Last Updated on November 26, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
Ovarian cancer is a big threat to women’s health. It causes 140,000 deaths worldwide every year. This high number highlights the seriousness of ovarian cancer fatality and shows why it’s so important to raise awareness and understand the disease better.
Ovarian cancer is the deadliest gynecologic cancer. It’s important to understand its survival rate and what affects patient outcomes. By learning more about it, we can help those affected and try to improve their survival chances.
Key Takeaways
- Ovarian cancer is a leading cause of death among gynecologic malignancies.
- The global mortality rate for ovarian cancer is significant, with 140,000 deaths annually.
- Understanding ovarian cancer prognosis is key for patient support and treatment.
- Survival rates vary based on several factors, including disease stage and treatment.
- Awareness and education are vital to better ovarian cancer outcomes.
The Nature of Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer starts in the ovaries, which are key for women’s reproductive health. It’s a complex disease with big health impacts for women globally.
What is Ovarian Cancer?
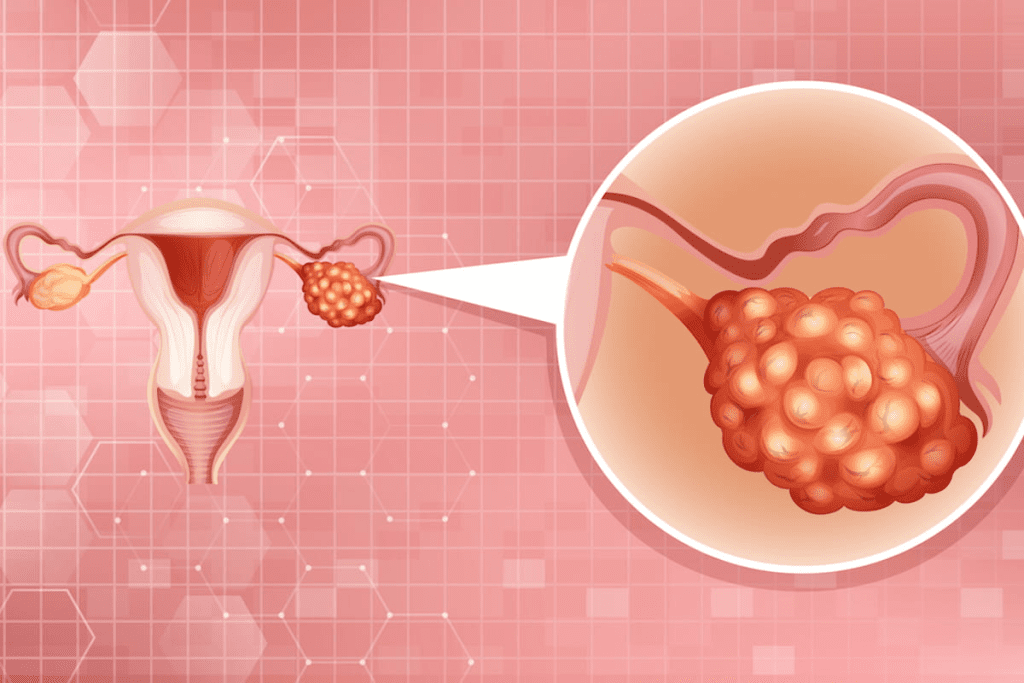
Ovarian cancer happens when cells in the ovaries grow the wrong way, forming tumors. Malignant tumors are cancerous and can spread, posing a serious threat if not caught early.
The ovaries are important for making eggs and hormones that control the menstrual cycle and support pregnancy. When cancer hits these organs, it can mess with these vital functions, causing health problems.
Types and Classifications
Ovarian cancer isn’t just one disease; it’s several types based on where it starts. The main types are:
- Epithelial ovarian cancer, which starts in the outer layer of the ovaries and is the most common type.
- Germ cell ovarian cancer, which begins in the cells that produce eggs and is more common in younger women.
- Stromal ovarian cancer, which develops in the connective tissue of the ovaries.
Knowing these types is key for finding the right treatment and understanding the outlook.
