Last Updated on November 26, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
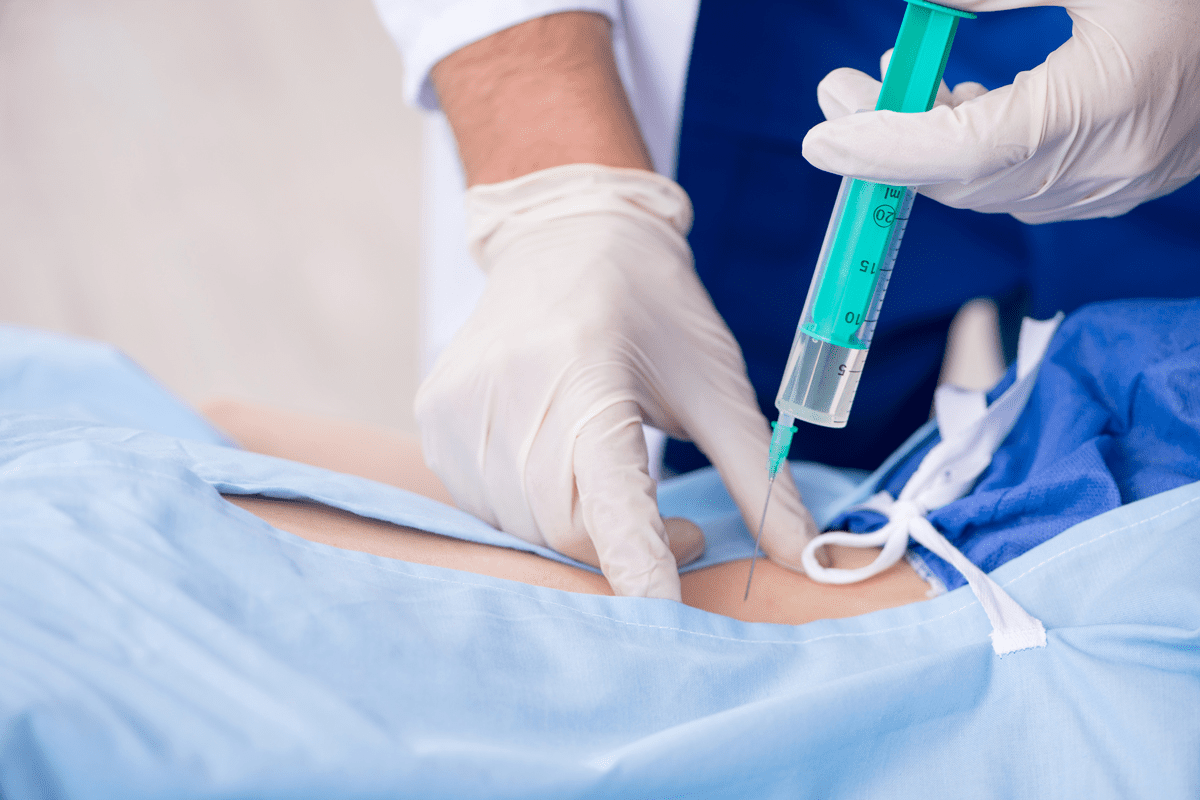
Knowing about the kidney biopsy procedure is key for those facing it. A percutaneous renal biopsy takes a small piece of kidney tissue for a microscope check. Considering a kidney bypass? Our ultimate guide explains the renal bypass procedure, recovery, and critical side effects to know.
We’ll walk you through the steps, from getting ready to the biopsy itself, and what happens next. We aim to ease worries and get you ready for a renal biopsy procedure.
Key Takeaways
- A kidney biopsy is a test to check for kidney damage or disease.
- The test is usually done with a percutaneous renal biopsy method.
- Knowing about it can help ease patient worries.
- We’ll talk about recovery and possible side effects to prepare you.
- We’ll use simple language to explain the procedure and its parts.
