Feeling pain or leg pain can worry you and make daily tasks hard. At Liv Hospital, we know that leg discomfort is common in adults. It can come from muscle strain, too much use, or problems with blood vessels.
Studies show that up to 73 percent of adults have lower limb pain at some time. Women tend to have it more often. We’ll look at why you might have pain in lower left leg. This will help you understand what’s causing it and find ways to feel better.
Key Takeaways
- Muscle strain and overuse are common causes of lower leg pain.
- Vascular disorders can contribute to leg discomfort.
- Nerve impairment may lead to pain in the lower left leg.
- Bone injuries can also cause leg pain.
- Understanding the cause is key to effective leg pain relief.
Understanding the Causes of Lower Left Leg Pain
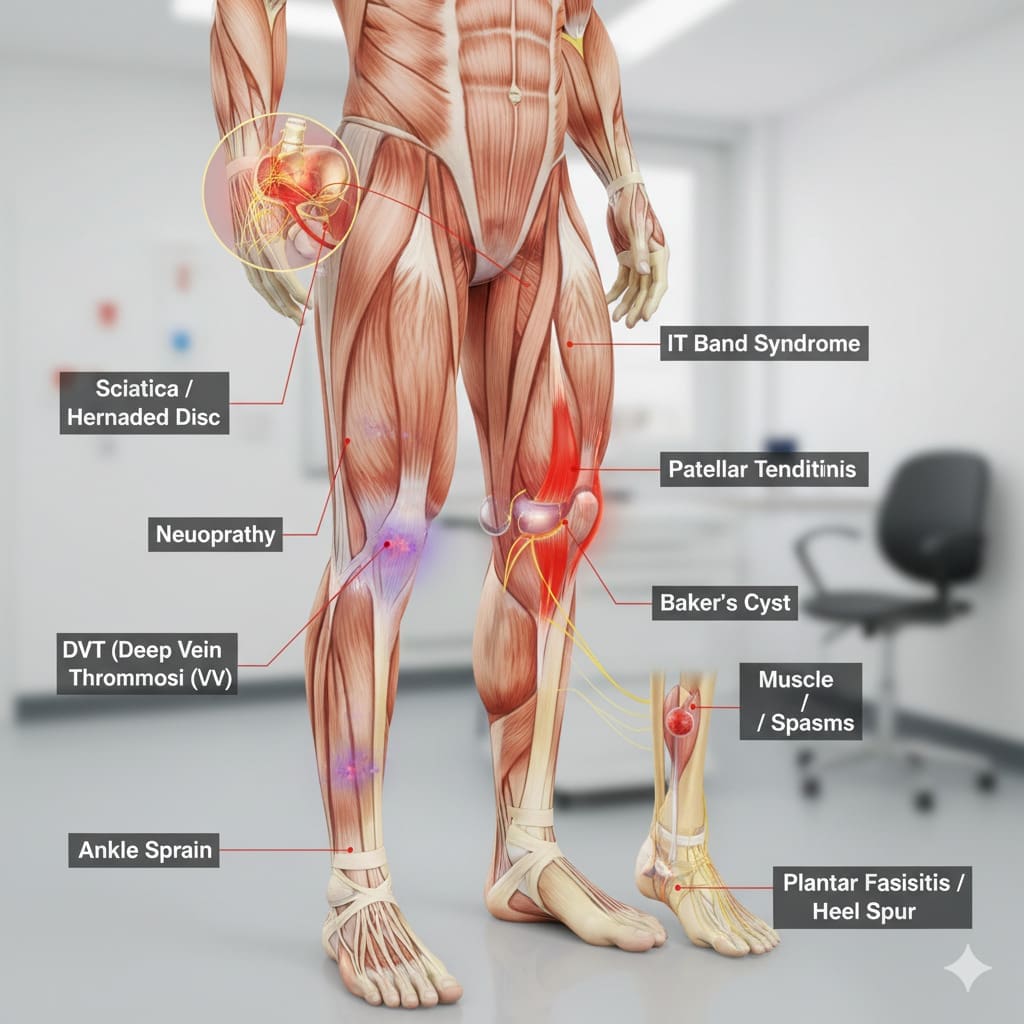
Figuring out why your lower left leg hurts is key to feeling better. Pain in this area can come from many things, like muscle strains or serious health issues.
