its location, and the patient’s health. We’ll look at the different ways brachytherapy is delivered, focusing on temporary and permanent implants.
Removable Applicators and Catheters for Temporary Treatments
Temporary brachytherapy uses removable devices to target tumors. These devices are put in during a small surgery and taken out once the radiation dose is given.
Benefits of temporary implants include:
- Flexibility in treatment planning
- Ability to deliver high doses of radiation
- Reduced risk of radiation exposure to others
Permanent Seed Implantation for Long-Term Radiation Delivery
Permanent brachytherapy involves placing small radioactive seeds or pellets near the tumor. These seeds give off radiation over time, providing a steady dose to the area.
Key aspects of permanent seed implantation include:
- Permanent placement of radioactive material
- Gradual delivery of radiation over time
- Minimally invasive procedure
Here’s a comparison of temporary and permanent brachytherapy implants:
| Characteristics | Temporary Implants | Permanent Implants |
| Duration | Short-term (days to weeks) | Permanent |
| Device | Removable applicators/catheters | Radioactive seeds/pellets |
| Radiation Delivery | High dose rate, short duration | Low dose rate, continuous |
In conclusion, the choice between temporary and permanent implants in brachytherapy depends on many factors. These include the cancer type, location, and the patient’s health. Knowing the differences between these methods is key for effective treatment planning.
High-Dose Rate vs. Low-Dose Rate Brachytherapy Techniques
Brachytherapy is a type of internal radiation therapy. It uses two main techniques: high-dose rate (HDR) and low-dose rate (LDR) brachytherapy. These methods have different uses, benefits, and effects on patients.
HDR Brachytherapy: Powerful, Brief Radiation Sessions
High-dose rate brachytherapy gives a high dose of radiation in a short time. It’s often used for tumors that are easy to reach and need a strong dose to shrink them.
Key benefits of HDR brachytherapy include:
- Short treatment duration, usually a few minutes to hours
- High dose delivery directly to the tumor site
- Minimized exposure to surrounding healthy tissues
Doctors say HDR brachytherapy is precise and effective. It has fewer side effects.
LDR Brachytherapy: Continuous Low-Level Radiation Exposure
Low-dose rate brachytherapy gives radiation at a lower dose for a longer time. It’s often used for prostate cancer.
The advantages of LDR brachytherapy include:
- Prolonged exposure to radiation, which can be more effective for certain tumor types
- Potential for better tumor control with lower dose rates
- Often results in fewer side effects due to the lower dose rate
“LDR brachytherapy has become a standard treatment option for prostate cancer, with excellent long-term outcomes and quality of life for patients.”
Clinical Considerations for Treatment Selection
Choosing between HDR and LDR brachytherapy depends on several factors. These include the cancer type, tumor size and location, and the patient’s health. We carefully consider these factors to choose the best brachytherapy technique for each patient.
Factors influencing treatment selection include:
| Factor | HDR Brachytherapy | LDR Brachytherapy |
| Tumor Type | Suitable for various cancers | Often used for prostate cancer |
| Treatment Duration | Short, fractionated treatment | Continuous treatment over several days |
| Dose Rate | High dose rate | Low dose rate |
Understanding HDR and LDR brachytherapy helps us tailor treatments. This way, we can improve outcomes and reduce side effects for each patient.
Cancer Types Most Effectively Treated With Internal Radiation
Brachytherapy is a key treatment for many cancers. It uses radioactive material placed close to the tumor. This method targets the cancer precisely.
Prostate Cancer: A Primary Application for Brachytherapy
Prostate cancer often gets treated with brachytherapy treatment. Radioactive seeds are put in the prostate gland. This method helps kill the tumor while protecting healthy tissues.
Gynecological Cancers: Cervical, Uterine, and Vaginal Applications
Brachytherapy also helps with gynecological cancers like cervical, uterine, and vaginal cancers. A radiation implant is placed in the affected area. It’s great for tumors that can be reached through the vagina or cervix.
Breast Cancer Conservation Therapy with Brachytherapy
In breast cancer, brachytherapy is a conservative option. It delivers radiation directly to the tumor after a lumpectomy. This method, called accelerated partial breast irradiation (APBI), is faster than traditional treatments. It has shown good results for many patients.
Head, Neck, and Other Emerging Applications
Brachytherapy is also being looked at for head and neck cancers. Its precision makes it effective in complex areas. Research and new techniques are making brachytherapy even more promising for cancer treatment.