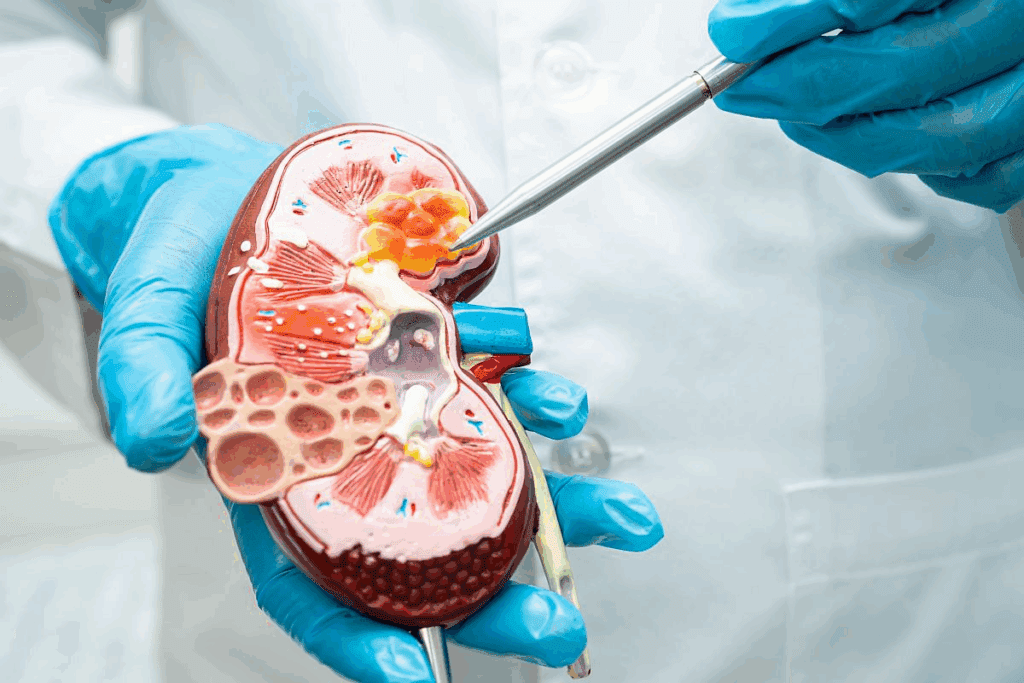
What is a Kidney Biopsy?

A kidney biopsy is when a small piece of kidney tissue is taken for a close look. This is a key test to see how well the kidneys are working and find any problems.
We do a kidney biopsy to find kidney issues that other tests can’t spot. It helps us plan treatments, see how kidney disease is progressing, or check if current treatments are working.
Definition and Purpose
A kidney biopsy, or renal biopsy, is a test where a piece of kidney tissue is taken for study. Its main goal is to diagnose and manage kidney diseases.
This biopsy helps us understand how much damage there is to the kidneys. It also helps find the cause of kidney disease and guides treatment. It’s a key tool for getting detailed information about kidney health.
Types of Kidney Biopsies
There are different kidney biopsies, each with its own use and benefits. The main types are:
- Percutaneous Biopsy: This is the most common, where a needle is used to get a tissue sample through the skin.
- Open Biopsy: This is a surgical method where a piece of kidney tissue is removed, usually under general anesthesia.
- Laparoscopic Biopsy: A less invasive surgery where a laparoscope is used to get the tissue sample.
| Type of Biopsy | Description | Indications |
| Percutaneous Biopsy | Needle inserted through the skin | Common kidney issues |
| Open Biopsy | Surgical removal under anesthesia | Complex cases or when other methods are not feasible |
| Laparoscopic Biopsy | Less invasive surgical method | Specific cases where direct visualization is needed |
Knowing about the different kidney biopsies and their uses helps both patients and doctors make better choices about tests.
When is a Kidney Biopsy Necessary?
Knowing when a kidney biopsy is needed helps patients understand their health better. A kidney biopsy takes a small piece of kidney tissue for testing. It gives insights into kidney health and can spot problems.
Medical Conditions Requiring Biopsy
Some health issues might need a kidney biopsy. These include:
- Abnormal blood or urine test results, like blood in the urine or too much protein in the urine
- Kidney dysfunction or failure
- Nephrotic syndrome, which causes severe swelling due to kidney damage
- Suspected kidney disease or damage
A biopsy can find the root cause of kidney problems. This helps in choosing the right treatment.
Diagnostic Benefits
A kidney biopsy has many benefits for diagnosis. It can:
- Give a clear diagnosis of kidney disease
- Find out why the kidneys are not working right
- Help decide the best treatment by showing the kidney’s condition
Doctors can understand the kidney’s health better. They can then plan a treatment that works well.
Treatment Planning
The results of a kidney biopsy are key for planning treatment. They help doctors to:
- Choose the best treatment for the patient’s specific problem
- Keep track of how kidney disease is getting worse
- Change treatment if needed, based on the biopsy findings
Understanding the kidneys through a biopsy lets doctors give more tailored care. This can lead to better results for patients going through kidney biopsy recovery or renal biopsy recovery.