How It Develops and Spreads
Ovarian cancer usually starts in the outer layer of the ovaries and can grow and spread in different ways. It can invade nearby tissues and organs or spread through the lymphatic system or bloodstream to distant sites. The ability of ovarian cancer to spread silently, often without noticeable symptoms until it has advanced, makes early detection challenging.
As ovarian cancer gets worse, it can affect other parts of the body, leading to complications. Knowing how it develops and spreads is essential for finding effective treatments.
Ovarian Cancer Fatality: Understanding the Statistics
Ovarian cancer is a serious issue. It’s a leading cause of cancer deaths in women worldwide. We’ll look at global and U.S. stats to grasp the problem’s size.
Global Mortality Figures
Ovarian cancer causes a lot of deaths globally. Each year, about 140,000 women die from it. This shows how big a problem ovarian cancer is worldwide.
The high death rate from ovarian cancer is due to late diagnosis and the disease’s aggressiveness. Knowing these numbers is key to fighting ovarian cancer.
United States Death Rates
In the U.S., ovarian cancer is among the top five cancer killers in women. The death rate from ovarian cancer in the U.S. is a big concern. It shows we need more research and better treatments.
Recent data shows the U.S. ovarian cancer death rate is alarming. Many deaths are due to this disease each year. We must keep watching these numbers to find ways to get better.
Comparison to Other Cancer Types
Ovarian cancer has a very high mortality rate compared to other cancers. This is because it’s hard to catch early and is very aggressive.
Seeing how ovarian cancer compares to other cancers helps us focus our efforts. It also shows we need more awareness and early detection methods to save lives.
Factors Influencing Ovarian Cancer Survival
Ovarian cancer survival depends on many factors. These include age, genetics, and healthcare access. Knowing these factors helps patients and doctors make better treatment choices.
Age and Overall Health
Age and health at diagnosis are key in ovarian cancer survival. Older patients or those with health issues often face a tougher fight. This is because they may not recover as well from treatment.
Age-related risks are very important. Research shows older women are more likely to be diagnosed late. This increases their risk of death.
Genetic and Hereditary Factors
Genetic mutations, like in BRCA1 and BRCA2, greatly affect ovarian cancer risk and survival. Women with these mutations are at higher risk. They may also have different survival chances than those without these mutations.
Genetic testing is key in finding high-risk individuals. It helps in planning preventive measures and early detection.
Access to Healthcare
Getting quality healthcare is vital for ovarian cancer survival. Patients with access to specialized care, like gynecologic oncologists, have better chances. This is because they get the best treatment possible.
Socioeconomic Considerations
Socioeconomic status also plays a role in ovarian cancer survival. It affects healthcare access, health knowledge, and treatment costs. Disparities in healthcare are seen across different income levels.
| Factor | Impact on Survival |
| Age | Older patients have poorer prognosis |
| Genetic Mutations | Increased risk and potentially different survival outcomes |
| Access to Healthcare | Improved survival with quality care |
| Socioeconomic Status | Disparities in healthcare access and outcomes |
Stage-by-Stage Survival Analysis
Ovarian cancer survival rates depend on the disease’s stage at diagnosis. Knowing these rates helps patients and doctors make better treatment choices.
Stage 1 Ovarian Cancer Survival
Patients with Stage 1 ovarian cancer have a much better outlook. The five-year survival rate is about 90%. This is because the cancer is mostly in the ovaries. It can often be treated with surgery and sometimes chemotherapy.
Stage 2 Ovarian Cancer Prognosis
Stage 2 ovarian cancer has spread to other parts of the pelvis. The five-year survival rate is around 70%. Treatment usually includes surgery and chemotherapy to kill any remaining cancer cells.
Stage 3 Ovarian Cancer Fatality
Stage 3 ovarian cancer has spread to the abdomen or lymph nodes. The fatality rate is higher. The five-year survival rate is about 39%. Treatment is more intense, often involving surgery and chemotherapy.
Stage 4 Ovarian Cancer Survival
Stage 4 ovarian cancer has spread to distant organs. Unfortunately, the survival rate is the lowest, at about 17%. Treatment aims to manage symptoms and slow the disease’s growth, often with chemotherapy.
