A nuclear stress test shows how blood flows into the heart when you’re active or resting. It’s key for diagnosing and managing heart issues.
The test usually takes 3 to 4 hours. You’ll go through several steps to check your heart’s function under stress and at rest.
Knowing what to expect can ease any worries or nerves you might have. The test uses a small amount of radioactive material in your blood. This helps create images of your heart.
Key Takeaways
- A nuclear stress test is used to diagnose and manage heart conditions.
- The test duration is typically around 3 to 4 hours.
- You will undergo a series of procedures to assess your heart’s function.
- The test involves injecting a small amount of radioactive material into your bloodstream.
- Understanding the test procedure can help alleviate concerns or anxiety.
Understanding Nuclear Stress Tests: Purpose and Importance
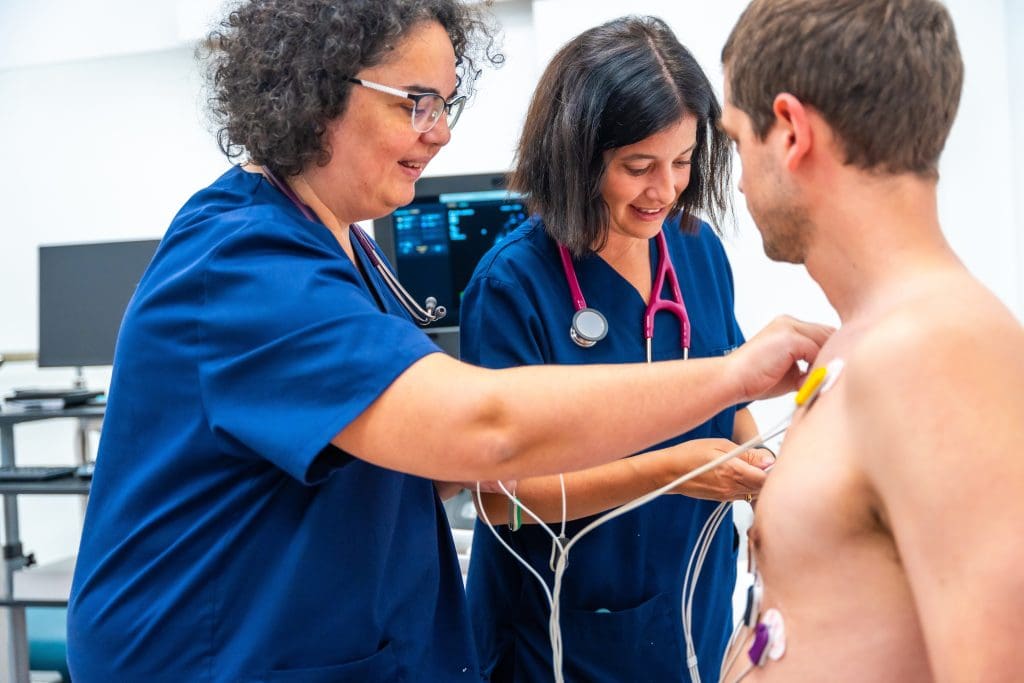
The nuclear stress test, also known as myocardial perfusion imaging, is key in diagnosing heart disease. It helps doctors see how the heart works under stress. This is important for spotting problems linked to coronary artery disease.
What is a Nuclear Stress Test?
A nuclear stress test checks the heart’s function when it’s stressed, usually through exercise or medicine. A tiny amount of radioactive material is given through the bloodstream. This material lights up the heart muscle, letting a camera take detailed images.
This test shows how well the heart muscle gets blood, mainly when active. It spots areas that might not get enough blood, a sign of coronary artery disease.
Why Doctors Order Nuclear Stress Tests
Doctors use nuclear stress tests for many reasons, mainly to find and manage heart disease. The test is great for:
- Diagnosing coronary artery disease
- Assessing heart attack risk
- Checking if treatments for heart disease work
- Finding heart damage from past heart attacks
By seeing how the heart works under stress, doctors can make better treatment plans for each patient.
Conditions Diagnosed Through Nuclear Stress Testing
Nuclear stress tests help find several heart problems, including:
| Condition | Description |
| Coronary Artery Disease | A condition where the coronary arteries become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup. |
| Heart Attack | A condition where the blood flow to the heart is severely blocked, causing damage to the heart muscle. |
| Ischemia | A condition where the heart muscle does not receive enough oxygen and nutrients due to reduced blood flow. |
By accurately diagnosing these conditions, doctors can give the right treatment on time. This improves patient results.
