Last Updated on October 31, 2025 by
Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) is a common surgery for treating urinary problems caused by an enlarged prostate. While it is effective, we must consider the complications.
TURP surgery risks include short-term trouble urinating, urinary tract infections, and dry orgasm. These risks highlight the importance of selecting hospitals with high standards of care and innovative approaches to patient safety.
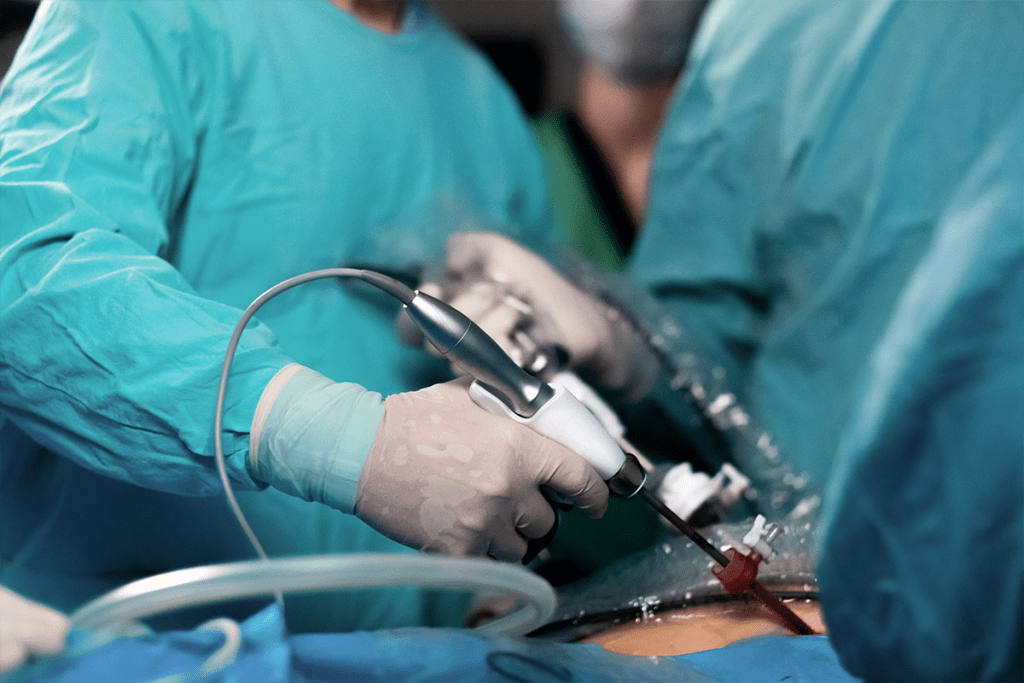
At hospitals like Liv Hospital, patient safety is our top priority. We adopt innovative approaches to minimize risks associated with TURP surgery, ensuring the best possible outcomes for our patients.
Men with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) often look into TURP surgery. TURP, or Transurethral Resection of the Prostate, helps with urinary problems from an enlarged prostate. Doctors operate prostate issues with advanced surgical techniques, ensuring symptom relief, improved urinary flow, and better patient health outcomes.
TURP removes prostate tissue through the urethra. This relieves pressure on the urethra and improves urine flow. It’s for men with moderate to severe urinary symptoms from BPH.
A urologist uses a resectoscope through the urethra to access the prostate. This allows for the precise removal of prostate tissue, blocking the flow.
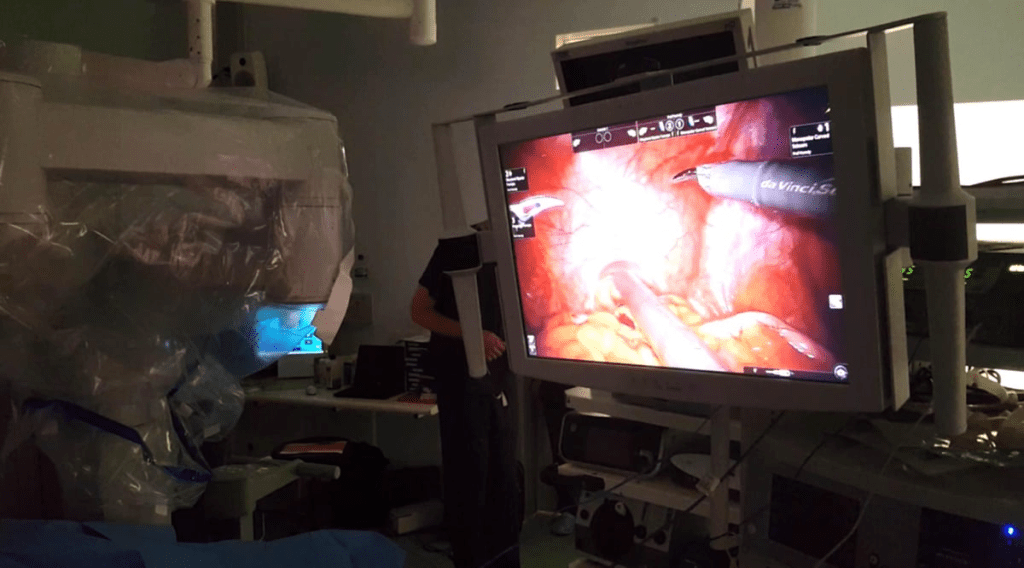
BPH is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland. It causes urinary difficulties. TURP is a preferred treatment for BPH because it effectively reduces symptoms and improves quality of life.
By removing the obstructing prostate tissue, TURP helps restore normal urine flow. This reduces the risk of complications like urinary tract infections and bladder damage.
