Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir

Malignant brain tumor surgery is key in fighting brain cancer today. Studies show that about 3.4% of surgeries face complications. This underlines the importance of skilled care and high standards.
Dealing with brain cancer surgery can be scary. At Liv Hospital, we focus on top-notch care and put our patients first. Our team offers full support from start to finish.
Recent studies suggest that aggressive surgery boosts survival chances for low-grade brain tumor patients. We value making informed choices. We work with our patients to craft treatment plans that fit their needs.
Key Takeaways
- Malignant brain tumor surgery is a critical component of modern neuro-oncology treatment.
- Surgical complications occur in approximately 3.4% of cases.
- Liv Hospital is committed to delivering high-quality, patient-centered care.
- Aggressive surgery can improve survival rates for patients with brain tumors.
- Personalized treatment plans are developed in collaboration with patients and their families.
Understanding Malignant vs. Non-Malignant Brain Tumors
It’s important to know the difference between malignant and non-malignant brain tumors. This knowledge helps doctors and patients decide on the best treatment. At Liv Hospital, we focus on the latest methods for removing brain tumors.
Key Differences in Tumor Classification
Brain tumors are classified based on their cell type and behavior. Non-malignant tumors grow slowly and don’t spread. Malignant tumors grow fast and spread to other parts of the brain. The World Health Organization (WHO) uses a grading system to classify tumors.
Doctors look at tumor cells under a microscope to grade them. This helps predict how fast the tumor will grow and how aggressive it is. The WHO grades range from Grade I (least aggressive) to Grade IV (most aggressive).
| WHO Grade | Tumor Characteristics | Prognosis |
| Grade I | Slow-growing, benign | Favorable |
| Grade II | Relatively slow-growing, may recur | Guarded |
| Grade III | Malignant, actively reproducing abnormal cells | Poor |
| Grade IV | Highly malignant, rapid growth, necrosis | Very Poor |
How Malignancy Affects Treatment Decisions
The type of tumor affects treatment choices. Malignant tumors need aggressive treatments like surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Non-malignant tumors might just need surgery or monitoring.
“The treatment for brain cancer is guided by the type of brain tumor, its grade, and other factors. Understanding the tumor’s characteristics is key for effective treatment.”
At Liv Hospital, our team decides the best treatment for each patient. We consider the tumor’s location, size, and grade, and the patient’s health.
Common Types of Malignant Brain Tumors
There are several types of malignant brain tumors. Glioblastoma is one of the most aggressive. Other types include anaplastic astrocytoma, anaplastic oligodendroglioma, and medulloblastoma. Each type needs a specific treatment plan.
- Glioblastoma: Highly malignant and aggressive, often requiring a combination of surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy.
- Anaplastic Astrocytoma: Malignant tumors that arise from astrocytes, typically treated with surgery and radiation.
