Last Updated on November 4, 2025 by mcelik
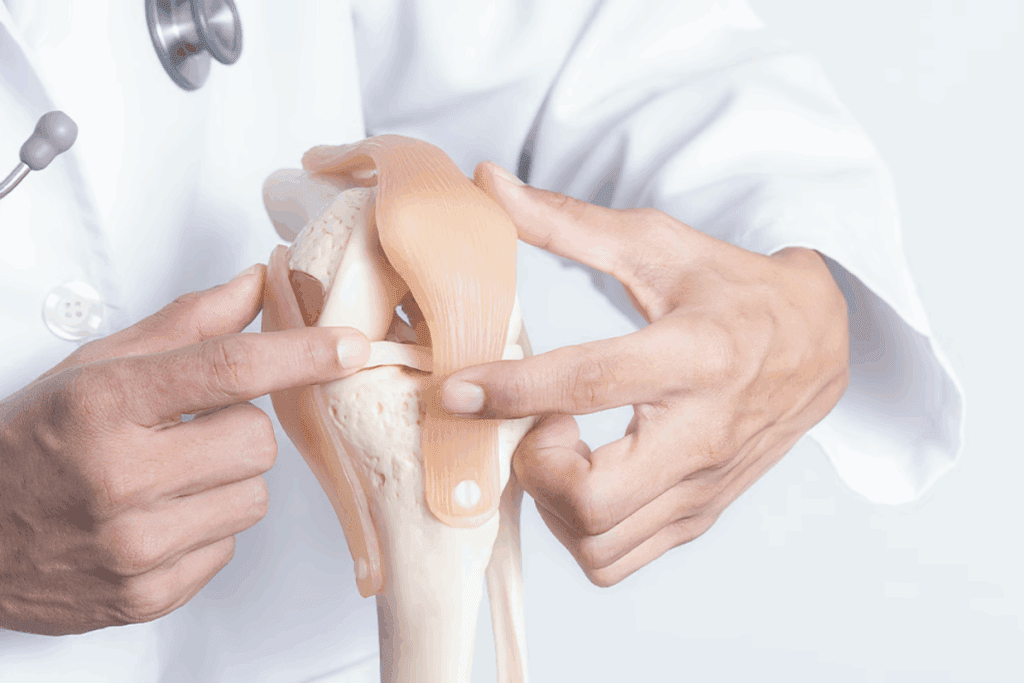
A herniated disc can cause a lot of pain and discomfort. Millions of people worldwide suffer from this condition. It happens when the soft inner gel of the disc leaks out through a tear in the outer disc. So, is herniated disc serious? It can be, depending on the severity and if the herniated material presses on nearby nerves. Symptoms include sharp or burning pain in the back, leg, or arm, numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness. In severe cases, it can affect mobility or cause loss of bladder or bowel control. Early diagnosis and treatment are important to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Knowing how serious a herniated disc is important for treatment. The symptoms can be mild or severe. They include pain, numbness, and weakness in the back and legs.
We will look into what it means for your health to have a herniated disc.
It’s important to know about herniated discs to understand their health risks. A herniated disc happens when the soft center leaks out through a tear. This can cause pain and nerve damage.
When a disc herniates, it can press on nerves. This leads to back or leg pain, numbness, or weakness. The symptoms depend on where and how big the herniation is.
The process of a disc herniation starts with wear and tear. As the disc wears down, it becomes more likely to herniate. The outer layer gets weaker, raising the risk.
Herniated discs can happen anywhere in the spine. But they’re most common in the lumbar region (lower back) and the cervical region (neck). The lower back bears more weight, making it more prone to herniations.
Figuring out if a herniated disc is serious means looking at how it affects nerves and the spine. The seriousness of a herniated disc can differ a lot from person to person. This depends on several important factors.
