Last Updated on November 4, 2025 by mcelik

Degenerative disc disease affects millions globally. It happens when spinal discs lose their cushioning, leading to complications. A big worry is spinal cord compression, which can be serious.
Studies show that degenerative disc disease can cause spinal cord compression. This can lead to symptoms like numbness, weakness, and even paralysis. We’ll look into how paralysis risk spine is connected to degenerative disc disease, offering insights into the condition and its risks.
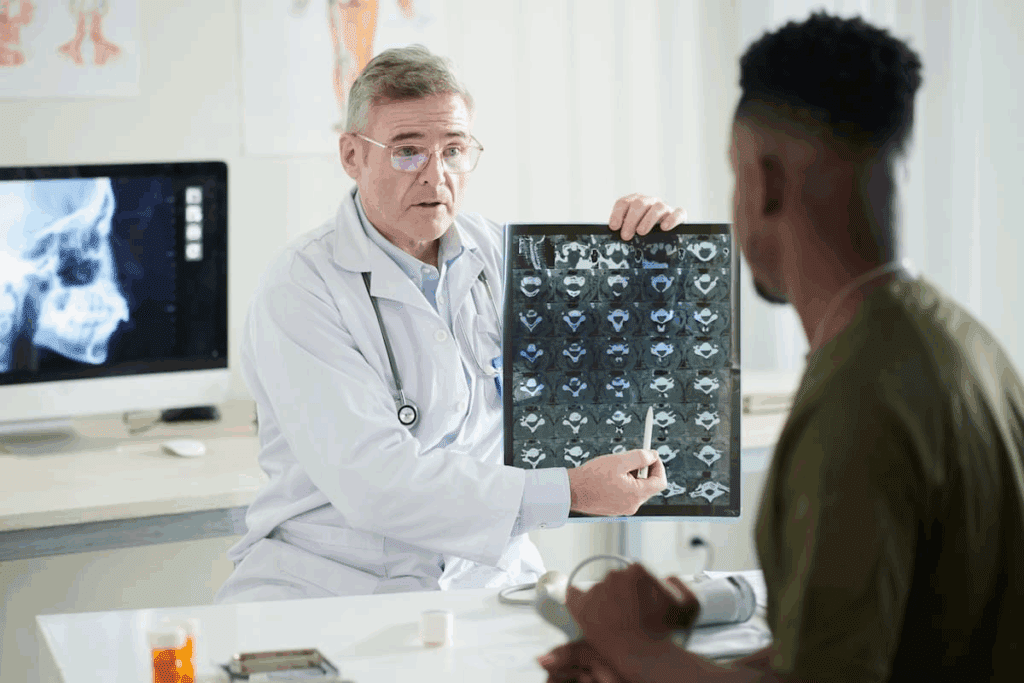
It’s key to understand degenerative disc disease to see how it affects our spine. This condition affects millions globally, causing pain and serious issues.
As we get older, our spinal discs naturally wear out. These discs cushion our vertebrae. When they degenerate, problems arise.
Disc degeneration makes discs lose water, becoming stiff and more likely to crack. This can cause discs to bulge or herniate, pressing on nerves and leading to pain.
Many things can increase your risk of getting degenerative disc disease. Age is a big one, as it’s more common in older people. Other factors include genetics, smoking, and jobs that involve heavy lifting.
People who’ve had spinal injuries or disc problems before are also at higher risk. Knowing these risks can help prevent the condition from getting worse.
In the U.S., degenerative disc disease is common, affecting many people. It’s more common with age, with a lot of adults having it by 50.
It affects both men and women, but some studies say men might be slightly more affected. The impact on quality of life is big, making it a major health concern.
Disc degeneration and neurological function are closely linked. Healthy spinal discs protect the spinal cord and nerve roots. Their degeneration can cause serious neurological problems.
Healthy spinal discs act as shock absorbers. They cushion the vertebrae, allowing for flexible movement. They also keep the nerve roots from being compressed.
When discs are healthy, they spread the load evenly. This protects the spinal cord and nerve roots from damage.