An ovarian cancer diagnosis can be scary. But knowing the survival rates for each stage helps. It’s important for patients to talk about their prognosis with their doctors.
5-Year Survival Rate for Ovarian Cancer Patients
Knowing the 5-year survival rate is key for ovarian cancer patients and their families. It shows how likely someone is to survive. The rate is the percentage of people who live 5 years after being diagnosed.
Defining 5-Year Survival
The 5-year survival rate is a common way to measure cancer patient outcomes. It shows the number of people alive 5 years after being diagnosed. This helps compare survival rates between different cancers and stages.
But remember, the 5-year survival rate is not a prediction for one person. It’s an average based on many people. Many things can affect how long someone lives, like their health, cancer stage, and treatment.
Current Statistics in the United States
In the U.S., the 5-year survival rate for ovarian cancer is about 49%, says the American Cancer Society. But, this rate changes a lot based on when the cancer is found.
| Stage at Diagnosis | 5-Year Survival Rate |
| Localized (Stage I) | 92% |
| Regional (Stage II-III) | 73% |
| Distant (Stage IV) | 31% |
Early detection makes a big difference. When ovarian cancer is caught early, the survival rate is much higher. This is compared to when it’s found later.
Factors That Improve 5-Year Outcomes
Several things can help ovarian cancer patients live longer. These include:
- Early detection: Finding cancer early greatly improves survival chances.
- Effective treatment plans: Personalized treatments that include surgery, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy can help.
- Overall health: Being in good health also helps with survival.
Beyond 5 Years: Long-term Survival
While the 5-year survival rate is important, long-term survival is also key. Thanks to better treatments, many ovarian cancer patients now live longer.
Research shows that with the right care, some patients can live for 10 years or even 20 years after diagnosis.
Ovarian Cancer Mortality Trends in America
It’s key to know how ovarian cancer deaths change over time in America. We look at these trends to spot patterns and what affects death rates.
Historical Death Rate Patterns
Ovarian cancer has long been a top cause of death in gynecologic cancers in the U.S. Death rates have slowly gone down over the years. This is thanks to better treatments and finding cancer early.
Medical data shows a small drop in ovarian cancer death rates. This shows how healthcare has improved.
Current Mortality Statistics
Ovarian cancer is a big killer of women in the U.S. today. The American Cancer Society says about 13,000 women die from it each year.
We look at today’s numbers to see how ovarian cancer affects different groups and places.
| Year | Estimated Deaths | Age-Adjusted Death Rate |
| 2018 | 13,980 | 6.8 per 100,000 |
| 2019 | 13,680 | 6.6 per 100,000 |
| 2020 | 13,140 | 6.4 per 100,000 |
Regional and Demographic Variations
Where you live and who you are can affect your risk of dying from ovarian cancer. People with BRCA mutations face a higher risk. Also, where you get healthcare can change your chances of survival.
Places with easy access to special healthcare tend to have fewer deaths. This shows how important good healthcare is.
By knowing these trends and differences, we can make our fight against ovarian cancer in America more effective.
Why Ovarian Cancer Often Has Poor Outcomes
Ovarian cancer is a complex and challenging disease. It is often diagnosed late, which makes outcomes poor. The disease’s complexity and late detection are key reasons for these outcomes.
The Silent Killer: Late Detection Issues
Ovarian cancer is often called “the silent killer” because it can be asymptomatic or have vague symptoms early on. This makes it hard to catch early, leading to poor outcomes.
“The lack of effective screening methods for ovarian cancer means that most cases are diagnosed at an advanced stage, when the disease is more difficult to treat.”
Being diagnosed late affects survival rates. Early detection leads to better survival chances. This is because the disease is easier to treat when caught early.
Aggressive Biological Behavior
Ovarian cancer is aggressive, with many tumors being high-grade and growing fast. This aggressiveness leads to poor outcomes, as the disease can spread quickly.
The aggressive nature of ovarian cancer means it can progress quickly. This makes timely and effective treatment essential.
Challenges in Treatment Response
Getting ovarian cancer to respond to treatment is hard. While initial treatments may work, resistance often develops. This leads to recurrence.
