Cardiac procedures are key in diagnosing and treating heart issues. With heart-related illnesses on the rise, it’s vital to know the most common ones.
Did you know that over 1 million cardiac catheterizations are done every year in the United States? This shows how important tools like the nuclear stress test procedure are for checking heart health.
The nuclear stress test is a major tool in cardiology. It helps doctors figure out the best treatment for patients having heart surgery or other cardiac procedures.
Key Takeaways
- Cardiac procedures are essential for diagnosing and treating heart conditions.
- The nuclear stress test is a key diagnostic tool in cardiology.
- Over 1 million cardiac catheterizations are done annually in the United States.
- Understanding cardiac procedures helps patients make informed decisions about their heart health.
- Cardiac diagnostic tools help determine the best treatment for patients.
Understanding Cardiac Procedures
Cardiac procedures have changed cardiology a lot. They help doctors diagnose and treat heart problems better. These procedures include many tests and treatments for the heart.
Definition and Purpose of Cardiac Procedures
Cardiac procedures are medical steps to find and fix heart issues. They include tests to see what’s wrong and treatments to fix it. A cardiac imaging test is a key test that shows the heart’s shape and how it works.
The main goal of these procedures is to check the heart and find problems early. For example, tests like echocardiography or nuclear medicine scans give doctors important info. This helps them decide the best treatment.
Diagnostic vs. Interventional Procedures
Diagnostic tests check the heart’s health and find problems. Some examples are:
- Cardiac stress tests, which check how the heart works when stressed.
- Echocardiograms, which use sound waves to see the heart.
- Nuclear medicine scans, like myocardial perfusion imaging, which check blood flow to the heart.
Interventional procedures treat heart problems. They can be simple or complex, like surgeries or catheter-based treatments.
A top cardiologist says, “Choosing between tests and treatments depends on the patient’s needs and test results.” This shows how important it is to tailor care to each person.
Evolution of Cardiac Care
Cardiac care has grown a lot, thanks to new tech and understanding of heart disease. Now, we use less invasive methods and better imaging. We also focus more on preventing heart problems.
As we learn more about heart disease, cardiac procedures will keep being key in cardiology. Using the newest in imaging and treatments, we can make patients’ lives better.
The Most Common Cardiac Diagnostic Tests
Cardiac diagnostic tests are key in modern cardiology. They help doctors diagnose and treat heart issues. These tests are vital for understanding heart health and finding the best treatment.
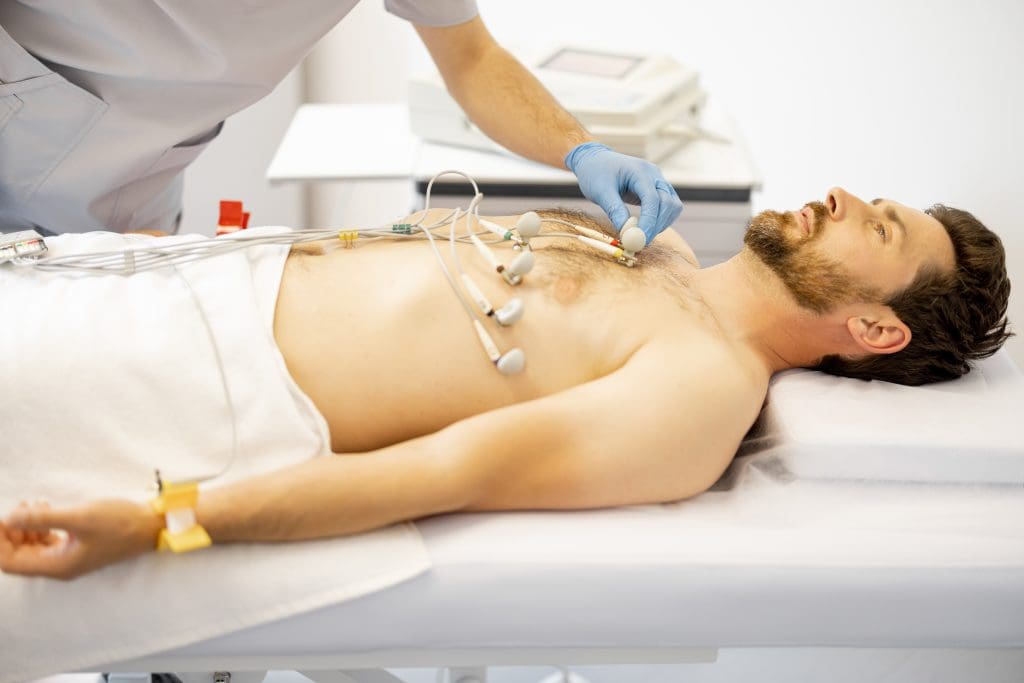
Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG)
An Electrocardiogram, or ECG/EKG, is a non-invasive test. It records the heart’s electrical activity. It helps find heart rhythm problems, blocked arteries, and heart damage.
