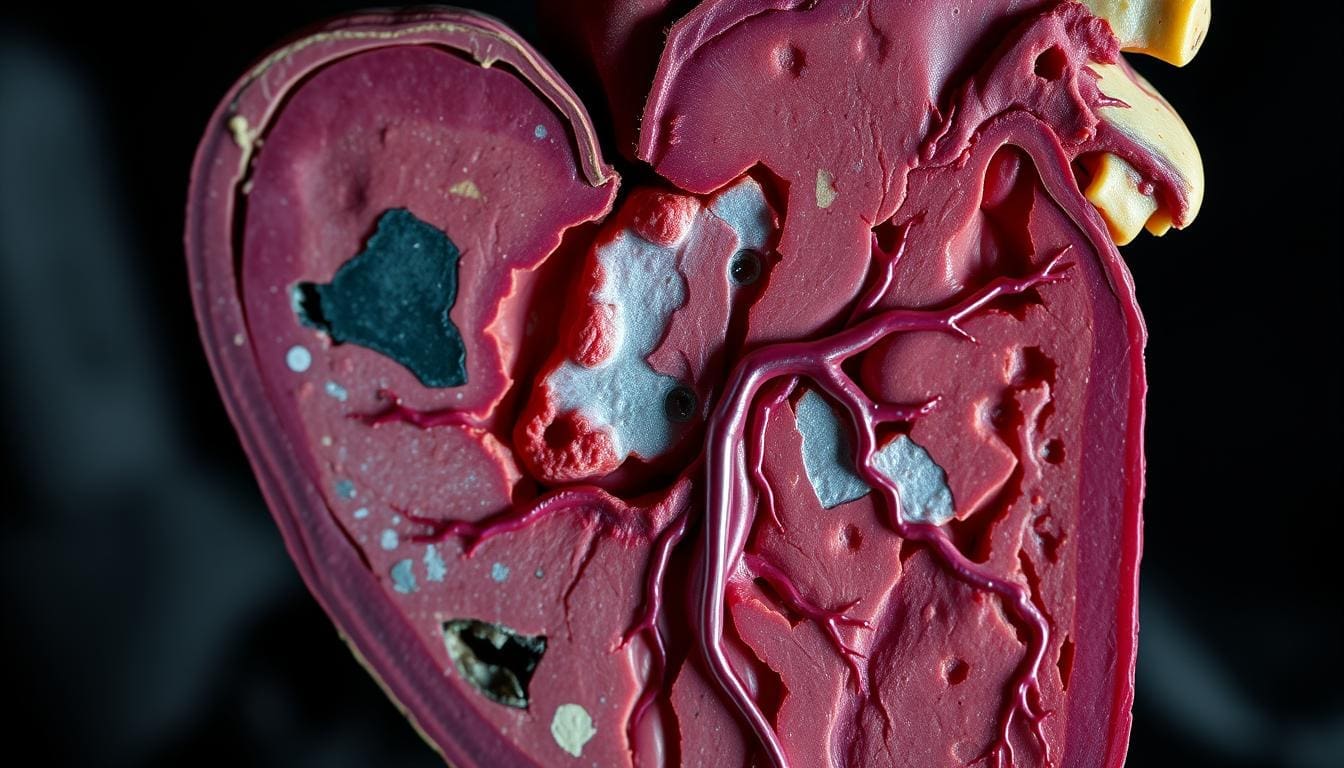
Ischemic heart disease (IHD) is a big health problem worldwide. Knowing about it is key to preventing and treating it early. At Liv Hospital, we focus on giving top-notch care to those with heart issues.
Ischemic heart disease happens when the heart muscle doesn’t get enough oxygen-rich blood. This often leads to a heart attack. We’ll look at 7 important facts about IHD, including symptoms and types, to help you understand it better.
We want to help patients by giving them the knowledge they need. By knowing about IHD, its symptoms, and types, people can get help quickly. This could save lives.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding ischemic heart disease is crucial for prevention and early treatment.
- IHD is a leading cause of death worldwide, emphasizing the need for awareness.
- Early detection and management of IHD can significantly improve patient outcomes.
