Knowing how your cervix changes during ovulation is key for those trying to get pregnant or just wanting to know their body better. The cervix, a muscular organ at the base of the uterus, is vital for fertility. When you ovulate, it becomes high, soft, open, and wet. This is called the SHOW pattern. This ultimate guide to the ovulating cervix position reveals essential fertility secrets. Learn the surprising key changes to feel for.
At Liv Hospital, we know how important it is to understand these changes. They help people on their fertility journey. By watching how the cervix changes, you can learn a lot about your fertility.
Key Takeaways
- The cervix undergoes significant changes during ovulation, becoming high, soft, open, and wet.
- Understanding these changes can help individuals track their fertility.
- Monitoring the cervix can provide valuable insights into the menstrual cycle.
- The SHOW pattern is a key indicator of ovulation.
- Liv Hospital is dedicated to supporting individuals in their fertility journey.
Understanding Your Cervix and Its Role in Fertility
Learning about the cervix and its changes can help us understand fertility better. The cervix is key to the female reproductive system. It plays a big role in getting pregnant and keeping reproductive health good.
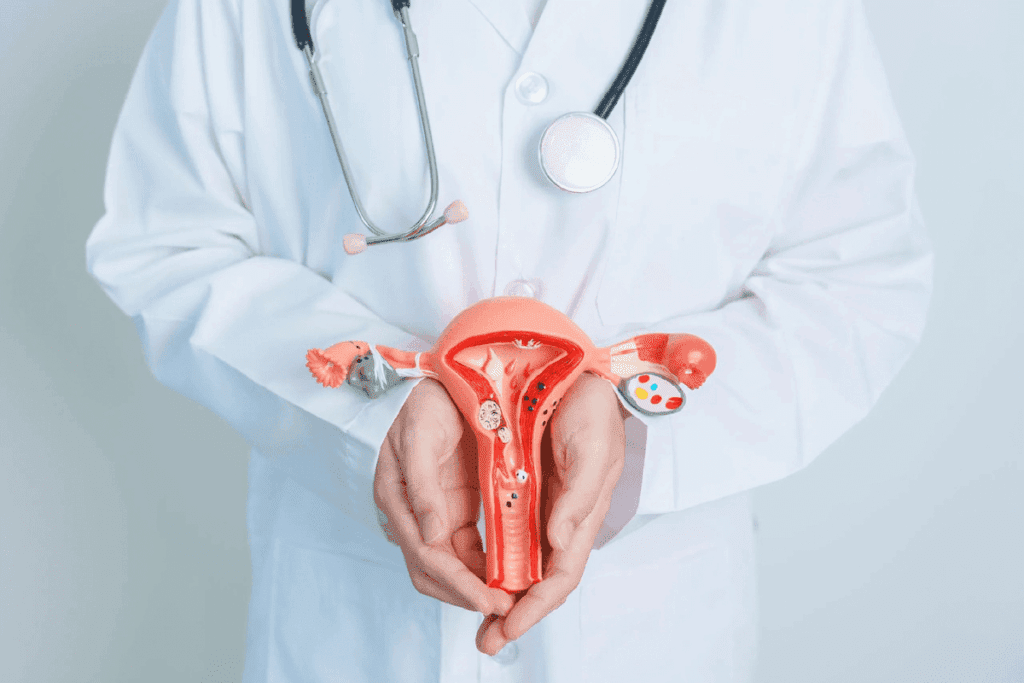
The Anatomy of the Cervix
The cervix is a muscular, cylindrical organ at the uterus’s lower end. It connects the uterus to the vagina. It’s about 2-3 centimeters long. It has a small, narrow passage called the cervical canal. This passage lets sperm and menstrual blood pass through.
How the Cervix Functions Throughout the Menstrual Cycle
The cervix changes a lot during the menstrual cycle due to hormone changes. These changes are important for fertility. The cervix makes cervical mucus, which changes in consistency and amount. This mucus helps or blocks sperm from getting into the uterus.