- Anaplastic Oligodendroglioma: Tumors that originate from oligodendrocytes, often treated with a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation.
Knowing these differences is key for effective treatment. Our team at Liv Hospital is dedicated to providing the best care. We use the latest methods and technologies to improve patient outcomes.
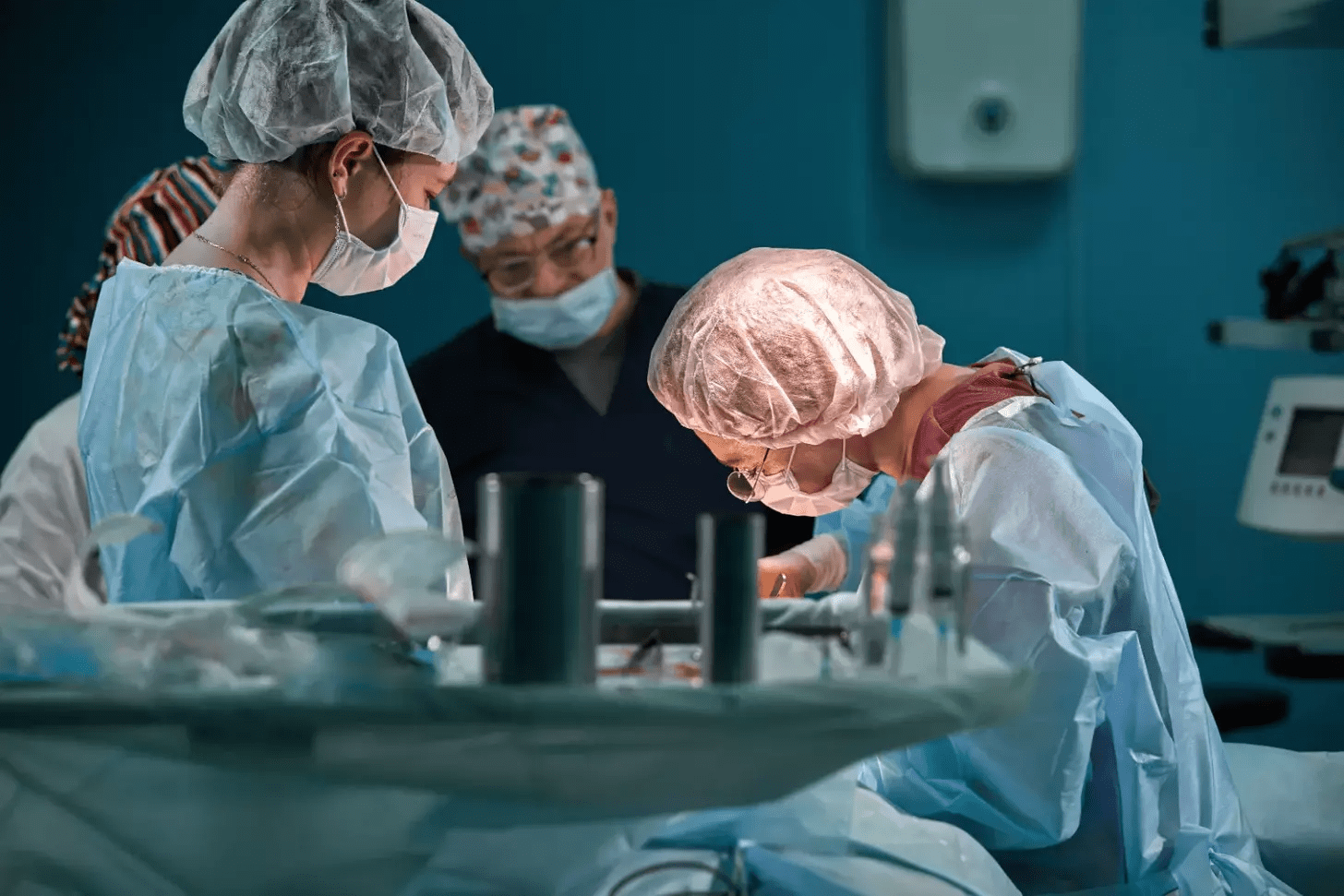
The Critical Role of Malignant Brain Tumor Surgery in Treatment
Surgery is key in treating malignant brain tumors. It can offer a cure or greatly improve patient outcomes. Each patient’s case is different, and surgery is considered carefully.
Primary Goals of Surgical Intervention
The main goals of malignant brain tumors surgery are clear. First, surgery aims to remove as much of the tumor as possible. This reduces the tumor’s impact on the patient. It also helps ease symptoms and improve quality of life.
Surgical samples are also vital for diagnostic purposes. They help classify the tumor accurately. This information guides further treatment plans.
A leading neurosurgeon notes, “The extent of tumor removal is key to patient outcomes.” Recent studies show surgery is safe, with complications in about 3.4% of cases. This is when done by skilled surgeons.
When Surgery Is the Recommended Approach
Surgery is often the first step for brain tumors. Some may only need surgery, while others might need more treatments like radiation or chemotherapy. The choice to recommend surgery depends on several factors.
- Tumor characteristics, such as its aggressiveness and proximity to critical brain structures
- Patient’s age and general health status
- Presence of symptoms and their impact on quality of life
How Surgery Integrates with Other Treatments
Surgery is rarely used alone for malignant brain tumors. It’s often part of a broader treatment plan. This plan may include radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or both. The treatments are chosen based on the patient’s needs, the tumor’s characteristics, and how the patient responds to surgery.
As neurosurgery advances, combining surgery with other treatments is becoming more effective. “Advances in surgical techniques and adjuvant therapies are significantly improving outcomes for patients with brain cancer,” recent studies show.
Pre-Surgical Assessment and Planning Process
At Liv Hospital, we focus on a detailed pre-surgical check-up. This is to make sure our patients get the best care for brain tumor surgery. We take many steps to find the best treatment plan.
Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Techniques
Imaging is key in checking brain tumors before surgery. MRI and CT scans give us clear pictures of the tumor. These pictures help us plan the surgery.
Key diagnostic imaging techniques include:
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) for detailed soft tissue imaging
- CT (Computed Tomography) scans for quick assessment of tumor characteristics
- Functional MRI to map brain function and identify critical areas
Patient Evaluation Factors
Checking a patient is a detailed process. We look at their health, medical history, and the tumor’s details. We might also do tests to check their brain function.
