Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
MRI is key in telling apart benign from malignant tumors. It gives us detailed clues for accurate diagnoses and care plans. MRI is the top choice for spotting and understanding brain tumors without surgery.
MRI shows us the size and shape of tumors, helping us tell if they are benign or malignant. By looking at these signs, we can figure out what kind of tumor it is. This helps us plan the best treatment. Understand malignant brain tumor MRI signs. See 7 crucial differences on the scan that help distinguish a benign from a malignant mass.
Key Takeaways
- MRI is the gold standard for detecting and characterizing brain tumors.
- Distinct imaging features on MRI help differentiate benign from malignant tumors.
- A systematic approach to analyzing MRI scans is critical for accurate diagnosis.
- MRI provides unmatched detail for precise diagnoses and individualized care.
- Effective treatment plans can be developed based on MRI findings.
Understanding Brain Tumors and MRI Technology
Advances in MRI technology have greatly improved brain tumor diagnosis. Brain tumors are abnormal cell growths in the brain, ranging from benign to malignant. Knowing about these tumors and how to detect them is key for treatment.
What Are Brain Tumors and Their Classification
Brain tumors are divided by their origin and behavior. Primary tumors start in the brain, while metastatic ones spread from other parts. The World Health Organization (WHO) uses a system to classify tumors based on their features and behavior.
| Tumor Type | Origin | Malignancy |
| Primary Brain Tumor | Originates in the brain | Can be benign or malignant |
| Metastatic Tumor | Spreads to the brain from other parts | Malignant |
How MRI Works in Brain Tumor Detection
MRI technology uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed brain images. It’s great for finding brain tumors because it shows their size, location, and type.
In summary, knowing about brain tumors and MRI’s role in finding them is essential. Accurate tumor classification and MRI imaging help doctors plan treatments.
Can MRI Detect Brain Tumors? Capabilities and Limitations
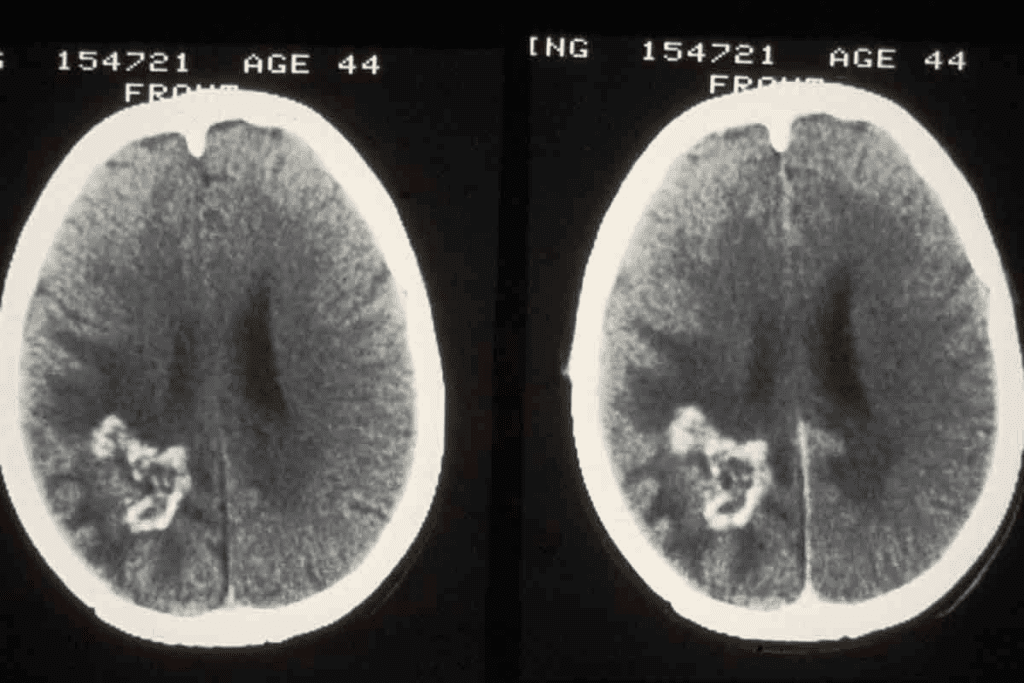
MRI technology has changed neurology, helping us find brain tumors. It gives us detailed brain images for diagnosis and tracking. But, how well does MRI find brain tumors, and what can’t it do?
