Last Updated on October 22, 2025 by mcelik
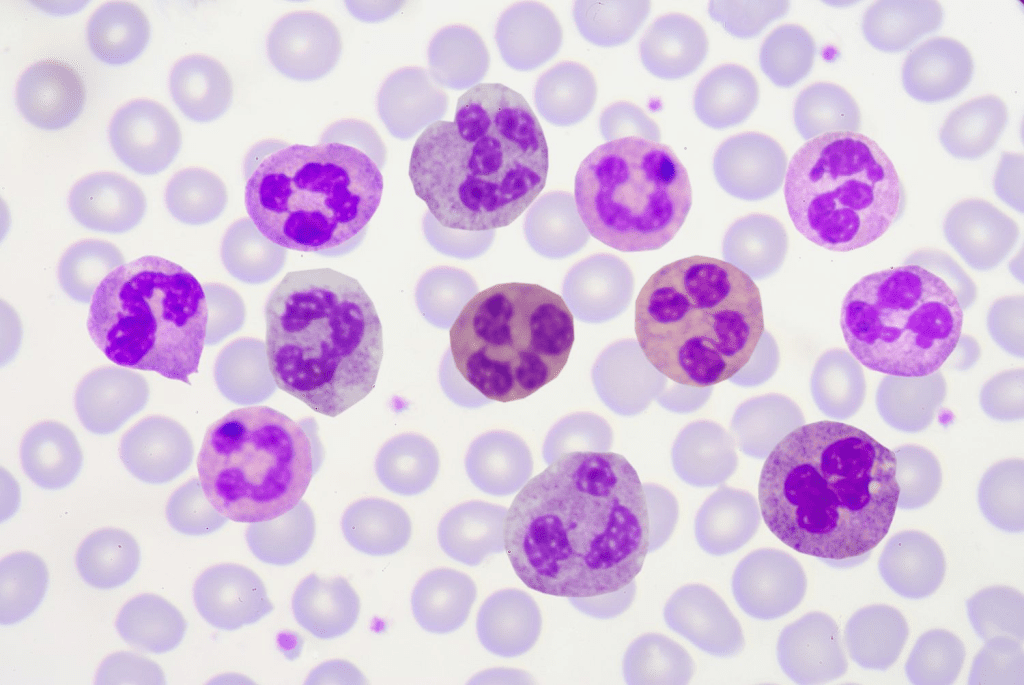
Nuclear medicine has transformed disease diagnosis, particularly for infections and inflammation, by using advanced imaging techniques like SPECT scans. One important procedure in this field is the Leukocyte Scan, which involves labeling white blood cells with a radioactive tracer to detect areas of inflammation or infection in the body. By tracking these labeled leukocytes, SPECT scans provide detailed images that help localize inflammatory sites, improving accuracy in diagnosing infectious and inflammatory conditions. This integration of a Leukocyte Scan with SPECT imaging has greatly enhanced the ability to see inflammation functionally within the body.
SPECT scans, with leukocyte labeling, are a key tool for finding infections. They help doctors find where inflammation is with great precision.
This tech is key for diagnosing and treating many conditions. It shows how important SPECT scans are for spotting inflammation.

Healthcare experts use SPECT imaging to understand inflammation better. This tool is key in modern medicine. It offers insights that were hard to get before.
SPECT technology detects gamma rays from a body-introduced radiotracer. The Symbia Intevo SPECT/CT systems use advanced tech for high-quality images. These images help diagnose conditions like inflammation.
A radiopharmaceutical is injected to mark inflammation areas. The SPECT scanner picks up gamma radiation from this tracer. It creates detailed, three-dimensional images of the body’s inside.
SPECT imaging spots inflammation by showing where the radiotracer gathers. This happens because of more blood flow and vessel openness, signs of inflammation.
Leukocyte imaging labels white blood cells with a tracer. These cells go to infection or inflammation sites. This lets doctors find the exact spot of inflammation.
The scan gives important info on inflammation’s size and where it is. This helps doctors make better care plans for patients.
