Did you know the average person goes to the bathroom 4-7 times a day? This number can change a lot, based on how much water you drink, your health, and how big your bladder is.
Knowing how long you can go without peeing is key to keeping your urinary system healthy. The bladder is a muscle that holds urine. How much it can hold varies from person to person. Usually, a healthy adult bladder can hold 400-600 milliliters of urine.
We’ll look at what affects how often you pee and what happens if you hold it too long. By understanding these things, we can take better care of our bodies and listen to what they need.
Key Takeaways
- The average person urinates 4-7 times in 24 hours.
- Bladder capacity varies from person to person.
- A healthy adult bladder can hold 400-600 milliliters of urine.
- Fluid intake and overall health affect urination frequency.
- Understanding urination patterns is key to urinary health.
Understanding th

Urination is more than just a natural function; it shows how well we’re doing health-wise. Our urinary system filters out waste from our blood and gets rid of it. This keeps our fluids and electrolytes in balance.
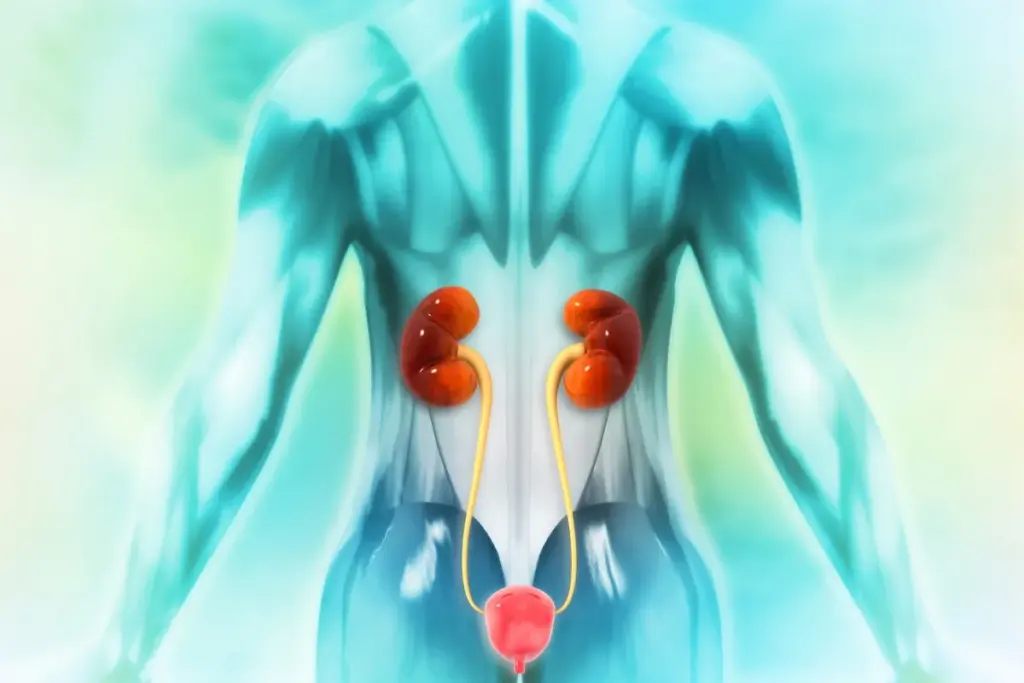
The system includes the kidneys, bladder, and ureters. It works together to make, store, and release urine. Knowing how it works helps us see why urination is so important.
The Importance of Peeing for Health
Peeing helps our body get rid of waste and toxins. The kidneys filter a lot of blood each minute, removing harmful substances. This keeps us healthy.
“The kidneys filter waste from the blood, which then becomes urine.”
NIH transcript
If we don’t pee often, toxins can build up. This can lead to serious health problems. So, understanding the role of urination is key to staying healthy.
How the Body Produces Urine
Urine starts in the kidneys. These tiny units called nephrons filter the blood. Waste and extra fluids become part of the urine.