Key aspects of ECG/EKG:
- Measures heart rate and rhythm
- Detects abnormal heartbeats (arrhythmias)
- Identifies signs of heart damage or ischemia
Echocardiogram
An Echocardiogram is an ultrasound test. It uses sound waves to create heart images. It shows heart structure and function, like valve and chamber conditions.
Benefits of Echocardiogram:
- Assesses heart valve function
- Evaluates heart chamber size and function
- Detects abnormalities such as tumors or blood clots
Cardiac Catheterization
Cardiac Catheterization is an invasive procedure. It involves inserting a catheter into a blood vessel and guiding it to the heart. It’s used to diagnose and treat heart conditions, like blocked coronary arteries.
| Procedure | Purpose | Benefits |
| Coronary Angiography | Visualize coronary arteries | Identify blockages or narrowing |
| Angioplasty | Open blocked arteries | Restore blood flow to the heart |
Holter Monitoring
Holter Monitoring is a 24- to 48-hour ECG test. It records the heart’s activity over a long time. It’s great for finding irregular heart rhythms that a standard ECG might miss.
Advantages of Holter Monitoring:
- Monitors heart activity over an extended period
- Detects intermittent arrhythmias
- Correlates symptoms with heart activity
Nuclear Stress Test Procedure: An Overview
A nuclear stress test is a detailed way to check how well the heart works when it’s stressed. It uses tiny amounts of radioactive material to make heart images. This lets doctors see how the heart performs during activity or stress.
What is a Nuclear Stress Test?
A nuclear stress test, or myocardial perfusion imaging, is a non-invasive test. It helps doctors find and manage heart problems. A small amount of radioactive tracer is injected into the blood. This tracer lights up the heart muscle and is seen by a camera.
The test is done in two parts: at rest and during stress. Stress can be from exercise, like walking on a treadmill, or from medicine that mimics exercise.
When is a Nuclear Stress Test Recommended?
We suggest a nuclear stress test for those with heart disease symptoms like chest pain or shortness of breath. It’s also for those who’ve had a heart attack or certain heart surgeries. The test checks for blockages in the heart’s arteries and the heart’s overall health.
It’s also used to see if treatments for heart disease are working. It helps figure out the risk of future heart issues.
How Nuclear Stress Tests Differ from Regular Stress Tests
Nuclear stress tests show more than regular stress tests. They give detailed images of blood flow and heart function. This lets us see heart health issues that regular tests might miss.
The info from a nuclear stress test is key for making the right decisions about patient care. It tells us if more tests or treatments are needed.
Preparing for a Nuclear Stress Test
Preparing for a nuclear stress test involves key steps to ensure accurate results.. These steps help get accurate results and make the experience smoother. We know that going through a test can be stressful. So, we’re here to help you through the preparation.
