Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir

Hernias can affect individuals of any age, but their prevalence increases as people get older. The decision to undergo hernia surgery depends on various factors, including the patient’s overall health and the type of hernia present.
Understanding the optimal age hernia repair timing is crucial for effective treatment. While some hernias may require immediate attention, others might allow for a more flexible approach to surgery.
Factors such as the patient’s age considerations for hernia and overall health play a significant role in determining the best course of action.

Hernias are a common condition that affects people of all ages in different ways. A hernia occurs when an organ or tissue bulges through a weakened area in the muscle or connective tissue that normally holds it in place. Understanding the different types of hernias and their impact across various age demographics is crucial for effective treatment and management.
There are several types of hernias, each with its own characteristics and prevalence across different age groups. The most common types include:
Hernias can affect individuals at any age, from infants to the elderly, with varying implications:
| Age Group | Common Hernia Types | Implications |
| Infants and Children | Umbilical, Inguinal | Often congenital, may require early intervention. |
| Young Adults | Inguinal | Can be exacerbated by physical activity or heavy lifting. |
| Middle-Aged Adults | Inguinal, Hiatal | Increased incidence due to aging and lifestyle factors. |
| Seniors | Hiatal, Inguinal | May have more complications due to comorbidities. |
Age is a significant factor in determining the appropriate treatment for hernias. For instance, surgical approaches may vary between children and adults due to differences in overall health, the presence of comorbidities, and the likelihood of complications. Understanding these factors helps healthcare providers make informed decisions about the timing and type of intervention.
The decision to undergo hernia surgery is influenced by the patient’s age, overall health, and the severity of symptoms. For young adults, the decision may be influenced by lifestyle and activity level, while for seniors, the presence of other health issues may play a more significant role.
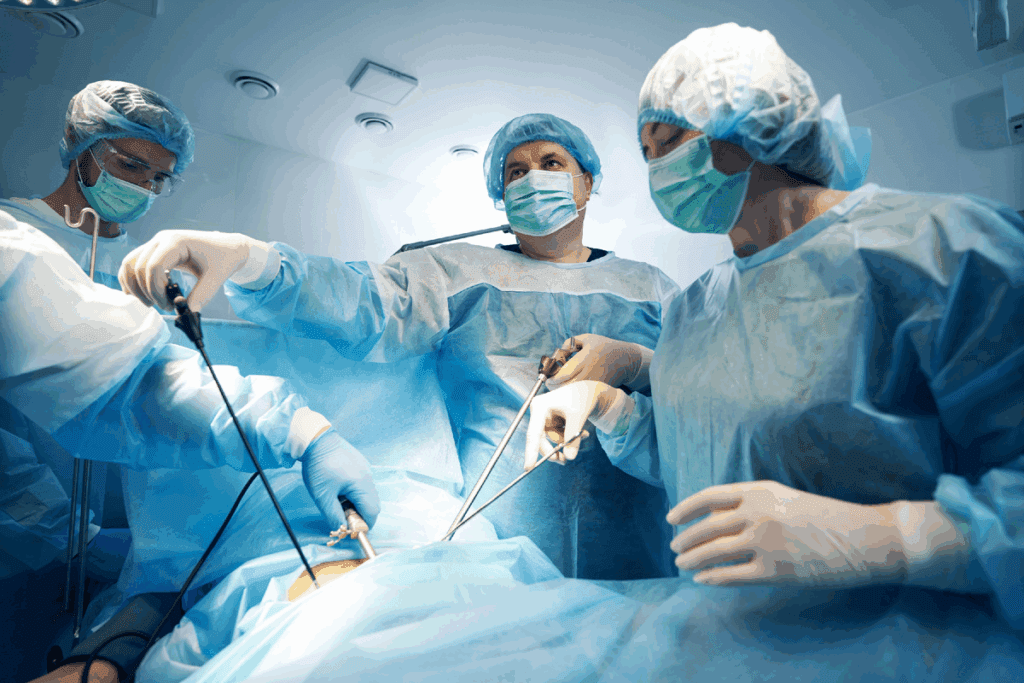
The optimal timing for hernia repair is a complex issue that medical professionals approach by evaluating individual patient needs. While age is a consideration, it is not the sole determining factor.
