Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
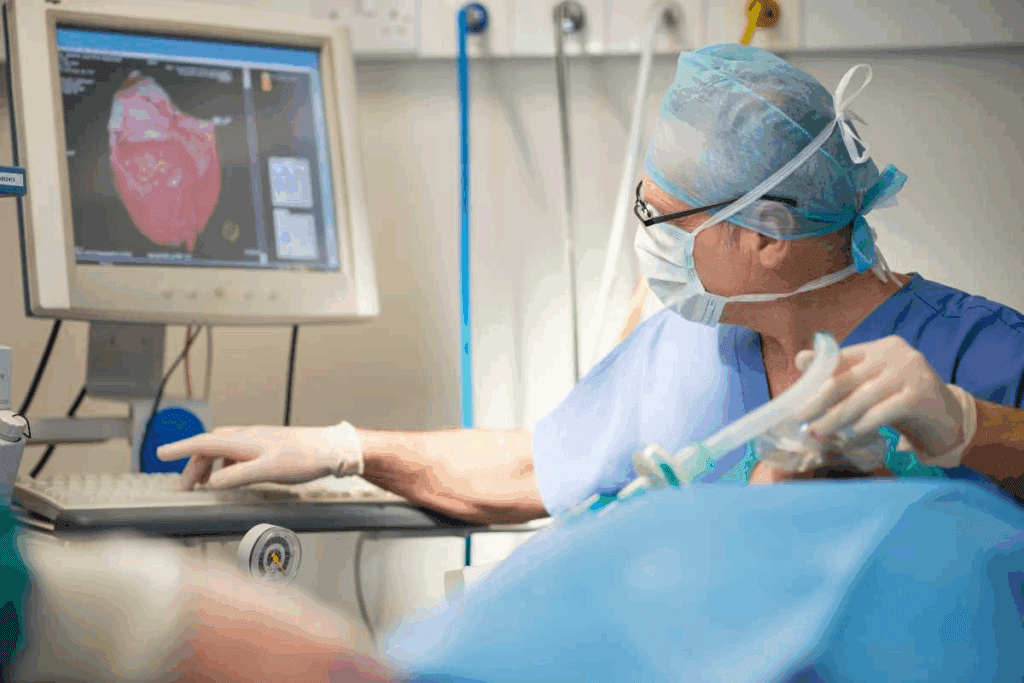
During complex heart surgery, a highly skilled professional called a perfusionist runs the heart-lung machine. This critical role is performed by a trained perfusionist specialist who manages the patient’s circulation and oxygenation during the procedure.
We count on perfusionists to run the heart-lung machine. It takes over the heart and lungs’ functions during surgery. This lets the surgical team do complex repairs and procedures safely.
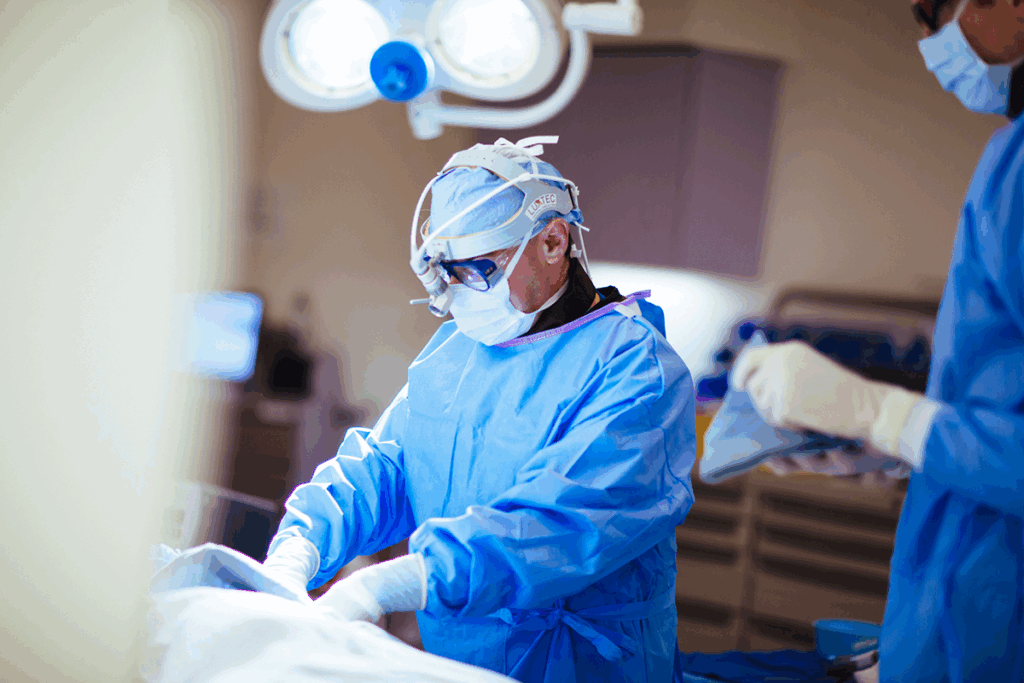
Perfusionists manage the equipment that takes over the heart and lungs during cardiac surgery. This role is key for the success of complex heart procedures.
Perfusionists are vital in cardiac surgery. They run the heart-lung machine that circulates blood. This machine is essential for keeping patients alive during surgery.
During heart surgery, perfusionists mainly operate the heart-lung machine. They divert blood from the heart and lungs, oxygenate it, and return it to the body. This process needs careful monitoring to keep the patient safe.
