Last Updated on November 13, 2025 by
Is Leukemia in Kids Curable? Understanding Childhood Leukemia Survival Rates
Childhood leukemia used to be a scary diagnosis. But thanks to medical science, treatment outcomes have greatly improved. Now, kids have a better chance of beating this disease.
Today, treating childhood leukemia is much more hopeful. The 5-year survival rate for acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is now over 90%. This is thanks to data from places like SEER and the Children’s Oncology Group.

Modern medicine is making a big difference in treating leukemia in kids. It shows how far we’ve come. And it gives families around the world new hope.
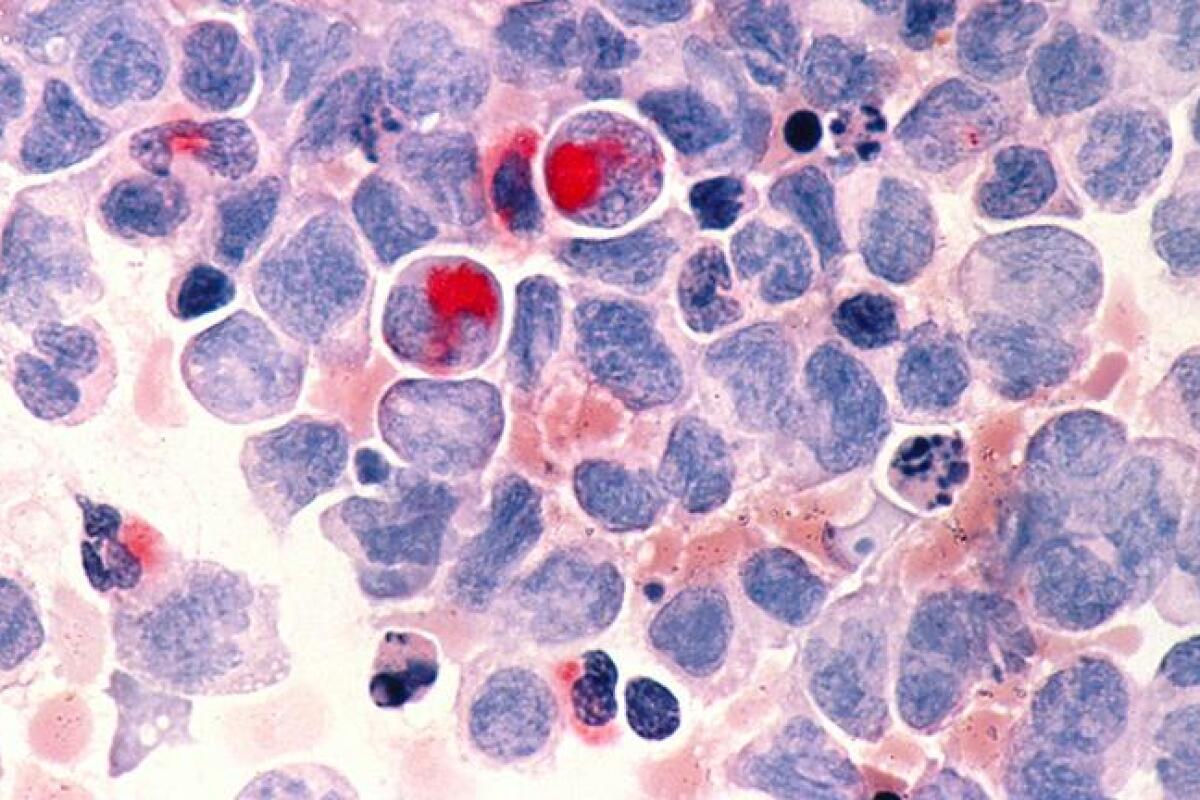
It’s important to know about childhood leukemia to help kids get better. Leukemia is the most common cancer in kids. We need to understand its different types and how it works.
There are two main types of childhood leukemia: Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) and Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML). ALL is the most common, making up about 80% of cases. AML is less common but also affects kids.
ALL and AML are different in how they grow and how they’re treated. ALL makes too many immature lymphocytes, causing problems like anemia and infections. AML grows abnormal myeloid cells, leading to similar issues.
