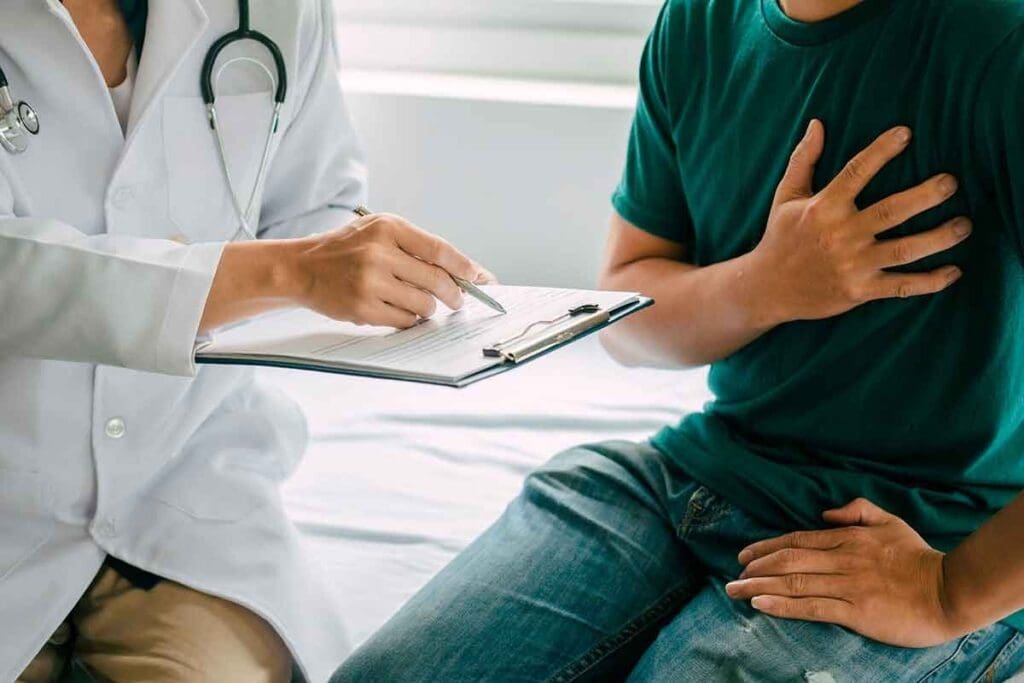
Ablation is a medical procedure that destroys abnormal tissue. This includes tumors or problematic heart cells. It uses energy sources like heat, cold, lasers, or chemicals. Learn is an ablation considered surgery and how heart ablation works to treat AFib safely.
Cardiac ablation, also known as catheter ablation, is a minimally invasive procedure. It creates scars to stop the electrical impulses that cause irregular heart rhythms.
At Liv Hospital, our teams use advanced medical technology. This provides effective solutions with less downtime and lower risk. Patients and their families need to understand ablation and its uses. This helps them make informed decisions about their care.
Key Takeaways
- Ablation is a medical procedure that destroys abnormal tissue using various energy sources.
- Cardiac ablation is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat irregular heart rhythms.
- Liv Hospital offers advanced medical technology for effective treatment with less downtime.
- Ablation is used to treat various medical conditions, including certain cancers and heart rhythm disorders.
- Understanding ablation is key for patients to make informed decisions about their care.
Understanding Ablation in Medical Context
In the medical field, ablation means destroying or removing diseased tissue. It’s used in many areas, like oncology and cardiology. Ablation is a key treatment for many conditions, being less invasive than surgery.
Etymology and Historical Development of Ablation
The word “ablation” comes from the Latin “ablatio,” meaning “to take away.” It started with removing tissue or body parts. Now, it includes many minimally invasive methods.
As Expert, a cardiologist, says, “Ablation has changed how we treat heart rhythm problems. It’s safer and more effective for patients.”
Basic Principles of Medical Ablation Procedures
Medical ablation uses energy like heat or cold to kill diseased tissue. It’s often used for atrial fibrillation (AFib), a heart rhythm issue. Tests like blood tests and echocardiograms help diagnose AFib.
“Ablation is a highly effective treatment for AFib, improving patients’ quality of life.
In oncology, ablation treats tumors in organs like the liver and lung. It works by destroying diseased tissue with energy, protecting healthy tissue nearby.
Types of Medical Ablation Procedures
Ablation is a minimally invasive technique used in many fields, like oncology and cardiology. It offers tailored treatments for different conditions. There are several types of ablation procedures, each using a different energy source or method.