Pre-Test Instructions
Before your test, there are a few things to do. Wear comfy clothes and shoes for exercise because you’ll be active during the test. Also, don’t eat caffeine or some medicines that might mess up the test results.
Medication Considerations
Tell your doctor about any medicines you’re taking. Some might need to be changed or stopped before the test. This includes beta-blockers, nitrates, and some asthma meds. Your doctor will tell you how to handle your meds before the test.
Dietary Restrictions
There are dietary rules to follow for a precise test. Avoid big meals before the test. Instead, have a light meal or snack. Also, stay away from fatty foods and caffeine on test day.
By following these tips, you help make sure your test is safe and works well. This gives your healthcare team the info they need to care for you better.
Step-by-Step Nuclear Stress Test Process
We’ll walk you through the nuclear stress test step by step. This test is key to seeing how your heart works when stressed.
Initial Resting Images
The test starts with resting images. A tiny amount of radioactive tracer is given to you. Our camera then takes pictures of your heart when it’s not working hard.
Exercise or Pharmacological Stress Phase
Next, you’ll either walk on a treadmill or take medicine to stress your heart. This part is important to see how your heart works at rest and when stressed. It’s vital to follow our instructions closely for the best results.
If walking on a treadmill is hard for you, don’t worry. We can use medicine to make your heart work hard, just like exercise.
Post-Stress Imaging
After stressing your heart, we take more images. These images are compared to the ones taken when your heart was at rest. This gives us a full picture of how your heart functions.
Duration and What to Expect
The whole test usually takes a few hours. You’ll be with us for this time, and we’ll watch your heart and take the needed pictures. It’s a simple process, and we’re here to help you every step of the way.
Here’s what you can expect during the test:
- You’ll need to lie very quietly on a table during the pictures.
- Our team will keep an eye on your heart rhythm and blood pressure.
- You might feel some side effects from the medicine or exercise, but we’ll take care of it.
Knowing what happens in a nuclear stress test can make you feel more ready and calm. Our team is committed to giving you the care and support you need during this test.
Interpreting Nuclear Stress Test Results
Understanding your nuclear stress test results is key to your heart care. We look at the images to see how your heart works under stress.
Normal vs. Abnormal Findings
A normal test means your heart works fine under stress, with no big blockages. But, an abnormal test might show your heart muscle isn’t getting enough blood. This could mean you have coronary artery disease or other heart problems.
Abnormal results can show how bad the problem is and where it is. We look at how much blood flow is reduced and if there’s scar tissue from heart attacks.
What Your Results Mean
Your test results tell us a lot about your heart health. If they’re normal, your heart is pumping well and there’s no big disease. But, if they’re not, you might need more tests or treatments.
If the test shows your heart isn’t getting enough blood, we might do more tests. We could also suggest lifestyle changes, medicines, or even surgery like angioplasty or CABG.
Follow-Up Recommendations
We’ll give you personal advice based on your test results. If they’re normal, we might just check in regularly and suggest ways to keep your heart healthy. But, if they’re not, we’ll talk about what to do next. This could be more tests, changes in your lifestyle, or treatments.
| Result Type | Implications | Follow-Up Actions |
| Normal | Heart functions properly under stress | Routine monitoring, preventive measures |
| Abnormal | Potential coronary artery disease or other cardiac issues | Further testing, lifestyle changes, medical interventions |
By understanding your test results, we can make a plan to keep your heart healthy and improve your overall well-being.
Coronary Angioplasty and Stent Placement
Coronary angioplasty and stent placement are key cardiac procedures to fix blood flow to the heart. They help those with coronary artery disease. This disease narrows or blocks arteries due to plaque buildup.
Procedure Overview
Coronary angioplasty, or PTCA, is a minimally invasive procedure to open blocked arteries. A catheter with a balloon tip is used. The balloon inflates to push aside plaque and widen the artery.
Stent placement often follows angioplasty. A small, mesh-like device (stent) is placed to keep the artery open.