Detection Accuracy of MRI for Brain Lesions
MRI is great at finding brain lesions, like tumors. Studies show MRI is very accurate, thanks to advanced methods like diffusion-weighted imaging. Experts say MRI is the top choice for brain tumor diagnosis because it’s so precise.
While MRI is very good at finding brain lesions, it has its limits. It can be hard to tell different tumor types or spot small lesions. “MRI’s accuracy in finding brain tumors depends on the MRI sequence used and the radiologist’s skill,” a top neuroradiologist notes.
When Additional Diagnostic Methods Are Needed
Even with MRI’s power, sometimes more tests are needed to confirm a diagnosis. For example, if MRI shows a tumor, a biopsy might be needed to know the tumor’s type and grade. CT scans or PET scans might also be used with MRI for a fuller picture of the tumor.
Advanced MRI techniques like MR spectroscopy or functional MRI can give more details about the tumor. As MRI technology improves, we can better diagnose and treat brain tumors.
Malignant Brain Tumor MRI: General Characteristics
MRI is key in spotting malignant brain tumors by showing specific traits. When we look at MRI scans, we see certain signs that help tell them apart from benign tumors.
Common Features of Malignant Lesions
Malignant brain tumors show certain signs on MRI that indicate they are aggressive. These include irregular margins, heterogeneous enhancement, and necrosis. Irregular margins mean the tumor is growing into the brain. Heterogeneous enhancement shows different blood flow and activity levels.
Necrosis, or dead cells in the tumor, is a sign of malignancy. It looks like dark spots on T1 images and bright spots on T2 images. These spots are often surrounded by uneven enhancement.
“The presence of necrosis within a brain tumor is a strong indicator of malignancy, as it reflects the tumor’s rapid growth outpacing its blood supply.”
Typical Appearance of Primary vs. Metastatic Malignant Tumors
Primary and metastatic malignant brain tumors look different on MRI. Primary tumors, like glioblastoma, grow into the brain tissue, making their edges hard to see. They show uneven enhancement and may have necrosis.
| Characteristics | Primary Malignant Tumors | Metastatic Malignant Tumors |
| Margins | Infiltrative, irregular | Well-defined, often multiple |
| Enhancement Pattern | Heterogeneous, with necrosis | Variable, often ring enhancement |
| Necrosis | Common | Less common, but can occur |
Metastatic tumors, though, are clear and might look the same, often with ring enhancement. They usually show up in more than one place.
Knowing these MRI signs is key to diagnosing and treating malignant brain tumors. By spotting the typical traits of primary and metastatic tumors, we can make better treatment plans and help patients more.
Key MRI Sign #1: Irregular and Infiltrative Margins
Irregular and infiltrative margins are a key sign of malignant brain tumors on MRI scans. These margins are important in telling benign from malignant lesions. We will look at how these margins are checked and why they matter in diagnosis.
Border Characteristics of Malignant Tumors
Malignant brain tumors show irregular and infiltrative margins. This is a sign of their aggressive nature. These margins mean the tumor is spreading into the brain tissue around it, making surgery hard.
Comparison with Well-Defined Borders of Benign Tumors
Benign tumors, on the other hand, have well-defined borders. This means they have a clear edge from the brain tissue around them. This is key for doctors when they look at MRI scans to tell benign from malignant tumors.
| Tumor Characteristic | Benign Tumors | Malignant Tumors |
| Margin Characteristics | Well-defined borders | Irregular and infiltrative margins |
| Growth Pattern | Slow-growing, non-invasive | Rapid growth, invasive |
Distinguishing between benign and malignant brain tumors is critical for diagnosis and treatment. MRI’s skill in showing these differences makes it essential in neuro-oncology.
Key MRI Sign #2: Heterogeneous Enhancement Patterns
When we look at brain tumors on MRI, one key sign is the heterogeneous enhancement pattern. This pattern is very important in telling us if a tumor is benign or malignant.
