Last Updated on November 25, 2025 by
Not treating a kidney stone can cause serious health problems. Nephrolithiasis, or kidney stones, can cause kidney pain and flank pain. But the biggest worry is the complications that can happen if not treated.

Ignoring kidney stone symptoms can harm your health quietly. Up to 50“67% of people with untreated kidney stones might get chronic kidney disease (CKD). They face a 22“46% higher risk of losing kidney function over time. It’s important to get help quickly to avoid serious problems, like infections that can be deadly.
It’s important to know about kidney stones to prevent and treat them. Kidney stones, or nephrolithiasis, are hard deposits made of minerals and salts. They form inside the kidneys. The kidneys are in the lower back, filtering waste from the blood.
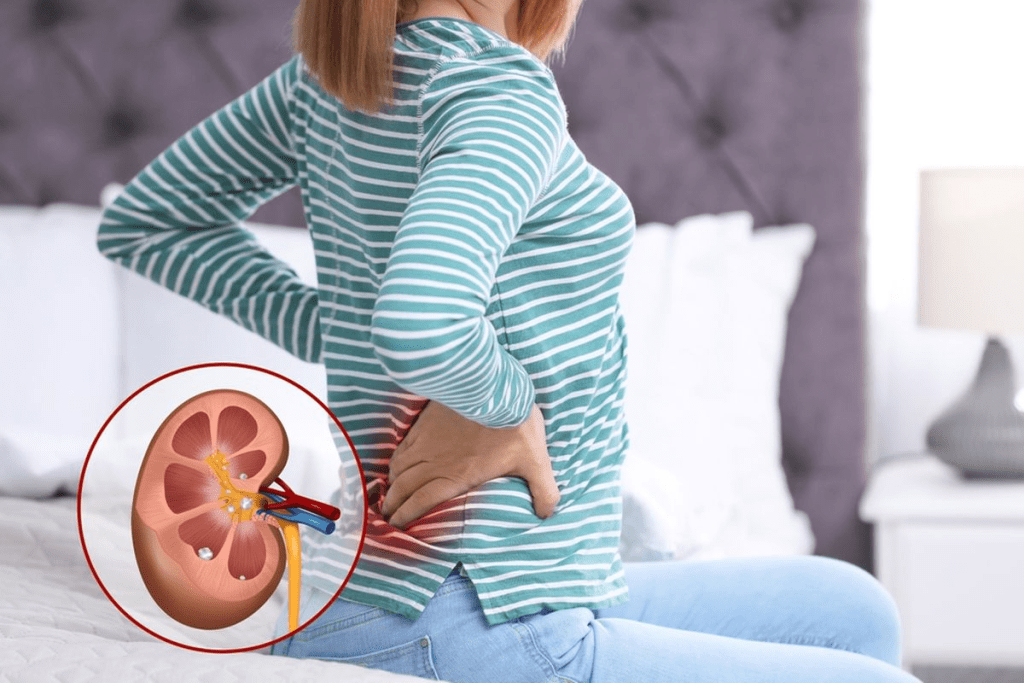
Kidney stones form when minerals in the urine crystallize and clump together. This can happen due to dehydration, diet, and genetics.
Stones usually form in the kidneys but can also occur in other parts of the urinary tract.
Several factors can lead to kidney stones. These include:
There are several types of kidney stones, each with different compositions:
Knowing about the different types of kidney stones and their causes helps in prevention and treatment.
Knowing the signs of kidney stones can help with treatment. These stones can cause mild discomfort or severe pain.
Flank pain is an early sign of kidney stones. It feels like a dull ache or sharp pain on one side of the back or abdomen. It’s vital to notice these signs early to get medical help quickly.
Other early signs include changes in how often you urinate and blood in your urine. Some people might also feel nauseous or vomit.
Kidney stones often cause severe pain, known as renal colic. This pain is intense and can move from the flank to the lower abdomen or groin. Renal colic pain is usually crampy and comes and goes.
This pain is so bad that people might pace or change positions to find relief.
Sometimes, kidney stone symptoms mean you need emergency care. Severe pain, fever, chills, or trouble urinating are signs to seek help right away.
It’s important to know when symptoms are a medical emergency. For example, a blockage can cause infection or harm the kidney.
“Prompt medical intervention is critical to prevent long-term damage and complications.”-Experts highhlight.
If you think you have a kidney stone or have severe symptoms, get medical help without delay.