Nuclear medicine uses advanced technology and special radiotracers to detect inflammation. Techniques like SPECT imaging are key in diagnosing and managing inflammatory conditions.
Inflammation shows up in several ways, like increased blood flow and temperature. It also involves the buildup of white blood cells (leukocytes) at the affected area. These signs help the body fight off infections and injuries.
Leukocytes are important in this fight. They move towards the inflammation site. This movement is guided by chemical signals like cytokines and chemokines.
“The ability to visualize and quantify inflammation using nuclear medicine techniques has significantly improved diagnostic accuracy and patient care.”
Radiotracers are substances that give off radiation. This radiation can be seen by nuclear medicine imaging, like SPECT. These tracers are made to focus on specific processes, like inflammation.
One way to do this is by labeling leukocytes with tracers like Tc-99m HMPAO or Indium-111 Oxine. These labeled cells then gather at the inflammation site. They send out signals that SPECT imaging can capture.
| Radiotracer | Application | Characteristics |
| Tc-99m HMPAO | Leukocyte labeling | High affinity for leukocytes, short half-life |
| Indium-111 Oxine | WBC scintigraphy | Longer half-life, high sensitivity for infection |
The right radiotracer depends on the situation and what the imaging needs to show. Knowing how these tracers work helps doctors understand SPECT images better.
The leukocyte scan, also known as the white blood cell (WBC) scan, is the top choice for finding infections. It uses the body’s natural fight against infection. White blood cells help spot where inflammation or infection is happening.
A WBC scan labels a patient’s white blood cells with a radioactive tracer. This tracer goes to areas of infection or inflammation. It helps doctors see exactly where the infection is, making it easier to plan treatment.
First, a patient’s blood is drawn to get white blood cells. These cells are then labeled with a special tracer, like Tc-99m HMPAO or Indium-111 Oxine. After that, the labeled cells are put back into the patient’s body.
They go to where the infection is. A gamma camera takes pictures of the tracer, showing where the infection is.
Leukocyte imaging is used in many cases. This includes suspected osteomyelitis, infections in prosthetic joints, and inflammatory bowel disease. It helps doctors see the infection clearly, making it easier to treat.
| Clinical Condition | Use of Leukocyte Scan |
| Osteomyelitis | Diagnosing bone infections by highlighting areas of leukocyte accumulation. |
| Prosthetic Joint Infections | Identifying infection in prosthetic joints, aiding in differentiation from loosening or other complications. |
| Inflammatory Bowel Disease | Assessing the extent and severity of inflammation in the bowel. |
Knowing how leukocyte scans work helps doctors make better choices for patients. This leads to better care and results.
SPECT imaging uses special radiotracers to spot inflammation in the body. These tools are key for diagnosing and understanding inflammatory processes.
Tc-99m HMPAO is a top choice for labeling white blood cells. It’s lipophilic, which means it can get into cells easily. This makes it great for showing where inflammation or infection is happening.
Using Tc-99m HMPAO has many benefits. It labels cells well and gives clear images. It’s perfect for finding infections and inflammation in different parts of the body.
Indium-111 Oxine is another good option for labeling white blood cells. It works well without harming the cells. It’s great for spotting long-term infections and inflammation.
One cool thing about Indium-111 Oxine is it works well even after some time has passed. But, it needs careful handling to work best.
Gallium-67 Citrate has been around for a long time to find inflammation and infection. It sticks to proteins in inflamed areas. It’s good for finding infections in the lungs or lymph nodes.
Even though Gallium-67 Citrate has some downsides, like a long half-life, it’s very useful. It’s a key tool for finding inflammation.
When you’re getting ready for a SPECT scan, knowing what to expect can help. This scan is a key tool for finding and checking inflammation in the body. Learning about the steps involved can make the whole process easier and more comfortable.
Getting ready for a SPECT scan starts before you arrive. You’ll need to get there at least 30 minutes early. This time is for paperwork and getting ready for the blood draw.