Nerve compression happens when discs degenerate and lose height. This causes the vertebrae to collapse, narrowing the spinal canal. This puts pressure on the spinal cord and nerve roots.
Disc herniation is another cause of nerve compression. It occurs when the disc material bulges out and presses on nearby nerves. We will look into these mechanisms to see how they affect neurological function.
Nerve compression from disc degeneration can cause both temporary and permanent damage. Temporary damage might be mild and reversible, often fixed with treatment. But, severe or prolonged compression can cause permanent damage.
This damage can lead to chronic pain, numbness, or paralysis. Knowing the difference between temporary and permanent damage is key. It helps decide the best treatment and prevent long-term problems.
It’s vital to seek medical help quickly to avoid permanent nerve damage. Understanding nerve compression and its effects helps patients and doctors create effective treatment plans. These plans protect neurological function and spinal health.
To understand the dangers of paralysis risk in spine disc disease, we need to know a lot about it. Degenerative disc disease is a common problem that can affect the spine. If not treated, it can lead to serious issues.
The chance of paralysis from disc disease alone is low. But, some things can make this risk higher. Research shows that while many people have disc degeneration, paralysis is rare. It’s important for both patients and doctors to know the risks and take steps to avoid them.
Traumatic spinal injuries, like those from accidents, are much more likely to cause paralysis. These injuries can damage the spinal cord severely right away. On the other hand, paralysis from disc disease usually happens slowly because of gradual pressure or irritation.
There are several things that can make paralysis risk higher for people with disc disease. These include:
Knowing these risk factors is key for early action and preventing serious problems. Doctors can spot patients at higher risk and start the right treatment. This helps lower the chance of paralysis and improves how well patients do.
Disc degeneration in the cervical spine is a big worry because it’s close to the brain and spinal cord. The cervical spine, with seven vertebrae in the neck, holds the head and allows for movement. Degeneration here can cause serious problems.
The cervical region faces serious risks from disc degeneration because of its shape. The spinal cord, which connects to the brain, runs through here. Disc degeneration can harm the spinal cord, leading to big neurological problems.
Quadriplegia, or paralysis of all four limbs, is a risk with cervical disc disease. The risk depends on how bad the disc degeneration is, other spinal issues, and overall health. Quick medical help is key for severe symptoms or fast worsening of nerve problems.
It’s important to know the warning signs of severe cervical problems. Symptoms that need quick medical help include:
Knowing these risks and symptoms helps people get medical help early. This can prevent serious damage to the nervous system. Regular checks and early action are key to avoiding long-term problems from cervical spine disc degeneration.
Thoracic spine disc disease is less common but can cause severe problems. The middle part of the spine, the thoracic spine, has a special design. This design can make disc disease more serious.
The thoracic spine is less flexible than other parts of the spine. This makes disc wear less common here. But, when it does happen, it can be more serious because of the tight spinal canal and important nerves.
One serious problem with thoracic disc disease is paraplegia. This is when the lower half of the body becomes paralyzed. It happens when the disc presses on the spinal cord too much. The risk is higher if the disease is not treated early.
It’s important to know the signs of thoracic disc disease to avoid serious problems. If you have severe back pain, numbness in your legs, weakness, or trouble with bladder or bowel control, see a doctor right away. Early treatment can greatly improve your chances of recovery.
We stress the need for quick medical check-ups for these symptoms. Getting a diagnosis and treatment early can prevent long-term damage to your nerves.
Lumbar disc degeneration can lead to serious issues, like lower body paralysis in severe cases. It affects the lower spine and can cause pain and mobility problems. This condition is a serious concern.
As we get older, our lumbar discs can wear down. This can cause pain and, in rare cases, nerve damage. It’s important to know about these risks to get help early.
Cauda equina syndrome is a serious issue caused by compressed nerves in the lower spine. It’s a medical emergency because it can cause permanent nerve damage if not treated quickly.
Symptoms include severe back pain, numbness in the legs, and problems with the bladder or bowel. Quick medical help is needed to avoid lasting damage.
“Time is of the essence when dealing with cauda equina syndrome; prompt surgical intervention is crucial to prevent irreversible neurological deficits.”
