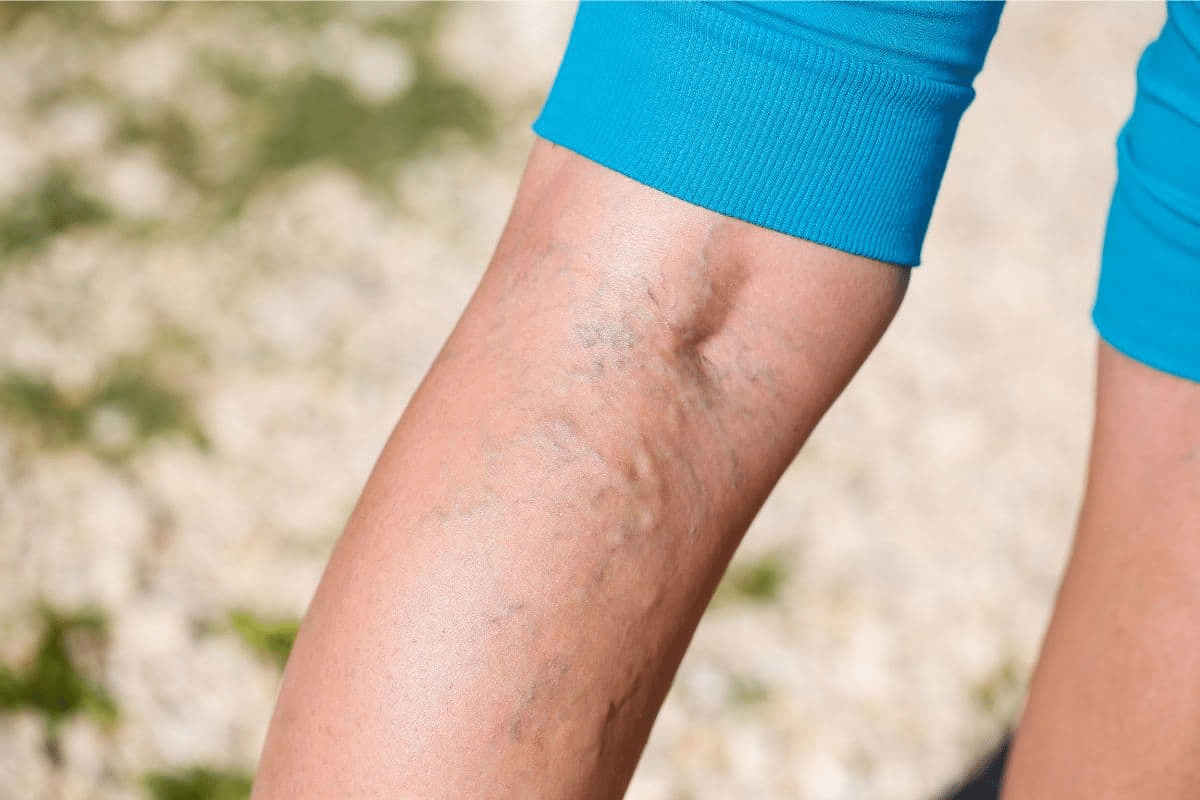
Vein inflammation is a common issue in hospitals and clinics. Phlebitis is the term for when the vein’s inner wall gets inflamed.
This problem is quite common. It affects 13 to 56 percent of people in hospitals. Knowing the signs and symptoms of phlebitis is key for good phlebitis management.
The inflammation of a vein shows in several ways. You might feel pain, see redness, swelling, and feel a cord in the vein. Spotting these signs early is vital for treatment.