The perfusionist works with the surgical team to keep the patient’s vital signs safe. This teamwork is key for a successful surgery.
The heart-lung machine is critical because it lets surgeons operate on a stopped heart. It takes over the heart’s function, allowing for delicate repairs and replacements. This makes the surgery safer and more manageable.
The machine does many important things, like circulating blood, adding oxygen, and controlling temperature. The perfusionist must manage these functions to keep the patient safe.
| Function | Description | Perfusionist’s Role |
| Blood Circulation | Circulates blood throughout the body | Monitor and adjust blood flow |
| Oxygenation | Adds oxygen to the blood and removes carbon dioxide | Manage oxygen levels and gas exchange |
| Temperature Control | Regulates the patient’s body temperature | Adjust temperature settings as needed |
In summary, perfusionists are vital in cardiac surgery. They operate the heart-lung machine and ensure patient safety. Their skills are essential for the success of complex heart surgeries.
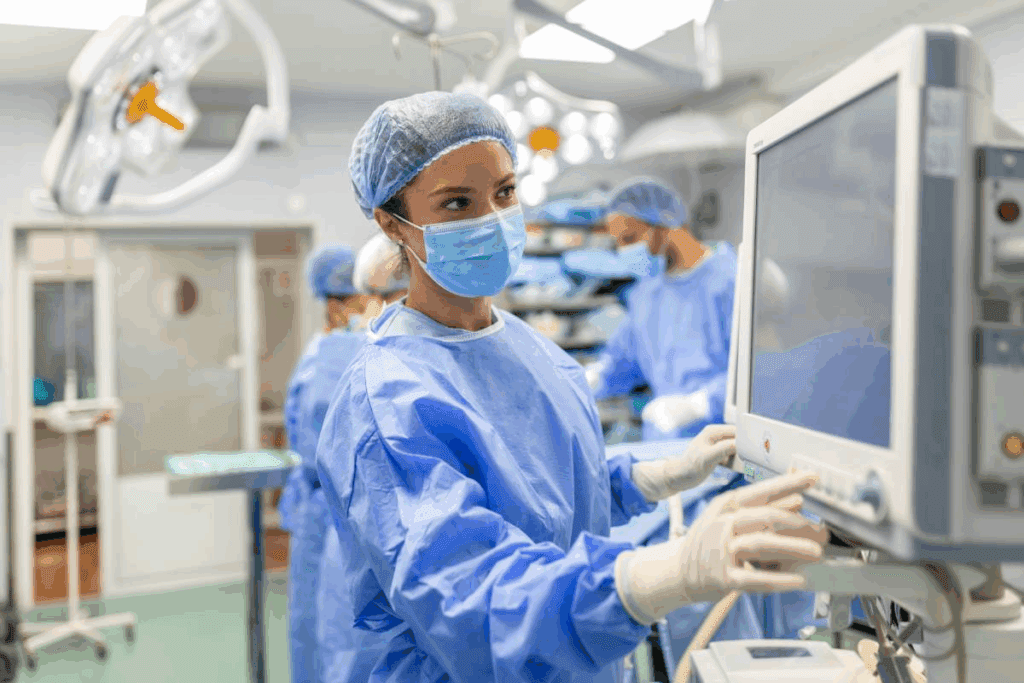
In the high-stakes environment of cardiac surgery, perfusionists are the trained professionals who operate the heart-lung machine.