When ovulation happens, the cervix is softer, higher, and more open. This makes it easier for sperm to get into the uterus. Key Functions of the Cervix:
- Produces cervical mucus to help sperm pass
- Allows sperm into the uterus during ovulation
- Protects the uterus from infection
- Is very important during childbirth
Cervical Characteristic | Pre-Ovulation | During Ovulation | Post-Ovulation |
Cervical Mucus | Thick, cloudy | Clear, slippery | Thick, cloudy |
Cervical Position | Low | High | Low |
Cervical Os | Closed | Slightly open | Closed |
By knowing these changes and the cervix’s role in fertility, women can better understand how conception works.
The Hormonal Dance: What Triggers Cervical Changes
The cervix changes a lot because of estrogen and progesterone. These hormones are key for getting pregnant and keeping the reproductive system healthy.
Estrogen’s Effect on Cervical Position and Texture
Before ovulation, estrogen levels go up. This makes the cervix softer and more open for sperm. The cervix also moves up and opens more. The mucus in the cervix helps sperm get to the egg.
When estrogen is at its highest, the cervix is ready for sperm. This is the best time to get pregnant because the cervix is perfect for sperm to reach the egg.
Progesterone’s Role After Ovulation
After ovulation, progesterone levels go up. This hormone helps the fertilized egg stick to the uterus. Progesterone makes the cervix stiffer and harder to get through. The mucus in the cervix gets thicker, making it harder for sperm to pass through.
This change in hormones means the fertile time is over. It marks the start of the luteal phase.
Hormone | Effect on Cervix | Phase of Menstrual Cycle |
Estrogen | Cervix softens, becomes higher and more open | Follicular phase, before ovulation |
Progesterone | Cervix firms up, becomes lower and less open | Luteal phase, after ovulation |
Knowing how estrogen and progesterone affect the cervix helps us understand fertility and reproductive health better.
Ovulating Cervix Position: The SHOW Pattern Explained
Knowing the SHOW pattern is key for women wanting to get pregnant. It shows when you’re most fertile. The SHOW pattern means Soft, High, Open, and Wet, showing the best cervix state for ovulation.
When you ovulate, your cervix changes a lot. These changes help sperm get into your uterus. It’s all part of a complex process that gets your body ready for a baby.
Soft: Why Your Cervix Softens During Fertility
At your most fertile time, your cervix gets softer. It feels like your lips, not the tip of your nose. This happens because estrogen levels go up, making the cervix more flexible.
High: Understanding Cervical Height Changes
As you get closer to ovulation, your cervix moves up. This change is small and might take some getting used to. The move is linked to hormonal shifts in your cycle.
Open: How and Why the Cervical Os Dilates
The opening of your cervix gets a bit wider during ovulation. This makes it easier for sperm to get into your uterus. How much it widens can differ from woman to woman.
Wet: Cervical Fluid Changes During Ovulation
When you ovulate, your cervical fluid gets more and feels like raw egg whites. This kind of mucus helps sperm move through your cervix and into your uterus.
Cervical Characteristic | Change During Ovulation | Purpose |
Softness | Becomes softer | Facilitates sperm passage |
Height | Rises higher in the vaginal canal | Related to hormonal changes |
Opening | Dilates slightly | Allows sperm to enter the uterus |
Cervical Fluid | Becomes more abundant and egg-white-like | Nourishes and facilitates sperm motility |
The SHOW pattern is a natural part of your reproductive cycle. It helps increase your chances of getting pregnant during ovulation. By knowing these changes, you can better understand your body’s fertility signals.
How to Check Your Cervical Position
Learning to check your cervical position is key to understanding your body and fertility. It involves simple steps that offer insights into your menstrual cycle and when you might be fertile. By following good hygiene and positioning, you can track changes in your cervix.
Proper Hand Hygiene and Positioning
First, make sure your hands are clean to avoid infections. Wash them well with soap and warm water, then dry. It’s important to find a comfortable position for checking your cervix. You can squat, sit on the toilet, or stand with one leg up on the bathtub edge. Pick what feels most comfortable for you.
Tips for Comfortable Positioning:
- Squat on the floor or on the toilet.
- Stand with one leg up on the bathtub edge.
- Sit on the toilet with your legs apart.
Best Time of Day for Cervical Checks
The evening is usually the best time to check your cervix, after being active during the day. This is because your cervix is more accessible after moving. But, pick a time that fits your schedule and stick to it.