Several things help decide how serious a herniated disc is. These include:
To understand the possible complications, let’s look at the outcomes based on the severity of the herniation:
| Severity Level | Symptoms | Potential Complications |
| Mild | Minimal pain, occasional discomfort | Limited impact on daily activities |
| Moderate | Noticeable pain, some numbness or tingling | Some limitations in physical activities |
| Severe | Significant pain, pronounced numbness, or weakness | Potential for nerve damage, significant impact on daily life |
In some cases, a herniated disc is a medical emergency. This is true if it causes severe symptoms like:
If you have any of these symptoms, getting medical help right away is key. Quick action can greatly improve outcomes and prevent lasting damage.
Herniated disc symptoms can vary a lot. Knowing them is important for getting the right medical care. We’ll look at symptoms from mild to severe to help you know when to worry.
Mild to moderate symptoms include pain and discomfort in one area. You might feel pain that radiates to the arms or legs. For example, a herniated disc in the lower back can cause pain in the buttocks, thighs, or calves.
You might also feel numbness or tingling in the affected areas. A leading academy of orthopaedic surgeons says most people with herniated discs get better with rest, physical therapy, and pain meds.
Severe symptoms need immediate medical help. These include progressive numbness or weakness in the legs or arms, loss of bladder or bowel control, and trouble walking. These signs can mean nerve compression or damage.
“Emergency medical care is necessary if you experience sudden severe pain, weakness, or paralysis, as these could be signs of a serious condition like cauda equina syndrome.”
-As highlighted by experts
Watch your symptoms closely and get medical help if they get worse. Increased pain, numbness, or weakness are signs to watch for. Early treatment can greatly improve your outcome and prevent long-term problems.
When a disc herniates, it can put pressure on surrounding nerves, potentially causing damage. This compression can lead to a variety of symptoms. These symptoms range from mild discomfort to severe pain and neurological deficits.
A herniated disc occurs when the soft inner gel of the disc leaks out. This happens through a tear in the outer disc. The leaked material can compress nearby nerves, disrupting their normal function.
The compression can cause inflammation, pain, and potentially nerve damage if not addressed. Nerve compression due to a herniated disc is a serious condition that requires medical attention. The severity of the compression and the resulting symptoms depend on the location of the herniated disc and the extent of the nerve involvement.
Recognizing the signs of nerve damage is key for timely intervention. Common symptoms include:
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s essential to seek medical evaluation. This is to prevent further nerve damage and avoid long-term consequences.
We know dealing with a herniated disc is tough. But early diagnosis and treatment can greatly improve outcomes. By addressing nerve compression and damage promptly, individuals can reduce the risk of long-term neurological deficits. This can also improve their quality of life.
Pain from herniated discs changes over time. It’s important to know how pain can get worse. This helps us understand when we need to see a doctor.
Pain from herniated discs can feel different. It often starts as a dull ache in the back. This pain can then spread to the legs or arms.
A herniated disc in the lower back can cause sciatica. This is pain that goes down the sciatic nerve. On the other hand, a disc in the neck can cause pain or numbness in the neck, shoulders, or arms.
Some pain is normal with a herniated disc. But changes in pain can mean things are getting worse. It’s important to watch for these signs.
Signs that things are getting worse include:
| Pain Characteristic | Possible Indication |
| Increasing pain intensity | Worsening herniation or nerve compression |
| Pain radiating to new areas | Further nerve involvement or irritation |
| Numbness or tingling | Nerve damage or compression |
It’s key to notice changes in pain to manage herniated discs well. If you see these signs, see a doctor right away. They can help figure out what’s going on and how to treat it.
It’s important to know how a herniated disc can lead to paralysis. This happens when the disc presses on or damages nearby nerves. The chance of this happening depends on several things.
There are a few things that make it more likely for a herniated disc to cause paralysis. These include:
Cauda equina syndrome is a serious condition that can result from a herniated disc. It happens when nerves in the lower spine get compressed. This can lead to paralysis, loss of bladder or bowel control, and other severe symptoms.
Cauda equina syndrome is a medical emergency. If you have symptoms like:
You need to get medical help right away. Quick treatment can help a lot and prevent long-term damage.