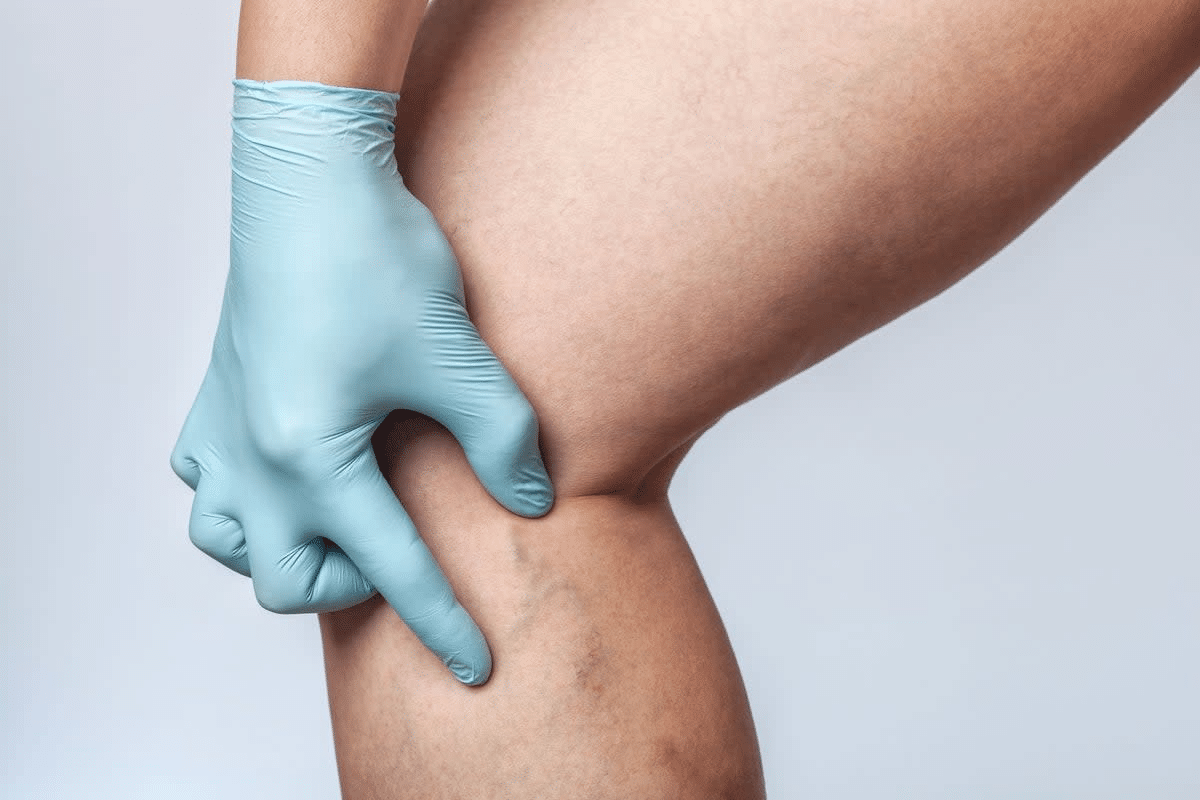
Phlebitis is when a vein gets inflamed. It can happen for many reasons, like thrombophlebitis. This can affect both superficial and deep veins, causing different symptoms and health issues.
Phlebitis means a vein is inflamed, often with a blood clot inside. It can be different based on where and how the vein is affected.
Types of Phlebitis:
Phlebitis is common, with different rates based on causes and risk factors. Superficial thrombophlebitis is more common, but deep vein thrombophlebitis is more dangerous.
|
Type of Phlebitis |
Estimated Incidence per 100,000 Person-Years |
|---|---|
|
Superficial Thrombophlebitis |
20-40 |
|
Deep Vein Thrombophlebitis |
5-10 |
Phlebitis can have a big impact on health. It can cause pain and discomfort or even life-threatening problems like pulmonary embolism. Knowing about phlebitis and its risks is key to managing it well.
Managing phlebitis means treating the inflammation and blood clot. It also means fixing the underlying issues to stop it from coming back.