How Long Does It Take to Do a Stress Test: Complete Timeline
Many patients ask how long a nuclear stress test takes. Knowing the timeline can ease their worries. This test checks how well the heart works when it’s stressed, often through exercise or medicine.
Pre-Test Registration and Preparation Time
The first step is registration and getting ready, which takes about 30 minutes to an hour. During this time, patients fill out forms and learn about the test. Medical staff also prepare the patient for what’s to come.
Duration of the Actual Testing Procedure
The test itself lasts about 1 to 2 hours. This includes the time for the first injection, the stress part, and the imaging. It’s a detailed process to check the heart’s health.
Post-Test Monitoring Period
After the test, patients are watched for 30 minutes to 1 hour. This is to make sure they’re okay right after the test. It’s a safety check by the medical team.
Total Time Commitment for Patients
In total, patients should plan to spend 3 to 4 hours at the testing site. This includes getting ready, the test itself, and the monitoring after. It gives a clear idea of what to expect.
Knowing the total duration of a nuclear stress test helps patients plan their day. It also reduces anxiety about the unknown. By understanding each step, patients can prepare better for the test.
The stress test timeline might change a bit for each patient. It depends on their needs and the testing facility’s rules.
Types of Nuclear Stress Tests and Their Durations
Nuclear stress tests come in different types, each with its own way of working and time needed. Knowing about these can help patients get ready for their test.
Exercise Nuclear Stress Tests (Treadmill or Bicycle)
Exercise nuclear stress tests are the most common. They make you work out on a treadmill or bicycle to stress your heart. The test itself lasts about 30-60 minutes. But, getting ready and recovering can take several hours.
Key aspects of exercise stress tests include:
- Monitoring of heart rate and blood pressure
- Injection of a radiotracer to visualize heart function
- Imaging after the stress test to compare with resting images
Chemical/Pharmacological Stress Tests
For those who can’t exercise, chemical or pharmacological stress tests are used. These tests use medicine to stress the heart, like exercise does. The test itself lasts about 30-60 minutes.
Medications used include adenosine, regadenoson, and dobutamine.
Two-Day Protocol vs. Same-Day Protocol
Nuclear stress tests can be done in two ways: same-day or two-day protocols. The same-day protocol has two radiotracer injections, one at rest and one after stress. Imaging is done right after each injection. The two-day protocol spreads these injections over two days, which might be easier for some.
SPECT vs. Other Nuclear Imaging Methods
The most common imaging method is Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT). SPECT gives detailed 3D images of the heart’s function and blood flow. Other methods, like PET, might also be used. They offer different benefits in image quality and radiation exposure.
The Nuclear Stress Test Procedure: Step-by-Step
Learning about the nuclear stress test can ease worries for those about to have it. This test checks how well the heart works when stressed. Stress is usually caused by exercise or medicine.
Initial Radiotracer Injection
The test starts with a small dose of radioactive material, called a radiotracer, given through a vein. This material is key for taking pictures of the heart at rest and under stress.
First Round of Imaging
After the radiotracer is given, the patient lies under a gamma camera. This camera picks up the radiation from the radiotracer. The first images are taken when the patient is calm, showing the heart’s normal function.
The Stress Portion (Exercise or Medication)
The next part of the test increases the heart rate. This is done through exercise on a treadmill or medicine that mimics exercise. It’s important to see how the heart handles stress.
Second Radiotracer Injection and Imaging
When the stress test reaches its peak, more radiotracer is given. Then, more images are taken with the gamma camera. These images are compared to the first ones to see how the heart performs under stress.
The nuclear stress test is a key tool for doctors. It helps them understand heart blood flow and function. This is vital for diagnosing and treating heart disease.
Physical Discomfort During Nuclear Stress Tests
When getting ready for a nuclear stress test, knowing what might hurt can ease worries. These tests are key for doctors, but they can be uncomfortable for patients.
Discomfort from IV Placement and Injections
Getting an IV line can be the first uncomfortable part. A small needle is used to put a catheter in a vein, usually in the arm. Some might feel a pinch or stinging when the IV is put in. The radiotracer injection can also make you feel warm or flushed, but this is usually mild and doesn’t last long.
Physical Exertion During Exercise Stress Tests
Exercise stress tests require physical effort. You’ll walk on a treadmill or pedal a bike to raise your heart rate. This can be tough, but it’s important for checking how your heart works under stress.