- Resistance to chemotherapy is a significant issue.
- Limited targeted therapy options are currently available.
- The development of new treatments is an area of ongoing research.
Improving treatment response and overcoming resistance are key to better outcomes for ovarian cancer patients.
High Recurrence Rates
Ovarian cancer often comes back, even after initial treatment success. This can happen months or years later.
| Stage at Diagnosis | Recurrence Rate |
| Stage I | 10-20% |
| Stage II | 30-40% |
| Stage III | 60-70% |
| Stage IV | 80-90% |
Understanding and addressing recurrence is vital for improving survival rates in ovarian cancer patients.
Recurrence and Its Impact on Long-term Survival
Long-term survival in ovarian cancer is often complicated by the risk of recurrence. Ovarian cancer recurrence is a significant challenge that affects patient outcomes. We will explore the frequency of recurrence, survival rates after recurrence, the importance of monitoring, and treatment options for recurrent disease.
Frequency of Ovarian Cancer Recurrence
Ovarian cancer recurrence is a common issue, affecting a significant proportion of patients. Studies indicate that the majority of ovarian cancer patients will experience recurrence within two years of initial treatment.
Survival Rates After Recurrence
Survival rates after recurrence vary based on several factors, including the timing of recurrence and the effectiveness of subsequent treatments. Generally, the prognosis is more favorable when recurrence is detected early and treated promptly.
Monitoring and Early Detection of Recurrence
Regular monitoring is key for detecting recurrence early. This involves a combination of imaging studies, such as CT scans, and serum CA-125 level checks. Early detection allows for timely intervention, potentially improving outcomes.
Treatment Options for Recurrent Disease
Treatment for recurrent ovarian cancer depends on several factors, including previous treatments and the extent of recurrence. Options may include surgery, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or participation in clinical trials.
| Treatment Option | Description | Considerations |
| Surgery | Surgical intervention to remove recurrent tumors. | Feasibility depends on the extent and location of recurrence. |
| Chemotherapy | Use of chemotherapeutic agents to control recurrence. | Choice of agent depends on previous chemotherapy exposure. |
| Targeted Therapy | Treatments targeting specific molecular characteristics of the tumor. | Requires molecular profiling of the tumor. |
Understanding the complexities of ovarian cancer recurrence is essential for improving patient outcomes. By recognizing the frequency of recurrence, understanding survival rates after recurrence, and utilizing effective monitoring and treatment strategies, we can work towards improving long-term survival for ovarian cancer patients.
Treatment Approaches and Survival Outcomes
Effective treatment of ovarian cancer needs a mix of strategies. We will look at the different treatments and how they affect survival.
Surgical Interventions and Prognosis
Surgery is often the first step in treating ovarian cancer. It aims to remove as much of the tumor as possible. Cytoreductive surgery has been shown to improve survival rates when successful. “The goal of surgical intervention is to achieve optimal debulking, which significantly influences patient prognosis,” according to recent studies.
We will explore the details of surgical interventions. This includes the role of laparoscopy and the benefits of minimally invasive surgery in certain cases. The skill of the surgeon and the extent of the disease at diagnosis are key in determining the outcome of surgery.
Chemotherapy Effectiveness
Chemotherapy is a key part of treating ovarian cancer, mainly for advanced stages. Platinum-based chemotherapy is often used, with carboplatin and paclitaxel being standard first-line treatments. The success of chemotherapy depends on several factors, including the cancer stage, patient health, and genetic factors.
We will look at how chemotherapy improves survival rates. We will also discuss emerging resistance patterns that challenge treatment effectiveness. “Chemotherapy remains a vital component of ovarian cancer treatment, but its effectiveness varies based on individual patient factors,” as noted by oncologists.
Targeted Therapies and Immunotherapy
Targeted therapies and immunotherapy are newer approaches in treating ovarian cancer. PARP inhibitors have shown promise, mainly in patients with BRCA mutations. Immunotherapies, including checkpoint inhibitors, are being explored for their ability to enhance the body’s immune response against cancer cells.