The medical consensus generally recommends surgery based on the type of hernia, symptoms, and overall health rather than age alone. For instance, hernias that are symptomatic or at risk of complications are often recommended for surgical repair regardless of the patient’s age.
Several factors contribute to the decision-making process, including:
When considering hernia repair, it’s crucial to balance the risks and benefits of surgery across different age ranges. For younger patients, the benefits often include preventing future complications and reducing symptoms. For older adults, the decision involves weighing the potential benefits against the risks associated with surgery and anesthesia.
Key considerations for different age groups include:
While age can play a role in the decision-making process, individual factors such as overall health, lifestyle, and the presence of symptoms often outweigh age considerations. A comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare provider is essential to determine the best course of action.
Ultimately, the decision for hernia repair should be personalized, taking into account the unique needs and circumstances of each patient.
Hernia repair in pediatric patients involves unique challenges that necessitate specialized care. Children’s bodies are still developing, and their anatomy and physiology differ significantly from adults, requiring tailored approaches to hernia surgery.
Congenital hernias are a common issue in infants, often presenting as inguinal hernias. These occur when there is a failure in the closure of the processus vaginalis during fetal development. Early diagnosis is crucial to prevent complications such as incarceration or strangulation.
“The timely repair of congenital hernias in infants is essential to prevent potential complications and ensure the child’s healthy development,” according to pediatric surgical guidelines.
The timing of hernia repair in children depends on several factors, including the child’s age, the size of the hernia, and their overall health. Elective surgery is often recommended to avoid emergency situations that can arise if the hernia becomes incarcerated or strangulated.
Pediatric hernia surgery has evolved, with minimally invasive techniques becoming more prevalent. Laparoscopic surgery, for instance, offers the advantage of smaller incisions, less postoperative pain, and quicker recovery times. The choice between open and laparoscopic repair depends on the surgeon’s expertise, the child’s anatomy, and specific case requirements.
The use of mesh in pediatric hernia repair is a topic of debate among surgeons. While mesh can reduce the risk of recurrence in adults, its use in children is considered on a case-by-case basis, weighing the benefits against potential long-term risks.
The decision to perform hernia surgery on adolescents must take into account their stage of growth and development. Adolescents with hernias require a nuanced approach that considers both the immediate need for surgery and the long-term implications of the procedure.
During adolescence, the body undergoes significant changes that can impact the timing and approach to hernia surgery. Growth spurts and developmental stages can affect the hernia’s behavior and the body’s response to surgery. Surgeons must consider these factors when deciding the optimal time for surgical intervention.
For teenagers, the presence of a hernia can be particularly concerning due to its impact on daily activities and self-image. The surgical team must balance the need for effective hernia repair with the adolescent’s overall health and well-being.
Recovery from hernia surgery in adolescents generally follows a predictable pattern, with most teenagers able to return to their normal activities within a few weeks. However, individual recovery rates can vary based on factors such as overall health, the complexity of the surgery, and adherence to post-operative instructions.
Teenagers and their families should be prepared for a recovery period that includes rest, gradual return to activities, and follow-up care to ensure the best possible outcomes. By understanding the recovery expectations, adolescents can better navigate the post-surgery period and achieve a successful result.
Balancing the demands of career and personal life, young adults must carefully consider the timing of hernia surgery. This age group often faces unique challenges, from career advancement to family obligations, making the decision to undergo surgery particularly complex.
For young adults, the decision between a proactive approach to hernia surgery and watchful waiting can be influenced by several factors, including the severity of symptoms and the impact on daily life. A proactive approach involves scheduling surgery as soon as possible to prevent potential complications, such as incarceration or strangulation of the hernia.