Thermal Ablation Techniques
Thermal ablation uses heat to kill diseased tissue. Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a well-known method. It uses a probe to emit electrical currents that create heat to destroy tissue. Microwave ablation (MWA) works by using microwaves to heat up and treat tumors and lesions.
Cryoablation Methods
Cryoablation, or cryotherapy, freezes abnormal cells to death. It’s great for treating some heart conditions and cancers. Freezing the diseased tissue helps remove it and promotes healthy growth.
Chemical and Laser Ablation Approaches
Chemical ablation uses chemicals to destroy diseased tissue. It’s not as common, but used in certain cases. Laser ablation uses a laser to precisely target and destroy tissue. It’s often used for treating benign prostatic hyperplasia and some tumors.
| Ablation Technique | Method | Common Applications |
| Thermal Ablation | Uses heat to destroy tissue | Tumor treatment, cardiac arrhythmias |
| Cryoablation | Uses extreme cold to destroy tissue | Cardiac arrhythmias, certain cancers |
| Chemical Ablation | Uses chemicals to destroy tissue | Specific cases where other methods are not suitable |
| Laser Ablation | Uses a laser to destroy tissue | Tumor treatment, benign prostatic hyperplasia |
Each ablation technique has its own benefits. The choice depends on the patient’s condition and the type of diseased tissue. Knowing about these procedures helps in making better treatment choices.
Ablation Applications Beyond Cardiology
Ablation is used in many fields, like oncology, gynecology, and neurology. Ablation means removing or destroying damaged tissue. Knowing what the medical term ablation means is key for everyone involved. The correct spelling is “ablation,” as in how do you spell ablation.
It’s used for more than just heart diseases. In oncology, for example, it treats tumors in various organs.
Oncological Ablation for Tumor Treatment
Oncological ablation uses methods like radiofrequency ablation (RFA) or cryoablation to kill tumors. It’s great for treating tumors in the liver, kidney, and lung.
| Organ | Ablation Technique | Success Rate |
| Liver | RFA | 80% |
| Kidney | Cryoablation | 85% |
| Lung | RFA | 75% |
Gynecological Ablation Procedures
In gynecology, ablation helps with heavy menstrual bleeding. Endometrial ablation removes the uterus lining to lessen or stop bleeding.
Neurological Applications of Ablation
Neurological ablation treats conditions like chronic pain and some movement disorders. It uses methods like stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) or radiofrequency ablation.
These examples show ablation’s wide use and effectiveness in many medical areas.
Cardiac Ablation: Purpose and Applications
Cardiac ablation is a medical procedure to treat irregular heart rhythms. It targets and scars the heart tissue, causing arrhythmia. This technique is ketoor for treating many heart conditions.
Treating Arrhythmias with Ablation
Catheter ablation uses radiofrequency energy to destroy heart tissue , causing irregular heartbeats. It aims to restore a normal heart rhythm. This improves the patient’s quality of life.
To perform the procedure, a catheter is inserted through a leg vein and guided to the heart. The catheter then emits energy to scar the problematic tissue. This stops the abnormal electrical signals causing the arrhythmia.
Common Heart Conditions Requiring Ablation
Several heart conditions can be treated with cardiac ablation, including:
- Atrial fibrillation
- Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)
- Ventricular tachycardia
These conditions are characterized by irregular heartbeats that can be debilitating. Cardiac ablation offers a solution by directly addressing the source of the arrhythmia.
| Condition | Description | Ablation Success Rate |
| Atrial Fibrillation | Irregular, often rapid heart rhythm | 60-80% |
| Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) | Rapid heart rate originating above the ventricles | 90-95% |
| Ventricular Tachycardia | Rapid heart rate originating in the ventricles | 70-85% |
When Doctors Recommend Cardiac Ablation
Doctors recommend cardiac ablation when other treatments fail. This includes when medications don’t work or when the condition is severe. The decision is made after a thorough evaluation and diagnostic tests.
Understanding whether cardiac ablation is considered surgery is key. It’s not traditional surgery but involves catheters to reach the heart. This can lead to debate among medical professionals.
Is an Ablation Considered Surgery? Defining Medical Classifications
Whether ablation is seen as surgery depends on several factors and medical terms. Ablation, like cardiac ablation, treats heart issues by destroying bad electrical paths in the heart. It’s a procedure that doesn’t need big cuts or open surgery.
This makes people wonder if it’s surgery or not. It’s often called a ‘minimally invasive surgical approach.’ But it doesn’t have the big cuts of traditional surgery.
Traditional Surgery vs. Minimally Invasive Procedures
Traditional surgery means big cuts to reach the treatment area. But cardiac ablation uses small cuts or body openings. It uses catheters throughthe veinss in the groin to reach the heart.