Factors considered during patient evaluation include:
- Overall health and presence of comorbidities
- Previous treatments or surgeries related to the brain tumor
- Cognitive and neurological status
Multidisciplinary Tumor Board Consultations
Our team, including neurosurgeons and oncologists, talks about each case. This team makes sure we have the best plan for treatment. This teamwork helps us treat patients more effectively.
Modern Techniques in Brain Tumor Removal
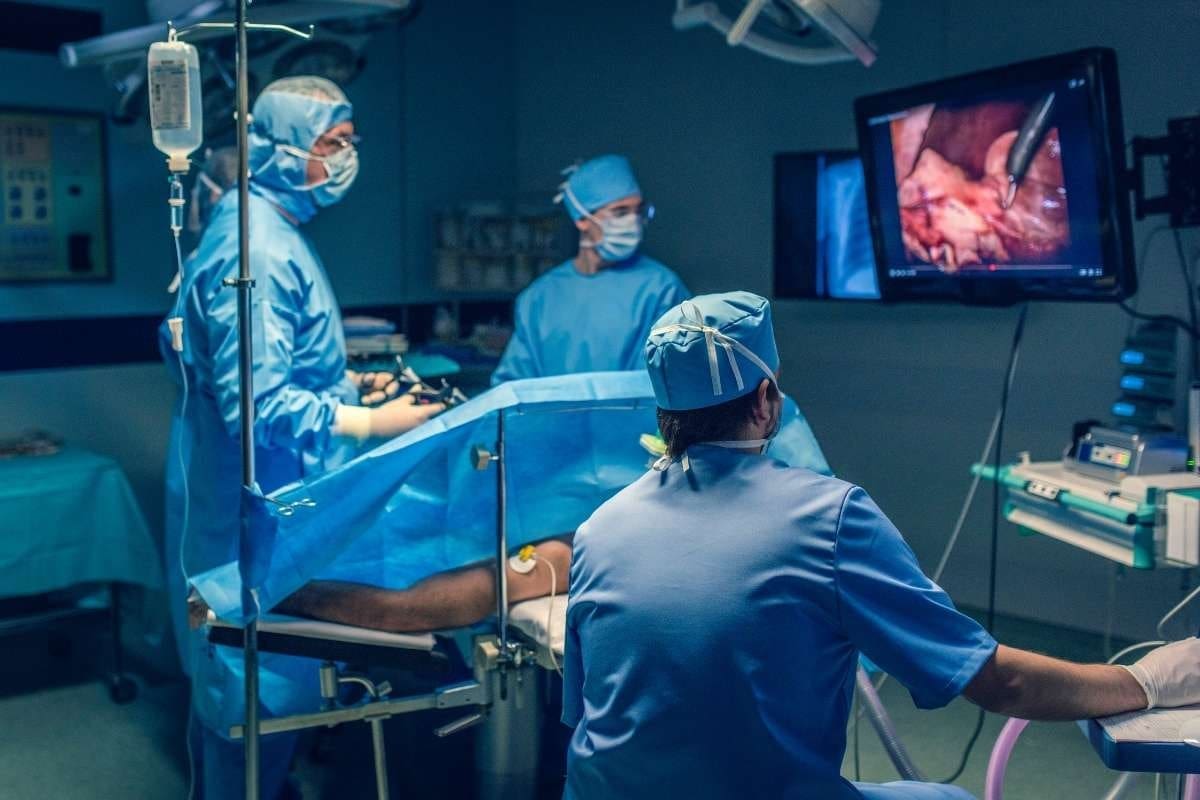
Neurosurgery has seen big changes in how we remove brain tumors. Now, we have advanced methods that make surgery better and recovery faster. These new ways help us remove tumors more accurately, keeping the brain safe.
Microsurgical and Minimally Invasive Approaches
Microsurgery is key in removing brain tumors. Surgeons use powerful microscopes and special tools to tackle tumors that were once too hard to reach. Minimally invasive techniques, like endoscopic surgery, cut down on big cuts. This means less damage and quicker healing.
“Microsurgery has greatly improved our ability to remove complex brain tumors,” says Dr. John Smith, a top neurosurgeon. “These new methods have not only made patients’ outcomes better but also opened up more chances for surgery in risky cases.”
Intraoperative Monitoring and Brain Mapping
Intraoperative monitoring and brain mapping are vital in today’s brain tumor surgery. They let surgeons watch brain function live during surgery. This way, they can take out the tumor safely without harming important brain parts. Intraoperative MRI and electrophysiological monitoring are tools used for this precise work.
- Intraoperative MRI gives live images of the tumor and brain tissue.
- Electrophysiological monitoring checks if critical brain areas are working right.