Other rare types in kids include Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) and Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML). These are more common in adults.
Childhood leukemia is different from adult leukemia in many ways. Kids’ leukemia is often more aggressive but also more treatable. For example, ALL is more common in kids and has a higher cure rate than in adults.
Genetic and molecular differences also play a big role. Kids’ leukemia has different mutations than adults’, which can change treatment results.
“The biology of childhood leukemia is distinct from that of adult leukemia, necessitating tailored treatment approaches.”
In summary, knowing about childhood leukemia is key to helping kids. By understanding the differences between ALL, AML, and other types, doctors can create better treatment plans. This helps improve outcomes for kids with leukemia.
Childhood leukemia treatment has seen big changes over the years. These changes have greatly improved survival rates. This progress comes from ongoing research, clinical trials, and new medical technologies.
In the 1960s, kids with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) had a 14% chance of surviving five years. Now, that number is over 90%, thanks to better treatments.
The leap from 14% to over 90% survival is a huge win. It shows the hard work of researchers and doctors. Key steps include better chemotherapy, supportive care, and central nervous system prophylaxis to fight relapse.
Several new treatments have greatly helped kids with leukemia. These include:
These treatments have not only saved more lives but also made life better for many patients. A leading oncologist says, “The progress in treating childhood leukemia is a beacon of hope for families worldwide.”
“The progress in childhood leukemia treatment is one of the most significant achievements in modern oncology.”

The future of treating childhood leukemia looks bright. Ongoing research aims for even better treatments. It’s vital to keep supporting research and making the latest treatments available to all.
Knowing the survival rates for childhood leukemia is key for parents and doctors. Leukemia is the top cancer in kids, and we’ve seen big improvements in treatment.
There are different types of leukemia, each with its own survival rate. The two main types are Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) and Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML).
ALL is the most common leukemia in kids, making up 80% of cases. The 5-year survival rate for childhood ALL has surpassed 90%. This shows a high chance of long-term survival with today’s treatments.
Treatment for ALL includes chemotherapy, corticosteroids, and sometimes targeted therapy. The high survival rate for ALL comes from years of research and clinical trials.
AML is less common in kids but harder to treat than ALL. The 5-year survival rate for AML is around 60%. AML treatment often involves intensive chemotherapy and, in some cases, stem cell transplantation.
Even though AML’s survival rate is lower, it’s getting better with new therapies and better diagnostic tools. Research into targeted therapies and personalized medicine is ongoing, giving hope for better survival rates.
Knowing these survival rates helps doctors and families make better treatment choices. Both ALL and AML need quick and effective treatment. Ongoing research aims to keep improving survival rates for these conditions.
Today, treating pediatric leukemia involves new and better ways to help kids. We’ve learned a lot about fighting childhood leukemia. Now, there are many therapies to help kids beat the disease.
Chemotherapy is a key part of treating leukemia in kids. Multi-agent chemotherapy protocols aim to kill leukemia cells while keeping side effects low. These plans are always being updated to make them safer and more effective.
When kids get chemotherapy, doctors carefully pick the right dose and schedule. Age-specific protocols are very important. Kids’ bodies work differently than adults, so their treatment needs to be tailored.
Targeted therapies are also being used to fight leukemia. These treatments aim at specific problems in leukemia cells. This makes treatment more focused and effective.
Immunotherapies, like monoclonal antibodies and CAR-T cell therapy, are showing great promise. They use the body’s immune system to attack cancer cells.
Stem cell transplantation is a big help for some kids with leukemia. It replaces bad bone marrow with healthy stem cells. These can come from the patient or a donor.
Doctors decide if a stem cell transplant is right based on many things. This includes the type of leukemia, how likely it is to come back, and the patient’s health.
Knowing what affects leukemia treatment in kids is key for parents and doctors. Thanks to new medical discoveries, kids with leukemia have a better chance of getting better. But, several important factors can change each child’s outcome.
The age a child is diagnosed with leukemia matters a lot. Kids between 1 and 9 years old usually have a better chance of beating the disease. The American Cancer Society says kids in this age group have the highest survival rates for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL).