On the other hand, watchful waiting involves monitoring the hernia for any changes or worsening of symptoms. This approach may be suitable for individuals with minimal symptoms, but it requires careful monitoring and follow-up with a healthcare provider.
Lifestyle factors play a significant role in the decision-making process for young adults considering hernia surgery. The recovery period, which can range from a few days to several weeks, may impact work, family, and social responsibilities.
“The decision to have hernia surgery should be based on a thorough evaluation of how it will affect one’s quality of life and long-term health goals.”
A General Surgeon
Young adults should consider the following lifestyle impacts:
By carefully weighing these factors and discussing them with a healthcare provider, young adults can make an informed decision about the best time for hernia surgery that aligns with their personal and professional goals.
Middle-aged adults, typically between 40 and 60 years old, experience a peak incidence of hernias due to various risk factors. This age group is significant for hernia occurrence, and understanding the factors at play can help in making informed decisions about surgical interventions.
Several risk factors contribute to the increased incidence of hernias in middle-aged adults. These include:
Addressing these risk factors can help mitigate the likelihood of developing a hernia. For instance, maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular exercise can reduce abdominal pressure and strengthen abdominal muscles.
The outcomes of hernia surgery in middle-aged adults are generally positive, with most patients experiencing significant relief from symptoms. However, the recovery timeline can vary based on overall health, the type of surgery performed, and the presence of any complications.
On average, middle-aged adults can expect to return to their normal activities within a few weeks following surgery. Factors influencing recovery include:
By understanding these factors and working closely with healthcare providers, middle-aged adults can optimize their surgical outcomes and recovery.
For seniors, the decision to have hernia surgery involves weighing the potential benefits against the risks associated with their age and health status. As people age, the presence of comorbidities and the overall health condition play significant roles in determining the suitability of surgical intervention.
Seniors often have multiple health conditions, known as comorbidities, which can complicate surgical procedures and recovery. Conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can increase the risk of complications during and after surgery.
Table: Common Comorbidities and Their Impact on Hernia Surgery
| Comorbidity | Potential Impact on Surgery |
| Diabetes | Increased risk of infection and delayed healing |
| Heart Disease | Higher risk of cardiac complications during surgery |
| COPD | Increased risk of respiratory complications post-surgery |
To mitigate risks, surgeons often adopt modified surgical approaches for older patients. These can include less invasive techniques, such as laparoscopic surgery, which may reduce recovery time and minimize complications.
Ultimately, the decision to undergo hernia surgery as a senior should be influenced by the potential impact on quality of life. Surgery can significantly alleviate symptoms, improve mobility, and enhance overall well-being, but it’s crucial to balance these benefits against the potential risks and complications.
By carefully evaluating individual health status, comorbidities, and the potential benefits of surgery, seniors and their healthcare providers can make informed decisions that optimize their quality of life.
Debunking the myths around age limits for hernia surgery reveals a more nuanced reality. While age is a consideration in medical decisions, it is not the sole determining factor for undergoing hernia surgery. Both very young and elderly patients can successfully undergo the procedure, but the decision-making process involves a complex evaluation of individual health factors.
The belief that there’s an upper age limit for hernia surgery is misleading. Advances in medical technology and surgical techniques have made it possible for older adults to undergo hernia repair safely. The decision to operate is based more on the patient’s overall health, presence of comorbidities, and the potential benefits of surgery rather than age alone.
Similarly, the notion that children are too young for hernia surgery is not entirely accurate. Infants and young children can undergo hernia repair, especially if the hernia is symptomatic or there’s a risk of complications. The timing and approach may vary based on the child’s age, size, and overall health.
Hernia surgery is a common procedure that can be performed on a wide range of ages, from infants to the elderly. The key to a successful outcome lies in careful patient selection and personalized care.