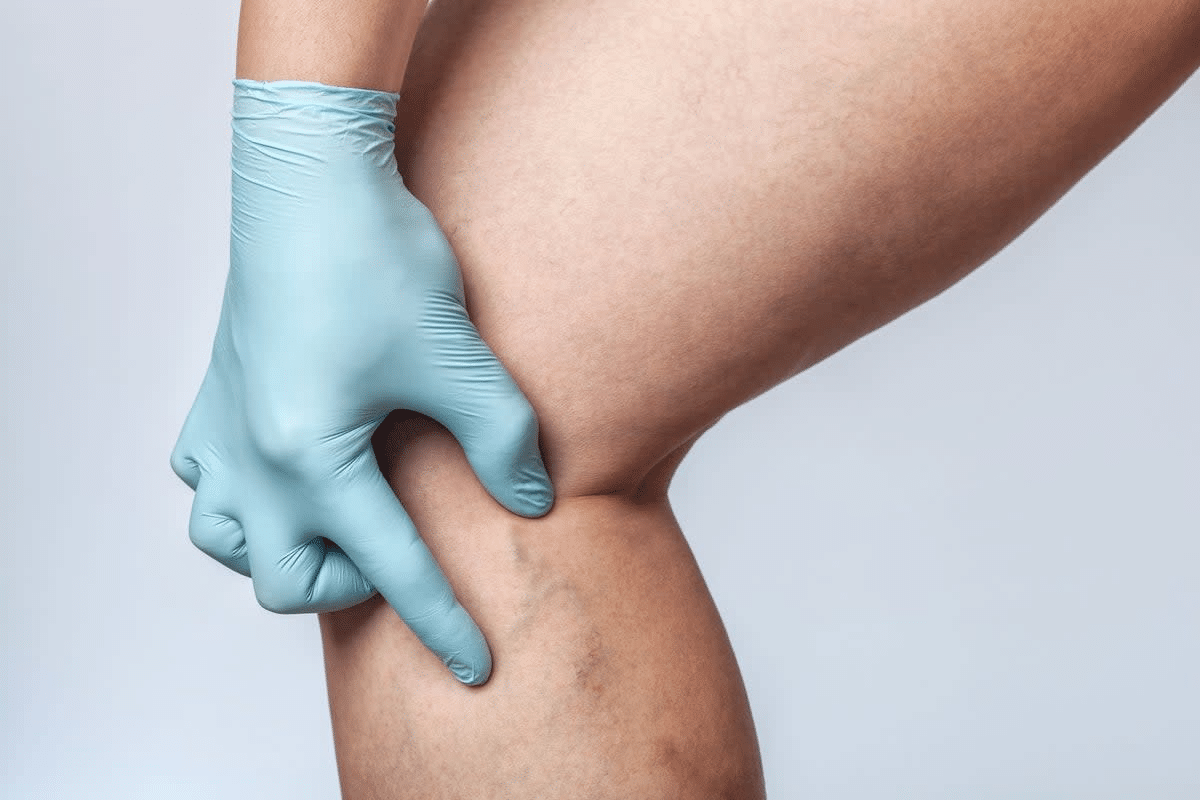
It’s important for both patients and doctors to know about phlebitis. The word “phlebitis” means “vein inflammation.” This condition can take different forms, each with its own name.
Phlebitis is when a vein gets inflamed. It can happen for many reasons like infection or injury. Thrombophlebitis is when a blood clot forms in the vein that’s inflamed. This clot can be either close to the surface or deep inside the vein.
Knowing the difference between phlebitis and thrombophlebitis is key. This is because a clot changes how you treat it. Thrombophlebitis can be either superficial or deep vein thrombophlebitis (DVT), each with its own health risks.
Superficial nodular phlebitis is a type of phlebitis. It’s when nodules form in the superficial veins. This condition is often painful and can cause inflammation. The nodules can be felt and may be red and warm.
The word “phlebitis” comes from Greek. “Phleps” means vein and “itis” means inflammation. Knowing where medical terms come from can help us understand them better. The words for phlebitis and related conditions come from ancient Greek and Latin.
Using the right medical terms is vital for correct diagnosis and clear communication. By knowing the terms for phlebitis, people can understand their condition and the treatments they need.
Phlebitis is not just one condition. It’s a range of vein inflammation, split into types based on where and why it happens. Knowing these types is key for the right diagnosis and treatment.
Superficial thrombophlebitis is when a blood clot inflames a surface vein. It shows up as pain, redness, and swelling along the vein. It’s often linked to varicose veins and can be caused by IVs or injections.
Deep vein thrombophlebitis affects deep veins, usually in the legs. It’s more serious because clots can break loose and cause a pulmonary embolism. Symptoms include swelling, pain, and warmth in the leg.