Genetics and biology also shape a child’s prognosis. Some genetic changes, like the Philadelphia chromosome in ALL, can impact the outcome. How well the leukemia cells react to treatment is also a big factor.
Key genetic factors include:
How well a child responds to first treatment is a big sign of their future. Kids who quickly go into remission usually do better than those who don’t. This shows why it’s important to watch how a child reacts to treatment and adjust plans as needed.
“The ability to achieve complete remission within the first few weeks of treatment is a critical factor in determining long-term survival.”
Going to specialized pediatric cancer centers is also very important. These places have teams of experts in treating childhood leukemia. Being treated here can lead to better results because of the use of proven treatments and support services.
By knowing these factors, parents and doctors can better understand and tackle childhood leukemia treatment. This helps make informed choices about care.
The journey of a child with leukemia doesn’t end with treatment. It’s about managing relapse risk and watching long-term health. Achieving remission is just the start. Managing relapse and long-term survival are key in pediatric leukemia care.
Relapse happens in about 13% of pediatric leukemia cases. It’s a tough setback for kids and families. Factors like age, leukemia type, and treatment response play a role in relapse risk.
Knowing these helps us create better treatment plans. This aims to lower relapse risk.
Children who relapse have a 49% five-year survival rate. We’re working to boost these numbers with new treatments and care. Survival after relapse depends on when it happens and how well the first treatment worked.
Our goal is to give the best care for a second remission. This aims to improve long-term survival.
Long-term care is vital for leukemia survivors. Regular check-ups are key to watch for treatment side effects and health issues. This care helps survivors live well into adulthood.
We’ve made big strides in treating childhood leukemia. Survival rates have gone up a lot. Places like Liv Hospital are leading the way with top-notch care.
Looking ahead, the outlook for leukemia treatment is bright. Research is pushing forward with new treatments. We’re getting better at understanding and fighting leukemia.
For kids with leukemia, the chance of a cure is getting better. Over 90% of kids with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) are now surviving. This shows how far medical care has come. We’re dedicated to keeping improving care for these kids.
We’re combining the latest treatments with caring for our patients. This is creating a brighter future for kids with leukemia. It’s giving hope to families everywhere.
Yes, leukemia can be cured in children. The cure rate varies based on the type of leukemia and other factors. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL), the most common type, has a survival rate over 90%.
ALL survival rate is over 90%. AML’s rate is about 60%. These numbers have grown thanks to better treatments.
Treatment for childhood leukemia has greatly improved. It used to have a 14% survival rate. Now, over 90% of ALL cases are cured. New treatments like targeted therapies and immunotherapies have been key to this progress.
Today, treatments include chemotherapy made for kids, targeted therapies, immunotherapies, and stem cell transplants. These methods have greatly improved outcomes for children with leukemia.
Several factors influence leukemia’s curability and prognosis in children. These include age at diagnosis, genetic and biological factors, how well the child responds to treatment, and access to specialized pediatric cancer centers.
Managing relapse involves post-relapse treatments. These can include more chemotherapy, targeted therapies, or stem cell transplants. The survival rate after relapse is about 49%.
Long-term monitoring and follow-up care are vital. They help catch and manage any late effects of treatment. This ensures the best possible outcomes for children with leukemia.
Chemotherapy is a main treatment for leukemia. But, some cases might need additional treatments like targeted therapies, immunotherapies, or stem cell transplants. This depends on the type of leukemia and how well the child responds to initial treatment.
Getting care at specialized pediatric cancer centers is very important. They offer advanced treatments and supportive services tailored for children with cancer. This improves their chances of a good outcome.
Our World in Data. (2025). Childhood leukemia: how a deadly cancer became treatable. https://ourworldindata.org/childhood-leukemia-treatment-historyChildhood leukemia used to be a scary diagnosis. But thanks to medical science, treatment outcomes have greatly improved. Now, kids have a better chance of beating this disease.
American Cancer Society. (2025). Prognostic Factors and Survival Rates for Childhood Leukemia. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/leukemia-in-children/detection-diagnosis-staging/survival-rates.html
Devilli, L., et al. (2021). Long-term and quality of survival in patients treated for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Frontiers in Pediatrics. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7967269/
Today, treating childhood leukemia is much more hopeful. The 5-year survival rate for acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is now over 90%. This is thanks to data from places like SEER and the Children’s Oncology Group.