Early recognition and intervention are key to managing the risk of paralysis from herniated discs. By knowing the risk factors and recognizing cauda equina syndrome symptoms, patients can get the care they need quickly. This can help prevent severe complications.
We stress the need to see a doctor if you have severe symptoms. It’s important to consult healthcare professionals for support and treatment options for herniated discs.
Untreated herniated discs can lead to chronic problems that affect your life a lot. If a herniated disc isn’t treated, it can cause ongoing health issues. These issues can make daily activities hard and impact your overall health.
One major issue from untreated herniated discs is chronic pain. This pain can be mild or very severe and lasts a long time. It can affect not just your back but also your legs or arms, depending on where the disc is.
Chronic pain from herniated discs can really limit what you can do. It makes simple tasks hard and keeps you from being active. It’s important to know that chronic pain is not just long-term pain. It’s a condition that needs special care.
There’s also a chance of permanent neurological changes if a herniated disc presses on nerves for a long time. This can cause numbness, weakness, or even paralysis in bad cases.
Permanent damage to nerves can really change your life. It can make it hard to work, be active, or enjoy hobbies. Getting treatment for a herniated disc early is key to avoiding these problems.
We stress the need to see a doctor if symptoms don’t get better or get worse. Early treatment can greatly lower the risk of long-term problems from herniated discs.
A herniated disc can really change your life, affecting how you move and feel. It’s tough to live with it, but knowing how it impacts daily life helps. We can find ways to manage these effects.
One big problem with a herniated disc is how it limits physical activities. Even simple actions like bending or lifting can hurt. People often have to change their daily routines to avoid making things worse.
For example, those who love outdoor activities or sports might have to cut back or stop. This change is hard, both physically and mentally. It affects their hobbies, social life, and fitness.
A herniated disc also affects work and overall happiness. The pain can make it hard to do job tasks, like manual labor or sitting for long hours. It can even stop you from traveling.
Some people have to take long breaks from work or even change careers. This impacts their money, mental health, and sense of purpose.
| Aspect of Life | Impact of Herniated Disc | Management Strategies |
| Physical Activities | Limitations in bending, lifting, and walking | Physical therapy, gentle exercises |
| Work Life | Difficulty in performing job duties | Workplace accommodations, flexible hours |
| Quality of Life | Chronic pain, reduced social interactions | Pain management, counseling |
Understanding how herniated discs affect daily life and mobility helps us manage better. Working with healthcare professionals is key. They can help create a plan that improves both physical and emotional health.
To find out how serious a herniated disc is, doctors use imaging tests and neurological exams. These tools help them see how bad the condition is. Then, they can choose the best treatment.
Imaging tests are key in finding herniated discs. The main tests are:
| Imaging Test | Primary Use | Key Findings |
| MRI | Diagnosing herniated discs and nerve compression | Detailed images of soft tissues, including discs and nerves |
| CT Scan | Visualizing bony structures and detecting bone spurs | Images of bone structures, useful for surgical planning |
| X-rays | Ruling out fractures, tumors, or other bone-related issues | Basic images of bone structures |
Neurological exams are important to see how a herniated disc affects nerves. These exams include:
These tests help find out if there’s nerve damage or compression. They guide the treatment plan.
Misdiagnosis can happen if tests are misread or if other conditions are not checked. The dangers of misdiagnosis include:
So, it’s very important to get a detailed check-up from a skilled doctor. This ensures the right diagnosis and treatment plan.
Many people find relief from herniated disc symptoms through conservative treatment options. These methods focus on reducing pain, improving function, and avoiding surgical intervention whenever possible.
One of the initial steps in conservative treatment involves resting the affected area and modifying activities to avoid exacerbating the condition. This might mean taking regular breaks to rest, avoiding heavy lifting, and changing the way you perform certain tasks.
By giving the spine a chance to heal and reducing the strain on the herniated disc, individuals can often experience a reduction in symptoms. It’s important to balance rest with appropriate levels of activity to prevent stiffness and maintain muscle strength.