Septic phlebitis is a rare but serious vein infection. It can happen from bacteria in IVs or from infections spreading. It needs quick antibiotic treatment to avoid serious problems.
Mechanical phlebitis is caused by vein irritation, often from IV catheters. Risks include the catheter’s size, material, and where it’s placed. Symptoms can get better by removing or changing the catheter.
In summary, phlebitis covers a range of vein issues, each with its own signs and treatment needs. It’s important to know these differences to give the right care and manage the condition well.
It’s important to know the signs of phlebitis to get help quickly. Phlebitis is when veins get inflamed. It shows in different ways that need fast action.
Pain and tenderness in the vein are common in phlebitis. This pain can be mild or very bad. It gets worse when you move or press on it. Pain management is key to treating phlebitis and improving life quality.
Redness or erythema is a key sign of phlebitis. The area looks red or inflamed because of more blood flow. It also feels warm when you touch it.
Swelling and warmth are symptoms of phlebitis. The affected area swells up because of inflammation. The skin feels warm or hot to the touch. These signs show how the body reacts to inflammation.
A palpable venous cord is a tender, cord-like structure in the vein. It’s a sign of phlebitis, like superficial thrombophlebitis. The cord is tender and may show other signs of inflammation.
Knowing these signs is key to spotting and treating phlebitis early. If you notice any, see a doctor right away to avoid serious problems.
Phlebitis in the arm can cause veins to become bumpy and sore. This happens because the veins get inflamed. This inflammation can be caused by many things, like IV catheters.
Phlebitis in the arm shows symptoms like pain, redness, and swelling. It can be either superficial or deep. Superficial thrombophlebitis is more common in the arms.
One clear sign of phlebitis in the arm is bumps on the veins. These bumps can hurt when touched and may be red and warm.
IV catheters often cause phlebitis in the arm. This can happen from irritation, infection, or reactions to the catheter or what’s being infused.
Sore veins are a big sign of phlebitis in the arm. Look for signs like redness, warmth, and swelling. Also, watch for pain or tenderness along the vein.
|
Symptom |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Pain and Tenderness |
Pain or tenderness along the affected vein |
|
Redness and Swelling |
Visible redness and swelling around the vein |
|
Warmth |
The affected area may feel warm to the touch |
|
Bumps or Lumps |
Formation of bumps or lumps along the vein |
Phlebitis in the leg shows different signs. It’s a vein inflammation that can happen anywhere but is more serious in the legs. Knowing the symptoms is key to managing it.
In the legs, phlebitis causes pain, tenderness, redness, and swelling. The skin might feel warm. You might also feel a cord or lump in the vein.
Pain and swelling are common. Feeling warmth or tenderness is also a sign. Spotting these symptoms early is important for treatment.
Vein lumps on the foot and ankle are a sign of phlebitis. These lumps happen when the vein gets inflamed and becomes more noticeable.
Phlebitis often goes with varicose veins. People with varicose veins are more at risk. Knowing this helps in managing and preventing phlebitis.
Spotting an inflamed vein in the leg is easy. Look for redness, swelling, and a cord that feels hard. The area might be warm or tender.
Seeing these signs early helps. It means you can get help sooner and avoid bigger problems.
It’s important to know what causes phlebitis to prevent and manage it. Phlebitis, or vein inflammation, can come from medical procedures, health conditions, and lifestyle choices.
Using intravenous catheters is a big risk for phlebitis. These catheters are needed for medicine and fluids but can irritate veins. The risk goes up with longer use, bigger sizes, and wrong placement.
A study in the Journal of Vascular Access found that following best practices can lower phlebitis risk.
Some medical conditions raise the risk of phlebitis. These include blood clotting issues like thrombophilia and inflammation causes like varicose veins.
Common Medical Conditions:
The American Heart Association says people with vascular diseases are more likely to get phlebitis.
Lifestyle and environment also matter for phlebitis risk. Being immobile, smoking, and being overweight can increase it.
“Lifestyle changes, like exercise and quitting smoking, can lower phlebitis risk.” – Medical Expert, Vascular Specialist
Knowing these risk factors helps people take steps to avoid phlebitis.