Sciatica is a common symptom of lumbar disc degeneration, causing pain along the sciatic nerve. In severe cases, it can lead to a loss of mobility, making it hard to walk or do daily tasks.
The transition from sciatica to mobility loss is gradual. It starts with pain and can lead to muscle weakness. Getting help early can manage symptoms and stop further decline.
It’s important to know the difference between weakness and paralysis in lumbar disc degeneration. While weakness is common, paralysis is less common but more severe.
Weakness in the lower body can come from nerve issues, causing less muscle strength. Paralysis, however, means no motor function at all. It’s a serious outcome of untreated or advanced lumbar disc degeneration.
Understanding these differences helps in getting the right medical care and managing recovery hopes.
Many people think disc disease always leads to paralysis. They often fear the worst. We want to clear up the confusion between pain-related immobility and true paralysis.
Pain-related immobility and true paralysis are not the same. Pain-related immobility happens when pain makes it hard to move. True paralysis is when nerves are damaged, causing a loss of muscle function.
For example, someone with bad sciatica might not be able to move because of pain. But this is not the same as true paralysis, where muscles don’t work at all.
How fast disc disease gets worse can vary a lot. Some people might not see much change for years. But others might see it get worse faster.
Things like age, lifestyle, and other health issues can affect how fast it gets worse.
| Progression Rate | Characteristics | Typical Outcomes |
| Slow | Minimal degeneration over time | Little to no symptoms |
| Moderate | Gradual degeneration with some symptoms | Manageable pain and limited mobility |
| Rapid | Significant degeneration with severe symptoms | Severe pain, significant mobility loss |
Disc disease can cause symptoms that last a short time or forever. Symptoms that get better with treatment are temporary. But, symptoms that don’t get better might be permanent.
It’s crucial to see a doctor if symptoms get worse or if you notice any signs of nerve damage. Getting help early can help avoid permanent damage.
Knowing the truth about disc disease and paralysis helps people deal with their condition better. We stress the need for accurate diagnosis and proper treatment. This helps manage symptoms and avoid long-term harm.
Spinal stenosis is a serious problem that can happen because of disc degeneration. It can cause severe neurological issues. We need to know how disc degeneration leads to spinal stenosis and the neurological problems that follow.
Disc degeneration can cause the spinal canal to narrow. This happens for several reasons, like:
When the spinal canal narrows, it can press on the spinal cord or nerve roots. This can cause neurological symptoms.
The neurological problems from spinal stenosis can differ based on where and how severe it is. Common symptoms include:
| Symptom | Description |
| Pain | Radiating pain in the arms or legs |
| Numbness | Numbness or tingling in the extremities |
| Weakness | Muscle weakness in the affected limbs |
Managing spinal stenosis well is key to avoid permanent nerve damage.
To manage spinal stenosis, we use different treatments, such as:
Understanding spinal stenosis’s causes and symptoms helps us create effective treatment plans. This way, we can prevent long-term neurological damage.
Disc herniation is a serious issue that can lead to paralysis. It happens when the soft center of the disc leaks out. This can press on nerves, causing paralysis if not treated quickly.
Knowing the emergency signs of disc herniation is key. Look out for:
Acting fast is crucial when dealing with severe disc herniation. Early treatment can greatly improve outcomes. The sooner nerves are relieved, the better the recovery chances.
| Timeframe | Potential Outcome |
| Within 24 hours | Significant recovery potential |
| 24-48 hours | Moderate recovery potential |
| After 48 hours | Reduced recovery potential |
Recovery from disc herniation varies. It depends on the herniation’s severity, how quickly treatment starts, and the patient’s health.
Key factors influencing recovery include:
Understanding these factors helps both patients and doctors make better treatment plans.
End-stage disc disease is a critical point in the degenerative process. It has big effects on how our nerves work. At this stage, the changes can cause lasting damage to our nerves.
Advanced disc degeneration shows severe changes. These include a big loss of disc height, tears in the disc, and sometimes, the disc can herniate. These issues can make the spine unstable, making the problem worse.