Pre-Scan Instructions: Keep taking your regular medicines unless your doctor tells you not to. Wear comfy clothes and avoid jewelry or metal items that might mess with the scan.
The first step in the SPECT scan is drawing blood. This is usually from your arm’s vein. The blood is then used to make and label white blood cells with a special tracer.
Labeling Process: The blood cells are mixed with a tracer like Tc-99m HMPAO or Indium-111 Oxine. This makes the cells glow, so they show up in scans where there’s inflammation.
The SPECT scan itself takes 30 to 60 minutes. But, you might be there longer because of getting ready and after the scan. You’ll lie on a table that moves to take pictures from different angles.
Patient Positioning: The tech will help you get into the right spot. This makes sure the scanner can see the area you’re interested in.
| Procedure | Duration | Description |
| Blood Drawing | 5-10 minutes | Drawing blood for leukocyte labeling |
| Labeling Process | 30-60 minutes | Labeling leukocytes with radiotracer |
| SPECT Scan | 30-60 minutes | Capturing images of inflammatory sites |
SPECT inflammation scan results give us important information about inflammation in the body. It’s key to understand these results well for diagnosis and treatment.
When looking at SPECT scans, it’s important to know the difference between normal and abnormal results. Normal scans show the radiotracer evenly distributed. But, if there’s uneven uptake, it might mean inflammation or infection.
Abnormal findings can show up as specific or spread-out patterns. Specific patterns might point to a localized issue, while spread-out patterns suggest a bigger problem.
Radiologists have special ways to spot inflammation on SPECT scans. They look at how the radiotracer is taken up and compare it to normal tissues or past scans. They also use advanced tools to make their job more accurate.
Quantitative analysis techniques help measure the radiotracer uptake more precisely. This helps doctors tell different inflammatory conditions apart and track how the disease is changing or responding to treatment.
Quantitative analysis in SPECT scans means measuring the radiotracer uptake in certain areas. This is done using methods like standardized uptake values (SUVs) and other semi-quantitative tools.
Using these methods, doctors can get a clearer picture of inflammation. This is really helpful for tracking how the disease is progressing and how well treatments are working.
SPECT imaging is key in diagnosing and managing inflammatory conditions. It gives detailed info on the body’s inflammatory processes. This makes it a valuable tool in clinical practice.
Osteomyelitis, a bone infection, is hard to diagnose with regular imaging. SPECT inflammation imaging is very sensitive in finding bone infections. It’s great when other tests don’t work.
It shows how far the infection has spread and if treatment is working.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), like Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis, can be checked with SPECT. It shows how much inflammation is in the bowel. This is key for managing the disease well.
In cases of fever of unknown origin (FUO), SPECT can find the cause. It spots areas with more leukocytes. This helps find the fever’s source, guiding further tests and treatments.
Spotting infections in prosthetic joints is tricky. SPECT/CT combines SPECT with CT. It gives both functional and anatomical info. This makes diagnosing prosthetic joint infections more accurate.
SPECT’s wide range of uses in detecting inflammation shows its importance in medicine. It helps find and assess inflammatory conditions. This greatly helps in patient care and treatment planning.
Perfusion changes are a key sign of inflammation, and SPECT imaging sheds light on these changes. Inflammation brings more blood to the affected area. This is how the body responds to injury or infection.
SPECT can spot perfusion changes because it tracks radiotracers in the body. As inflammation grows, blood flow patterns change. SPECT can see these changes.
Inflammation starts a series of changes in blood vessels. These include wider blood vessels, more leaky blood vessels, and more immune cells. Vasodilation means more blood flow, a key sign of inflammation.
The blood vessels also let more fluid, proteins, and immune cells out. This helps bring immune cells and helpers to the inflamed area. SPECT imaging can spot these changes by seeing where radiolabeled tracers build up.
Looking at blood flow patterns with SPECT helps doctors diagnose inflammation. They can see how severe and where the inflammation is. This helps them understand the problem better.