Preparing for a Kidney Biopsy
A kidney biopsy needs careful preparation to avoid risks and get accurate results. We’ll guide you through the steps to help you feel ready and confident.
Medical Evaluations
We do thorough medical checks before the biopsy. We look at your health history, do blood tests, and check your blood pressure. These steps help us plan the biopsy safely.
Medication Adjustments
Some medicines can make bleeding more likely during and after the biopsy. We might ask you to stop taking these medicines before the procedure. Always talk to your doctor before changing your medicines.
Dietary Restrictions
You might need to fast or eat a special diet before the biopsy. This keeps your stomach empty, which is safer with anesthesia. We’ll tell you exactly what to do and for how long.
Mental Preparation
Having a kidney biopsy can be stressful. It helps to understand the procedure, ask questions, and talk to your doctor about worries. Support from family and friends is also important.
By following these steps and working with your healthcare team, you can have a smooth kidney biopsy. Good preparation is key to safety and accurate results.
The Kidney Biopsy Procedure Step-by-Step
The kidney biopsy procedure is a detailed process. It helps doctors diagnose and manage kidney issues. We’ll guide you through each step, from preparation to the biopsy itself.
Pre-Procedure Protocol
Before starting, our team follows a strict protocol. This ensures your safety and the success of the procedure. Here’s what we do:
- We review your medical history to spot any risks.
- We run blood tests to check your health and kidney function.
- We give you antibiotic prophylaxis to prevent infection, if needed.
- We make sure you have an IV line for medication during the procedure.
Positioning and Anesthesia
During the biopsy, you’ll be awake and on your abdomen or side. We use local anesthesia to numb the area. This makes the procedure less painful.
Locating the Kidney
We use imaging guidance, like ultrasound or CT scans, to find the kidney. This ensures the needle goes in the right spot.
- The imaging device shows us where the kidney is and how deep.
- We mark the best spot on your skin for the needle.
Needle Insertion and Sample Collection
With the kidney found and the area numbed, we insert the needle. A biopsy needle collects a small kidney tissue sample.
- The needle goes through the skin and into the kidney, guided by imaging.
- After collecting the sample, it’s sent to the lab for analysis.
By following these steps, we ensure a safe and effective kidney biopsy. This gives us the information we need for your diagnosis and treatment.
Percutaneous Renal Biopsy Technique
We use the percutaneous renal biopsy technique to safely get kidney tissue samples. These samples are key for diagnosing kidney diseases. This method has changed nephrology by letting us directly check kidney tissue.
Equipment and Tools
The procedure needs special tools, like a 14-18 gauge biopsy needle. We also use imaging tools like ultrasound or CT scanners. The choice of equipment depends on the patient’s condition and the doctor’s choice.
- Biopsy needle
- Ultrasound or CT scanner
- Local anesthesia
- Sterile equipment for the procedure
Ultrasound Guidance
Ultrasound guidance is often used in percutaneous renal biopsy. It gives real-time images for precise needle placement. This makes the biopsy safer and more accurate.
CT-Guided Approach
For some cases, a CT-guided approach is better. It’s used when the kidney is hard to reach or more precise guidance is needed. CT guidance gives detailed images, making the procedure safer and more effective.
Sample Handling
After getting the kidney tissue sample, we handle it carefully. The sample is put in a fixative solution and sent to the pathology lab for analysis.
- Place the sample in a fixative solution.
- Label the sample correctly.
- Send the sample to the pathology laboratory promptly.
Alternatives to Kidney Biopsy and Traditional Biopsies
Kidney biopsy is a key tool for diagnosis, but not all patients need it. New medical tech has opened up other ways to check for kidney disease.
Non-Invasive Diagnostic Methods
New, non-invasive tests are getting better. They include ultrasound and CT scans. These can show what’s going on in the kidneys without taking tissue samples.
Researchers are also looking at biomarkers in blood and urine. These can show kidney damage or disease. This might mean fewer biopsies are needed.
When Alternatives Are Appropriate
Choosing the right test depends on many things. This includes the patient’s health, how bad the kidney disease is, and any other health issues. For those at risk from biopsy, like those with bleeding disorders, non-invasive tests are safer.
Also, if the diagnosis is pretty clear from other tests, a biopsy might not be needed. Clinical judgment is key in picking the best test for each patient.
Comparing Effectiveness
Non-invasive tests have many benefits, but they’re not always better than biopsy. Biopsy is the top choice for some kidney problems because it looks at tissue directly.