People with advanced disc degeneration often have symptoms like chronic pain and nerve problems. The symptoms depend on where and how bad the degeneration is.
Long-term disc disease can really hurt our nerves. It can cause ongoing pain, numbness, weakness, and even permanent damage.
The impact isn’t just local. It can affect many areas of our life, making it hard to enjoy our daily activities.
Severe disc deterioration really affects our quality of life. It can make it hard to move, hurt our mental health, and make everyday tasks tough.
It’s important to have a plan that helps with both physical and mental health. This way, we can improve our lives and manage the symptoms better.
Understanding end-stage disc disease and its effects helps doctors create better plans. These plans aim to improve our quality of life and outcomes.
Spotting neurological problems early is key to managing disc disease. We do this with a mix of clinical checks and advanced imaging. Understanding how disc wear affects nerves is part of the diagnosis.
Checking patients is vital for catching nerve issues early. We test muscle strength, reflexes, and how sensitive you are. These tests spot small changes that might mean nerve trouble.
By using these tests together, we get a full picture of your nerve health. This helps us find where problems might be starting.
Imaging is key for seeing the spine and finding nerve compression spots. We use MRI and CT scans to see how bad disc wear is. These scans show if nerves or the spinal cord are being squished.
These scans give us important details about your spine. They help us see how disc disease affects your nerves.
EMG and NCS are important for finding nerve damage. EMG looks at muscle electrical activity. NCS checks nerve signal speed and strength.
By combining clinical checks, imaging, and EMG/NCS, we can accurately find and treat nerve problems in disc disease. This helps stop further nerve damage.
Certain symptoms need quick medical help to avoid serious damage, especially with degenerative disc disease. It’s important to spot these red flags early to act fast.
Sudden weakness or paralysis in limbs is a big warning sign. It could mean serious nerve problems or damage. This could lead to permanent disability if not treated right away. If you lose strength or can’t move your arms or legs suddenly, go to the emergency room.
Problems with bladder or bowel control are serious signs. Losing bladder control, trouble urinating, or sudden bowel incontinence need quick doctor visits. These could mean cauda equina syndrome or other serious issues that need fast action.
Severe or getting worse neurological symptoms, like numbness, tingling, or pain, suggest nerve damage. If you notice these signs, especially if they get worse, get medical help fast. Quick action can help avoid long-term damage to your nerves.
In summary, knowing these emergency signs and getting medical help right away is key. It helps prevent serious damage and ensures the best care for those with degenerative disc disease.
Effective treatment strategies are key to stopping neurological decline in degenerative disc disease patients. We know managing this condition needs a mix of approaches, fitting each patient’s needs.
For those with mild to moderate nerve compression, starting with conservative treatments is common. These include physical therapy to boost mobility and strength, pain management through meds or injections, and lifestyle changes like staying healthy and quitting smoking.
These methods aim to ease symptoms, cut down inflammation, and stop nerve damage. By tackling the root causes of nerve compression, we help patients avoid more serious surgeries and enhance their life quality.
When conservative treatments fail or nerve compression is severe, surgery might be needed. Options include discectomy to remove the herniated disc and spinal fusion to stabilize the spine.
Choosing surgery is when the benefits of treatment outweigh surgery risks. Early surgery can prevent permanent nerve damage and greatly improve outcomes for those with severe degenerative disc disease.
When it comes to treating degenerative disc disease, timing is everything. Early treatment, whether conservative or surgical, can change the disease’s course. It prevents permanent nerve damage and boosts recovery chances.
We stress the need for quick medical checks for those showing signs of neurological decline. Knowing the treatment options and their effects helps patients make informed choices. This leads to better neurological outcomes.
Real patient stories give us a deep look into severe disc disease. They show us how the condition affects people and why quick action is key.
Many case studies show how timely action can lead to recovery. For example, a patient with cervical disc disease lost strength in their limbs. After emergency surgery, they regained strength and mobility.
These stories stress the need for quick medical help. Early treatment can greatly improve results, stopping long-term damage. They also show the need for a treatment plan that fits each patient’s needs.