Types of Stents
There are several stent types used in stent placement:
- Bare-metal stents
- Drug-eluting stents
- Bioresorbable vascular scaffolds
Each stent type has its own benefits. The choice depends on the patient’s condition and medical history.
Recovery and Aftercare
After heart surgery or cardiac procedures like coronary angioplasty and stent placement, recovery is key. Patients need to watch for complications, manage medications, and make lifestyle changes to avoid more heart disease.
Following post-procedure instructions and attending follow-up appointments is vital for a smooth recovery.
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
For many, Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) is a lifeline. This surgery creates new paths for blood to reach the heart. It’s a big step, but it’s been helping people for decades.
When CABG is Necessary
CABG is for those with severe heart disease. It’s needed when other treatments won’t work. We look at many factors to decide if it’s right for you.
These include how bad the disease is and how well your heart is working. If your heart’s main artery is blocked, CABG might be the best choice.
Choosing CABG means we’ve checked your heart with tests. We talk to you about why we think it’s best. We also answer any questions you have.
Surgical Approach
The surgery opens your chest to reach your heart. A machine keeps your blood flowing while your heart stops. Then, we use grafts to bypass the blocked areas.
In some cases, we do the surgery without stopping your heart. This is called off-pump CABG. It might be safer for you.
Post-Operative Care
Right after surgery, you’ll be in the ICU. We watch for any problems and help with pain and breathing. We also make sure your heart is okay.
As you get better, we help you move around. We give you tips for when you go home. Our team supports you all the way to help you heal and stay healthy.
Heart Valve Repair and Replacement
Heart valve repair and replacement are key for fixing valve problems. The heart’s valves are essential for blood flow. Damage or disease can cause serious health issues.
Common Valve Problems
Valve issues can be stenosis, where the valve is too narrow, or regurgitation, where it leaks. These problems can come from congenital defects, infections, or aging.
To find valve problems, doctors use echocardiograms, electrocardiograms, and sometimes cardiac catheterization. Knowing the problem’s nature and severity helps choose the right treatment.
Surgical vs. Transcatheter Approaches
For a long time, cardiac surgery was the main way to fix valves. This method opens the chest to reach the heart. But, new tech has brought transcatheter approaches, which are less invasive.
Transcatheter methods use catheters through blood vessels to reach the heart. This is great for those at high risk for open-heart surgery complications.
Types of Replacement Valves
There are two main types of replacement valves: mechanical and biological. Mechanical valves are strong and last long but need lifelong anticoagulant meds to prevent blood clots.
Biological valves, made from animal tissue, are less likely to cause blood clots. They don’t need long-term anticoagulation but might need to be replaced later.
The choice between mechanical and biological valves depends on the patient’s age, lifestyle, and health.
Cardiac Ablation Procedures
Cardiac ablation is a new way to treat heart rhythm problems. It’s a small procedure that destroys bad electrical paths in the heart. This helps fix irregular heartbeats.
Treating Arrhythmias
Arrhythmias happen when the heart beats irregularly. Cardiac ablation works well for these problems. It gets rid of the bad signals that cause the irregular heartbeat.
Doctors choose cardiac ablation when other treatments don’t work. They look at each patient’s situation to decide if this is the right choice.
Catheter Ablation Techniques
Catheter ablation uses thin tubes to get to the heart. These tubes send energy to kill the bad tissue. It’s less invasive than surgery and helps patients recover faster.
There are two main types: radiofrequency ablation and cyroablation. Radiofrequency uses heat, while cryoablation uses cold. The choice depends on the patient’s condition and health.
Success Rates and Outcomes
How well cardiac ablation works depends on the arrhythmia and the patient. Catheter ablation often works well for SVT and atrial flutter.
We watch patients closely after the procedure. We check if it worked and manage any problems. While it can greatly improve life, there are risks. We talk about these risks with our patients before the procedure.