A perfusionist is a highly skilled healthcare professional. They operate and maintain the heart-lung machine and other equipment. This equipment supports patients’ cardiovascular and respiratory systems during surgery.
Perfusion is the process of supplying blood or other fluids to organs or tissues. It uses a vascular system or artificial apparatus. In cardiac surgery, perfusion involves using a heart-lung machine to take over the heart and lungs’ functions. This allows surgeons to operate on a heart that is not beating.
The formal definition of perfusion highlights the critical role perfusionists play. They maintain the patient’s physiological stability during complex surgical procedures.
Perfusionists have several primary duties in the operating room, including:
The following table summarizes the key responsibilities of a perfusionist during cardiac surgery:
| Duty | Description |
| Operating the Heart-Lung Machine | Responsible for setting up and operating the heart-lung machine to support the patient’s cardiovascular system during surgery. |
| Monitoring Patient Status | Continuously monitors the patient’s vital signs and physiological status to ensure optimal perfusion. |
| Adjusting Perfusion Parameters | Adjusts the heart-lung machine settings as needed to maintain optimal blood flow and oxygenation. |
| Collaboration with Surgical Team | Works closely with surgeons and anesthesiologists to ensure a coordinated and successful surgical procedure. |
The history of cardiovascular perfusion is filled with innovation. It started to save lives in complex cardiac surgeries. This field has grown a lot, changing how we do cardiac surgeries today.
It all began in the mid-20th century with the first heart-lung machines. These early devices were key to modern cardiac surgery.
The first heart-lung machine was a big step forward. It let surgeons work on a heart that wasn’t beating. These early machines were simple and sometimes caused problems. But they were the start of better things to come. Now, these machines are much better and safer.
Today, cardiovascular perfusion has made huge strides. Modern heart-lung machines have better monitoring, oxygenation, and control. These changes have made surgeries safer.
Some big updates include:
These changes have helped patients more and let surgeons do more surgeries.
Being a cardiac perfusionist is a complex job. It involves getting ready for surgery, managing it, and caring for the patient after. We are key members of the cardiac surgical team. We run the heart-lung machine, which replaces the heart and lungs during surgery.
We start by making sure all equipment works right. This means checking the heart-lung machine and having all needed supplies ready. We also look over the patient’s medical history to spot any possible problems.
These steps help make sure the surgery goes well.
During surgery, we focus on the cardiopulmonary bypass machine. We watch the patient’s vital signs and adjust the machine to keep blood flowing and oxygen levels right.
Good communication with the surgical team is key. We work together to solve any problems and keep the patient safe.
After surgery, we keep playing a big role in the patient’s care. We help wean the patient off the heart-lung machine, watch their recovery, and support the ICU team.
We make sure the patient’s care is smooth from the operating room to the ICU.