The reality is that age guidelines for hernia repair are not one-size-fits-all. Surgeons consider a variety of factors, including the patient’s health status, the type of hernia, and the potential risks and benefits of surgery.
The timing of hernia surgery is not solely dependent on age but on several key medical factors. While age can influence the decision-making process, other critical elements play a significant role in determining the optimal time for surgical intervention.
The size of the hernia and its rate of progression are crucial factors in deciding when surgery is necessary. Larger hernias or those that are growing rapidly may require sooner intervention to prevent complications. Monitoring the size and growth rate is essential for determining the best surgical timing.
The severity of symptoms experienced by the patient also influences the timing of hernia surgery. Patients with severe pain or discomfort may benefit from earlier surgical intervention to improve their quality of life. Conversely, those with mild symptoms might be advised to wait under close medical supervision.
The risk of complications, such as incarceration or strangulation, is another critical factor that affects the timing of hernia surgery. Hernias that are at a higher risk of these complications may necessitate earlier surgical repair to prevent serious health issues.
In conclusion, while age is a consideration in hernia treatment, it is the medical factors such as hernia size, symptom severity, and the risk of complications that ultimately determine the best timing for hernia repair surgery.
Hernia repair surgery encompasses a range of techniques, with the most appropriate method being determined by the patient’s age and health status. Surgeons consider various factors when deciding on the surgical approach, ensuring the best possible outcomes for patients across different age groups.
The decision between open and laparoscopic surgery is influenced by the patient’s age, overall health, and the complexity of the hernia. Laparoscopic surgery, with its smaller incisions and potentially quicker recovery, is often considered for younger patients or those with less complex hernias. In contrast, open surgery might be preferred for older patients or cases where the hernia is more complicated.
The use of mesh in hernia repair is a common practice, but its application varies across age groups. For younger patients, the durability of the mesh is a significant consideration, while for older patients, the focus is on minimizing recovery time and reducing the risk of complications. Mesh selection and placement are tailored to the individual patient’s needs, taking into account their age, health status, and lifestyle.
Ultimately, the choice of surgical technique for hernia repair is a nuanced decision that balances the patient’s age, health, and personal preferences. By considering these factors, surgeons can optimize outcomes and improve the quality of life for patients undergoing hernia surgery.
The recovery process following hernia surgery is not one-size-fits-all; it differs substantially among various age demographics. Understanding these differences is crucial for patients and healthcare providers to manage expectations and optimize post-operative care.
Children typically recover quickly from hernia surgery, often returning to their normal activities within a few days to a week. The rapid healing process in children is attributed to their overall health and the fact that they usually don’t have the comorbidities seen in older adults.
Parents are advised to monitor their child’s activity levels and follow the surgeon’s instructions regarding post-operative care. Generally, children’s recovery is straightforward, with minimal complications.
Adults, particularly those between 20 and 60 years old, tend to have a recovery timeline that can vary based on their overall health, the type of surgery performed (open vs. laparoscopic), and their physical condition before surgery. Most adults can expect to return to their normal activities within 2 to 4 weeks.
Lifestyle factors, such as smoking and physical activity level, can significantly impact the recovery process. Adults who are physically fit and non-smokers typically have a smoother and faster recovery.
| Age Group | Typical Recovery Time | Factors Influencing Recovery |
| Pediatric | 1-7 days | Overall health, surgical technique |
| Adults (20-60) | 2-4 weeks | Lifestyle factors, physical condition, comorbidities |
| Seniors (65+) | 4-6 weeks or more | Comorbidities, physical condition, type of surgery |
Seniors often face a longer and more challenging recovery due to the presence of comorbidities and reduced physical reserves. Careful pre-operative assessment and post-operative care are critical to mitigate risks and ensure the best possible outcomes.
Seniors may require additional support during the recovery period, including physical therapy and home care, to help them regain their strength and independence.