To understand heterogeneous enhancement, we need to know about contrast enhancement in brain tumors. Contrast enhancement uses a contrast agent, like gadolinium, to show certain brain areas on MRI scans. Tumors often show up because they break the blood-brain barrier, letting the contrast agent get in.
Understanding Contrast Enhancement in Brain Tumors
Contrast enhancement is key in MRI for brain tumors. It helps find the tumor’s presence, size, and sometimes its type. The way and how much a tumor grows can differ a lot between tumor types.
Heterogeneous enhancement means the contrast doesn’t take up evenly in a tumor. This shows up as different intensities on MRI images after contrast is added.
Significance of Non-Uniform Enhancement
Heterogeneous enhancement often means the tumor is malignant. Malignant tumors have irregular blood flow, dead cells, and bleeding. This leads to uneven enhancement on MRI. For example, glioblastomas, a type of aggressive brain tumor, often show uneven enhancement because of their messy blood vessels.
To show how important heterogeneous enhancement is, let’s look at a table comparing benign and malignant brain tumors:
| Characteristics | Benign Tumors | Malignant Tumors |
| Enhancement Pattern | Typically homogeneous | Often heterogeneous |
| Contrast Uptake | Uniform | Variable, with areas of necrosis or hemorrhage |
| Implication | Suggests a more organized tumor structure | Indicates possible malignancy with irregular vascularity |
In conclusion, MRI shows heterogeneous enhancement patterns are a big sign of malignancy in brain tumors. Knowing and spotting these patterns is key to correct diagnosis and treatment plans.
Key MRI Sign #3-4: Necrosis and Surrounding Edema
MRI scans are key in spotting brain tumors by showing signs like necrosis and edema. These signs help doctors diagnose and understand brain cancer better.
Central Necrosis as a Malignancy Indicator
Central necrosis in brain tumors shows they are cancerous. It happens when the tumor grows too fast and can’t get enough blood. This leads to cell death in the tumor’s center.
On MRI, necrosis looks like a dark spot in the tumor. It shows the tumor is aggressive.
The necrotic areas look different on MRI because of dead cells and blood. This makes the tumor look uneven.
Peritumoral Edema: Extent and Significance
Peritumoral edema is swelling around the tumor seen on MRI. The amount of swelling varies by tumor type. Cancerous tumors usually have more swelling.
Edema is important because it affects the brain around the tumor. It can cause pressure and harm brain function. MRI helps doctors see how much swelling there is.
Knowing about necrosis and edema helps doctors treat brain tumors better. These signs help figure out how serious the cancer is and what treatment to use.
Key MRI Sign #5-7: Mass Effect, Diffusion Restriction, and Perfusion Abnormalities
When we look at brain tumors, MRI signs like mass effect, diffusion restriction, and perfusion abnormalities are key. These signs help us understand how aggressive a tumor is.
Mass Effect and Midline Shift
The mass effect happens when a tumor pushes brain structures away. This is common in malignant tumors. It can cause a midline shift, where brain tissue gets pushed too far.
We check the mass effect by seeing how much the brain is shifted. A big shift means the tumor is very aggressive and might need quick treatment.
Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Tumor Characterization
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is a special MRI scan. It shows how water moves in the tumor. This tells us about the tumor’s cells and if it’s dead.
Malignant tumors have less water movement because they’re very dense. This shows up as bright on DWI and dark on ADC maps. It helps us tell if a tumor is bad or not.
Perfusion MRI and Blood Flow Patterns
Perfusion MRI looks at how blood flows through tumors. Malignant tumors have more blood flow because they grow new blood vessels.
We use DSC perfusion MRI to see how much blood is in the tumor. More blood means the tumor is likely aggressive. This helps us tell if a tumor is serious or not.
| MRI Sign | Characteristics of Malignant Tumors | Clinical Significance |
| Mass Effect | Significant displacement of surrounding brain structures | Potential for midline shift and compression of vital structures |
| Diffusion Restriction | Hyperintensity on DWI, hypointensity on ADC | Indicates high cellularity, helps differentiate from benign lesions |
| Perfusion Abnormalities | Increased rCBV on perfusion MRI | Suggests neoangiogenesis, associated with high-grade malignancies |
By looking at these MRI signs, we can really understand a tumor. This helps us plan the best treatment and improve patient care.