The process has three stages: filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. In filtration, the kidneys remove waste and excess. Reabsorption puts back what we need. Secretion adds more waste to the urine.
|
Stage |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Filtration |
Removal of waste and excess substances from the blood |
|
Reabsorption |
Returning necessary nutrients and water back into the bloodstream |
|
Secretion |
Adding additional waste products to the urine |
Factors Influencing Urine Production
Many things can change how much urine we make. Hydration, diet, and medications are big factors. For example, too much caffeine or alcohol can make us pee more. A salty diet can also affect how we hold onto water.
- Hydration levels: Drinking enough water is essential for urine production.
- Diet: Certain foods and beverages can affect urine production and composition.
- Medications: Some medications, such as diuretics, are designed to increase urine production.
Knowing these factors helps us take care of our urinary health. By watching our hydration, diet, and meds, we support our body’s natural processes.
Average Time Between Urination
Many people worry about how often they pee. This worry can be due to age, gender, and health. Knowing the usual time between pees can help check if your pee habits are normal.
Typical Urination Frequency
A healthy adult usually pees 4 to 7 times a day. But, how often you pee can change. It depends on how much water you drink, how active you are, and your surroundings.
Key factors influencing typical urination frequency include:
- Fluid intake: Drinking more water, like coffee or beer, makes you pee more.
- Age: Older folks might pee more because their bladders get smaller and change with age.
- Health conditions: Some health issues, like diabetes or UTIs, can make you pee more often.
Variations Based on Age and Gender
How often you pee can change a lot with age and gender. For example:
- Children: Kids have smaller bladders and pee more often than adults.
- Older Adults: As we get older, our bladders get weaker and smaller, leading to more trips to the bathroom.
- Gender Differences: Hormonal changes in pregnancy make women pee more. Men, as they age, might pee more due to prostate issues.
It’s important to remember that these changes are normal. But, if you pee way more or less than usual, talk to a doctor. They can check if there’s a health problem.
Physical Factors Affecting Urination
Understanding what affects urination can help us take care of our bladder health. Many things can change how often we need to go to the bathroom. Knowing these can greatly improve our health.
Hydration Levels
How much we drink affects how often we need to urinate. Drinking more means our body makes more urine, so we go more often. Drinking less means our urine is more concentrated, so we go less often.
Monitoring hydration is key. We can check by looking at our urine. It should be pale yellow. If it’s dark yellow or amber, we might be dehydrated.
Diet and its Impact
What we eat and drink also matters. Some foods and drinks, like caffeine and alcohol, make us urinate more often.
Eating a lot of salt can also affect urination. Salt can raise blood pressure and cause fluid retention, making us produce more urine.
Medications and Their Effects
Some medicines can change how often we need to urinate. For example, diuretics help with high blood pressure and swelling by making us urinate more.
Other medicines, like those for depression or high blood pressure, can also affect urination. It’s important to know the side effects of any medicine we take.
|
Factor |
Effect on Urination Frequency |
|---|---|
|
Increased Hydration |
Increases frequency |
|
Caffeine/Alcohol Consumption |
Increases frequency |
|
High Salt Diet |
Increases frequency |
|
Diuretics |
Significantly increases frequency |
Mental Factors and Urination
The mind-body connection is key in how we urinate. Stress and anxiety greatly impact our urinary habits. We’ll look into how these mental factors affect our bathroom visits.
The Role of Stress
Stress changes how our body works, including urination. When stressed, our body goes into “fight or flight” mode. This can lead to more trips to the bathroom.
Studies show stress can make some people urinate more often.
To see how stress affects urination, check out this table:
|
Mental State |
Effect on Urination |
|---|---|
|
High Stress |
Increased Urinary Frequency |
|
Low Stress |
Normal Urinary Frequency |
|
Anxiety |
Variable Urinary Frequency |
Anxiety and Urinary Frequency
Anxiety also plays a role in how often we need to use the bathroom. People with anxiety might find they need to go more often. Anxiety can change how our body works, including our urinary system.
Key Points to Consider:
- Mental factors like stress and anxiety can impact urination.
- Stress can lead to increased urinary frequency in some individuals.
- Anxiety can cause variable changes in urinary frequency.
Understanding the link between mental health and urination helps manage urinary health. Recognizing stress and anxiety signs can help control their impact on urination.