What to Feel For: A Step-by-Step Guide
To check your cervical position, gently insert your index or middle finger into your vagina. Be careful not to cause discomfort. You should feel your cervix at the end of your vaginal canal. Look for these characteristics:
Cervical Position Characteristics:
Characteristic | Description |
Position | Note whether your cervix feels high, low, or somewhere in between. |
Texture | Observe if your cervix is firm, soft, or somewhere in between. |
Opening | Check if the cervical os is open, closed, or slightly open. |
By regularly checking your cervical position and paying attention to these characteristics, you can gain a deeper understanding of your fertility and menstrual cycle. Remember, the key to accurately tracking your cervical position is consistency and patience.
Cervix Position Before Ovulation: The Early Follicular Phase
Knowing the cervix’s position and feel before ovulation is key for tracking fertility. The cervix changes a lot in the menstrual cycle. These changes help figure out when a woman is most fertile.
Right after menstruation, the cervix shows certain signs. We’ll look at these signs and how they change as ovulation gets closer.
Post-Menstruation Cervical Characteristics
Right after your period, the cervix feels firm and low in the vagina. It’s like the tip of your nose. The cervical os, or opening, is usually closed. These changes happen because of hormonal shifts after your period.
The cervix is getting ready for an egg to be fertilized. Even though it seems the same, it’s actually changing a bit because of rising estrogen levels.
Gradual Changes as Ovulation Approaches
As ovulation gets closer, the cervix starts to change. It becomes softer, feeling more like lips. This softening means the body is getting ready for ovulation. The cervix also moves higher in the vagina, making it harder to feel during self-exams.
The cervical os starts to open a bit, but it’s not fully open yet. These changes are mainly because of rising estrogen levels.
Knowing these changes can help women find their fertile time. By watching how the cervix changes, women can learn more about their cycle. This can help them get pregnant.
It’s important to remember that everyone’s cervix is different. Things like age, childbirth, and health can affect how the cervix feels. So, it’s key for women to get to know their own cervix over time.
What Does the Cervix Feel Like During Ovulation?
Ovulation brings changes to the cervix that are both small and important. These changes help the body get ready for fertilization.
Texture Comparisons: The “Lips vs. Nose Tip” Analogy
When ovulation happens, the cervix gets softer, like lips. This is different from its usual firmness, which feels like the tip of the nose. The softening is because of hormone changes, mainly more estrogen.
Position Changes: How High Is “High”?
The cervix also moves higher in the vagina during ovulation. This is called being “high.” It might be harder to feel during self-exams, but it’s a normal part of ovulation.
Opening Size: What “Open” Really Means
The cervical os, or the cervix opening, gets a bit wider during ovulation. This isn’t a big change, but it’s enough for sperm to get through. How open it is can differ from woman to woman, but it’s more open than other times in the cycle.
Cervical Characteristic | Pre-Ovulation | During Ovulation |
Texture | Firm (like nose tip) | Soft (like lips) |
Position | Lower | Higher |
Opening Size | Closed or slightly open | Slightly more open |
Knowing about these changes can help women track their fertility better. By noticing the cervix’s texture, position, and openness, they can learn more about their cycle.
Does Your Cervix Open During Ovulation?
Ovulation and cervical changes are closely linked. The cervix changes in a significant way during ovulation. This change helps with fertility.
The Degree of Cervical Dilation During Fertility
When you ovulate, your cervix opens a bit. This makes it easier for sperm to get through. This opening is not as big as during labor but is very important.
The amount of opening varies from woman to woman. But it’s usually not very big.
To understand cervical dilation better, here’s a table:
Phase | Cervical Dilation | Cervical Texture |
Pre-Ovulation | Closed | Firm |
During Ovulation | Slightly Open | Soft |
Post-Ovulation | Closed | Firm |
How Many Days the Cervix Remains Open
The cervix stays open for about 1-2 days. This matches the peak time for getting pregnant. This short time is key for sperm to reach the egg.
The Purpose of Cervical Opening During Ovulation
The main reason for the cervix opening is to let sperm into the uterus. This increases the chance of getting pregnant. It’s a key part of how we get pregnant.
In short, the cervix does open during ovulation, a bit. This opening is key for getting pregnant. Knowing this helps women understand how conception works.