We will discuss the latest in targeted therapies and immunotherapy. These treatments offer new hope, mainly for those with recurrent or resistant disease.
Clinical Trials and Emerging Treatments
Clinical trials are vital in advancing ovarian cancer treatment. We will review ongoing trials looking at new therapies, including angiogenesis inhibitors and personalized medicine approaches. Joining clinical trials gives patients access to cutting-edge treatments that may improve survival.
“The future of ovarian cancer treatment lies in the continued exploration of new therapeutic strategies and the integration of emerging treatments into clinical practice,” as emphasized by researchers in the field.
Early Detection: The Key to Reducing Fatality
Early detection is key in fighting ovarian cancer, boosting survival chances. Ovarian cancer is often called a “silent killer” because its symptoms are vague. This makes it hard to catch early. But, knowing the signs and using screening tests can greatly help patients.
Recognizing Warning Signs
Spotting ovarian cancer signs is the first step. Common signs include bloating, pelvic pain, and trouble eating. These symptoms can also mean other things, but if they last, see a doctor.
Current Screening Limitations
Ovarian cancer screening has its limits. There’s no perfect test for all women, even those with symptoms. Tests like ultrasound and the CA-125 blood test are used. But, they can lead to false alarms, causing worry and surgery.
High-Risk Population Monitoring
Women at high risk, like those with certain genes, need closer checks. They might get regular blood tests and ultrasounds. This is to catch cancer early, when it’s easier to treat.
Impact of Early Diagnosis on Survival
Early diagnosis is vital for beating ovarian cancer. Finding it early can raise survival rates by a lot. Studies show early-stage cancer can have a 90% five-year survival rate. But, late-stage cancer has much lower chances.
Early detection is the cornerstone of improving ovarian cancer survival rates. It is vital that both healthcare providers and women are aware of the risk factors and symptoms to facilitate timely diagnosis and intervention.
Risk Factors Associated with Higher Mortality
Ovarian cancer mortality is influenced by many factors. These include genetic, environmental, and medical history elements. Knowing these factors helps identify those at higher risk and can lower mortality rates.
BRCA Mutations and Other Genetic Factors
Genetic mutations are key in ovarian cancer risk. BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations are well-known for increasing this risk. Women with these mutations face a higher risk and often have cancer at a more advanced stage.
Other genetic syndromes, like Lynch syndrome, also raise ovarian cancer risk. Genetic testing can spot these mutations. This allows for early action and may lower mortality.
| Genetic Factor | Relative Risk Increase | Recommendations |
| BRCA1 Mutation | Up to 40% | Regular screening, consider prophylactic surgery |
| BRCA2 Mutation | Up to 20% | Regular screening, consider prophylactic surgery |
| Lynch Syndrome | Variable, up to 12% | Regular screening, management of other associated cancers |
Age-Related Risks
Age is a big risk factor for ovarian cancer. Most cases happen in women over 50. The risk grows with age, peaking in the 70s.
Women over 50 should know their risk. They should talk about screening with their healthcare provider.
Lifestyle and Environmental Influences
Lifestyle and environmental factors also affect ovarian cancer risk. For example, obesity and talc powder use in the genital area increase risk.
Medical History Considerations
A woman’s medical history can also impact her risk. Conditions like endometriosis and infertility raise the risk.
Women with these conditions should be aware of their risk. They should talk to their healthcare provider about monitoring and preventive measures.
Ovarian Cancer vs. Other Gynecologic Cancers
Gynecologic cancers have different impacts, with ovarian cancer being very deadly. We will look at the differences in death rates, finding cancer early, and why ovarian cancer is so fatal compared to others.
Comparative Mortality Rates
Ovarian cancer has a higher death rate than other gynecologic cancers. Medical sources show its death rate is higher than cervical, uterine, or vaginal cancers. The five-year survival rate for ovarian cancer is about 48%, which is lower than many other gynecologic cancers. This is mainly because ovarian cancer is often found late, making treatment harder.
Detection Challenges Unique to Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer is deadly because it grows quietly. Unlike other gynecologic cancers, it often doesn’t show symptoms until it’s too late. This late detection is a big reason for its high death rate. We will talk about the challenges in finding ovarian cancer early and how it compares to finding other gynecologic cancers.