Pacemaker and Defibrillator Implantation
Cardiac care has made big strides, making pacemaker and defibrillator implants safer and more effective. These devices help manage heart rhythm issues, greatly improving patients’ lives.
Indications for Device Therapy
Pacemakers and defibrillators are for patients with certain heart rhythm problems. Pacemakers help with slow heart rates. Defibrillators, or ICDs, protect against dangerous arrhythmias.
Choosing to implant a pacemaker or defibrillator is a detailed process. We look at medical history, symptoms, and test results. We consider how severe symptoms are, any heart disease, and the risk of sudden death.
Implantation Process
Implanting pacemakers and defibrillators is a minor surgery. We do it under local anesthesia to keep patients comfortable.
We place the device under the skin, usually in the chest. Thin wires (leads) go through a vein into the heart. They monitor the heart’s rhythm and deliver therapy when needed.
Living with a Cardiac Device
Adapting to a pacemaker or defibrillator takes some time, but most patients can get back to normal quickly. We give detailed care and monitoring instructions.
It’s key for patients to know how their device works and its impact on daily life. Regular check-ups are also important to ensure the device is working right.
Understanding pacemakers and defibrillators helps patients make better care choices. We’re here to support them every step of the way.
Minimally Invasive Cardiac Procedures
Minimally invasive cardiac procedures have changed cardiology. They offer safer options than traditional surgery. Now, we can treat heart problems with less risk and faster recovery.
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR)
TAVR is a new way to treat severe aortic stenosis. This method uses a catheter to replace the valve through the femoral artery. It’s less risky than surgery, with less pain and shorter stays in the hospital.
MitraClip for Mitral Regurgitation
MitraClip is a new treatment for mitral regurgitation. This procedure clips the mitral valve together to fix the problem. It’s great for those who can’t have open-heart surgery.
Benefits of Minimally Invasive Approaches
These new procedures have many benefits. They include:
- Smaller incisions, less scarring, and lower infection risk
- Less pain and quicker recovery
- Shorter hospital stays and faster return to activities
- Lower risk of complications, even for high-risk patients
| Procedure | Benefits | Typical Candidates |
| TAVR | Less invasive, reduced risk, shorter recovery | High-risk patients with severe aortic stenosis |
| MitraClip | Minimally invasive, improves valve function | Patients with mitral regurgitation not suitable for open-heart surgery |
As cardiology advances, TAVR and MitraClip will be key in treating heart issues. We aim to offer the latest treatments for the best patient outcomes and quality of life.
Risks and Complications of Cardiac Procedures
It’s important to know the risks and complications of cardiac procedures. These procedures are lifesaving but come with risks. They have changed how we treat heart diseases.
Common Complications
Cardiac procedures can lead to several complications. Some common ones are:
- Bleeding or hemorrhage
- Infection
- Reaction to anesthesia
- Stroke or transient ischemic attack
- Heart attack or cardiac arrest
These complications can vary in severity. They depend on the patient’s health, the procedure type, and the medical team’s expertise.
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of complications from cardiac surgery. These include:
- Age: Older patients are generally at higher risk.
- Pre-existing conditions: Conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and kidney disease can complicate recovery.
- Type of procedure: More complex procedures may have higher risks.
- Overall health: Patients with poor overall health or frailty are at increased risk.
Knowing these risk factors helps in deciding if a cardiac procedure is right for a patient. It also helps in planning preventive measures.
Prevention Strategies
To reduce the risks of cardiac procedures, several strategies are used. These include:
- Pre-operative optimization: Ensuring that the patient’s condition is as stable as possible before the procedure.
- Intra-operative care: Using advanced monitoring and surgical techniques to minimize risks during the procedure.
- Post-operative care: Providing meticulous care after the procedure to prevent complications and promote recovery.
By understanding the risks and using these prevention strategies, we can improve patient outcomes. This reduces the chance of complications from cardiac procedures.