- Liv Hospital offers advanced, patient-centered care for ischemic heart conditions.
- Knowing the symptoms and types of IHD is essential for timely medical intervention.
Understanding Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD): Definition and Importance
It’s key to grasp Ischemic Heart Disease to tackle its big health impact. IHD, or coronary heart disease, happens when heart arteries get narrowed or blocked. This reduces blood flow to the heart muscle.
What Is IHD in Medical Terms?
IHD is when the heart’s oxygen need doesn’t match the blood supply. This usually comes from atherosclerosis, where plaque builds up in heart arteries. This narrowing can cause symptoms like angina, heart attacks, and heart failure.
The term IHD is used a lot in medicine. Knowing what IHD means is vital for doctors to treat it right.
The Global Impact of Ischemic Heart Disease
IHD greatly affects global health, being a top cause of illness and death. The World Health Organization (WHO) says IHD leads to millions of deaths yearly.
- IHD causes over 9 million deaths worldwide each year.
- The cost of IHD is huge, with big healthcare expenses and lost work time.
- IHD cases are rising, due to older populations and lifestyle changes.
We must tackle IHD with strong prevention and treatment plans. Knowing about IHD’s definition and global effects helps us fight this major health issue.
The Pathophysiology of Ischemic Heart Disease
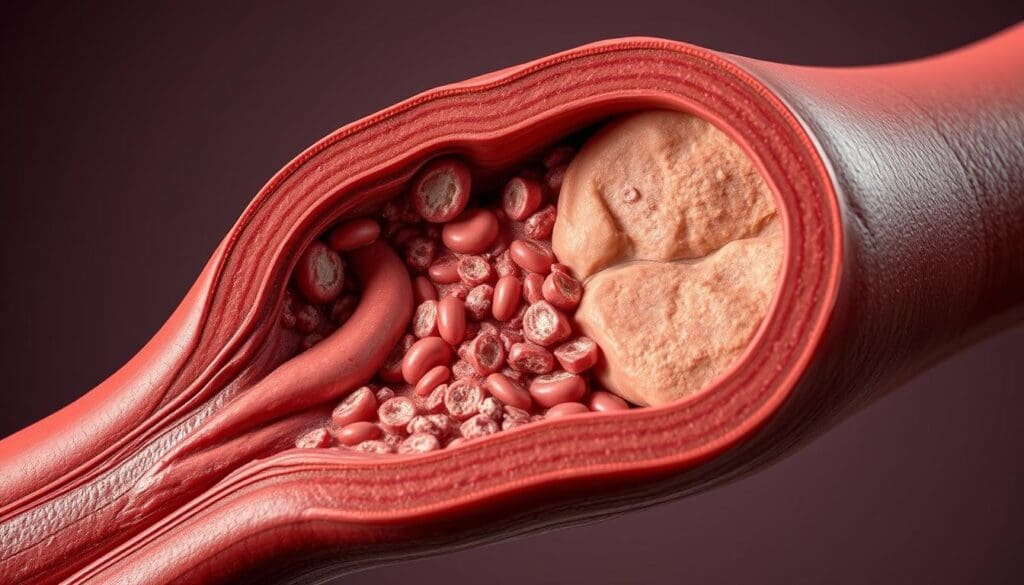
Ischemic heart disease starts with coronary artery disease and atherosclerosis. It happens when the heart muscle doesn’t get enough oxygen-rich blood. This is often because of blocked coronary arteries.
Coronary Artery Disease and Atherosclerosis
Coronary artery disease is a big reason for IHD, causing less blood to reach the heart. Atherosclerosis is the main cause, where plaque builds up in the arteries. This makes them narrow or block.
This buildup starts with lipids, macrophages, and smooth muscle cells in the artery walls. It’s a slow process.
As atherosclerosis gets worse, it can create complex lesions. These include fibrous plaques and calcified deposits. These can rupture, causing a blockage in the arteries.
From Restricted Blood Flow to Myocardial Damage
When the heart muscle doesn’t get enough blood, it leads to myocardial ischemia. This is when the heart muscle doesn’t get enough oxygen and nutrients. If this goes on too long, it can cause a myocardial infarction, or heart attack.