The distinction between emergency and elective hernia surgery is vital, as age-related risks can significantly impact surgical outcomes. Emergency hernia surgery is often required when complications such as strangulation or incarceration occur, posing higher risks, particularly in older adults.
Strangulation and incarceration are serious complications that can arise from hernias, necessitating emergency surgery. The risk of these complications varies by age, with older adults being more susceptible due to potential comorbidities and decreased physical resilience.
“The risk of strangulation is a significant concern in older adults, often necessitating urgent surgical intervention,” notes a study on age-related risks in hernia surgery. This highlights the importance of timely medical evaluation for hernia symptoms across all age groups.
Outcomes for hernia surgery can differ significantly between emergency and elective procedures. Emergency surgeries, often performed under less ideal conditions, tend to have higher complication rates compared to planned surgeries.
A comparison of outcomes reveals that elective hernia repair tends to have better results, with lower morbidity and mortality rates, especially in younger patients. In contrast, emergency surgeries, while lifesaving, carry higher risks, particularly in older populations.
Key Considerations for Age-Related Risks
Understanding these age-related risks is crucial for making informed decisions about hernia surgery, whether it’s an emergency or elective procedure. By considering the patient’s age, overall health, and specific risk factors, healthcare providers can optimize surgical outcomes.
Beyond age, several key factors influence the decision-making process for hernia treatment. The decision to undergo hernia surgery involves a complex interplay of various health-related, personal, and surgical factors.
A comprehensive health assessment is crucial in determining the suitability of a patient for hernia surgery. This evaluation includes reviewing the patient’s medical history, current health status, and potential risks associated with surgery.
The assessment considers various health factors, including:
Patient preferences and quality of life play a significant role in the decision-making process. Patients’ personal values, expectations, and concerns about their condition and potential surgery are taken into account.
Factors considered under patient preferences include:
Shared decision making between patients and healthcare providers is essential for making informed decisions about hernia surgery. This collaborative approach ensures that patients are fully informed about their treatment options, risks, and benefits.
The shared decision-making process involves:
| Component | Description |
| Patient Education | Providing patients with accurate and understandable information about their condition and treatment options. |
| Risk and Benefit Analysis | Discussing the potential risks and benefits associated with hernia surgery. |
| Personalized Recommendations | Tailoring recommendations based on the patient’s unique health profile and preferences. |
By considering these factors and engaging in a collaborative decision-making process, patients and healthcare providers can make informed decisions about hernia surgery that are tailored to the individual’s needs and circumstances.
The preparation process for hernia surgery varies significantly across different age groups, from pediatric to senior patients. Effective preparation is crucial for ensuring the best possible outcomes, minimizing risks, and enhancing recovery. Understanding the specific needs of patients at different stages of life is essential for healthcare providers to tailor their approach.
For children, preparing for hernia surgery involves careful consideration of their overall health and developmental stage. Parents or guardians play a crucial role in this process, ensuring that the child follows pre-surgical instructions carefully. This includes:
Adults preparing for hernia surgery should focus on optimizing their overall health to reduce surgical risks. This involves:
For senior patients, pre-surgical optimization is critical due to the potential presence of comorbidities. This includes:
By tailoring preparation to the patient’s age and health status, healthcare providers can significantly improve outcomes for hernia surgery across all age groups.
Understanding the long-term outcomes and recurrence rates after hernia surgery is crucial for patients and healthcare providers. The success of hernia repair is influenced by various factors, including the patient’s age at the time of surgery.
In pediatric patients, hernia surgery has shown excellent long-term outcomes with low recurrence rates. Studies have indicated that the recurrence rate in children is less than 1%, making it a highly successful procedure in this age group. The use of laparoscopic techniques has further improved outcomes by reducing recovery time and minimizing complications.