Those with advanced disc degeneration face big challenges like chronic pain and limited movement. But, with the right care, many can live well. Outcomes can differ a lot based on how bad the degeneration is, the patient’s health, and following treatment advice.
Patients who have had neurological symptoms from severe disc disease teach us a lot. First, getting medical help fast if symptoms get worse or if there’s neurological trouble is crucial. Second, a team effort in care, including doctors, physical therapists, and sometimes surgery, is often needed.
“I was diagnosed with severe disc disease and experienced significant neurological symptoms. Thanks to timely surgery and subsequent physical therapy, I was able to regain my mobility and return to my normal activities.”
A patient with severe disc disease
These stories show the complexity of managing severe disc disease. They highlight the need for a treatment plan that’s made just for each patient. By learning from these experiences, doctors can better care for those with this tough condition.
To stop degenerative disc disease from getting worse, we need to make lifestyle changes and get medical help early. Knowing what makes the disease get worse helps us protect our spine and keep our nerves working well.
Changing our lifestyle can really help slow down degenerative disc disease. Keeping a healthy weight is key because extra weight puts more stress on our spine. Regular exercise, especially things that make our core stronger and more flexible, helps our spine and keeps nerves safe.
Physical therapy is very important in stopping degenerative disc disease from getting worse. A good physical therapy plan can make your spine stronger, more flexible, and better supported by muscles.
| Physical Therapy Component | Benefits |
| Core Strengthening | Makes your spine more stable and supported |
| Flexibility Exercises | Makes moving easier and reduces stiffness |
| Posture Education | Helps keep your spine in the right position and reduces strain |
It’s important to keep an eye on degenerative disc disease to catch any signs of nerve problems early. Working with your doctor helps you spot warning signs and act fast to avoid serious damage.
By making lifestyle changes, doing physical therapy, and keeping an eye on your condition, you can lower your risk of nerve damage. Taking care of your spine and managing degenerative disc disease helps you stay healthy and live well.
It’s important to know the risk of paralysis from degenerative disc disease. This knowledge helps people get the right medical care. By spotting risk factors and warning signs early, you can lower the chance of serious problems.
Looking at your personal risk means checking how bad your disc disease is. Also, see if you have any neurological symptoms. Your overall health matters too. If you have disc disease or symptoms, talk to a doctor to figure out what to do next.
Being proactive about managing your disc disease can help avoid paralysis. Keeping your spine healthy is crucial. Regular check-ups and acting fast when problems arise are key to stopping your condition from getting worse.
Yes, it can. If not treated, or if it gets worse, it might lead to paralysis. The risk depends on where and how bad the disc is.
Factors include how bad the disc is, where it is (cervical, thoracic, or lumbar), and other spinal issues like stenosis or herniation.
Cervical disc problems are closer to the spinal cord. This can harm all four limbs if the cord is compressed or damaged.
Look out for sudden weakness or paralysis in arms or legs, severe pain, numbness, or tingling, and trouble with bladder or bowel control.
Yes, thoracic disc disease is rare but serious. It can cause spinal cord compression, leading to paraplegia if not treated quickly.
Cauda equina syndrome is a serious condition where nerves in the lower spine are compressed. It’s often caused by lumbar disc problems. It can cause paralysis, bladder or bowel issues, and severe pain.
Pain-related immobility is about severe pain that stops you from moving. True paralysis is when you lose motor function due to nerve damage or compression.
Yes, it can. Spinal stenosis compresses the spinal cord or nerve roots. This can cause numbness, weakness, or paralysis.
Watch for sudden severe pain, numbness, or weakness in limbs, loss of bladder or bowel control, and trouble walking or standing.
Doctors use clinical exams, MRI, and tests like electromyography or nerve conduction studies to check for nerve damage.
Options include physical therapy, pain management, and surgery for severe nerve compression or spinal cord damage.
Yes, staying healthy, exercising, and good posture can protect your spine and lower the risk of neurological problems.
Physical therapy strengthens muscles, improves flexibility, and reduces pain. This can lower the risk of neurological issues.
Regular checks let doctors catch any worsening early. This allows for quick action to prevent serious problems like paralysis.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!