But, for some issues, non-invasive tests can be just as good or even better. For example, imaging can spot problems that biopsy might miss. It’s important to compare different tests to find the best one for each patient.
In short, while kidney biopsy is very useful, there are other options. These can be better for some patients. We keep working to find the best ways to diagnose and treat kidney disease.
Immediate Post-Biopsy Care
After a kidney biopsy, it’s important to follow a careful recovery plan. This period is key for watching for complications and keeping your health in check.
Monitoring Vital Signs
Our team will watch your vital signs closely after the biopsy. They’ll check your blood pressure, heart rate, and temperature. This helps us spot and fix any problems quickly.
| Vital Sign | Normal Range | Action if Abnormal |
| Blood Pressure | 90/60 mmHg – 120/80 mmHg | Notify medical staff if consistently high or low |
| Heart Rate | 60-100 beats per minute | Alert staff if irregular or outside range |
| Temperature | 97.7°F – 99.5°F (36.5°C – 37.5°C) | Report any fever or significant deviation |
Pain Management
Managing pain is a big part of your care after the biopsy. We’ll give you the right medicine and tell you how to take it. If the pain isn’t right, let us know.
Activity Restrictions
We’ll tell you to avoid certain activities for a while after the biopsy. This means no heavy lifting, hard exercise, or bending.
- Avoid heavy lifting for at least 24 hours
- Refrain from strenuous activities for 2-3 days
- Limit bending or straining for a few days post-biopsy
When to Alert Medical Staff
Know when to call for help. If you have severe pain, heavy bleeding, or a fever, contact us right away.
By following these steps and talking with your healthcare team, you can have a safe recovery from your kidney biopsy.
Kidney Biopsy Recovery Timeline
Knowing what to expect after a kidney biopsy is key. It helps patients plan their care and manage their recovery. The process has several stages, each with its own rules and precautions.
First 24 Hours
The first 24 hours are very important. Most patients stay in the hospital or clinic for a few hours. They are watched for any immediate problems. It’s best to rest at home the rest of the day and avoid hard activities.
First Week
In the first week, patients should not do too much. Avoid heavy lifting, bending, or exercise. It’s important to watch for signs of trouble, like a lot of pain, bleeding, or fever.
Long-Term Recovery
After a while, most people get back to normal. They can start doing their usual activities in about a week to 10 days. But, how fast you recover can depend on your health and if any problems come up.
Follow-Up Appointments
Going to follow-up appointments is key. They help check how you’re doing and if any problems have started. These visits usually happen a few days to a week after the biopsy. They might include blood tests and scans.
Here’s a quick guide to help you understand the recovery:
| Recovery Stage | Activity Level | Monitoring Requirements |
| First 24 Hours | Rest, avoid strenuous activities | Close monitoring for complications |
| First Week | Limited physical activity | Watch for signs of complications |
| Long-Term Recovery | Gradual return to normal activities | Follow-up appointments |
By knowing the kidney biopsy recovery timeline, patients can prepare better. This makes the recovery smoother and more comfortable.
Home Care During Kidney Biopsy Recovery
After a kidney biopsy, taking care of yourself at home is key. It helps avoid problems and speeds up healing. When you get home, focus on a few important things to make your recovery smooth and safe.
Wound Care
Keeping the biopsy site clean and dry is critical. Use a bandage as your doctor tells you to. Try not to touch the area to lower infection risk.
Key wound care steps include:
- Keep the dressing clean and dry
- Change the dressing as instructed by your healthcare provider
- Monitor the site for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or discharge
Activity Guidelines
Rest is important, but you should also start doing light activities. Avoid hard work, heavy lifting, and bending for 24 to 48 hours after the biopsy.
| Activity | Recommended Timing |
| Light activities (e.g., walking) | Resume as tolerated immediately |
| Moderate activities (e.g., household chores) | Avoid for 24-48 hours |
| Strenuous activities (e.g., heavy lifting, contact sports) | Avoid for 1-2 weeks |
Diet and Hydration
Eating well and drinking lots of water are important for recovery. Drink plenty of fluids unless your doctor tells you not to. This helps your kidneys work better.
Eating a balanced diet with fruits, vegetables, and whole grains helps too. Eat light, nutritious foods in the first few days after the biopsy.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While at home, watch for signs of trouble. If you have severe pain, heavy bleeding, fever, or swelling, get help right away.