Recovery and Rehabilitation After Cardiac Procedures
Recovering from a cardiac procedure is as important as the surgery itself. A good recovery plan is key to the best results. It helps you get back to full health.
Immediate Post-Procedure Care
Right after your procedure, care is vital for a smooth recovery. It’s important to follow your doctor’s instructions closely. This includes watching for complications, managing pain, and taking your medicine as directed.
Key aspects of immediate care include:
- Rest and avoiding strenuous activities
- Monitoring the incision site for signs of infection
- Managing pain through prescribed medications
- Following a specific diet as recommended by your healthcare provider
Cardiac Rehabilitation Programs
Cardiac rehab programs help patients recover and improve heart health. They include exercise, education on heart-healthy living, and stress management.
The benefits of cardiac rehabilitation include:
- Improved heart function and overall cardiovascular health
- Enhanced physical strength and endurance
- Better management of risk factors for heart disease
- Reduced symptoms and improved quality of life
Long-term Lifestyle Modifications
Long-term lifestyle changes are key to keeping the benefits of cardiac procedures. We suggest a heart-healthy lifestyle. This includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and avoiding smoking.
Key lifestyle modifications include:
- Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins
- Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or other aerobic exercises
- Managing stress through techniques like meditation or yoga
- Maintaining a healthy weight and managing cholesterol and blood pressure levels
By focusing on these recovery and rehabilitation aspects, we help patients achieve the best outcomes after cardiac procedures.
Conclusion: The Future of Cardiac Care
Looking ahead, cardiac care is changing fast. New ways to diagnose and treat heart issues are emerging. These include less invasive surgeries and new valve replacements.
Research is also key in shaping cardiac care’s future. There’s a big push for preventive care. This means focusing on lifestyle changes and early treatments to prevent heart disease.
New surgery technologies are making complex procedures safer and more precise. As these advancements grow, we’ll see better treatments for many heart conditions.
By keeping up with these new developments, we’re moving towards better, more accessible cardiac care. This care will be tailored to each patient’s needs, making it more effective than ever.
FAQ
What is a nuclear stress test, and how does it differ from a regular stress test?
A nuclear stress test uses a small amount of radioactive material. It shows how the heart and blood flow work under stress. Unlike a regular stress test, it gives detailed images of the heart’s blood flow. This helps check for coronary artery disease.
How do I prepare for a nuclear stress test?
To get ready, don’t eat or drink for a few hours before. Avoid certain medicines and wear comfy clothes. We’ll give you all the details you need.
What happens during a nuclear stress test?
First, you’ll get resting images. Then, you’ll do either exercise or take medicine to stress your heart. After that, more images are taken. The whole thing takes a few hours.
What are the risks associated with cardiac procedures?
Cardiac procedures might have risks like bleeding or infection. But, our team and facilities are top-notch. We minimize these risks.
What is the difference between coronary angioplasty and CABG?
Coronary angioplasty uses a balloon and stent to open blocked arteries. CABG is surgery that uses grafts to bypass blocked arteries.
How long does it take to recover from cardiac surgery?
Recovery time varies by person and procedure. You might stay in the hospital for days. Then, you’ll need weeks to months at home to fully recover.
What is cardiac rehabilitation, and how does it help?
Cardiac rehab is a program with exercise, education, and support. It helps patients recover from heart procedures and improves heart health.
Can I undergo cardiac procedures if I have other health conditions?
We’ll check your health and decide the best treatment. Some conditions might need special care or different treatments.
How do I know if I need a pacemaker or defibrillator?
Your doctor will decide based on your heart condition and history. These devices help control your heartbeat and prevent dangerous arrhythmias.
What are the benefits of minimally invasive cardiac procedures?
Procedures like TAVR and MitraClip have many benefits. They have smaller incisions, less pain, and faster recovery than open-heart surgery.