Physical therapy plays a key role in the conservative treatment of herniated discs. A tailored exercise program can help strengthen the muscles around the spine, improve flexibility, and enhance posture.
Some of the exercises that may be recommended include:
Physical therapists can also provide manual therapy techniques, such as massage or mobilization, to help manage pain and improve function.
Medications are often used as part of a treatment plan to manage pain and inflammation associated with herniated discs. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can be effective for mild to moderate pain.
For more severe pain, healthcare providers may prescribe stronger medications or recommend alternative treatments like epidural steroid injections.
The following table summarizes the conservative treatment approaches for herniated discs:
| Treatment Approach | Description | Benefits |
| Rest and Activity Modification | Reducing strain on the herniated disc through rest and changing activities | Reduces symptoms, allows healing |
| Physical Therapy and Exercises | Tailored exercise programs to strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and posture | Strengthens muscles, improves flexibility, enhances posture |
| Medications for Pain Management | Using medications to manage pain and inflammation | Reduces pain, manages inflammation |
By combining these conservative treatment approaches, many individuals can find significant relief from herniated disc symptoms and improve their quality of life.
To know when surgery is needed for a herniated disc, we must look at how severe it is. We will talk about when surgery is a good choice, the different types of surgery, and how well they work.
Surgery is usually an option when other treatments don’t help, or if nerves are badly compressed. If pain is so bad it stops you from doing daily things, surgery might be needed.
There are many ways to fix herniated discs. The right surgery depends on the patient’s situation and what the doctor thinks is best.
How well herniated disc surgery works can vary. But, it often helps a lot by reducing pain, improving nerve function, and making life better.
Knowing how long it takes to heal from a herniated disc is key. It helps set realistic goals and speeds up the healing. The time it takes can change based on how bad the herniation is, the treatment’s success, and your health.
We’ll talk about the usual healing times and what can speed up or slow down recovery. This will help you know what to expect while you’re getting better.
The time it takes to heal from a herniated disc varies. It can be a few weeks or several months. The healing process goes through three main stages: acute, subacute, and chronic.
| Recovery Phase | Duration | Characteristics | Treatment Focus |
| Acute | 0-6 weeks | Intense pain and inflammation | Rest, pain management, and gentle exercises |
| Subacute | 6-12 weeks | Pain subsides, regaining mobility | Physical therapy, exercises |
| Chronic | 3-6 months and beyond | Significant improvement, possible residual pain | Maintenance exercises, lifestyle modifications |
Several things can affect how fast you recover from a herniated disc. These include:
By knowing these factors and working with your healthcare team, you can improve your recovery from a herniated disc.
To prevent herniated disc complications, a mix of medical care and lifestyle changes is key. Knowing the risks and taking action early can greatly lower the chance of serious problems.
Acting fast is vital when dealing with herniated discs. If symptoms don’t get better or get worse, see a doctor right away. Diagnostic imaging, like MRI or CT scans, helps figure out how bad the herniation is. This guides the right treatment.
Quick treatment can stop the problem from getting worse. It might even avoid serious issues like nerve damage or cauda equina syndrome.
Changing your lifestyle is important to avoid herniated disc problems. Keeping a healthy weight eases the pressure on your spine. Regular exercise makes your back muscles stronger and improves your flexibility.
Also, using good posture and ergonomic furniture can help. These steps help manage your current issue and keep your spine healthy overall.
Living with a herniated disc can be tough, but the right strategies can help. It’s about combining medical care, lifestyle changes, and ongoing care. This helps prevent problems and improves life quality.
Ongoing care is key to managing a herniated disc. Regular health check-ups, staying at a healthy weight, and doing the right physical activities are important. Physical therapy helps strengthen muscles and improve spine flexibility.
To stop herniated disc symptoms from coming back, make lifestyle changes. Improve your posture, take breaks when sitting or standing for a long time, and avoid heavy lifting. Exercise routines that build core strength and flexibility are also good.