TURP is different from other prostate surgeries, like laser prostatectomy or open prostatectomy. Unlike these, TURP is performed through the urethra. This avoids external incisions and reduces recovery time.
While other procedures may be suitable for some patients, TURP is widely used and effective. It has a proven track record and a relatively low risk of complications.
When looking at operation prostate options, knowing about TURP is key. It’s important to understand how TURP compares to other surgical procedures and TURP alternatives. And how it can address issues related to an enlarged prostate and surgery.
The time right after TURP surgery can bring several complications. It’s key for both patients and doctors to know these risks. This helps in setting the right expectations and making smart choices.
Bleeding and hematuria are big worries after TURP, hitting 13-25% of patients. Hematuria, or blood in the urine, can really upset patients. We keep a close eye on these issues to act fast.

Severe bleeding might lead to needing a blood transfusion, affecting 9-29% of patients. We do our best to avoid this, but it’s something to think about when looking into TURP surgery.
About 1.7% of patients might need ICU care after TURP. This number drops with some laser treatments, showing the need to talk about the types of prostate surgery risks with your doctor.
Acute urinary retention is another issue after TURP. Even though the surgery aims to fix urinary problems, some face retention issues later. We help patients deal with these problems for the best results.
Knowing the possible immediate problems with TURP helps patients get ready for surgery and recovery. It’s important to think about the risks and benefits. This includes looking at the least amount of side effects for a prostate bore out and how it affects your life quality.
Infections are a big worry after TURP surgery. It’s important to know about the risks of infections and how they can affect patients.
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common after TURP, happening in 14-18% of cases. These infections can cause pain, longer hospital stays, and more treatments. It’s key for patients to know about UTI risks, like with enlarged prostate.
Postoperative sepsis is a serious infection risk, affecting 9-16% of TURP patients. It can be deadly and needs quick medical help. This shows how critical good post-op care and watching is.
Many things can raise the chance of infection after TURP. These include the patient’s health, how the surgery is done, and post-op care. For example, those with urinary problems or long surgeries are at higher risk. Knowing these can help lower infection risks.
Hospital quality greatly affects infection rates after TURP. Top-notch hospitals with strict infection control and quality care have fewer infections. Patients should ask about a hospital’s infection control and success rates before choosing where to have TURP.
TURP surgery can lead to long-term issues that affect a person’s quality of life. It’s good for treating Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH). But knowing about these possible problems helps in making the right choice for prostate surgery.
About 8-13% of patients may continue to experience lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) after TURP. These symptoms include urgency, needing to urinate often, and weak urine flow. A study on the National Center for Biotechnology Information website shows that managing these symptoms often needs ongoing treatment.
Factors that can lead to persistent LUTS include:
TURP can also cause changes in sexual function, affecting many patients. These changes can include retrograde ejaculation, erectile dysfunction, and decreased libido. It’s important for patients to talk about these possible changes with their healthcare provider before surgery.
The chance of sexual function changes varies. Factors that can influence this include:
Bladder neck contracture and urethral strictures are possible long-term complications of TURP. These conditions can cause obstructive urinary symptoms and might need more surgery. The risk of these complications depends on the surgical technique and postoperative care.
TUR syndrome is a rare but serious complication of TURP. It happens when the body absorbs the irrigating fluid during surgery, leading to serious health issues. Other rare complications include urinary incontinence and chronic pain.
It’s important for patients considering TURP surgery to know about these possible long-term complications. By understanding the risks and talking to healthcare providers, patients can make better decisions about their treatment options.
Understanding the risks and benefits of TURP surgery is key. We’ve talked about the possible complications, like immediate issues and long-term problems. These can affect how well you function after surgery.
Hospitals like Liv Hospital focus on keeping patients safe. They use new ways to lower the risks of TURP. Choosing a trusted healthcare provider means you get top-notch care and advice.
Thinking about a surgical procedure, a TURP for an enlarged prostate? It’s important to think about the good and bad sides. Talk to your doctor about your needs and worries. This way, you can decide what’s best for your prostate surgery.
We aim to give patients all the care and support they need. This lets them take charge of their health and make smart choices. Our goal is to provide world-class healthcare. We support patients every step of the way, ensuring they get the best care for their prostate surgery.
TURP, or Transurethral Resection of the Prostate, is a surgery for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH). It removes extra prostate tissue through the urethra, without any cuts outside. We use a resectoscope to see the prostate and remove tissue.
TURP is a top choice for BPH because it greatly improves urinary symptoms. It’s safer than many other treatments and is often seen as the best option for severe BPH.
Right after TURP, patients might face bleeding, need blood transfusions, or have urinary problems. Infections can also happen. We use advanced techniques and care to lower these risks.
To avoid infections, we follow strict cleanliness and use antibiotics when needed. We also watch patients closely for any signs of infection.
Long-term issues can include ongoing urinary problems, sexual function changes, and urethral strictures. These are rare but we work to prevent them and support affected patients.
TURP aims to remove extra prostate tissue, not the whole gland. Sometimes, we don’t remove the whole gland if it’s not needed.
TURP and laser surgery treat BPH but differently. Laser surgery uses heat to remove tissue, while TURP uses a resectoscope. We choose based on the patient’s needs and history.
Look for a hospital with high standards, experienced surgeons, and good post-op care. We aim to provide top care from start to finish.
TUR syndrome is a rare complication of TURP, caused by fluid absorption during surgery. We closely monitor patients to prevent this risk.
Yes, options include medication, lifestyle changes, and other surgeries like laser. We help patients choose the best treatment for them.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!