Lying Stil for Imaging: Comfort Challenges
After the radiotracer is given, you’ll need to lie down for imaging. This can be hard, mainly for those with back or joint pain. Some might feel trapped, but new machines are made to be more open.
Common Physical Sensations Reported by Patients
People might feel different things during a nuclear stress test. These can include:
- Fatigue or tiredness, mainly after exercise tests
- A temporary increase in heart rate and blood pressure
- Shortness of breath during exercise
- Mild headache or dizziness
- Discomfort or pain from lying down for imaging
| Common Discomforts | Causes | Duration |
| IV placement discomfort | Needle insertion for IV | Temporary |
| Physical exertion discomfort | Exercise on treadmill or bicycle | During the test |
| Lying stil discomfort | Remaining stil on imaging table | During imaging |
Knowing what might hurt can help you get ready for your test. It makes the experience less scary.
Chemical Stress Tests: Medication Effects and Sensations
Chemical stress tests use special medicines to act like exercise on the heart. They’re key for people who can’t do regular exercise tests because of health issues or physical limits.
Adenosine and Regadenoson (Lexiscan) Effects
Adenosine and Regadenoson are medicines used in these tests. Adenosine makes blood vessels wider, which can make you feel flushed or short of breath. Regadenoson is more precise and better for people with lung problems.
These medicines might make you feel dizzy, have headaches, or feel chest pain. But these feelings don’t last long.
Dipyridamole (Persantine) Side Effects
Dipyridamole is another test medicine, often paired with a special dye. It can cause headaches, dizziness, and nausea. Some people might feel flushed or have chest pain, but these symptoms go away soon after the test.
“The use of dipyridamole in stress tests has been associated with a higher incidence of side effects compared to other agents, but it remains a valuable tool in cardiac imaging.” –
Source: Journal of Nuclear Cardiology
Dobutamine Effects and Sensations
Dobutamine is for those who can’t handle other medicines. It makes your heart beat faster and work harder, like exercise. You might feel your heart racing, feel anxious, or shake. These feelings are uncomfortable but usually don’t last long.
How Long Do Chemical Stress Tests Take
How long a chemical stress test takes depends on the test and your health. The actual test is about 30 minutes to an hour. But, you’ll need to spend several hours at the testing place, including getting ready and recovering.
It’s very important to listen to your doctor’s instructions. This ensures the test is done safely and right.
Patient Experiences: How Uncomfortable Is the Test Really?
Patient experiences with nuclear stress tests offer insights into what to expect. While everyone’s experience is different, knowing common discomforts helps prepare patients.
Common Discomfort Levels Reported
Many patients find the test manageable. Some feel mild discomfort from the IV or radiotracer injection. Others might feel more discomfort during the stress test.
Common sensations reported include:
- Mild discomfort or pain at the IV site
- Feeling flushed or experiencing a metallic taste during the radiotracer injection
- Shortness of breath or fatigue during exercise stress tests
- Dizziness or nausea during pharmacological stress tests
Factors That Affect Comfort During Testing
Several factors can impact comfort during a nuclear stress test. These include physical health, fitness, and any medical conditions.
Key factors include:
- Physical condition: Patients who are more physically fit may tolerate exercise stress tests better.
- Underlying health conditions: Certain conditions, such as heart disease or lung disease, may affect a patient’s comfort during the test.
- Anxiety or stress: Patients who are anxious or stressed may experience more discomfort during the procedure.
Tips from Previous Patients for Managing Discomfort
Previous patients have shared tips for managing discomfort. These include:
- Communicating with the medical staff about any concerns or discomfort
- Using relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation, to reduce anxiety
- Staying hydrated and avoiding heavy meals before the test
Comparing Discomfort to Other Medical Procedures
Many patients compare the discomfort of a nuclear stress test to other medical procedures. Most find it tolerable compared to other tests.
Some comparisons include:
- Less discomfort than a colonoscopy or endoscopy
- Similar to a routine blood draw, but with additional stress or exercise components
- More comfortable than an MRI or CT scan for some patients, due to the shorter duration and less confinement
Preparing for Your Nuclear Stress Test
Getting ready for a nuclear stress test involves several steps. These steps help you feel more comfortable during the test. They also make sure the test results are accurate.