In cases like osteomyelitis, SPECT shows where the infection is. For inflammatory bowel disease, it shows how bad the inflammation is. SPECT is a key tool for diagnosing and managing inflammation without surgery.
Healthcare professionals can now see how labeled leukocytes move to infection sites. This is thanks to nuclear medicine. It has changed how we look at the immune system.
The first step is labeling leukocytes with a radioactive tracer. This is often done with Tc-99m HMPAO or Indium-111 Oxine. Then, these cells are put back into the patient.
Next, a gamma camera tracks their movement. They go to areas with infections or inflammation. This lets doctors see where the infection is.
Tracking labeled leukocytes has many benefits. It is very specific and sensitive. This is true even when other methods can’t find the infection.
Nuclear medicine is key in tracking immune cells. It helps diagnose and treat infections and inflammation. This leads to better care for patients.
It’s key to know how well SPECT works in finding inflammation. Its success depends on its sensitivity and specificity.
The sensitivity of SPECT shows how well it spots inflammation. High sensitivity means it’s good at finding the condition. On the flip side, specificity shows how well it misses the condition when it’s not there. Finding a good balance between these two is important for accurate diagnosis.
SPECT imaging is promising for spotting inflammation. Studies show it does a good job of balancing sensitivity and specificity. But, how well it works can change based on the condition and the tracer used.
SPECT, like any test, can make mistakes. False positives happen when it says there’s inflammation when there isn’t. False negatives occur when it misses inflammation when it’s there. Knowing why these mistakes happen helps us understand SPECT results better.
Many things can change how well SPECT works. The type of tracer used, when the scan is done, and the patient’s condition all play a part.
| Factor | Impact on Diagnostic Performance |
| Radiotracer Used | Affects how well it spots inflammation |
| Timing of the Scan | Best timing helps find inflammation better |
| Patient-Related Factors | Can affect how accurate SPECT results are, leading to false positives and negatives |
Knowing these factors helps doctors use SPECT better. This can lead to better care for patients.
SPECT for detecting inflammation has its limits. These include technical issues and factors related to the patient. Knowing these challenges helps in accurately reading SPECT images and making better clinical decisions.
SPECT imaging for inflammation has technical hurdles. One big issue is its lower image resolution compared to MRI or CT scans. This makes it hard to pinpoint where inflammation is, mainly in complex areas.
Key technical constraints include:
Factors related to the patient can also impact SPECT image quality. These include the patient’s size, movement during the scan, and other health issues that might affect how the radiotracer is taken up.
Notable patient-related factors are:
Reading SPECT images can be tough due to these factors. But, there are ways to improve accuracy. Using SPECT/CT, which combines functional and anatomical data, and advanced image processing can help. These methods can correct for common image problems.
Solutions to interpretation challenges include:
Diagnosing inflammatory diseases often requires different imaging methods. SPECT, PET, and MRI are among these options, each with its own benefits. It’s important to know how they differ to choose the best diagnostic tool.
SPECT and PET are nuclear medicine techniques for finding inflammation. They have some similarities but also key differences. SPECT uses radiotracers like Tc-99m HMPAO for leukocyte labeling. PET, on the other hand, uses 18F-FDG, a glucose analog that shows up in areas with high metabolic activity, like inflammatory sites.
SPECT is better at labeling and tracking specific cells, like leukocytes, for a more focused approach. But PET is more sensitive and has better resolution, making it better for spotting small inflammatory changes.
| Characteristics | SPECT | PET |
| Radiotracer | Tc-99m HMPAO | 18F-FDG |
| Sensitivity | High for specific infections | Very High for metabolic activity |
| Resolution | Lower compared to PET | Higher |
| Cell Tracking | Specific cell types (leukocytes) | Metabolic activity |
MRI is a strong tool for looking at inflammatory conditions, mainly in soft tissues. It doesn’t use ionizing radiation and gives detailed anatomical info. But, MRI’s ability to spot inflammation is more qualitative and not as sensitive as SPECT for some infections.