Why Ovarian Cancer is Often the Deadliest
Ovarian cancer is aggressive and often comes back. It can also resist chemotherapy, making treatment harder. We will look at why ovarian cancer is the deadliest and what this means for patients and doctors.
It’s important to understand the death rates and finding cancer early for ovarian cancer compared to others. By focusing on these differences, we can tackle ovarian cancer’s unique challenges better.
Prevention Strategies to Reduce Ovarian Cancer Risk
To lower ovarian cancer risk, we need a mix of understanding what helps, thinking about surgery, and living healthy. Every woman’s situation is different, so it’s key to know what’s right for her.
Protective Factors
Some things can help protect against ovarian cancer. These include:
- Breastfeeding: It’s been found to lower ovarian cancer risk.
- Oral Contraceptives: Using them can also reduce the risk.
- Tubal Ligation: Getting one’s tubes tied may lower the risk too.
A study in a medical journal found that using oral contraceptives for over five years can greatly lower ovarian cancer risk.
“Oral contraceptive use is associated with a reduced risk of ovarian cancer, with the greatest risk reduction observed with longer durations of use.”
Prophylactic Surgery for High-Risk Women
Women at high risk, often due to genetic mutations like BRCA1 or BRCA2, might consider surgery. This is to prevent ovarian cancer.
| Surgical Option | Description | Risk Reduction |
| Prophylactic Salpingo-Oophorectomy | Removal of the ovaries and fallopian tubes | Up to 90% reduction in ovarian cancer risk |
| Salpingectomy | Removal of the fallopian tubes | Potential reduction, emerging data |
A leading oncologist says, “Prophylactic salpingo-oophorectomy is very effective for high-risk women. But it’s a big decision that needs careful thought and advice.”
Lifestyle Modifications
Our lifestyle choices can also help prevent ovarian cancer. Some things we can’t change, but others we can.
- Diet and Nutrition: Eating lots of fruits, veggies, and whole grains is good.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise can lower cancer risk, including ovarian cancer.
- Avoiding Risk Factors: Try to avoid harmful chemicals and radiation.
By using these prevention strategies, women can lower their ovarian cancer risk. It’s important to talk to a healthcare provider to find the best plan for each woman’s situation.
Advances Improving Ovarian Cancer Survival
Ovarian cancer treatment is changing fast. Breakthroughs in genetic testing and personalized medicine are leading the way. We’re learning more about ovarian cancer’s genetics and molecular makeup. This knowledge is helping us develop new treatments to better patient outcomes.
Breakthrough Treatments
Recently, new treatments have been introduced. These are changing how we manage ovarian cancer. Some of these include:
- PARP Inhibitors: These target cancer cells’ genetic weaknesses, mainly in those with BRCA mutations.
- Immunotherapy: It uses the immune system to fight cancer, giving hope to those with advanced disease.
- Angiogenesis Inhibitors: These drugs cut off tumors’ blood supply, slowing their growth and improving treatment results.
These treatments are not just increasing survival rates. They’re also making life better for ovarian cancer patients.
Genetic Testing and Personalized Medicine
Genetic testing is key in managing ovarian cancer. It helps identify high-risk patients and tailor treatments to their genetic profiles. BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations are major factors in ovarian cancer risk and treatment response.
Personalized medicine, guided by genetic testing, allows doctors to:
- Choose the best treatment based on the tumor’s genetic makeup.
- Find family members at higher risk, helping them get early treatment.
This approach is greatly improving outcomes for ovarian cancer patients.
Research Directions and Hope for the Future
Research is moving forward, bringing new hope for ovarian cancer treatment. Some promising areas include:
- Liquid Biopsy: A non-invasive test that can find cancer DNA in the blood, changing early detection and monitoring.
- Cancer Vaccines: Vaccines that could prevent or treat ovarian cancer by boosting the immune system against cancer cells.
- Targeted Therapies: New drugs that target specific molecular mechanisms driving ovarian cancer growth and progression.