Cervix Changes After Ovulation: The Luteal Phase
After ovulation, the cervix starts to change due to hormonal shifts. This marks the start of the luteal phase. These changes are key to understanding fertility and knowing when the fertile window ends.
Timeline of Post-Ovulation Cervical Changes
Right after ovulation, the cervix starts to go back to its original state. This usually happens in a few days. It becomes firmer, lower, and more closed as progesterone levels go up. This change shows the end of the fertile time.
The time it takes for these changes can differ from person to person. But usually, the cervix goes back to its original state in 3 to 5 days after ovulation.
How to Identify the End of Your Fertile Window
To know when your fertile window ends, track cervical changes and other fertility signs. Watching your cervix regularly helps you get to know your body’s patterns. Here are some tips:
- Check your cervix at the same time every day to establish a baseline.
- Note the position, texture, and opening of your cervix.
- Combine cervical observations with basal body temperature tracking and cervical mucus observations for a more accurate fertility assessment.
By tracking these changes and your cervical position and texture, you can better figure out when your fertile window ends. This knowledge helps you make smart choices about your reproductive health.
Common Variations in Cervical Position and Texture
It’s important to know that cervical patterns can differ a lot among people. There are general guidelines for cervical position and texture, but every woman’s body is unique.
Many factors can affect these variations, like hormonal changes, age, and reproductive history. Knowing these differences helps women understand cervical changes better. This knowledge is key for tracking fertility.
Individual Differences in Cervical Patterns
Just like fingerprints, cervical patterns are unique to each person. Some women might see big changes in their cervical position and texture during their cycle. Others might notice smaller changes.
These differences can come from many things, like health, body type, and hormonal balance. It’s important for women to get to know their own cervical patterns. This helps them know what’s normal for them.
How Age and Childbirth Affect Cervical Feel
Age and childbirth can change how the cervix feels. As women get older, they might notice changes in their cervical texture and position. This is because of natural aging and hormonal changes.
Childbirth, and vaginal delivery in particular, can also affect the cervix. Women who have had vaginal births might see changes in their cervical texture and the size of the cervical os. This is different from women who haven’t given birth or who have had cesarean sections.
Factor | Effect on Cervix |
Age | Potential changes in texture and position due to hormonal shifts |
Vaginal Childbirth | Possible changes in cervical texture and os size |
Hormonal Balance | Influences cervical mucus and position |
When “Normal” Varies: Understanding Your Personal Pattern
“Normal” can mean different things for different women. What’s normal for one person might not be the same for another. This is because of the unique factors that affect each person’s reproductive health.
By tracking and understanding cervical changes, women can learn a lot about their fertility. This approach to fertility awareness helps women make informed decisions about their health and family planning.
Combining Cervical Position Tracking with Other Fertility Signs
Healthcare providers suggest tracking cervical position with other fertility signs for a better understanding. This method gives a clearer view of your fertile window. It helps in planning to conceive or avoid pregnancy.
Basal Body Temperature and Cervical Position
Basal body temperature (BBT) tracking is a key method for monitoring fertility. When paired with cervical position tracking, it offers a deeper look into your menstrual cycle. Typically, BBT increases after ovulation, while cervical position changes are more noticeable before and during ovulation. This combination helps identify your fertile days.
To track BBT and cervical position effectively, keep a consistent routine. Take your temperature every morning, before getting out of bed. Record it with your cervical position observations. This dual tracking helps spot the subtle changes that signal ovulation.
Cervical Mucus Observations
Cervical mucus observations are vital for fertility tracking, alongside cervical position. Cervical mucus changes throughout the menstrual cycle, becoming more abundant, clear, and elastic during the fertile window. Observing these changes with cervical position gives a clearer picture of fertility.
When tracking cervical mucus, note its texture, color, and quantity. During ovulation, the mucus is clear and stretchy, aiding sperm passage. Combining this with cervical position tracking offers a detailed view of your fertile days.
Using Fertility Apps to Track Multiple Signs
Fertility apps are popular for tracking various signs, including cervical position, BBT, and cervical mucus. These apps help spot patterns and correlations, giving a deeper understanding of fertility.
When picking a fertility app, look for one that tracks multiple signs and offers personalized insights. Many apps also have cycle forecasting and fertility windows, which are great for planning conception or avoiding pregnancy.