How Medical Professionals Categorize Ablation
Doctors usually see ablation as a minimally invasive procedure, not traditional surgery. Aresource on cardiac ablation says it’s low-risk. But it can cause bleeding, infection, or heart damage.
Insurance and Billing Classifications for Ablation
Insurance and billing can see ablation differently. Some might call it surgery, while others don’t. It depends on the insurance and the procedure details.
| Classification Criteria | Traditional Surgery | Minimally Invasive Procedure |
| Incision Size | Large | Small |
| Recovery Time | Longer | Shorter |
| Risk of Complications | Higher | Lower |
In summary, cardiac ablation is mostly a minimally invasive procedure. Knowing this helps patients choose the right treatment.
The Heart Ablation Procedure: Step by Step
Knowing about the heart ablation procedure is key for those thinking about it. It’s used to treat heart rhythm problems. The process uses energy to destroy the bad electrical paths in the heart.
Pre-Procedure Preparation
Before the procedure, tests are done to see how the heart works. These tests include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): To record the heart’s electrical activity.
- Echocardiogram: An ultrasound test to visualize the heart’s structure.
- Blood tests: To check for underlying conditions that could affect the procedure.
Patients are told to stop eating and drinking before the procedure. They also need to tell their doctor about any medicines they take.
During the Ablation Process
A doctor uses a flexible tube called a catheter to reach the heart. This tube goes through a blood vessel in the groin. The doctor uses X-rays or echocardiography to guide it.
Once in the heart, the catheter sends energy to the problem area. This energy creates lesions that stop the bad electrical paths.
Immediate Post-Procedure Care
After the procedure, patients are watched for a few hours. They might feel some discomfort or soreness where the catheter was. This usually goes away on its own.
Instructions for aftercare include:
- Resting for the rest of the day.
- AAvoid heavylifting or strenuous activities for a few days.
- Following the doctor’s instructions about medicines.
Many wonder if a heart ablation is oconsideredsurgery. Knowing the steps shows it’s not as invasive as surgery.
Benefits of Heart Ablation Compared to Traditional Surgery
Heart ablation is now a top choice for treating heart issues. It’s a minimally invasive procedure that fixes heart problems by destroying bad electrical paths in the heart.
One big plus of heart ablation is how fast you can get back to normal. Unlike open-heart surgery, which takes a long time to recover from, heart ablation lets you go home quickly. This means less time in the hospital and a faster recovery.
Reduced Recovery Time and Hospital Stay
Because it’s less invasive, heart ablation leads to quicker healing. This means you can get back to your daily life sooner. It greatly improves your quality of life.
Lower Risk of Complications
Heart ablation is safer than traditional surgery. It has fewer risks of complications like infections or bleeding. This makes it a safer choice for many patients.
Long-Term Effectiveness Rates
Research shows heart ablation works well for some heart problems, like atrial fibrillation. It offers long-term benefits, helping many people feel better and live better lives.
In summary, heart ablation beats traditional surgery in many ways. It’s faster, safer, and more effective. As technology gets better, more people will have access to this life-changing treatment.
Potential Risks and Complications of Cardiac Ablation
It’s important to know the risks and complications of cardiac ablation before you decide to have it. This procedure is usually safe and works well for some heart problems. But, t’s not without any risks.
Common Side Effects
Some common side effects include pain or discomfort where the catheter was put in. You might also see swelling or bruising at the site. Fatigue is another common side effect. Minor bleeding or a hematoma at the site is possible t, oo.
Serious but Rare Complications
Even though they’re rare, serious complications can happen. These include cardiac tamponade, where fluid builds up around the heart. Pulmonary vein stenosis, where the pulmonary veins narrow, is another risk. Stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) can also occur. There’s a chance of damaging the heart’s electrical system, which might need a pacemaker.
Risk Factors That Increase Complication Rates
Some things can make complications more likely. Being older, having other health issues like diabetes or kidney disease, and the type of arrhythmia being treated are factors. The skill of the operator and the number of procedures done at the center also play a role.
| Risk Factor | Description | Impact on Complication Rate |
| Older Age | Increased age can lead to more comorbidities and decreased physiological reserve. | Higher risk of complications |
| Presence of Other Medical Conditions | Conditions like diabetes or kidney disease can complicate the procedure and recovery. | Increased risk of complications |
| Type of Arrhythmia | Certain arrhythmias are more challenging to treat and may have higher complication rates. | Varies by arrhythmia type |
| Operator Experience | More experienced operators tend to have lower complication rates. | Lower risk with experienced operators |
Talking to your healthcare provider about these risks is key. They can help you understand how they might affect you. The question of is cardiac ablation is considered surgery comes up a lot. Even though it’s minimally invasive, knowing the risks is very important.