Consequences of Holding in Urine
Holding urine for too long can cause health problems. These range from mild discomfort to serious infections. “The longer urine stays in the bladder, the higher the risk of bacterial growth,” which can cause urinary tract infections (UTIs) (Source: Health websites). We will look at both the immediate effects and the long-term risks of this habit.
Short-Term Effects
In the short term, holding urine can cause a lot of discomfort. This includes:
- Pelvic pain due to the bladder being overdistended
- Urinary urgency, making it harder to control the bladder
- Increased risk of UTIs due to bacterial multiplication
These effects can often be fixed by letting the bladder empty. But, doing this repeatedly can lead to more serious problems.
Long-Term Risks
Long-term risks of holding urine include:
- Recurring UTIs: Frequent UTIs can lead to more severe kidney damage over time.
- Bladder Damage: Overstretching the bladder can result in long-term issues with bladder control.
- Kidney Stones: Concentrated urine can lead to the formation of kidney stones.
As “holding urine is a habit that can have serious health consequences”, it’s important to be aware of our urination habits. If we have trouble, we should seek medical advice.
How the Body Signals a Need to Pee
The feeling of a full bladder tells us it’s time to go, thanks to physical and brain signals. Our body’s ability to tell us when to pee is key for good health.
Sensation of Fullness
The feeling of being full in the bladder comes from it stretching with urine. As it gets bigger, it sends nerve signals to the brain. This tells us it’s time to pee, helping us avoid accidents.
Neurological Responses
The brain’s role in telling us to pee is complex. The bladder has nerves that help control when we pee. When it’s full, these nerves make the bladder muscle contract, sending a signal to the brain.
|
Component |
Function |
|---|---|
|
Bladder Stretching |
Triggers nerve signals as it fills with urine |
|
Sympathetic Nerves |
Inhibit urination, promoting urine storage |
|
Parasympathetic Nerves |
Stimulate the detrusor muscle to contract, promoting urination |
|
Brain Processing |
Interprets signals from the bladder, signaling the need to urinate |
In conclusion, feeling the need to pee involves both the bladder’s fullness and brain signals. Knowing how these work helps us keep our pee habits healthy.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Urinary problems might signal a bigger issue. It’s key to know when to see a doctor. Talking about urination issues might feel awkward, but it’s vital for your health.
Signs of Urinary Retention
Urinary retention means you can’t fully empty your bladder. This can cause discomfort and serious problems. Key signs include:
- Difficulty starting urination
- Weak or interrupted urine flow
- Feeling like your bladder is not fully empty
- Frequent urination with little output
If you notice these symptoms, get medical help right away. Early diagnosis can greatly improve treatment results.
Common Conditions That Affect Urination
Many health issues can impact how you urinate. Knowing about them can help you know when to seek help. Some common ones are:
|
Condition |
Description |
Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
|
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) |
Infections in the urinary system |
Burning sensation while urinating, frequent urination |
|
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) |
Enlargement of the prostate gland |
Difficulty starting urination, weak urine flow |
|
Overactive Bladder |
Frequent, urgent need to urinate |
Frequent urination, urgency, nocturia |
Knowing these conditions and their symptoms helps you know when to see a doctor. If you have persistent or severe symptoms, don’t hesitate to get medical help.
Tips for Healthy Urination Habits
Keeping your urination habits healthy is key for good urinary health. Simple tips can help lower the risk of urinary problems. They also boost our overall health.
Staying Hydrated
Drinking enough water is vital for healthy urination. It helps remove toxins and keeps the urinary system working right. Aim for at least eight glasses of water a day. But, your needs might change based on how active you are and where you live.
Tips for staying hydrated:
- Drink water all day long.
- Check your urine color; it should be pale yellow or clear.
- Don’t overdo it with caffeine and alcohol, as they make you lose water.
Recognizing Your Body’s Signals
It’s important to listen to your body’s signals for urination. Ignoring these can cause urinary retention and other issues. Always go when you feel the urge.
Signs that you need to urinate:
- A feeling of fullness or discomfort in the bladder.
- Frequent or urgent need to urinate.
- Pain or burning sensation while urinating.