Modern medicine is making a big difference in treating leukemia in kids. It shows how far we’ve come. And it gives families around the world new hope.
It’s important to know about childhood leukemia to help kids get better. Leukemia is the most common cancer in kids. We need to understand its different types and how it works.
There are two main types of childhood leukemia: Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) and Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML). ALL is the most common, making up about 80% of cases. AML is less common but also affects kids.
ALL and AML are different in how they grow and how they’re treated. ALL makes too many immature lymphocytes, causing problems like anemia and infections. AML grows abnormal myeloid cells, leading to similar issues.
Other rare types in kids include Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) and Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML). These are more common in adults.
Childhood leukemia is different from adult leukemia in many ways. Kids’ leukemia is often more aggressive but also more treatable. For example, ALL is more common in kids and has a higher cure rate than in adults.
Genetic and molecular differences also play a big role. Kids’ leukemia has different mutations than adults’, which can change treatment results.
“The biology of childhood leukemia is distinct from that of adult leukemia, necessitating tailored treatment approaches.”

In summary, knowing about childhood leukemia is key to helping kids. By understanding the differences between ALL, AML, and other types, doctors can create better treatment plans. This helps improve outcomes for kids with leukemia.
Childhood leukemia treatment has seen big changes over the years. These changes have greatly improved survival rates. This progress comes from ongoing research, clinical trials, and new medical technologies.
In the 1960s, kids with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) had a 14% chance of surviving five years. Now, that number is over 90%, thanks to better treatments.
The leap from 14% to over 90% survival is a huge win. It shows the hard work of researchers and doctors. Key steps include better chemotherapy, supportive care, and central nervous system prophylaxis to fight relapse.
Several new treatments have greatly helped kids with leukemia. These include:
These treatments have not only saved more lives but also made life better for many patients. A leading oncologist says, “The progress in treating childhood leukemia is a beacon of hope for families worldwide.”
“The progress in childhood leukemia treatment is one of the most significant achievements in modern oncology.”

The future of treating childhood leukemia looks bright. Ongoing research aims for even better treatments. It’s vital to keep supporting research and making the latest treatments available to all.
Knowing the survival rates for childhood leukemia is key for parents and doctors. Leukemia is the top cancer in kids, and we’ve seen big improvements in treatment.
There are different types of leukemia, each with its own survival rate. The two main types are Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) and Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML).
ALL is the most common leukemia in kids, making up 80% of cases. The 5-year survival rate for childhood ALL has surpassed 90%. This shows a high chance of long-term survival with today’s treatments.
Treatment for ALL includes chemotherapy, corticosteroids, and sometimes targeted therapy. The high survival rate for ALL comes from years of research and clinical trials.
AML is less common in kids but harder to treat than ALL. The 5-year survival rate for AML is around 60%. AML treatment often involves intensive chemotherapy and, in some cases, stem cell transplantation.
Even though AML’s survival rate is lower, it’s getting better with new therapies and better diagnostic tools. Research into targeted therapies and personalized medicine is ongoing, giving hope for better survival rates.
Knowing these survival rates helps doctors and families make better treatment choices. Both ALL and AML need quick and effective treatment. Ongoing research aims to keep improving survival rates for these conditions.
Today, treating pediatric leukemia involves new and better ways to help kids. We’ve learned a lot about fighting childhood leukemia. Now, there are many therapies to help kids beat the disease.
Chemotherapy is a key part of treating leukemia in kids. Multi-agent chemotherapy protocols aim to kill leukemia cells while keeping side effects low. These plans are always being updated to make them safer and more effective.
When kids get chemotherapy, doctors carefully pick the right dose and schedule. Age-specific protocols are very important. Kids’ bodies work differently than adults, so their treatment needs to be tailored.
Targeted therapies are also being used to fight leukemia. These treatments aim at specific problems in leukemia cells. This makes treatment more focused and effective.
Immunotherapies, like monoclonal antibodies and CAR-T cell therapy, are showing great promise. They use the body’s immune system to attack cancer cells.