The Heart Ablation Procedure: Step by Step
Learning about heart ablation can help patients get ready for it. Heart ablation, also known as catheter ablation, treats irregular heartbeats or arrhythmias. It uses catheters, needles, or probes guided by imaging to destroy the abnormal electrical pathways in the heart.
Pre-Procedure Preparation
Before heart ablation, patients have tests to understand their arrhythmia. These tests include electrocardiograms (ECGs), echocardiograms, and blood tests. Patients are told to stop certain medications that could affect the procedure. It’s also important to arrange for a ride home after the procedure.
During the Ablation Process
A doctor inserts a flexible tube called a catheter through a blood vessel in the groin. They guide it to the heart using imaging. The catheter delivers energy to the heart area, causing the arrhythmia. This energy can be heat or cold, aiming to destroy the tissue.
The procedure can take several hours. Patients are usually awake but sedated to reduce discomfort.
Immediate Post-Procedure Care
After the procedure, patients are watched for a few hours for any complications. They might feel soreness or discomfort at the catheter site, which usually goes away. Most patients can go home the same day, but some may need to stay overnight.
It’s important to follow the doctor’s instructions for post-procedure care. This includes any follow-up appointments and medication regimens.
| Aspect of Care | Details | Importance |
| Monitoring | Patients are monitored for complications post-procedure. | High |
| Medication | Following the doctor’s instructions on medication. | High |
| Follow-Up | Attending scheduled follow-up appointments. | High |
By understanding these steps, patients can better prepare for heart ablation. This makes the process less daunting.
Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions About Ablation Procedures
Knowing if ablation is surgery is key for those with heart issues. Cardiac ablation treats arrhythmias and is safe and effective.
Patients need to understand the good and bad of ablation. The debate on is ablation considered surgery or is a heartablation is considered surgery is ongoing. Yet, it’s seen as a minimally invasive method.
Patients should consider the benefits, like quick recovery and fewer complications. They should also think about the downsides. Talking to doctors is vital to choosing the right treatment.
FAQ
What does ‘ablation’ mean in medical terms?
Ablation is a medical procedure. It removes or destroys damaged or diseased tissue. This is often done using minimally invasive techniques.
Is cardiac ablation considered surgery?
Cardiac ablation is not traditional surgery. It’s a minimally invasive procedure. It uses catheters to destroy abnormal heart pathways.
What is the difference between ablation and traditional surgery?
Ablation is less invasive than traditional surgery. It uses smaller incisions and specialized instruments. These tools target specific body areas.
What are the benefits of cardiac ablation?
Cardiac ablation has many benefits. It reduces recovery time and lowers the risk of complications. It also improves symptoms for heart conditions like arrhythmias.
What are the risks and complications of cardiac ablation?
Cardiac ablation is generally safe. But it can cause bleeding, infection, or damage to the heart or tissues. Serious complications are rare but can happen.
How is cardiac ablation performed?
Cardiac ablation starts with inserting catheters through a leg vein. They are guided to the heart. There, they use energy to destroy abnormal pathways.
What is the recovery time for cardiac ablation?
Recovery from cardiac ablation is quick. Most people can get back to normal activities in a few days to a week.
Is ablation used for conditions other than heart problems?
Yes, ablation treats various conditions. This includes some cancers, gynecological disorders, and neurological conditions.
What are the different types of ablation procedures?
There are many ablation procedures. These include thermal, cryoablation, chemical, and laser ablation. Each uses different methods to destroy tissue.
How do medical professionals categorize ablation?
Doctors see ablation as a minimally invasive procedure. It’s different from traditional surgery. But,classifications can vary based on context and insurance.
What does the term ‘ablation’ mean in oncology?
In oncology, ablation means destroying cancer tumors. This is done using techniques like radiofrequency or cryoablation.
How is ablation spelled?
The correct spelling is ‘ablation’.
What is the definition of ablation in medical terms?
Ablation is a medical procedure. It removes or destroys damaged or diseased tissue.
References
Mauri, G., Cova, L., De Beni, S., Ierardi, A. M., Tondulli, L., & Varano, G. M. (2021). Thermal ablation of solid tumors. Seminars in Interventional Radiology, 38(2), 154–165.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8175114/



