By drinking enough water and paying attention to your body, you can keep your urination habits healthy. This helps avoid urinary problems.
Urination Across Different Cultures
Urination is a universal human act, but its meaning changes across cultures. Exploring how cultures view urination helps us understand the mix of biology, society, and personal behavior.
Norms and Taboos
Cultural norms about urination come from history, religion, and society. In some places, it’s rude to pee in front of others. In others, it’s okay. Knowing these norms helps us see the cultural side of urination. In many Asian cultures, squat toilets are common, and people follow specific rules and hygiene.
Taboos about urination also change. In some places, it’s seen as a way to purify. In others, it’s a private act that should stay hidden. How a culture sees urination affects how people see their own urine health and habits.
“The way a society views urination can reveal a lot about its values and beliefs regarding privacy, hygiene, and bodily functions.”
Public vs. Private Bathroom Etiquette
Etiquette in public and private bathrooms varies by culture. In some European countries, public restrooms are shared with little privacy. In contrast, many Asian and Western cultures value privacy, with individual stalls and doors.
Public bathroom rules also differ. For example, in Japan, strict hygiene is key, including wearing toilet slippers and washing hands well. These habits show cultural values on cleanliness and respect for others.
- In some cultures, public urination is okay or even normal under certain conditions.
- In other places, public urination is banned and seen as a big deal.
- Attitudes toward urination shape public health policies and bathroom designs.
Looking at cultural differences in urination helps us understand human behavior and health better. This knowledge can help make healthcare more fitting for people from different cultures.
Urinary Trends in Modern Society
Our bathroom habits are changing thanks to technology. As we live in a modern world, it’s key to see how these changes impact our health.
Digital Influence
Smartphones and other digital tools have changed our bathroom habits. People now spend more time in the bathroom, using their devices.
- More screen time means longer bathroom visits.
- Using bathroom time for leisure or work is becoming common.
- Digital devices can alter how we feel time and our body’s signals.
Evolving Social Norms
Social views on urination are changing too. With more open talks about health and hygiene, we’re seeing a shift. There’s more acceptance and understanding.
- Public restrooms are getting better and cleaner.
- There’s a growing focus on urinary health and its role.
- Changing views are helping reduce stigmas around urinary issues.
Future of Urinary Health
Medical technology and research are advancing fast. This means better health monitoring for our urine. Now, we can catch problems early and treat them sooner.
Advancements in Monitoring Technology
New gadgets and apps are coming to help us track our urine. Wearable devices and mobile apps can monitor our urination patterns. They give us insights into our urinary health.
These new tools will help doctors diagnose and treat urinary issues better. They’re a big step forward in health care.
Role of Ongoing Medical Research
Research into urination is uncovering new things about our health. It’s leading to new treatments and therapies. By understanding the causes of urinary problems, researchers can find better ways to help patients.
As research and technology keep improving, urinary health care will get even better. Staying up-to-date with the latest news can help us keep our urinary health in top shape.
FAQ
How much urine can the bladder hold?
A normal bladder can hold 400-600 milliliters of urine. But, this can go down with age or health issues.
Can you get a UTI from holding your pee?
Yes, not peeing often can raise UTI risk. Bacteria in urine can grow more.
How often should I be peeing?
Peeing frequency varies by age, gender, and health. But, it’s usually 4-7 times a day.
How long can a dog go without peeing?
Dogs can hold urine for 8-10 hours on average. But, it’s not healthy and can cause problems.
Why can’t I hold my pee?
You might have weak muscles, UTIs, or neurological issues. These can make it hard to hold urine.
How many times a day should I pee?
You should pee 4 to 7 times daily. This can change based on how much you drink and your activity level.
Is it bad to hold your pee?
Holding urine too long can cause discomfort and UTIs. It can even damage your kidneys. So, it’s best to pee when you need to.
I only pee 3 times a day, is this normal?
Peeing 3 times a day might be okay for some, depending on fluid intake. But, it’s wise to check with a doctor to be sure.
How much can a bladder hold urine?
Bladder capacity varies. But, on average, it can hold 400 to 600 milliliters of urine.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK606132/