Dietary Restrictions Before the Test
Following dietary restrictions is key when preparing for your test. You might need to fast for 4-6 hours before the test. Also, avoid caffeine and some medications that could affect the test results.
Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions. These will be based on your needs.
Medication Adjustments
Tell your doctor about all the medications you’re taking. This includes prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, and supplements. Some medications might need to be adjusted or stopped before the test.
Your doctor will tell you what changes are needed.
What to Wear and Bring
Wear comfortable clothes and shoes for exercise if you’re doing an exercise stress test. Bring a list of your medications, insurance information, and any medical records. Having these items ready can make the process easier.
Mental Preparation for the Procedure
Mental preparation is as important as physical preparation. Knowing what to expect can reduce anxiety. Talk to your healthcare provider about any concerns or questions.
Being informed and prepared can make the experience less stressful.
What to Expect After a Nuclear Stress Test
Knowing what happens after a nuclear stress test can ease your worries. Your medical team will guide you on post-test care and recovery. This helps you prepare for what’s next.
Immediate Post-Test Sensations
Right after the test, you might feel some effects from the radiotracer and the test itself. You could feel:
- Fatigue or tiredness
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Slight discomfort at the IV site
These feelings are usually short-lived and will go away by themselves. A cardiologist, says, “Most patients can go back to their usual activities soon after. But, it’s key to listen to your healthcare provider’s specific advice.”
“The post-test period is key for patients to see how their body reacts. It’s a time for rest and recovery.” – Nuclear Medicine Specialist
How Long the Radiotracer Stays in Your Body
The radiotracer used in nuclear stress tests leaves your body in a few hours to a couple of days. The exact time depends on:
| Factors | Influence on Radiotracer Duration |
| Metabolic Rate | Faster metabolism can reduce the duration |
| Hydration Level | Drinking plenty of water can help flush out the radiotracer |
| Type of Radiotracer | Different radiotracers have varying half-lives |
When You Can Resume Normal Activities
Most people can go back to their usual activities soon after the test. But, it’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s advice. Some activities might need to wait a bit.
Can You Drive After a Nuclear Stress Test?
In most cases, you can drive yourself home after the test. Unless you’ve taken medicine that could affect your driving. Always check with your healthcare provider for the best advice.
Understanding the post-test process can make your experience better and help you recover well. Always listen to your healthcare team’s guidance for the best results.
Safety Concerns and Possible Risks
Nuclear stress tests are useful for checking health, but they have safety issues. It’s important for patients to know these risks. This helps them make better health choices.
Radiation Exposure Levels and Safety
Nuclear stress tests use a small amount of radiation. This is because of the radiotracer used. Even though it’s safe, talking to your doctor about your risk is key, if you’ve had radiation tests before.
Radiation Safety Measures: Hospitals use strict rules to keep radiation doses low. You can also ask about the radiotracer and its radiation levels.
Risks of Chemical Stress Agents
Chemical stress agents are used for those who can’t exercise. They can cause side effects, from mild to severe. Common side effects include flushing, headaches, and shortness of breath.
Serious Side Effects: Though rare, serious side effects can happen. These include a big drop in blood pressure or heart rhythm problems. Some medical conditions make these risks higher.
Allergic Reactions to Radiotracers
Allergic reactions to radiotracers are rare but can happen. Tell your doctor about any allergies or past reactions to radiotracers.
- Symptoms of an allergic reaction include rash, itching, and trouble breathing.
- Medical staff are ready to handle allergic reactions with the right medicine.
Who Should Avoid Nuclear Stress Tests
Some people should not get nuclear stress tests because of health risks. Pregnant women and those with certain health issues should avoid them. This is because the test could harm the fetus or make health problems worse.
Talk to your doctor about your health history and any worries. They can decide if a nuclear stress test is right for you.
Interpreting Nuclear Stress Test Results
Understanding nuclear stress test results is key for both patients and doctors. These tests show how the heart works under stress. They help find problems that aren’t seen when the heart is at rest.
What Does a Nuclear Stress Test Show?
A nuclear stress test checks the heart’s blood flow and function during stress. It shows if the heart muscle gets enough blood flow. It also finds damaged or scarred heart tissue.
The test uses a radioactive tracer injected into the blood. The heart muscle absorbs it based on blood flow. Images are taken at rest and after stress to compare blood flow.
How Long It Takes to Get Results
Results usually come in 24 to 48 hours. But, this time can change based on the facility and test details.