Key factors contributing to successful outcomes in pediatric hernia repair include:
In adults, the long-term outcomes and recurrence rates vary based on factors such as the type of hernia, surgical technique, and patient health. Generally, recurrence rates range from 1-10%, with laparoscopic repairs often showing lower recurrence rates compared to open repairs. Lifestyle factors, such as smoking and obesity, can also impact recurrence rates.
Recurrence patterns in adults are influenced by:
For elderly patients, hernia surgery outcomes are generally good, but they are influenced by the presence of comorbidities and overall health status. While older adults may have higher risks associated with surgery, many experience significant improvement in quality of life post-operatively. Recurrence rates in this age group can be slightly higher due to factors like tissue weakness and comorbid conditions.
| Age Group | Recurrence Rate | Influencing Factors |
| Pediatric | <1% | Surgical technique, age |
| Adult | 1-10% | Surgical method, lifestyle, health |
| Elderly | Slightly higher than adults | Comorbidities, tissue strength |
In conclusion, understanding the long-term outcomes and recurrence rates by age is essential for making informed decisions about hernia surgery. By considering the specific needs and factors associated with different age groups, patients and healthcare providers can work together to achieve the best possible outcomes.
The optimal timing for hernia surgery is highly individualized, taking into account the patient’s age, overall health, and specific hernia characteristics. Achieving optimal results in hernia repair requires careful consideration of these factors to determine the best timing for surgery.
When evaluating age considerations in hernia treatment, healthcare providers must balance the risks and benefits of surgical intervention. For some patients, hernia repair may be recommended at a younger age, while others may benefit from delayed treatment.
Ultimately, the decision on when to undergo hernia surgery should be based on personalized timing that reflects the individual’s unique needs and health status. By following age guidelines for hernia repair, patients can achieve the best possible outcomes and minimize the risk of complications.
Consulting with a qualified healthcare provider is essential to determine the optimal age for hernia repair and develop an effective treatment plan tailored to the patient’s specific needs.
The best age for hernia surgery depends on various factors, including the type of hernia, overall health, and symptoms. While there is no one-size-fits-all answer, surgery is often recommended when symptoms become bothersome or when there’s a risk of complications.
There are no strict age limits for hernia surgery. Both pediatric and elderly patients can undergo surgery, but the decision is made on a case-by-case basis, considering the individual’s health status and potential risks.
Age influences treatment decisions as certain age groups may have different risks and benefits associated with surgery. For example, pediatric patients may require special consideration for their developing bodies, while elderly patients may have more comorbidities that impact surgical decisions.
Delaying hernia surgery can lead to complications such as strangulation or incarceration, which may require emergency surgery. The risk of these complications varies by age and overall health.
Yes, young children can undergo hernia surgery. In fact, some hernias in infants are congenital and may require early intervention to prevent complications.
The surgical approach for hernia repair can vary by age, with considerations for the patient’s overall health, the type of hernia, and potential risks. For example, laparoscopic approaches may be more commonly used in certain age groups.
Recovery expectations vary by age, with pediatric patients typically recovering quickly, adults having a moderate recovery time, and seniors potentially requiring more time and care during recovery.
Yes, seniors undergoing hernia surgery require special consideration due to the potential presence of comorbidities, which can impact surgical decisions and recovery.
Comorbidities can significantly impact hernia surgery decisions, particularly in older adults, as they may increase the risk of complications or affect the choice of surgical approach.
The use of mesh in hernia surgery is considered across various age groups, with the decision based on factors such as the type of hernia, patient health, and potential risks.
Yes, lifestyle factors can influence the decision to undergo hernia surgery, particularly for young adults who may need to balance recovery with career and other responsibilities.
Patient preferences and quality of life play a significant role in hernia surgery decisions, as patients and healthcare providers work together to weigh the benefits and risks of surgery.
Long-term outcomes of hernia surgery vary by age, with factors such as recurrence rates and overall health influencing the results.
Medical News Today (2025). A Guide to Double Voiding and Bladder-Emptying Techniques.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!