SPECT is better for finding infections in bones or prosthetic joints, where MRI might struggle. MRI, though, is better for soft tissue inflammation. It can be used with other techniques like diffusion-weighted imaging to improve its diagnostic power.
The right imaging modality depends on the clinical situation and the type of inflammation. SPECT is great for detecting and locating infections in bones or prosthetic materials. It’s also good for finding the cause of fever of unknown origin and certain inflammatory bowel diseases.
In summary, SPECT, PET, and MRI each have their own strengths and weaknesses in detecting inflammation. SPECT stands out because it can label and track leukocytes, making it very useful for specific clinical needs.
The world of SPECT technology is changing fast, with big steps forward in seeing inflammation. These new steps make SPECT scans better at finding and checking inflammatory diseases.
Hybrid imaging is a big leap in SPECT technology. It mixes SPECT with CT and MRI to give doctors a fuller picture of inflammation.
SPECT/CT is a top tool for seeing inflammation. It adds CT’s detailed body pictures to SPECT’s function info. This mix makes finding and pinpointing inflammation more precise.
SPECT/MRI is also becoming popular. MRI’s clear soft tissue views, when mixed with SPECT, help doctors see inflammation in tissues better.
| Hybrid Imaging Modality | Key Benefits | Clinical Applications |
| SPECT/CT | Combines functional and anatomical information, enhances accuracy | Infection imaging, inflammation detection |
| SPECT/MRI | Excellent soft tissue contrast, detailed inflammation assessment | Soft tissue inflammation, certain cancers |
Artificial intelligence (AI) is now used in SPECT image reading, including for inflammation. AI tools can sift through complex data, possibly making diagnoses more accurate and quicker.
AI helps spot small details that humans might miss. This can mean finding inflammation sooner and knowing how far it has spread more accurately.
AI in SPECT imaging is growing, and it’s expected to make SPECT scans even better at spotting inflammation.
SPECT imaging has become a key tool in
nuclear medicine
for spotting inflammation. It uses special tracers and advanced tech to give doctors vital info. This helps them make better choices for their patients.
SPECT scans are great at finding inflammation. They help doctors in many areas, like bone infections, bowel diseases, and unknown fevers. Special tracers help track where inflammation is happening.
As
inflammation diagnostics
gets better, SPECT will be even more important. New tech, like SPECT/CT, makes scans more accurate. Also, using AI to read images will help doctors even more.
In short, SPECT is a top-notch
diagnostic scan
that has changed how we fight inflammation. Its ability to show how inflammation works is essential in nuclear medicine today.
A SPECT scan is a way to see inside the body using special imaging. It uses tiny particles to show how different parts of the body work. This includes finding areas where there’s inflammation.
A leukocyte scan, or white blood cell scan, is a special imaging test. It uses tiny particles to track white blood cells. This helps find infections or inflammation in the body.
For SPECT scans, doctors often use Tc-99m HMPAO, Indium-111 Oxine, and Gallium-67 Citrate. These help highlight areas of inflammation.
To get ready for a SPECT scan, you might need a blood test. This blood is then mixed with a special particle. You might also need to follow certain diet or medicine rules. The exact steps depend on the scan and the particle used.
SPECT scans are used in many ways. They help find bone infections, check for inflammation in the gut, and diagnose infections in joints. They’re also good for finding the source of unknown fevers.
SPECT, PET, and MRI all help find inflammation, but in different ways. SPECT is great for bone infections. PET is very good at showing metabolic activity. MRI is excellent for soft tissue details. The right choice depends on the situation.
SPECT scans have some challenges. Technical issues, patient factors, and interpreting images can be tough. These can affect how accurate the scan is.
Recently, SPECT has improved a lot. New techniques like SPECT/CT and SPECT/MRI combine different views. Artificial intelligence also helps make readings more accurate.
Perfusion changes are key in SPECT scans. They show how blood flow changes in inflammation. This helps doctors diagnose conditions.
Immune system imaging with SPECT tracks white blood cells. This helps find infections or inflammation. It’s a powerful tool for understanding the immune system.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!