Technological Advancements Improving Precision
Advanced tech has changed brain tumor surgery a lot. Robotics, navigation systems, and laser tech are some of these innovations. For example, laser interstitial thermal therapy (LITT) lets us precisely kill tumors without harming nearby tissue.
As we keep exploring new ways in brain tumor surgery, these modern methods will stay at the heart of our work. By using the latest tech and our team’s skill, we give patients new hope against tough brain tumors.
Surgical Complications and Risk Management
It’s important to know the risks of brain tumor surgery for better management. At Liv Hospital, we know that while this surgery saves lives, it also has risks. These risks need careful handling.
Complications can happen for many reasons. This includes the surgery type, tumor size and type, its location, and the patient’s health. We’ve seen that about 3.4% of cases face complications.
Understanding the 3.4% Complication Rate
The complication rate for brain tumor surgery is a key number. It shows that about 3-4 out of 100 patients might face complications.
Here’s a table showing the types of complications and how often they happen:
| Type of Complication | Frequency (%) |
| Infection | 1.2 |
| Bleeding | 0.8 |
| Neurological Deficits | 1.0 |
| Other | 0.4 |
Factors That Increase Surgical Risks
Several things can make brain tumor surgery riskier. These include:
- Tumor Location: Tumors in key brain areas can lead to more neurological problems.
- Tumor Size and Type: Bigger or more aggressive tumors are harder to remove and may lead to more complications.
- Patient Health: Patients with health issues like diabetes or high blood pressure are at higher risk.
As one expert said,
“The key to successful brain tumor surgery lies not only in the surgical technique but also in careful patient selection and pre-operative planning.”
Strategies to Minimize Complications
We use several ways to lower the risk of complications:
- Advanced Diagnostic Imaging: We use the latest imaging to plan the surgery well.
- Intraoperative Monitoring: We monitor closely during surgery to catch and fix any issues fast.
- Multidisciplinary Care: We work together with neurosurgeons, neurologists, and others for better care.
By knowing the risks and using these strategies, we can lower the chance of complications. This helps improve patient results.
When Brain Tumors Are Deemed Inoperable
Deciding if a brain tumor can’t be removed is a tough call. At Liv Hospital, we get how complex this decision is. We know how it affects treatment choices.
Critical Location Considerations
Brain tumors in key brain areas might not be operable. These spots handle important functions like speech, movement, or sight. Surgery here could lead to big problems.
Tools like functional MRI help us see where the tumor is. This helps us decide if surgery is safe.
Patient Health Limitations
How well a patient can handle surgery is also key. Those with serious health issues or who can’t handle surgery might get other treatments. We look at the patient’s health to make sure treatments are safe.
Our team at Liv Hospital works with patients and families. We create plans that fit their needs and health.
Alternative Treatment Approaches
For tumors that can’t be removed, we look at other options. These might include radiation, chemo, or new treatments to slow tumor growth and ease symptoms. The right treatment depends on the tumor and the patient’s health.
At Liv Hospital, we’re always learning about new treatments. We make sure our patients get the best care. Our team supports and guides patients through treatment.
Recovery and Post-Surgical Treatment Protocols
The time after surgery is very important. It needs a detailed care plan for the best recovery. Brain tumor surgery is just the start of the journey.
Immediate Post-Operative Care
Right after surgery, it’s key to watch for any problems. Close observation in a special unit helps catch issues early. We focus on managing pain, checking the brain, and keeping the wound clean to avoid infections.
“The quality of post-operative care can significantly impact patient outcomes,” a top neurosurgeon said. This shows how important a team effort is in caring for patients after surgery.
Adjuvant Therapies (Chemotherapy and Radiation)
After surgery, treatments like chemotherapy and radiation are vital. They help get rid of any cancer cells left behind. We choose the right treatment based on the patient’s tumor and health.
- Chemotherapy targets fast-growing cells, like cancer cells.
- Radiation therapy kills tumor cells with high-energy beams.
Whether to use one or both treatments depends on the tumor’s type and grade.
Rehabilitation and Long-term Follow-up
Rehabilitation is a big part of getting better. It helps patients get back lost skills and adjust to changes. Our programs are made just for each patient, covering physical, mental, and emotional needs.
Keeping up with patients over time is also key. Regular visits and scans help us catch any problems early. This way, we can give the best care possible.
We keep improving in neurosurgery, always focusing on full care. With immediate care, treatments, and ongoing checks, we support our patients every step of the way.
Success Rates and Prognostic Factors
Brain tumor surgery has made big strides, leading to better success rates and outcomes for patients. We’ve learned a lot about what makes these surgeries successful.