Common Symptoms
People with lower leg pain often say they feel pain, swelling, and tenderness. The pain might be sharp, dull, or just a dull ache. It can be there all the time or only when they’re active. They might also find it hard to move their leg or feel unstable.
Characteristics of Lower Leg Pain
The kind of pain in your lower leg can tell you a lot about what’s wrong. For example, muscle strain might cause swelling and bruises. But nerve compression pain tends to be persistent and radiating. Knowing these details helps doctors figure out what’s going on.
| Cause | Characteristics | Associated Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Muscle Strain | Pain, swelling, bruising | Limited mobility, pain on movement |
| Nerve Compression | Radiating pain, numbness | Weakness, tingling sensations |
| Poor Circulation | Coldness, discoloration | Pain during activity, cramping |
Getting a correct diagnosis for lower leg pain means knowing the symptoms and what they mean. Doctors can then treat the real cause, helping you feel better and live a better life.
Muscle Strains and Overuse Injuries
Muscle strains and overuse injuries are common in the lower leg, mainly among those who do a lot of physical activities. The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons says muscle strains are common among athletes and those who exercise a lot.
Causes and Symptoms
Muscle strains happen when muscle fibers get stretched or torn. This can be due to too much use, sudden injury, or using the muscle the wrong way. Common symptoms include pain, swelling, and limited mobility in the affected area. Lower leg muscle strains can really hurt, making it hard to do daily activities and sports.
There are several reasons why muscle strains happen in the lower leg. These include:
- Overuse or repetitive strain on the muscle
- Sudden changes in exercise intensity or frequency
- Inadequate warm-up or cool-down exercises
- Poor training techniques or equipment
Knowing why muscle strains happen is key to preventing and treating them. A study in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy shows how important proper training and equipment are in avoiding overuse injuries.
Treatment and Prevention
To treat muscle strains, rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) are used. Physical therapy also helps by making the muscle strong and flexible again.
Preventing muscle strains is just as important. This includes:
- Gradually increasing exercise intensity and frequency
- Incorporating proper warm-up and cool-down routines
- Using the right training equipment and techniques
- Getting enough rest between intense workouts
| Treatment Method | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Rest | Avoiding activities that aggravate the condition | Allows the muscle to heal |
| Ice | Applying ice to reduce inflammation | Reduces pain and swelling |
| Compression | Using compression bandages to support the muscle | Provides support and reduces swelling |
| Elevation | Elevating the affected limb above heart level | Reduces swelling and promotes healing |
“Prevention is key when it comes to muscle strains and overuse injuries. By understanding the causes and taking proactive steps, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of injury and maintain optimal performance.”
Muscle Cramps and Spasms
Muscle cramps can suddenly stop you in your tracks. We’ll look at what causes them and how to find relief. This will help you manage and prevent them.
Causes and Relief Methods
Muscle cramps often come from dehydration, imbalanced electrolytes, or tired muscles. To ease the pain, you need to fix the root cause. Stretching and staying hydrated are key steps.
- Stretching: Gentle stretching can help relax the muscle and reduce cramping.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water and keeping electrolytes balanced can stop dehydration cramps.
Prevention Strategies
To avoid muscle cramps, make some lifestyle changes and listen to your body. Regular exercise, balanced diet, and adequate hydration are essential.
| Prevention Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Exercise | Engage in regular physical activity to improve muscle strength and flexibility. |
| Balanced Diet | Ensure adequate intake of essential nutrients, including potassium, magnesium, and calcium. |
| Adequate Hydration | Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated. |
Achilles Tendinitis and Other Tendon Inflammations
Achilles tendinitis is a condition that affects the tendon connecting the calf muscles to the heel bone. It leads to significant pain and discomfort. This condition is common among athletes and individuals who engage in activities that involve running or repetitive ankle motion.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of Achilles tendinitis include pain and stiffness in the Achilles tendon. This pain is usually felt in the morning or after periods of rest. The pain can be severe and may be accompanied by swelling and redness around the affected area.
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination. It may also include imaging tests such as X-rays or an MRI to rule out other conditions.