In the operating room, perfusionists are the unsung heroes. They keep patients alive by expertly managing the cardiopulmonary bypass machine. This machine takes over the heart and lungs’ functions, allowing surgeons to do complex repairs and surgeries.
“The perfusionist’s role is critical in ensuring the patient’s safety and the success of the surgical procedure,” says the American Society of ExtraCorporeal Technology.
The cardiopulmonary bypass machine has several key parts. The pump keeps blood flowing. The oxygenator adds oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. The heat exchanger controls the temperature, which is very important during surgery.
Perfusionists use many techniques to manage blood flow and oxygenation during surgery. They watch the patient’s vital signs closely and adjust the machine as needed. Effective communication with the surgical team is also key to keeping the patient stable.
They adjust the pump’s flow rate, manage oxygen levels, and keep blood at the right temperature. Perfusionists get a lot of perfusionist training to learn these skills. Many also take part in perfusionist programs to keep up with new advancements.
Many complex surgeries need skilled perfusionists to run the heart-lung machine. They are key in managing the cardiopulmonary bypass machine. This ensures patients get the care they need during detailed surgeries.
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting, or CABG, boosts blood flow to the heart. A perfusionist controls the heart-lung machine during CABG. This machine takes over the heart and lungs’ jobs, letting the surgical team do the bypass grafting.
We use the heart-lung machine to keep blood flowing and oxygen levels up. This keeps the patient stable during the surgery. The perfusionist is very important in watching and adjusting the machine to fit the patient’s needs.
Valve surgeries, like replacements and repairs, often need cardiopulmonary bypass. Perfusionists are essential in these surgeries. They manage the heart-lung machine to make sure blood is well-oxygenated and circulated.
In valve surgery, the perfusionist works with the surgical team. They keep the conditions right for the valve repair or replacement. This teamwork is key for the surgery’s success.
| Surgery Type | Role of Perfusionist | Key Responsibilities |
| CABG | Operating heart-lung machine | Monitoring blood circulation and oxygenation |
| Valve Replacements/Repair | Managing cardiopulmonary bypass | Maintaining optimal surgical conditions |
Perfusionists also work on other surgeries that need cardiopulmonary bypass or ECMO. These include complex aortic surgeries, cardiac tumor resections, and some lung surgeries.
They also help with ECMO procedures. ECMO gives vital support to patients with severe heart or lung failure. The perfusionist’s skill is vital in managing ECMO, ensuring patients get the right support during critical times.
To become a perfusionist, you need special education and training. Getting perfusionist certification is a big step in showing you’re ready for this job. Knowing about perfusionist career prospects can also help you decide on your career path.
In cardiac surgery, perfusionists are key players. They are essential for the success of complex surgeries. They work closely with surgeons and anesthesiologists.
Perfusionists do more than just operate the heart-lung machine. They also watch the patient’s health closely during surgery. Effective communication with the team is vital. This ensures everyone knows the patient’s status and any needed changes.
Perfusionists team up with surgeons and anesthesiologists to manage the patient’s health. They continuously monitor vital signs. They adjust the heart-lung machine to keep blood flow and oxygenation right.
They must be ready for emergencies like cardiac arrest. Adjusting the cardiopulmonary bypass machine is part of their job. They need clear communication with the team to respond well.
Clear communication is key during surgery’s critical moments. The perfusionist must tell the team about the patient’s condition and any needed changes. This keeps the team focused on the goal: a successful surgery.
Being a perfusionist is more than just operating the heart-lung machine. They are a vital part of the team. Their input is invaluable, helping achieve the best outcomes for patients.
Thinking about becoming a perfusionist? It’s a challenging but rewarding career. The perfusionist salary reflects the importance of their work. Look into accredited programs and the steps to become a certified perfusionist for a fulfilling perfusion job.
Becoming a perfusionist requires a lot of work. You need to study hard and get the right training. This path is filled with challenges but is rewarding.