How Internal Radiation Therapy Differs From External Beam Radiation
Internal radiation therapy and external beam radiation are two different ways to treat cancer. They both aim to kill cancer cells but use different methods. They also have different treatment times and side effects.
Targeted vs. Broad Radiation Delivery Approaches
Internal radiation therapy, or brachytherapy, puts radioactive materials right into or near tumors. This targeted approach gives high doses of radiation to the tumor area. It helps protect healthy tissues nearby.
External beam radiation therapy (EBRT) sends radiation from outside the body to the tumor. It can be harder to target the tumor exactly. This might mean more radiation goes to healthy tissues nearby.
- Internal Radiation: Direct placement of radioactive material within or near the tumor.
- External Beam Radiation: Radiation delivered from outside the body.
Treatment Duration and Frequency Comparisons
Brachytherapy can be done in one session or over a few days. It depends on whether it’s temporary or permanent.
External beam radiation, though, is given in many sessions over weeks. This lets normal tissues recover between treatments.
- Brachytherapy: Can be single session or several days.
- External Beam Radiation: Multiple fractions over several weeks.
Differential Side Effect Profiles Between Methods
Side effects from internal and external radiation can be different. Brachytherapy usually has fewer side effects. It delivers radiation directly to the tumor, protecting more tissue.
External beam radiation can cause more side effects because it affects a wider area. But, new technologies in EBRT have made it more precise. This helps reduce side effects.
It’s important for patients to know these differences. By comparing internal and external radiation, we can see the benefits and challenges of each. This helps patients make better choices for their care.
Advanced Imaging Technologies Guiding Modern Brachytherapy
Advanced imaging technologies are key in modern brachytherapy. They help make internal radiation treatment more precise and effective. This leads to better results for patients.
3D Imaging for Precise Radioactive Source Placement
Three-dimensional imaging helps place radioactive sources accurately. This is vital in brachytherapy radiotherapy. It ensures the cancer cells get the most dose while protecting healthy tissues.
We use 3D imaging like ultrasound, CT, and MRI. These tools give us detailed tumor info. This helps us create a treatment plan that fits each patient perfectly.
Real-Time Monitoring During Implantation Procedures
Real-time monitoring is key during brachytherapy. We use advanced imaging to watch the radioactive source placement live. This lets us make quick changes if needed.
This live monitoring is essential for the treatment’s success. It also helps avoid complications by making sure the radiation dose is right.
Computer-Optimized Dosimetry Planning
Computer-optimized dosimetry planning is a big part of brachytherapy. We use special software to figure out the best radiation dose. This considers the tumor and tissues around it.
This planning makes sure patients get the best internal radiation treatment. It helps improve treatment results and reduce side effects.
Organ Preservation and Quality of Life Benefits of Brachytherapy
Brachytherapy is a key treatment for cancer that helps keep organs working well. It uses internal radiotherapy to target tumors precisely. This way, it protects healthy tissues from harm.
One big plus of brachytherapy is it saves organ function. It keeps the organ working naturally, which is vital in some cancers.
Functional Outcomes Compared to Surgery
Studies show brachytherapy can match or beat surgery in keeping organs working. For example, in prostate cancer, it often keeps urinary and sexual functions better than surgery.
| Treatment | Preservation of Organ Function | Complication Rate |
| Brachytherapy | High | Low |
| Surgery | Variable | Moderate to High |
Reduced Treatment-Related Complications
Brachytherapy has fewer side effects than surgery or external beam radiation. It targets radiation closely, reducing harm to nearby tissues and organs.
In cervical cancer treatment, brachytherapy cuts down on complications like fistulae and severe stomach issues. This improves patients’ quality of life.
Impact on Daily Activities During and After Treatment
Brachytherapy has little impact on daily life, unlike more invasive treatments. Most patients can keep up with their routines easily. The treatment is usually well-tolerated, with few side effects.
After treatment, patients often bounce back quickly. They can get back to their usual activities fast. The treatment’s side effects are often milder than other cancer treatments.
In summary, brachytherapy is a big win for organ preservation and quality of life. Its targeted approach and minimal damage to healthy tissues make it a top choice for many cancers.
Safety Precautions and Considerations for Brachytherapy Patients
Brachytherapy’s success relies on more than just the treatment. It also depends on the safety steps patients take. These steps are key to protecting the patient, their loved ones, and the community.