A spine specialist says, “Managing a herniated disc long-term means more than just treatment. It’s about living a lifestyle that supports your spine.”
“The key to managing a herniated disc is not just medical treatment but also lifestyle changes that promote overall spinal health.”
Herniated discs and disability are closely linked, with many factors affecting the level of impairment. A herniated disc can greatly impact a person’s life, possibly leading to disability. We will look at when a herniated disc might be seen as a disability and what workplace accommodations are available.
A herniated disc is considered a disability if it severely limits major life activities. This decision is made based on the severity of symptoms, how it affect daily life, and work tasks. Chronic pain, limited mobility, and nerve damage are key factors in determining disability.
To get disability benefits or workplace adjustments, you need medical proof. This includes a diagnosis, treatment plans, and how your disc limits your functions. A detailed medical report is vital for supporting your claim.
Workplace adjustments are vital for those with herniated discs to keep working. Reasonable accommodations might include changing job duties, flexible hours, ergonomic changes, or less strenuous tasks. These can help you stay on the job.
Employers must offer these accommodations under disability laws, unless it’s too hard for the business. It’s important for employees and employers to talk openly about what works best for everyone.
Knowing your rights and the possible workplace adjustments is key for those with herniated discs. By understanding disability rights and work adjustments, you can manage your condition and keep a good quality of life.
Understanding if a herniated disc is serious and finding the right treatment is key. We’ve covered the severity, symptoms, and long-term effects of herniated discs. This knowledge helps in managing the condition well.
A herniated disc can really affect your daily life and how you move. But, getting the right care early can make a big difference. It’s important to see a doctor if your symptoms don’t get better or get worse.
Treatment for herniated discs includes both non-surgical and surgical methods. This includes physical therapy and managing pain. Knowing how to manage a herniated disc can prevent serious problems later on.
We suggest talking to a healthcare professional to find the best treatment for you. This way, you can get the care you need to handle your herniated disc effectively.
A herniated disc happens when the soft center of the disc leaks out. This leak goes through a tear in the outer disc. It can press on nerves, causing pain or discomfort.
The seriousness of a herniated disc depends on its location and size. It also depends on how it affects nearby nerves. Complications can include chronic pain, nerve damage, and in severe cases, paralysis or cauda equina syndrome.
Symptoms can range from mild to severe. They include back pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the arms or legs. This depends on the disc’s location and the nerves affected.
Seek immediate medical attention if you have severe pain, sudden numbness or weakness. Also, if you have loss of bladder or bowel control, or difficulty walking. These could be signs of a serious condition like cauda equina syndrome.
In rare cases, a herniated disc can cause paralysis. This is more likely if it presses on nerves that control muscle function. Cauda equina syndrome is a serious condition that requires emergency medical care.
Diagnosis involves a physical exam, medical history, and imaging tests like MRI or CT scans. Sometimes, neurological exams are done to check nerve function.
Treatment options include rest, physical therapy, and pain management medications. In severe cases or when conservative treatments fail, surgery may be needed.
Surgery is considered when conservative treatments don’t work. It’s also needed for severe nerve compression, significant weakness, or cauda equina syndrome.
Recovery time varies. It depends on the herniation’s severity, treatment effectiveness, and individual factors. Some people recover in a few weeks, while others may take several months.
While not all herniated discs can be prevented, there are ways to reduce the risk. Maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, practicing good posture, and lifting correctly can help.
Long-term management involves regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and possibly physical therapy or pain management. Lifestyle modifications can also help prevent recurrence.
In some cases, a herniated disc can qualify as a disability. This is if it significantly impacts daily life and work capabilities. Workplace accommodations may be available to support individuals with herniated discs.
Leaving a herniated disc untreated can lead to chronic pain and permanent neurological changes. It can also cause serious complications like cauda equina syndrome.
A herniated disc can limit physical activities and affect work capabilities. It can also impact the overall quality of life. Strategies for managing these effects include physical therapy, pain management, and lifestyle adjustments.
Management of Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Systematic Review. (n.d.).https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10683841/
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!