Stem cell transplantation is a big help for some kids with leukemia. It replaces bad bone marrow with healthy stem cells. These can come from the patient or a donor.
Doctors decide if a stem cell transplant is right based on many things. This includes the type of leukemia, how likely it is to come back, and the patient’s health.
Knowing what affects leukemia treatment in kids is key for parents and doctors. Thanks to new medical discoveries, kids with leukemia have a better chance of getting better. But, several important factors can change each child’s outcome.
The age a child is diagnosed with leukemia matters a lot. Kids between 1 and 9 years old usually have a better chance of beating the disease. The American Cancer Society says kids in this age group have the highest survival rates for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL).
Genetics and biology also shape a child’s prognosis. Some genetic changes, like the Philadelphia chromosome in ALL, can impact the outcome. How well the leukemia cells react to treatment is also a big factor.
Key genetic factors include:
How well a child responds to first treatment is a big sign of their future. Kids who quickly go into remission usually do better than those who don’t. This shows why it’s important to watch how a child reacts to treatment and adjust plans as needed.
“The ability to achieve complete remission within the first few weeks of treatment is a critical factor in determining long-term survival.”
Going to specialized pediatric cancer centers is also very important. These places have teams of experts in treating childhood leukemia. Being treated here can lead to better results because of the use of proven treatments and support services.
By knowing these factors, parents and doctors can better understand and tackle childhood leukemia treatment. This helps make informed choices about care.
The journey of a child with leukemia doesn’t end with treatment. It’s about managing relapse risk and watching long-term health. Achieving remission is just the start. Managing relapse and long-term survival are key in pediatric leukemia care.
Relapse happens in about 13% of pediatric leukemia cases. It’s a tough setback for kids and families. Factors like age, leukemia type, and treatment response play a role in relapse risk.
Knowing these helps us create better treatment plans. This aims to lower relapse risk.
Children who relapse have a 49% five-year survival rate. We’re working to boost these numbers with new treatments and care. Survival after relapse depends on when it happens and how well the first treatment worked.
Our goal is to give the best care for a second remission. This aims to improve long-term survival.
Long-term care is vital for leukemia survivors. Regular check-ups are key to watch for treatment side effects and health issues. This care helps survivors live well into adulthood.
We’ve made big strides in treating childhood leukemia. Survival rates have gone up a lot. Places like Liv Hospital are leading the way with top-notch care.
Looking ahead, the outlook for leukemia treatment is bright. Research is pushing forward with new treatments. We’re getting better at understanding and fighting leukemia.
For kids with leukemia, the chance of a cure is getting better. Over 90% of kids with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) are now surviving. This shows how far medical care has come. We’re dedicated to keeping improving care for these kids.
We’re combining the latest treatments with caring for our patients. This is creating a brighter future for kids with leukemia. It’s giving hope to families everywhere.
Yes, leukemia can be cured in children. The cure rate varies based on the type of leukemia and other factors. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL), the most common type, has a survival rate over 90%.
ALL survival rate is over 90%. AML’s rate is about 60%. These numbers have grown thanks to better treatments.
Treatment for childhood leukemia has greatly improved. It used to have a 14% survival rate. Now, over 90% of ALL cases are cured. New treatments like targeted therapies and immunotherapies have been key to this progress.
Today, treatments include chemotherapy made for kids, targeted therapies, immunotherapies, and stem cell transplants. These methods have greatly improved outcomes for children with leukemia.
Several factors influence leukemia’s curability and prognosis in children. These include age at diagnosis, genetic and biological factors, how well the child responds to treatment, and access to specialized pediatric cancer centers.
Managing relapse involves post-relapse treatments. These can include more chemotherapy, targeted therapies, or stem cell transplants. The survival rate after relapse is about 49%.
Long-term monitoring and follow-up care are vital. They help catch and manage any late effects of treatment. This ensures the best possible outcomes for children with leukemia.
Chemotherapy is a main treatment for leukemia. But, some cases might need additional treatments like targeted therapies, immunotherapies, or stem cell transplants. This depends on the type of leukemia and how well the child responds to initial treatment.
Getting care at specialized pediatric cancer centers is very important. They offer advanced treatments and supportive services tailored for children with cancer. This improves their chances of a good outcome.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!