To start, you must get a bachelor’s degree. You’ll need to take certain classes. Key undergraduate prerequisites include:
After your bachelor’s, you need to find an accredited perfusion program. The U.S. has many programs approved by the Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs (CAAHEP). These are usually master’s programs with both classroom and clinical training.
Top programs are at universities with strong ties to medicine. They offer great education and practical experience.
Clinical training is key. It lets you use what you’ve learned in real situations. Clinical training and residency programs give you hands-on experience in hospitals.
You’ll work with experienced perfusionists. You’ll learn to use machines, check patient health, and handle emergencies. This training is essential for becoming a skilled perfusionist.
Knowing what it takes to become a perfusionist helps you prepare. With the right education and training, you can excel in this important job.
Becoming a certified perfusionist is a tough process. It makes sure these experts can handle the heart-lung machine well during heart surgeries.
Certification is key for perfusionists. It shows they are skilled and care deeply about patient care. In the U.S., the American Board of Cardiovascular Perfusion (ABCP) is the main certifying body.
The ABCP gives exams for perfusionists to become certified. To get certified, they need to:
Certification isn’t just once; perfusionists must keep learning to stay certified. This keeps them up-to-date with new perfusion tech and methods.
Even though certification is national, states have their own rules. Some states need specific licenses or rules for perfusionists. So, it’s important for them to know the rules in their state.
Keeping up with new tech and methods is vital. The ABCP and other groups offer many educational chances. This helps perfusionists grow professionally.
| Certification Level | Description | Requirements |
| Certified Clinical Perfusionist (CCP) | Entry-level certification for new graduates | Completion of an accredited program, clinical experience, and passing the ABCP exam |
| Certified Perfusionist (CP) | Certification for experienced perfusionists | Meeting eligibility requirements, including experience and continuing education, and passing the ABCP exam |
By keeping high standards in certification and education, perfusionists are key to cardiac surgery success. They ensure patient safety during these surgeries.
Knowing what perfusionists earn is key for those thinking about this career. Their salary shows how important they are in heart surgery. It also highlights the need for a lot of skill.
Perfusionist pay varies a lot in the U.S. The cost of living, need for their services, and local health care rules play big roles.
Many things affect how much perfusionists get paid. These include:
Understanding these factors helps current and future perfusionists plan their careers. It helps them make smart choices about growing professionally.
The need for cardiac surgeries is growing, making the job of cardiovascular perfusionists more promising. These professionals play a key role in cardiac surgery and healthcare. They ensure patients get the best care during complex surgeries.
There’s a high demand for cardiovascular perfusionists today. This is because heart disease is becoming more common. Hospitals and healthcare facilities need skilled perfusionists to run heart-lung machines and other equipment for cardiac surgeries.
More cardiac surgeries are being done every year. This means more jobs for perfusionists. They’re also needed for other procedures that use cardiopulmonary bypass.
The future for cardiovascular perfusionists is bright. Advancements in medical technology and a focus on heart health will create new opportunities. Perfusionists will need to learn new skills as medical techniques improve.
Here are some areas where we can expect growth:
The role of perfusionists will stay important as healthcare changes. We’ll see new chances for them in research, education, and leadership in healthcare.
Cardiac perfusionists deal with many challenges every day. They face long surgeries and the pressure of making critical decisions. Their job is demanding and requires great precision and focus.
The job of a perfusionist is physically demanding. They spend long hours on their feet in a stressful setting. They must stay alert and focused for a long time, often under a lot of pressure.
The mental strain is also huge. Perfusionists have to make fast, accurate decisions that can affect patients’ lives. They manage the heart-lung machine and ensure patients get the right care during complex surgeries.
This responsibility can be very stressful. Perfusionists must stay calm and composed, even in emergencies.
Perfusionists are trained to handle emergencies during surgery. This includes equipment failures or unexpected patient reactions. They must solve problems quickly and effectively, often with little time to spare.