These emerging treatments and technologies offer great promise. They could significantly improve ovarian cancer survival rates and change the future of care for patients.
Conclusion
Understanding ovarian cancer fatality is key for patients, doctors, and researchers. Research shows ovarian cancer is complex and deadly. Survival rates depend on age, genetics, and healthcare access.
Ovarian cancer fatality rates are high worldwide and in the U.S. But, new treatments like surgery, chemotherapy, and targeted therapies are helping some patients live longer.
Early detection is vital to fight ovarian cancer. Spotting warning signs, watching high-risk groups, and finding good screening methods are important. We hope ongoing research will lead to better treatments and strategies against this disease.
In short, we need to keep raising awareness, doing research, and supporting those touched by ovarian cancer. Together, we can work towards better survival rates and lower fatality rates. This will help future generations understand and fight ovarian cancer better.
FAQ
What is the overall survival rate for ovarian cancer?
The survival rate for ovarian cancer depends on when it’s found. In the U.S., the 5-year survival rate is about 47%. Thanks to better treatments and early detection, survival rates have improved a lot.
How does ovarian cancer compare to other gynecologic cancers in terms of mortality?
Ovarian cancer is often the deadliest among gynecologic cancers. This is because its symptoms are not specific, leading to late detection. It has a higher mortality rate than other gynecologic cancers, showing the need for early detection.
What are the risk factors associated with higher ovarian cancer mortality?
Higher risk factors include BRCA mutations, older age, and family history of ovarian or breast cancer. Lifestyle and environmental factors also play a role. Knowing these can help identify who needs preventive measures and closer monitoring.
Can ovarian cancer be prevented or its risk reduced?
While we can’t prevent ovarian cancer entirely, there are ways to lower its risk. Options include prophylactic surgery, healthy lifestyle choices, and certain medications. It’s best to talk to a healthcare provider about these options.
What is the significance of the 5-year survival rate in ovarian cancer?
The 5-year survival rate is key in understanding ovarian cancer prognosis. It shows the percentage of patients alive 5 years after diagnosis. Better 5-year survival rates mean we’re making progress in treatment and care.
How does the stage of ovarian cancer at diagnosis impact survival?
The stage at diagnosis greatly affects survival. Early-stage ovarian cancer has a much better survival rate than advanced stages. Early detection is vital, and we encourage awareness of symptoms and screening for high-risk individuals.
What are the current treatment approaches for ovarian cancer, and how do they impact survival?
Current treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, targeted therapies, and immunotherapy. The choice depends on the cancer’s stage and type, and the patient’s health. Advances in these treatments have boosted survival rates, and research continues to find new therapies.
How often does ovarian cancer recur, and what are the survival rates after recurrence?
Recurrence is a big concern, with many patients facing it. Survival after recurrence varies based on several factors, including the time to recurrence and treatment effectiveness. Close monitoring and early detection of recurrence are key to better outcomes.
What advancements have improved ovarian cancer survival in recent years?
Recent years have seen improvements in treatment, including targeted therapies, immunotherapy, and genetic testing. Personalized medicine approaches have also shown promise in better outcomes.
Why is ovarian cancer often diagnosed at a late stage?
It’s often diagnosed late because its symptoms are nonspecific, similar to other common conditions. This highlights the need for more awareness of symptoms and better screening methods for early detection.
What is the role of genetic testing in ovarian cancer?
Genetic testing is vital for identifying BRCA mutations and other genetic factors that raise ovarian cancer risk. This information helps guide preventive measures and treatment decisions.
References
- Grossman, D. C., Curry, S. J., Owens, D. K., Bibbins-Domingo, K., Caughey, A. B., Davidson, K. W., … & Screening for Ovarian Cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. (2018). JAMA, 319(6), 588“594. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2672638
- Patni, R., & Skates, S. J. (2019). Screening for Ovarian Cancer: An Update. Current Oncology Reports, 21(3), 25. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6459072/
- Liberto, J. M., & Huskova, B. (2022). Current and Emerging Methods for Ovarian Cancer Diagnosis and Screening. Diagnostics, 12(6), 1361. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9221480/