The damage to the heart muscle depends on how long it’s been ischemic, the area affected, and if there’s collateral circulation. Knowing these factors helps doctors find better treatments for IHD.
Types of Ischemic Heart Disease: A Comprehensive Overview
It’s important to know the different types of Ischemic Heart Disease to treat it well. Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD) has many forms, each with its own signs and treatment needs.
There are three main types of IHD: stable angina, unstable angina, and silent ischemia. Each type needs a special care plan.
Stable Angina: Predictable Chest Pain
Stable angina causes chest pain that comes and goes. It happens when you’re stressed or active. Rest or medicine can make it go away. It shows the heart muscle isn’t getting enough oxygen when it needs it most.
People with stable angina can manage their symptoms with lifestyle changes and medicine. But, we must watch them closely. Stable angina can turn into a more serious heart disease.
Unstable Angina: A Warning Sign
Unstable angina is more serious than stable angina. It means the heart’s blood vessels are changing, which could lead to a heart attack. The pain is worse, lasts longer, and can happen without any effort.
Unstable angina is a medical emergency. We need to act fast to prevent a heart attack. Recognizing the signs and treating it quickly is key.
Silent Ischemia: The Hidden Threat
Silent ischemia is when the heart muscle doesn’t get enough blood, but there’s no pain. It’s often found during tests for other reasons or stress tests. Silent ischemia is as dangerous as the kind with pain, because people might not get help in time.
Finding and treating silent ischemia is hard but very important. We use tests to find it and then treat it to lower the risk.
The table below shows the main differences between the types of Ischemic Heart Disease:
| Type of IHD | Characteristics | Clinical Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Stable Angina | Predictable chest pain, triggered by exertion or stress, relieved by rest or medication | Indicates transient myocardial ischemia; manageable with lifestyle changes and medication |
| Unstable Angina | Severe, prolonged, and unpredictable chest pain, often at rest | Medical emergency; high risk of myocardial infarction; requires immediate evaluation and treatment |
| Silent Ischemia | Episodes of reduced blood flow without typical angina symptoms | Potentially dangerous due to lack of symptoms; requires diagnostic testing for detection |
In summary, knowing about the different types of Ischemic Heart Disease is key to good care. By understanding stable angina, unstable angina, and silent ischemia, we can give each patient the right care. This improves their health and life quality.
Ischemic Heart Attack: Symptoms and Warning Signs
Knowing the signs of an ischemic heart attack can save lives. It’s vital to spot symptoms early for quick medical help.
Classic Symptoms of Myocardial Infarction
The main signs of a heart attack include chest discomfort or pain. This pain can spread to the arm, neck, or jaw. It feels like a tight squeeze.
Shortness of breath is another common symptom. It can happen with or without chest pain.
Other signs might be cold sweats, nausea, or feeling lightheaded. Not everyone shows all these signs, and how bad they are can differ.
Gender Differences in Symptom Presentation
Studies have found gender differences in heart attack symptoms. Women often feel symptoms like shortness of breath, nausea, or fatigue more than chest pain. This can cause delays in getting help.
It’s key for both men and women to know the many symptoms. If you feel something odd or bad, get medical help right away. Quick action can greatly improve your chances of recovery.
7 Key Facts Everyone Should Know About IHD
Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD) is a big problem worldwide. It causes a lot of sickness and death. Knowing about IHD is key to preventing and managing it. We will look at seven important facts about IHD, like how common it is, its risk factors, and what the future holds.
Prevalence and Mortality Statistics
IHD is a big health issue everywhere. It’s behind a lot of deaths globally. We need to understand these numbers to see how big the problem is.
| Region | IHD Prevalence (%) | Mortality Rate (per 100,000) |
|---|---|---|
| Global | 4.5 | 120 |
| North America | 5.2 | 100 |
| Europe | 5.5 | 110 |
The table shows how common IHD is and how many people die from it in different places. These numbers show why we need to be aware and take steps to prevent it.
Risk Factor Awareness
Knowing the risk factors for IHD is important for preventing it. Big risks include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, smoking, and being overweight. Knowing these risks helps people take steps to avoid them.