Untreated kidney stones can harm your kidneys a lot. They might even lead to chronic kidney disease. We look at the dangers of not treating kidney stones, focusing on CKD.
Research shows that many people with untreated kidney stones get CKD. About 50% to 67% of cases can lead to this disease. This shows why treating kidney stones quickly is key.
Kidney stones can block urine flow, causing kidney pressure. This can cause inflammation and scarring. It makes the kidneys work less well over time.
Untreated kidney stones can badly harm your kidneys in the long run. CKD from untreated stones can lead to needing dialysis or a transplant. It’s vital to keep your kidneys healthy by treating stones properly.
We stress the need to treat kidney stones fast to avoid CKD. Knowing the risks and acting early can greatly lower your chance of getting CKD.
Untreated kidney stones can cause serious infections. This is a big risk for patients’ health. Kidney stones can block urine flow, creating a perfect spot for bacteria to grow.
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) often happen with kidney stones. A stone blocking urine flow lets bacteria multiply, causing infection. UTIs can be severe and need immediate medical attention to avoid worse problems.
Struvite stones, linked to UTIs, can lead to serious issues like end-stage renal disease. These stones form from magnesium ammonium phosphate and are common in UTI patients. Having struvite stones means a higher risk of chronic kidney disease.
In severe cases, untreated UTIs can turn into urosepsis, a life-threatening condition. This happens when the infection spreads to the blood. Urosepsis is a medical emergency that needs quick treatment. Early action is key to avoiding serious issues.
We know the danger of serious infection complications from untreated kidney stones is a big worry. It’s vital for patients to get medical help if they have UTI symptoms or other kidney stone issues.
Untreated kidney stones can harm your kidneys. They might cause damage and reduce kidney function. A stone blocking the urinary tract can lead to many problems.
One problem is hydronephrosis, where the kidney swells. This happens when urine can’t flow because of a stone. The buildup of urine puts pressure on the kidney.
Prolonged obstruction can lead to significant kidney damage. The high pressure can harm the kidney’s delicate parts. This can cause permanent damage if not treated quickly.
Damage from kidney stones involves complex processes. An obstructing stone increases pressure in the kidney. If this lasts too long, it can damage the kidney’s tissue permanently.
As stated by a leading medical expert, “The longer the obstruction, the higher the risk of permanent damage. This can lead to a decrease in kidney function.”
People who have had a kidney stone are more likely to get another. Studies show many will have another stone within a few years without prevention.
“The risk of recurrence is a critical concern, highlighting the need for effective management to prevent future stones and reduce complications.”
Preventing kidney stones and treating them early can greatly reduce discomfort and health problems. The American Urological Association suggests drinking more than 2.0“2.5 L of water a day. This helps lower the risk of getting calcium stones in the kidneys.
To avoid kidney stones, making smart food choices is key. Eating enough calcium (1000“1200 mg/d) and not too much sodium (2 or 3“5 g/d) helps. Also, eating more plant proteins and staying hydrated are important.
By choosing a healthier lifestyle and getting treatment when needed, you can avoid serious kidney stone problems. Treatment can include medicines or surgery. Natural products, like probiotics, may also help prevent kidney stones.
Your kidneys are in the lower back, one on each side of the spine. Kidney stones happen when minerals in your urine concentrate and crystallize. This can be due to dehydration, certain diets, or genetics.
Signs include severe flank pain, changes in how you urinate, and sometimes nausea or vomiting. If you have sudden, severe pain or other concerning symptoms, get medical help right away.
Renal colic is a severe pain from a kidney stone moving through your urinary tract. It’s very painful and can also cause nausea or vomiting.
Yes, untreated kidney stones can raise your risk of chronic kidney disease. Studies show that 50-67% of untreated cases might lead to CKD.
Kidney stones can block, infect, and inflame your kidneys. If not treated, this can make your kidneys work worse over time.
Struvite stones often come with urinary tract infections. They can form because of certain bacteria. These stones can increase the risk of end-stage renal disease.
Urosepsis is a serious condition where a urinary tract infection spreads throughout the body. Untreated kidney stones can raise your risk of urosepsis.
Hydronephrosis is when your kidney swells because of a blockage, often from a stone. If not treated, it can cause permanent damage.
To prevent kidney stones, stay hydrated, eat a balanced diet, and manage any health conditions you have.
Treatment for kidney stones depends on the stone’s size, location, and type. It can include medication, lifestyle changes, or surgery.
Nephrolithiasis is the medical term for kidney stones. Knowing the causes and risk factors can help in preventing and treating them.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!