They work closely with the surgical team, including surgeons and anesthesiologists. Good communication and teamwork are key in these critical moments. This ensures patients get the best care possible.
The challenges perfusionists face highlight the importance of their role in cardiac surgery. Despite the stresses and demands, many find the work rewarding. They know their skills and expertise help save lives.
The field of cardiovascular perfusion is seeing big changes. These changes are making cardiac surgeries better. New perfusion techniques are leading to better patient results and more precise surgeries.
Minimally invasive cardiac surgery is becoming more common. It helps patients recover faster and leaves less scarring. Perfusionists are key in these surgeries, using new techniques to help the surgical team.
New equipment for these surgeries is being developed. This equipment helps control blood flow and oxygenation precisely.
Automation and computer-assisted systems are changing perfusion technology. These systems make perfusion management more precise and reliable. They allow for real-time monitoring and adjustments, making surgeries safer and more effective.
Computer-assisted perfusion systems bring many benefits. They include:
The future of cardiac perfusion looks bright with ongoing innovation. New trends include more portable and versatile perfusion systems. There will also be more artificial intelligence and better training simulations for perfusionists.
| Trend | Description | Potential Impact |
| Portable Perfusion Systems | Compact, transportable perfusion equipment for use in various settings | Increased flexibility and accessibility for cardiac care |
| Artificial Intelligence Integration | AI-assisted decision-making and predictive analytics for perfusion management | Enhanced precision and proactive management of perfusion parameters |
| Advanced Training Simulations | Virtual reality and simulation-based training for perfusionists | Improved skill development and readiness for complex scenarios |
We are excited about the future of cardiovascular perfusion. We are committed to providing the best care for our patients. The ongoing evolution of perfusion technology promises great things for cardiac surgery, and we are proud to be leading the way.
Perfusionists are key to the success of heart surgeries. They run the heart-lung machine that keeps patients alive during these complex operations. We’ve looked at their important tasks, education, and career paths.
Perfusionists are the quiet heroes of the operating room. They work hard to ensure patients get the best care during heart surgery.
Being a perfusionist is both challenging and rewarding. It offers good job prospects and pay. As medical tech advances, so will the need for skilled perfusionists. This makes perfusion a promising career for those who want to help patients.
A perfusionist is a skilled healthcare worker. They run the heart-lung machine during heart surgery. This ensures the patient’s blood is well-oxygenated and flows throughout the body.
Perfusion is the act of supplying blood to the body’s tissues and organs. It’s key during surgeries where the heart is stopped or not working well.
A perfusionist’s main tasks include operating the heart-lung machine and watching the patient’s vital signs. They manage blood flow and oxygenation. They also work with the surgical team to make sure the surgery goes smoothly.
Perfusionists use the heart-lung machine to take the patient’s blood away from the heart and lungs. They oxygenate it and then return it to the body. This lets the surgical team work on a heart that’s not beating.
Perfusionists help with many surgeries, like coronary artery bypass grafting and valve replacements. They also assist in complex operations.
To be a perfusionist, you need to finish your undergraduate studies first. Then, you attend a perfusionist program and get clinical training and residency experience.
Perfusionists can get certified by the American Board of Cardiovascular Perfusion (ABCP). They pass a certification exam to show their skills and knowledge.
In the United States, perfusionists’ salaries vary by location. But, they are generally well-paid, reflecting their advanced training and important role in healthcare.
The job outlook for cardiovascular perfusionists is good. It’s because more people need cardiac surgery and new perfusion technologies are coming out.
Perfusionists face physical and mental challenges. They deal with emergencies, work long hours, and must stay focused during complex surgeries.
Perfusion technology is getting better. New techniques, automation, and computer-assisted perfusion are improving patient care and allowing for more surgeries.
Perfusionists are key members of the surgical team. They work with surgeons and anesthesiologists to ensure good communication, coordination, and patient care during surgeries.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!