- Severe pain
- Heavy bleeding or hematuria (blood in the urine)
- Fever or chills
- Increasing swelling or redness around the biopsy site
By following these tips, you can recover safely from your kidney biopsy. If you have questions or concerns, always ask your doctor for help and advice.
Potential Side Effects and Complications
It’s important for patients to know about the possible side effects and complications of a kidney biopsy. This procedure is usually safe but can have some risks.
Common Side Effects
Most people feel some side effects after a kidney biopsy. These are usually mild and don’t last long. Common side effects include:
- Pain or discomfort at the biopsy site
- Bruising or swelling around the biopsy area
- Blood in the urine (hematuria)
It’s essential for patients to monitor their condition and report any severe or persistent symptoms to their healthcare provider.
Serious Complications
Though rare, serious complications can happen. These may include:
- Significant bleeding requiring transfusion or additional surgery
- Infection at the biopsy site
- Arteriovenous fistula (an abnormal connection between an artery and a vein)
As one study noted, “The overall complication rate for kidney biopsies is relatively low, but being aware of these possible risks is key for patient safety”
“Complications after percutaneous renal biopsy: a multicenter retrospective study”
Risk Factors
Some factors can make complications more likely after a kidney biopsy. These include:
- Abnormal kidney function
- Bleeding disorders or taking anticoagulant medications
- Uncontrolled high blood pressure
Managing Complications
If complications happen, getting medical help quickly is important. Treatment options may include:
- Monitoring and supportive care for minor complications
- Interventional procedures to address bleeding or other serious complications
- Antibiotics for infections
By knowing about the possible side effects and complications of a kidney biopsy, patients can prepare better. They can also work closely with their healthcare team to reduce risks.
Conclusion
A kidney biopsy, also known as a renal biopsy, is a key diagnostic tool. It helps doctors understand kidney health and diseases. By looking at kidney tissue, they can spot and treat various conditions.
We’ve talked about the kidney biopsy process, from getting ready to recovering. The percutaneous renal biopsy is a common method. It involves putting a needle into the kidney to get tissue samples.
Even though it’s an invasive procedure, a kidney biopsy is vital for diagnosing kidney diseases. Knowing what to expect can make patients feel more confident during the process.
In the end, a kidney biopsy or renal biopsy is a critical tool for doctors. It helps them give accurate diagnoses and treatments. This leads to better health outcomes for patients.
FAQ
What is a kidney biopsy?
A kidney biopsy is a procedure where a small piece of kidney tissue is taken. It’s examined under a microscope. This helps diagnose and manage kidney conditions.
Why is a kidney biopsy performed?
A kidney biopsy is done to find out about kidney diseases. It also checks how well the kidneys are working. It helps plan treatment for patients with kidney failure or other issues.
How is a kidney biopsy performed?
A kidney biopsy is usually done by inserting a needle through the skin and into the kidney. This is done under ultrasound or CT scan guidance. The sample is then analyzed in a lab.
What are the different types of kidney biopsies?
There are two main types of kidney biopsies. The most common is percutaneous, where a needle is used. Open biopsy involves a surgical cut to access the kidney.
How do I prepare for a kidney biopsy?
To get ready for a kidney biopsy, you’ll need to have medical checks and adjust your meds. You’ll also need to follow a diet and mentally prepare. Your doctor will give you specific instructions.
What are the possible side effects of a kidney biopsy?
Side effects of a kidney biopsy include pain, bleeding, and bruising. Though rare, serious issues like infection or damage to nearby organs can happen.
How long does it take to recover from a kidney biopsy?
Recovery time from a kidney biopsy varies. Most people can go back to normal activities in a few days to a week. It’s important to follow your doctor’s post-biopsy care instructions.
What is the role of imaging guidance in kidney biopsy?
Imaging like ultrasound or CT scan helps locate the kidney during the biopsy. It ensures accurate sampling and reduces the risk of complications.
Are there alternatives to kidney biopsy?
Yes, there are non-invasive tests like imaging and blood work for diagnosing kidney conditions. But, a kidney biopsy is the best way to diagnose some diseases.
How is the kidney biopsy sample handled?
The biopsy sample is carefully sent to a lab for analysis. It’s examined under a microscope to diagnose diseases and plan treatment.
Can I undergo a kidney biopsy if I have a bleeding disorder?
People with bleeding disorders might need special care or other tests. Your doctor will decide if a kidney biopsy is safe for you.
How often are follow-up appointments needed after a kidney biopsy?
After a kidney biopsy, follow-up appointments are usually needed. They check on your recovery and review the biopsy results. How often you need to go back depends on your situation.