Key Risk Factors for IHD:
- Hypertension
- Hyperlipidemia
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- Obesity
Preventability and Early Intervention
IHD can often be prevented by making healthy choices and catching problems early. We can lower our risk by eating well, exercising, and managing health conditions.
Early intervention strategies include:
- Regular health check-ups
- Lifestyle modifications
- Managing risk factors
Long-term Prognosis and Quality of Life
The future for people with IHD depends on how serious it is and how well it’s managed. With the right treatment and lifestyle changes, many people can live active lives.
Knowing the important facts about IHD helps us take charge of our health. By understanding how common it is, its risks, and how to prevent it, we can all help reduce IHD’s impact worldwide.
Diagnosis of Ischemic Heart Disease
Getting a correct diagnosis for Ischemic Heart Disease is key. It needs a look at your medical history, a physical check-up, and advanced tests. We’ll walk you through how it’s done, showing why each step is important.
Initial Assessment and Medical History
The first step is a detailed look at your medical history and an initial assessment. This is crucial. It helps doctors spot risk factors and symptoms that might point to IHD. A detailed medical history can show past heart issues, family heart disease, and other health details.
Doctors also do a physical exam to find signs of heart disease or other issues that might be causing symptoms.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
To confirm IHD and see how severe it is, several tests are used. These include:
- Electrocardiography (ECG): A non-invasive test that records the heart’s electrical activity.
- Stress Test: Checks how well the heart works under stress.
- Coronary Angiography: Uses imaging to see the coronary arteries and find blockages.
- Cardiac Biomarkers: Blood tests that find proteins released when the heart is damaged.
A study in the International Journal of Emergency Medicine shows these tests are vital for catching IHD early. Learn more about why early detection.
Understanding Ischemic Defects in Test Results
It’s important to understand test results to diagnose IHD. Ischemic defects show up as odd readings on ECG, stress tests, or images. Knowing what these defects mean helps doctors figure out how bad the heart disease is and what treatment to use.
“The accurate interpretation of diagnostic test results requires expertise and a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s overall health condition.” This shows why a team effort is needed to manage IHD.
By combining initial checks, tests, and careful analysis, doctors can accurately diagnose IHD. They can then create a treatment plan that fits the patient’s needs.
Treatment Approaches for IHD and Acute Myocardial Infarction
Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD) and acute myocardial infarction need a team effort to treat. We’ll look at how to manage these conditions. This includes emergency care, medicines, and surgery.
Emergency Interventions
When someone has a heart attack, quick action is key. First, call for help and take aspirin if you have it. At the hospital, doctors will do several things:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) to check the heart
- Blood tests for heart markers
- Coronary angiography to see the arteries
These steps help figure out how bad the heart attack is and what to do next.
Medications and Their Roles
Medicines are crucial for IHD and heart attacks. Some important ones are:
- Antiplatelet agents (like aspirin) to stop blood clots
- Beta-blockers to slow the heart and lower blood pressure
- ACE inhibitors or ARBs to control blood pressure and heart work
- Statins to lower cholesterol
These drugs help prevent more heart problems and ease symptoms.
Surgical and Procedural Options
Some patients need surgery or procedures. These include:
- Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI), or angioplasty, with or without stenting
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) for more serious cases or when PCI can’t be used
These methods help get blood flowing to the heart again. This reduces damage and improves results.
By using emergency care, medicines, and surgery, we can manage IHD and heart attacks well. This improves patients’ lives and outcomes.
Prevention Strategies and Lifestyle Modifications
We can lower the risk of Ischemic Heart Disease by making healthy choices. This includes eating right, staying active, and managing health conditions. It’s all about making smart lifestyle changes.
Heart-Healthy Diet and Exercise
Eating a heart-healthy diet is key to preventing Ischemic Heart Disease. Focus on fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean proteins. Avoid saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol.
Regular physical activity is also vital. It helps keep your weight in check, lowers blood pressure, and boosts heart health.