Understanding the causes and risk factors is key for prevention and treatment. Overuse, sudden changes in exercise intensity, and inadequate footwear are common factors that contribute to the development of Achilles tendinitis.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for Achilles tendinitis focuses on reducing pain and inflammation. It aims to promote healing and prevent further injury. Common treatment approaches include:
- Rest and ice to reduce pain and inflammation
- Physical therapy to strengthen the calf muscles and improve ankle mobility
- Orthotics and supportive devices to reduce stress on the Achilles tendon
- Anti-inflammatory medications to manage pain and swelling
In some cases, more advanced treatments may be necessary. This includes corticosteroid injections or surgical intervention for severe cases.
| Treatment | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Rest and Ice | Reducing activity and applying ice to reduce inflammation | Reduces pain and inflammation |
| Physical Therapy | Exercises to strengthen calf muscles and improve ankle mobility | Improves strength and flexibility |
| Orthotics | Using shoe inserts or devices to reduce stress on the Achilles tendon | Reduces stress on the tendon |
Stress Fractures and Bone Injuries
Athletes and those who do high-impact activities often get stress fractures. These can cause a lot of pain in the lower leg. We’ll look at why they happen, what symptoms to watch for, and how to treat them.
Causes and Symptoms
Stress fractures and bone injuries in the lower leg come from too much strain on the bones. Pain that gets worse with activity and better with rest, swelling, and bruising are common symptoms. If not treated, they can get much worse.
Diagnosis and Recovery
To find out if you have a stress fracture, doctors will check you physically, ask about your health history, and use X-rays or MRI. Getting better usually means resting, not moving the area, and doing exercises to make the bone and muscles stronger. It’s important to listen to your doctor to heal right and avoid more harm.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition where a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs. It needs quick medical attention to avoid serious problems.
Recognizing DVT Symptoms
It’s key to know the symptoms of DVT to get help early. Common signs include:
- Swelling in the affected leg
- Pain or tenderness, often described as a cramp or soreness
- Redness or discoloration of the skin
- Warmth or a feeling of heat in the affected area
Some people with DVT might not show any symptoms. This makes it a silent danger.
Treatment and Complications
Treating DVT involves medicines and lifestyle changes. These help stop the clot from getting bigger and reduce risks. Common treatments are:
- Anticoagulant medications to thin the blood and prevent new clots
- Thrombolytic therapy to dissolve the clot in severe cases
- Use of compression stockings to reduce swelling
A big risk of DVT is pulmonary embolism. This happens when a clot part breaks off and goes to the lungs. It can block blood flow and is a medical emergency.
We stress the need to see a doctor if symptoms don’t go away or get worse. Early treatment can greatly improve DVT outcomes.
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
We often see patients with Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD). This condition makes it hard for blood to flow to the legs. It’s often linked to atherosclerosis, where plaque blocks the arteries.
Understanding Claudication Pain
One key sign of PAD is claudication pain. This is muscle pain or cramping in the legs when walking or exercising. The pain goes away when you rest.
This pain happens because the blood flow to muscles is too low. When you move more, your muscles need more oxygen. But with less blood flow, they can’t get enough.
Diagnostic Approaches
To find PAD, doctors use physical checks, medical history, and tests. The ankle-brachial index (ABI) is a key test.
- The ABI test compares ankle and arm blood pressure.
- A lower ABI means PAD might be present.
- Other tests include ultrasound, angiography, or blood tests to check for risk factors.
Management and Treatment
Managing PAD means changing your lifestyle and sometimes using medicine or surgery.
| Treatment Approach | Description |
|---|---|
| Lifestyle Modifications | Stop smoking, exercise, and eat right to manage risk factors. |
| Medications | Help with symptoms, improve walking, and lower heart risk. |
| Surgical Interventions | Procedures like angioplasty or bypass surgery to improve blood flow. |
“Early diagnosis and treatment of PAD can significantly improve the quality of life for patients by reducing symptoms and preventing complications.”
We stress the need to see a doctor if symptoms don’t get better or get worse. Knowing about PAD and how to manage it helps us improve patient care.
Why Pain in Lower Left Leg May Indicate Nerve Problems
Pain in the lower left leg might mean you have nerve problems. These issues can make you feel uncomfortable and impact your daily life. Knowing what causes and types of nerve pain are important for managing them.