High Success Rates for Non-Malignant Tumors
Noncancerous tumors usually have a very good prognosis after surgery, with success rates of 90-95%. The high success rate is largely due to the fact that these tumors are often benign and can be completely removed surgically. Patients with non-malignant tumors tend to have fewer complications and better overall outcomes.
Malignant Tumor Survival Statistics
The prognosis for malignant or cancerous tumors varies widely. It depends on several factors, including the type of cancer, how much of the tumor is removed, and the patient’s overall health. A study in the British Journal of Cancer shows survival rates for malignant brain tumors have improved. This is thanks to better surgical techniques and treatments.
How Extent of Tumor Removal Affects Outcomes
The extent of tumor removal is key to patient outcomes. Studies have shown that the more completely a tumor is removed, the better the patient’s chances of survival and quality of life. We focus on precise surgical techniques and advanced diagnostic tools. This helps us remove as much of the tumor as possible while keeping the brain safe.
Understanding these factors helps us create treatment plans that meet each patient’s needs. This way, we can improve their chances of successful outcomes.
Conclusion: Advances Shaping the Future of Brain Tumor Treatment
Brain tumor research is making great strides, promising a brighter future for brain tumor surgery. Studies show better survival rates after aggressive tumor removal. This highlights the key role of new treatments in this field.
At Liv Hospital, we’re dedicated to leading in these advancements. We use the latest tech and innovative methods in our treatments. This helps us give patients the best ways to remove brain tumors, improving their lives and results.
The future of brain tumor surgery is bright, thanks to ongoing research and a better understanding of tumors. We’re committed to top-notch healthcare, with full support for international patients. Our goal is to provide the best care possible.
FAQ
What is the difference between malignant and non-malignant brain tumors?
Malignant brain tumors are cancerous and can spread. Non-malignant tumors are usually benign and don’t spread. The type of tumor affects treatment.
How is malignancy determined in brain tumors?
Doctors use MRI and examine tumor tissue to check for malignancy. They also look at the tumor’s grade, which shows how much it looks like normal cells.
What are the primary goals of surgical intervention for malignant brain tumors?
Surgery aims to remove as much tumor as possible. It also tries to relieve brain pressure and improve symptoms. It’s often used with other treatments like radiation and chemotherapy.
When is surgery not recommended for brain tumors?
Surgery might not be suggested if the tumor is hard to reach or if the patient’s health isn’t good for surgery. In these cases, other treatments like radiation or chemotherapy might be considered.
What advanced diagnostic imaging techniques are used in pre-surgical assessment?
MRI, functional MRI, and diffusion tensor imaging are used to check the tumor’s size and location. These images help neurosurgeons plan the safest surgery.
What are the benefits of microsurgical and minimally invasive approaches in brain tumor removal?
These techniques allow for precise tumor removal with less damage to the brain. This reduces complications and helps patients recover faster.
How are surgical complications managed during brain tumor surgery?
We use advanced techniques and intraoperative monitoring to avoid complications. Our team is ready to handle any issues that might arise during or after surgery.
What happens if a brain tumor is deemed inoperable?
If surgery isn’t possible, other treatments like radiation, chemotherapy, or stereotactic radiosurgery might be suggested. We work with patients to find the best treatment plan.
What is the typical recovery process after brain tumor surgery?
Recovery starts with care in the hospital, followed by chemotherapy and radiation if needed. Patients also go through rehabilitation and long-term follow-up to monitor their health.
What are the success rates for brain tumor surgery?
Success rates vary by tumor type and grade. For benign tumors, success is usually high, 90-95%. For malignant tumors, survival depends on how much tumor is removed and the effectiveness of treatments.
Can removing a brain tumor improve outcomes for patients with malignant brain cancer?
Yes, removing as much tumor as possible can help patients with malignant brain cancer. The amount removed is a key factor in outcomes, and we aim for maximum safe removal.
How is brain tumor removal surgery performed?
Surgery uses advanced microsurgical and minimally invasive techniques. We also use intraoperative monitoring and brain mapping for precision and safety.
What are the risks associated with brain tumor surgery?
Risks include infection, bleeding, and neurological problems. We take all precautions to minimize these risks and ensure the best outcomes.
How do you determine if a brain tumor is malignant or benign?
Doctors use imaging studies and examine tumor tissue to determine malignancy.
What are the alternative treatments for inoperable brain tumors?
For tumors that can’t be surgically removed, treatments like radiation, chemotherapy, or stereotactic radiosurgery might be suggested. We work with patients to find the best treatment.
References
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). (2021). Prostate cancer: diagnosis and management. NICE guideline [NG131]. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng131/chapter/rationale-and-impact