- Eat a variety of fruits and vegetables daily
- Incorporate whole grains into your meals
- Choose lean protein sources like poultry and fish
- Limit foods high in saturated and trans fats
- Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week
Managing Existing Conditions
It’s crucial to manage health conditions like hypertension, diabetes, and high cholesterol. Work with your doctor to keep an eye on your health. Stick to your treatment plan and make lifestyle changes as advised.
- Monitor your blood pressure regularly
- Manage your blood sugar levels if you have diabetes
- Follow your medication regimen as prescribed
- Make dietary changes to help manage your condition
Regular Screening and Early Detection
Regular health screenings are vital for catching risk factors early. This includes checking blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood glucose levels. Early detection leads to better treatment outcomes.
By adopting these prevention strategies and lifestyle changes, we can lower the risk of Ischemic Heart Disease. This improves our heart health overall.
Conclusion: Living with and Beyond Ischemic Heart Disease
Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD) is a big health issue worldwide. But, with the right care and lifestyle changes, people with IHD can live full and active lives. We’ve looked at what IHD is, its types, symptoms, how it’s diagnosed, and how it’s treated.
Managing IHD means knowing a lot about it and taking action. Knowing the risks and how to lower them can help avoid heart attacks. We stress the need for early action and ongoing care to improve life quality and chances of recovery.
In summary, dealing with IHD needs a mix of medical care, lifestyle changes, and support. By living a heart-healthy life and working with doctors, people with IHD can face its challenges and enjoy a better life.
What is Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD)?
Ischemic Heart Disease, also known as coronary artery disease, happens when the heart’s blood supply is blocked. This reduces blood flow to the heart muscle.
What are the symptoms of an ischemic heart attack?
Signs of an ischemic heart attack include chest pain or discomfort. You might also feel short of breath or lightheaded. Pain in the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach is common. Women might feel sharp pain in the back or neck.
What are the risk factors for developing IHD?
High blood pressure, high cholesterol, and smoking are risk factors for IHD. Diabetes, obesity, and a lack of exercise also increase your risk. A family history of heart disease is another factor.
How is IHD diagnosed?
Doctors use a medical history, physical exam, and tests like an electrocardiogram (ECG) to diagnose IHD. Stress tests and imaging tests like echocardiography or coronary angiography are also used.
What is the difference between stable angina and unstable angina?
Stable angina is predictable chest pain that happens with exertion and goes away with rest. Unstable angina is unpredictable and can happen at rest. It’s a warning sign of a heart attack.
Can IHD be prevented?
Yes, IHD can be prevented or managed. Eating a heart-healthy diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and managing conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes are key.
What are the treatment options for IHD and acute myocardial infarction?
Treatment includes emergency care, medications like beta-blockers, and procedures like coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) or percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
What is silent ischemia?
Silent ischemia is when the heart muscle doesn’t get enough oxygen but doesn’t show symptoms. It’s found through tests like ECG or stress tests.
How can I manage my condition if I have IHD?
Managing IHD means taking your medications as directed, making healthy lifestyle choices, and seeing your doctor regularly. This helps monitor your condition and adjust treatment if needed.
Reference:
- “Global Epidemiology of Ischemic Heart Disease: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study” — PMC.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7384703/ (PMC)
- “Ischemic Heart Disease and Silent Ischemia” — American Heart Association.https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/heart-attack/about-heart-attacks/silent-ischemia-and-ischemic-heart-disease (www.heart.org)
- “Coronary Artery Disease” (includes IHD overview, types of angina: stable/unstable) — StatPearls / NCBI Bookshelf.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK564304/ (NCBI)
- “Silent Myocardial Ischemia — Diagnosis, Treatment and Prognosis” — Consultant360.https://www.consultant360.com/content/silent-myocardial-ischemia-diagnosis-treatment-and-prognosis (consultant360.com)
- “Angina (Chest Pain) — Types” — National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI).https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/angina/types (NHLBI, NIH)
- “Ischemia | Diagnosis & Disease Information” — Cardiology Advisor.https://www.thecardiologyadvisor.com/ddi/ischemia/ (The Cardiology Advisor)
“Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) – Fact sheet” — World Health Organization (WHO).https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds) (who.int)