By combining cervical position tracking with other signs and using fertility apps, you can understand your fertility better. This approach empowers you to make informed decisions about your reproductive health.
When to Consult a Healthcare Provider About Cervical Changes
Cervical changes are normal in the menstrual cycle. But, sometimes you need to see a doctor. It’s important to know when these changes are just normal and when they might mean something serious.
Unusual Cervical Symptoms That Warrant Attention
Some cervical symptoms need medical help. These include:
- Unusual or foul-smelling discharge
- Severe pain during cervical checks or intercourse
- Unexpected bleeding, like after sex or between periods
- Cervical lesions or abnormalities
If you notice any of these, see a doctor right away. They can check for any health problems.
Cervical Position Concerns During Fertility Treatments
Women trying to get pregnant need to watch their cervical changes closely. Treatments can change how your cervix works. But, if you notice big changes, talk to a fertility expert.
Symptom | Possible Concern | Action |
Absent or scant cervical mucus during fertile window | Potential issue with ovulation or hormonal imbalance | Discuss with fertility specialist |
Unusual cervical position or texture | Possible cervical or uterine issue | Consult healthcare provider |
Severe pain during cervical checks | Cervical or vaginal infection, or other pathology | Seek immediate medical attention |
Knowing about these concerns and talking to your doctor can help. This way, you get the right care when trying to get pregnant.
Conclusion: Empowering Your Fertility Journey Through Cervical Awareness
Knowing how your cervix changes can help a lot in your fertility journey. By noticing the small changes in your cervical position and feel, you learn a lot about your reproductive health.
Tracking your cervical awareness can show you when you’re most fertile. It helps you understand your hormone levels and make smart choices about having kids. By tracking your cervical position and other signs like basal body temperature and cervical mucus, you can better understand your fertility.
Empowering your fertility is more than just knowing your body. It’s about taking control of your reproductive health. By using what you learn from tracking your cervical changes, you can move through your fertility journey with confidence and make smart health choices.
We urge you to keep exploring your cervical awareness. Use this knowledge to empower your fertility journey. This way, you can get to know your body better and make informed choices about your reproductive health.
FAQ
Is the cervix lower during ovulation?
Actually, the cervix is higher during ovulation, not lower. This change is part of the SHOW pattern, showing peak fertility.
What does the cervix feel like during ovulation?
During ovulation, the cervix feels softer, like lips. This is different from its firmer feel, like a nose tip, at other times in the cycle.
Does your cervix dilate during ovulation?
Yes, the cervix opens slightly during ovulation. This makes it easier for sperm to pass through. But the opening is only a little bit.
How many days is the cervix open during ovulation?
The cervix is open for a short time, usually around ovulation. It can stay open for a few hours to a couple of days, depending on the person.
What is the cervix position before ovulation?
Before ovulation, the cervix is lower and firmer. As ovulation gets closer, it softens and rises. This shows the fertile window is coming.
How can I check my cervical position?
To check your cervical position, wash your hands first. Then, insert a finger into your vagina to feel the cervix. Do this at the same time each day, when you’re relaxed.
What are the changes in the cervix during ovulation?
During ovulation, the cervix becomes softer, higher, more open, and wetter. This is the SHOW pattern, helping sperm pass through and showing peak fertility.
Can the cervix position indicate fertility?
Yes, tracking cervical position can help understand fertility. Changes in the cervix’s position, texture, and openness can show the fertile window.
How does age and childbirth affect cervical feel?
Age and childbirth can change the cervix’s texture and position. For example, after childbirth, the cervix may feel different due to changes in its structure.
When should I consult a healthcare provider about cervical changes?
If you notice unusual cervical symptoms, like abnormal discharge or pain, see a healthcare provider. Also, if you’re trying to get pregnant and have concerns about your cervical position or texture, it’s best to consult a healthcare provider.
Can combining cervical position tracking with other fertility signs improve fertility awareness?
Yes, tracking cervical position with basal body temperature, cervical mucus observations, and using fertility apps can give a better understanding of your fertile window. This improves fertility awareness.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Cervical Changes During Ovulation: A Guide for Fertility Awareness. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC11837971/