Radiation Protection Guidelines for Patients with Implants
Patients with implants must follow certain radiation protection rules. These rules help reduce radiation exposure to others, mainly in the first few days after the implant. It’s important for patients to keep a safe distance from others, like children and pregnant women, as advised by their healthcare provider.
For those with permanent implants, the radiation levels will decrease over time. It’s vital to stick to the radiation safety tips given by the hospital or treatment center. This might mean sleeping in a separate bed from your partner for a few days and avoiding close contact with pregnant women and young children.
Special Considerations for Caregivers and Family Members
Caregivers and family members are key in supporting patients with brachytherapy. They should know about the radiation safety steps to reduce their exposure. This might mean spending less time close to the patient, mainly in the first days after the implant.
We suggest that caregivers and family members get advice from the healthcare team on safe interaction with the patient. This includes knowing when it’s okay to be close and how to handle any bodily fluids or items that might have come into contact with the radioactive material.
Follow-Up Care and Monitoring Protocol
Follow-up care is a big part of brachytherapy treatment. Patients need to go to scheduled appointments to check the treatment’s success and watch for side effects. These visits are also a chance for patients to talk about any safety or well-being concerns.
At these appointments, healthcare providers might do tests like imaging studies to see how the treatment is going. We stress the importance of sticking to the follow-up care schedule for the best results.
In summary, safety measures are essential for brachytherapy treatment. By following radiation protection guidelines, caregivers and family members can help while keeping risks low. We aim to offer full care and guidance throughout the treatment.
Conclusion: The Evolving Role of Brachytherapy in Modern Cancer Care
We’ve looked into brachytherapy, a key treatment for many cancers. It sends radiation right to the tumor, helping save organs and improve life quality for patients.
Brachytherapy is now used more often for cancers like prostate, cervical, and breast. It uses different methods to fit each patient’s needs. For more details, check out studies on the National Center for Biotechnology Information website.
As cancer treatment gets better, brachytherapy’s role will grow. Knowing its benefits helps doctors give patients the best care. This leads to better results and a better life for those fighting cancer.
FAQ
What is brachytherapy?
Brachytherapy is a way to treat cancer. It uses radioactive materials placed close to tumors.
How does brachytherapy target cancer cells?
It targets cancer cells by giving them a high dose of radiation. This helps protect healthy tissues nearby.
What types of radioactive materials are used in brachytherapy?
Isotopes like iodine-125, cesium-137, and iridium-192 are used. They come in seeds, pellets, or wires.
What is the difference between temporary and permanent radiation implants?
Temporary implants can be removed. Permanent implants stay in the body.
What is the difference between high-dose rate (HDR) and low-dose rate (LDR) brachytherapy?
HDR gives a high dose in a short time. LDR gives a low dose over a long time.
What types of cancer can be treated with brachytherapy?
It treats many cancers. This includes prostate, gynecological, breast, and head and neck cancers.
How does brachytherapy compare to external beam radiation therapy?
Brachytherapy targets the tumor directly. External beam radiation comes from outside the body. They have different side effects.
What role do advanced imaging technologies play in brachytherapy?
Technologies like 3D imaging help place radioactive sources. They also improve treatment planning.
What are the benefits of brachytherapy in terms of organ preservation and quality of life?
It helps keep organs working and reduces complications. This improves life quality for patients.
What safety precautions should be taken by brachytherapy patients?
Patients should follow radiation protection rules. Caregivers and family members should also take precautions to avoid radiation.
What is internal radiotherapy treatment?
It’s also known as brachytherapy. It involves placing radioactive materials near tumors to treat cancer.
What are sealed radiation therapy implants?
These implants use radioactive materials in a sealed container. They are placed near tumors.
How does internal beam radiation therapy differ from external beam radiation therapy?
Internal beam, or brachytherapy, targets the tumor directly. External beam radiation comes from outside the body.
References:
- Kim S, Holder DL, Laymon CM, et al. SPECT Imaging of Epilepsy: An Overview and Comparison with F-18 FDG PET. International Journal of Molecular Imaging. 2011;2011:813028. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3139140/
- Ponisio MR, McConathy J. The Role of SPECT and PET in Epilepsy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021;216(1):186-195. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.20.23336
- Baradaran-Salimi K, Wielepp T, Wiest R, et al. Brain perfusion SPECT in the presurgical evaluation of drug-resistant epilepsy: Estimating the rate of high-confidence seizure onset zone candidates. Epilepsy Res. 2024;205:107432. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11393367/