Types of Neuropathic Pain
Neuropathic pain in the lower leg can feel like sharp shooting pains, burning sensations, or numbness and tingling. These feelings can come and go or stay all the time. They might get worse when you move or at night. There are a few main types of neuropathic pain:
- Diabetic neuropathy
- Radiculopathy (nerve root pain)
- Peripheral neuropathy
Each type has its own reasons and signs. For example, diabetic neuropathy is linked to diabetes. Radiculopathy happens when a nerve in the spine gets compressed.
Diagnostic Process and Treatment Options
To find out if you have nerve pain in your lower leg, doctors will look at your medical history and do a physical exam. They might also do tests like nerve conduction studies or electromyography. Knowing what’s causing the pain is key to picking the right treatment.
There are many ways to treat neuropathic pain:
- Medications: anticonvulsants, antidepressants, or pain relievers
- Physical therapy: to improve mobility and strength
- Alternative therapies: acupuncture, nerve stimulation
It’s important to talk to doctors to find the best treatment for you. Sometimes, fixing the problem that’s causing the pain, like managing diabetes, can help.
Learning about neuropathic pain and how to diagnose and treat it can help you manage your condition. This can improve your life a lot.
Compartment Syndrome: Acute and Chronic Forms
Compartment syndrome is a serious condition. It happens when muscle compartments get too much pressure. This can be from injury or too much use.
This high pressure can cut off blood to muscles and nerves. This leads to pain, swelling, and serious problems if not treated fast.
Recognizing Compartment Syndrome
Symptoms of compartment syndrome include severe pain that doesn’t match the injury. You might also see swelling and tightness in the limb. Sometimes, people feel numbness or tingling, and the skin might feel cool.
It’s key to spot these signs early to avoid lasting harm.
Acute compartment syndrome is a medical emergency. If you think someone has it, get them to a doctor fast. Chronic compartment syndrome takes longer to develop. It often affects athletes who do the same thing over and over, like running.
Diagnostic Testing and Interventions
Doctors use tests and check muscle compartment pressure to diagnose. Treatment depends on how bad it is and what type it is. For severe cases, surgery to relieve pressure is needed right away.
For milder cases, rest, physical therapy, and changing how you do activities might help.
Knowing about compartment syndrome’s causes, symptoms, and treatments is important. Quick action and the right treatment can greatly help those with this condition.
Inflammatory and Infectious Conditions
Inflammatory and infectious conditions in the lower leg are more common than you might think. They can greatly affect your daily life. These issues range from mild to severe and include different infections and inflammatory diseases.
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
Skin and soft tissue infections in the lower leg can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. Symptoms include redness, swelling, warmth, and pain. Common types are cellulitis, abscesses, and necrotizing fasciitis.
| Infection Type | Causes | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cellulitis | Bacterial infection | Redness, swelling, pain | Antibiotics |
| Abscesses | Bacterial infection | Painful swelling, redness | Drainage, antibiotics |
| Necrotizing Fasciitis | Bacterial infection | Severe pain, swelling, redness | Surgical intervention, antibiotics |
Inflammatory Arthritis and Autoimmune Conditions
Inflammatory arthritis and autoimmune conditions can affect the lower leg. They cause pain and discomfort. Rheumatoid arthritis, for example, can lead to inflammation and pain in the joints.
Autoimmune conditions happen when the body attacks its own tissues. In the lower leg, this can cause pain, swelling, and stiffness.
Conclusion: When to Worry About Lower Left Leg Pain
Knowing when to see a doctor for lower left leg pain is key. We’ve talked about many reasons, like muscle strains and vascular issues. Lower leg pain hits up to 73 percent of adults at some point, making it a big health issue.
If you have ongoing or bad lower leg pain, finding the cause is important. Look for signs like swelling, redness, or warmth. Getting help early can stop bigger problems.
Think about your health history, lifestyle, and how bad the pain is. If you’re not sure what to do, talk to a doctor. Being quick to address lower leg pain can help avoid serious issues and keep you feeling better.
References
WebMD: Lower Leg Pain: Causes and Treatments
The Feet People: Causes of Lower Leg Pain at Night


