Understanding Normal vs. Abnormal Results
Normal results mean the heart works well and there are no big blockages. Abnormal results might show heart disease, past heart damage, or other heart problems.
| Result Type | Description | Implications |
| Normal | Heart is functioning properly; no significant blockages. | Low risk of coronary artery disease. |
| Abnormal | Possible coronary artery disease or previous heart damage. | May require further testing or treatment. |
Next Steps After Abnormal Findings
If results are abnormal, more tests like a coronary angiogram might be needed. Treatment could be lifestyle changes, medicine, or surgery like angioplasty or bypass grafting.
“The results of a nuclear stress test are a critical component in diagnosing and managing heart disease. Understanding these results can help patients take proactive steps towards improving their heart health.”
” Cardiologist
It’s vital for patients to talk to their doctor about their results. This helps understand what it means and what to do next.
Cost and Insurance Coverage for Nuclear Stress Tests
Many people wonder about the cost of nuclear stress tests and what insurance covers. Knowing this helps prepare for the test.
Average Cost of Nuclear Stress Tests
The cost of a nuclear stress test varies a lot. It depends on where you are, the facility, and the test type. Costs usually range from $1,000 to $3,000 or more. Always ask your healthcare provider or the facility for a precise quote.
Insurance Coverage Considerations
Most insurance plans cover nuclear stress tests if they’re needed. But, coverage can differ a lot. It depends on your insurance and policy. Always check your coverage before the test.
Questions to Ask Your Insurance Provider
To know your coverage, ask your insurance these questions:
- Is a nuclear stress test covered under my plan?
- What are the out-of-pocket costs for the test?
- Are there any specific requirements or restrictions for coverage?
- Do I need a referral from my primary care physician?
Factors That Affect Pricing
Several things can change the price of nuclear stress tests, including:
- The type of nuclear stress test performed (e.g., exercise vs. pharmacological)
- The facility’s charges (hospital vs. outpatient center)
- Geographic location
- Additional services or tests required
Knowing these factors helps estimate costs better and plan ahead.
Conclusion: Managing Expectations for Your Nuclear Stress Test
Understanding the nuclear stress test procedure and possible discomforts helps patients feel more prepared and less anxious. This knowledge helps you get ready for the test.
Getting ready for the test is key. You need to know about food rules, changing your meds, and what to wear. This info cuts down on stress and makes the test go smoother.
It’s true, you might feel some discomfort. This could be from the test itself, the IV, or lying down for scans. Knowing this ahead of time helps you feel more ready.
Being well-prepared makes the test easier and less stressful. This way, you can get through it without too much worry. It’s all about being ready and understanding what’s coming.
FAQ
How long does a nuclear stress test take?
A nuclear stress test usually takes 3-4 hours. This includes getting ready and the imaging time.
What is a nuclear stress test?
It’s a test that uses a tiny bit of radioactive material. It shows how the heart works when it’s stressed.
How is a nuclear stress test done?
First, a radiotracer is injected into your blood. Then, images are taken at rest and after stress.
What does a nuclear stress test show?
It reveals the heart’s blood flow and function. It can also spot blockages or damage.
Can I drive after a nuclear stress test?
No, it’s best not to drive right after. This is because the test’s medications can make you dizzy.
How long does the radiotracer stay in your body?
The radiotracer stays in your body for a few hours to a few days. This depends on the type and your body.
What are the risks of a nuclear stress test?
Risks include radiation exposure and allergic reactions. There are also side effects from the stress medications.
How do I prepare for a nuclear stress test?
You’ll need to follow dietary rules and avoid certain medications. Wear comfy clothes and be ready for a few hours.
What should I wear to a nuclear stress test?
Wear loose, comfy clothes. Avoid jewelry or anything that might get in the way.
How long does it take to get the results of a nuclear stress test?
Results are usually ready in a few hours to a few days. This depends on the facility and the case.
Can I eat before a nuclear stress test?
It depends on the test. You might need to avoid eating or drinking certain things before.
What are the common discomforts during a nuclear stress test?
You might feel the IV, get tired from exercise, or feel uncomfortable lying down. You might also have side effects from the medications.
How uncomfortable is a nuclear stress test?
Some discomfort is possible, but most people find it okay. Any discomfort is usually short-lived.
Who should avoid nuclear stress tests?
Some people should avoid it. This includes those with certain medical conditions or allergies to the radiotracer.