Managing phlebitis involves both non-pharmacological and pharmacological methods. Each treatment is tailored to the patient’s needs and the type of phlebitis.
Non-pharmacological methods are key in treating phlebitis. They include:
These methods are often the first line of treatment, mainly for mild cases.
Medication is often needed to manage symptoms and treat the cause of phlebitis. Common medications include:
The choice of medication depends on the cause, severity, and the patient’s health.
For severe phlebitis or complications, advanced treatments are needed. These include:
These treatments are for patients with severe symptoms or complications.
Managing infection in septic phlebitis is critical. This involves:
Quick and effective treatment of infection is vital to avoid serious issues.
Healthcare professionals use many methods to diagnose phlebitis. These include physical exams and advanced imaging. Accurate diagnosis is key to finding the right treatment.
A thorough physical exam is the first step. Doctors look for signs like redness, swelling, warmth, and tenderness. Palpation of the vein can reveal a palpable cord, a sign of phlebitis.
Doctors also check the patient’s medical history. They look for risk factors like recent intravenous catheter placement or venous disorders.
Imaging and lab tests are needed to confirm the diagnosis. Ultrasound is often used to check for venous inflammation and thrombosis.
Laboratory tests, like blood counts and inflammatory markers, help identify signs of infection or inflammation. Sometimes, more tests are needed to rule out other conditions.
Differential diagnosis is important to ensure phlebitis is correctly diagnosed. Conditions like cellulitis, lymphangitis, and deep vein thrombosis must be considered.
A detailed diagnostic approach combines physical exams, imaging, and lab tests. This helps doctors accurately diagnose phlebitis and create an effective treatment plan.
It’s important to know the warning signs of phlebitis to get medical help quickly. If phlebitis is not treated or managed well, it can cause serious problems. These problems can really affect your health.
Phlebitis can turn into deep vein thrombosis (DVT), which is a big risk. DVT happens when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs. Symptoms include swelling, pain, and color changes in the affected limb.
If you notice these symptoms, you should get medical help right away.
Phlebitis can also cause infections, often because of bacteria. Signs of infection include more redness, swelling, and warmth around the vein. You might also feel feverish or have chills.
Some symptoms need urgent medical care. These include:
If you or someone you know has these emergency signs, get help right away.
Untreated or repeated phlebitis can cause long-term venous insufficiency. This is when veins can’t properly return blood to the heart. It can lead to chronic swelling, pain, and skin changes in the affected limb.
Managing phlebitis well can help avoid this problem.
In summary, knowing the warning signs and complications of phlebitis is key to getting medical help on time. If you’re worried about symptoms, talk to a healthcare professional.
Managing phlebitis well is key to avoiding serious problems and easing symptoms. Knowing the signs of vein inflammation is the first step. This helps you take action against it.
Understanding what causes phlebitis helps you avoid it. Using treatments like non-medical methods and medicines can manage it. This helps prevent long-term problems with veins.
To fight vein inflammation, you need a full plan. This includes spotting symptoms, knowing the causes, and using good treatments. This way, you can lower your risk of serious issues and live better. Handling phlebitis well is essential for keeping your veins healthy.
Phlebitis is when a vein gets inflamed. It can happen anywhere in the body, like in the arms and legs.
Symptoms include pain, tenderness, and redness. You might also see swelling, warmth, and bumps on the veins.
It can show as redness, swelling, and a cord or lump on the vein. These signs are visible.
It’s a type of phlebitis in the superficial veins. It causes inflammation and clotting.
Yes, sometimes phlebitis can turn into deep vein thrombosis. This is a serious issue that needs quick medical help.
Doctors use a physical exam, medical history, and imaging tests like ultrasound to diagnose it.
Risk factors include intravenous catheters, certain health conditions, and a sedentary lifestyle.
Treatment includes non-medical methods, medications, and advanced care for severe cases. It also involves managing vein infections.
Some cases can’t be avoided, but you can lower your risk. This includes proper care of intravenous catheters and staying active.
Phlebitis is inflammation of a vein. Thrombophlebitis is when a blood clot causes vein inflammation.
Phlebitis is usually not life-threatening but can be painful. In some cases, it can lead to more serious issues like deep vein thrombosis.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!