Advanced MRI Techniques and Radiomic Models
Medical imaging is getting better, thanks to advanced MRI techniques and radiomic models. These tools help us understand brain tumors better. They make diagnoses more accurate and help decide on treatments.
MR Spectroscopy and Metabolic Signatures
MR spectroscopy lets us check brain tumors’ metabolism without surgery. It looks at metabolic signs to tell different tumor types apart. This info is key for making treatment plans.
Some metabolites show how aggressive a tumor is. For example, high choline levels mean the tumor is growing fast. Low N-acetylaspartate (NAA) levels mean brain cells are damaged.
Functional MRI and Tumor Mapping
Functional MRI (fMRI) maps brain function near tumors. It’s great for planning surgery, as it shows important brain areas to keep safe.
fMRI checks how the brain reacts to different things. It shows how tumors affect the brain. This helps surgeons plan safer, more precise surgeries.
Recent Advances in Radiomic Models for Tumor Differentiation
Radiomic models use medical images to tell tumors apart. New machine learning has made these models even better.
These models look at many imaging details to find patterns we can’t see. They’re good at telling primary and metastatic tumors apart. They also find genetic mutations.
As these technologies get better, we’ll be able to diagnose more accurately. This will lead to better care for patients.
Conclusion: From Imaging to Diagnosis and Treatment
We’ve looked at how MRI helps tell the difference between harmless and dangerous brain tumors. It shows seven important signs that help doctors diagnose.
MRI is key in finding and treating brain tumors. It gives detailed pictures that help doctors decide the best treatment. This leads to better care for patients.
In hospitals, MRI is a must-have tool. It helps doctors find and understand brain lesions very well. With advanced MRI, like diffusion-weighted imaging, we learn more about tumors.
What MRI scans show helps doctors choose the right treatment. This could be surgery or special medicines. As MRI gets better, so will our ability to diagnose and treat brain tumors.
Overall, MRI has changed how we handle brain tumors. Its growth will keep improving care and results for patients.
FAQ
Can MRI detect brain tumors?
Yes, MRI is very good at finding brain tumors. It shows the brain in detail. This helps doctors spot tumors and tell if they are cancerous.
What do tumors look like on MRI?
Tumors on MRI look different based on their type. Cancerous tumors often have unclear edges and don’t look the same everywhere. They might also cause swelling around them.
How accurate is MRI in detecting brain tumors?
MRI is very good at finding brain tumors. But, how well it works can change. This depends on the tumor, where it is, and the MRI method used.
Can MRI distinguish between benign and malignant brain tumors?
Yes, MRI can tell the difference between good and bad tumors. It looks at things like how clear the edges are and how the tumor reacts to contrast.
What is the role of contrast enhancement in MRI for brain tumors?
Contrast enhancement in MRI shows how blood moves through tumors. It helps doctors see if a tumor is likely to be cancerous. Uneven enhancement can mean it’s bad.
What are the typical MRI features of malignant brain tumors?
Bad tumors on MRI have unclear edges and don’t look the same everywhere. They might have dead spots in the middle and cause swelling.
Can MRI detect brain cancer?
Yes, MRI can find brain cancer. It’s a key tool for diagnosing and understanding brain cancer.
Does MRI show a brain tumor?
Yes, MRI can show brain tumors. It gives details about their size, where they are, and what they look like.
Would an MRI show a brain tumor?
Usually, yes, an MRI can show a brain tumor. But it depends on the tumor’s size, where it is, and what it is.
What does cancer look like on MRI?
Cancer on MRI looks like a mass with unclear edges and uneven enhancement. It can look different based on the tumor’s type and location.
How does MRI help in diagnosing and managing brain tumors?
MRI is key in finding and managing brain tumors. It gives doctors detailed images. This helps them plan treatment and check how well it’s working.
References
- Yu, H., et al. (2023). Differential diagnosis of intracranial malignant tumors using MRI based on morphological features and signal intensity ratio of lesions. Alternative Therapies in Health and Medicine. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37773646/