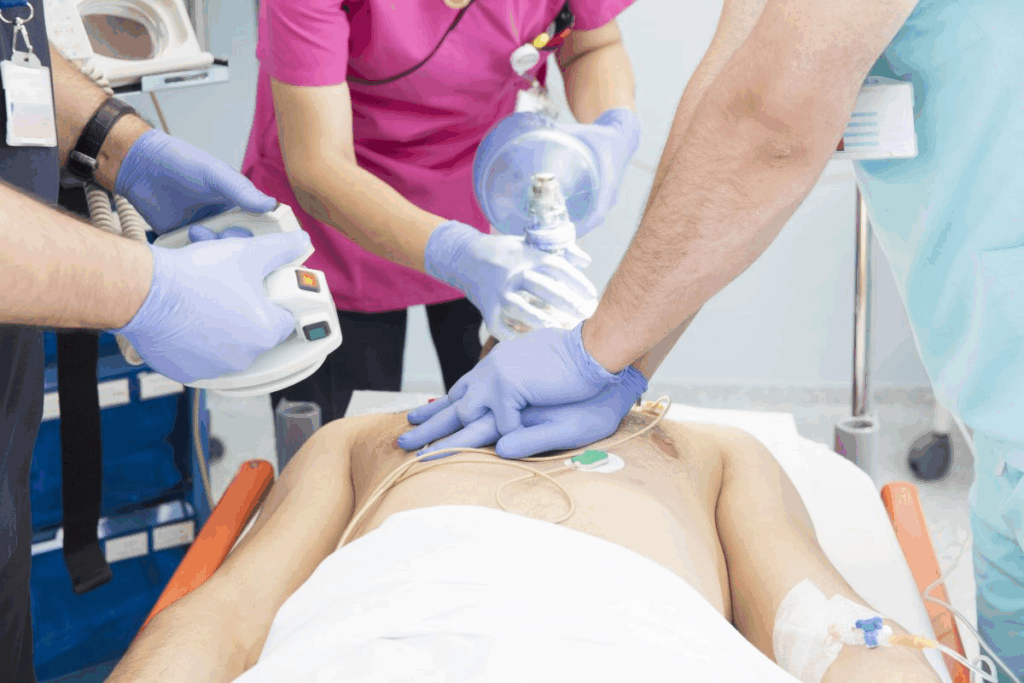
The term cardiopulmonary refers to the heart and lungs and their combined functions. It is a key concept in medicine. It deals with many conditions and treatments that affect these vital organs.
According to Merriam-Webster, recent examples on the web show the usage of “cardiopulmonary” in sentences related to medical conditions. This highlights its importance in understanding the heart and lungs’ connection.
At Liv Hospital, we understand the importance of cardiopulmonary health for overall wellbeing. Our experts aim to give a full understanding of this term and its role in medical condition Defining what does cardiopulmonary mean and explaining its medical relevance (heart and lungs).
Key Takeaways
- The term cardiopulmonary relates to the heart and lungs and their interdependent functions.
- Understanding cardiopulmonary health is key for spotting important symptoms early.
- Cardiopulmonary conditions affect both the heart and lungs, needing full care.
- Liv Hospital offers expert insights into cardiopulmonary health and its importance.
- Knowing cardiopulmonary medical terms helps patients understand their conditions and treatments.
What Does Cardiopulmonary Mean: Breaking Down the Term
The term “cardiopulmonary” comes from “cardio” and “pulmonary.” “Cardio” means heart, and “pulmonary” means lungs. This term is key in medicine because it talks about how the heart and lungs work together.
Etymology and Origin: Cardio + Pulmonary
The word “cardio” comes from the Greek “kardia,” which means heart. It’s used in many medical terms like “cardiology” and “cardiovascular.” “Pulmonary” comes from Latin “pulmo,” meaning lung. It’s used in medical terms about the lungs.
Together, “cardiopulmonary” means the heart and lungs’ connection. It’s used in medical procedures like CPR and heart-lung surgery.
Medical Context and Clinical Usage
In medicine, “cardiopulmonary” covers many conditions and procedures. For example, cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) checks how well the heart and lungs work together.
Term | Description | Clinical Significance |
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) | An emergency procedure that combines chest compressions with rescue breaths to manually preserve intact brain function | Critical for restoring circulation and breathing in cardiac arrest victims |
Cardiopulmonary Bypass | A technique that temporarily takes over the function of the heart and lungs during surgery | Essential for certain cardiac surgeries, allowing surgeons to operate on a stationary heart |
Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing (CPET) | A non-invasive diagnostic tool that assesses the functional competence of the cardiopulmonary system | Provides valuable information on a patient’s aerobic capacity and helps in diagnosing and managing heart and lung diseases |
The term “cardiopulmonary” is key to understanding heart and lung conditions and procedures. By understanding its roots, we see its importance in medicine.
The Cardiopulmonary System: Anatomy and Structure
Knowing how the cardiopulmonary system works is key to understanding our body’s health. It includes the heart and lungs, essential for getting oxygen and removing carbon dioxide. This system is vital for our well-being.
Heart Structure and Function
The heart pumps blood all over our body. It brings oxygen and nutrients to our tissues and takes away waste. It has four chambers: the right and left atria, and the right and left ventricles.
The heart’s design is for efficiency. It has valves to keep blood flowing in one direction. The heart’s cycle of contraction and relaxation keeps blood flowing smoothly.
Lung Structure and Function
The lungs are key for exchanging gases. They take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide. The right lung has three lobes, and the left has two.
The lungs and heart work together. They are essential for oxygenating blood. The movement of blood between the heart and lungs is vital for this process.
“The heart and lungs’ balance shows our body’s amazing health ability.” — Medical Expert
The heart and lungs are connected in the cardiopulmonary system. They work together to keep us healthy. StatPearls explains the system’s anatomy and physiology, showing its complexity and importance.
How the Heart and Lungs Work Together
It’s important to know how the heart and lungs work together. They make sure our body gets the oxygen it needs and gets rid of carbon dioxide.
The heart and lungs work together in a complex way. The heart pumps blood, and the lungs breathe in and out. This ensures our body gets the oxygen it needs.
The Oxygen Transport Process
The oxygen transport process is key to getting oxygen to our body’s tissues. It starts when we breathe in air. The oxygen then goes into our bloodstream.
Oxygen Transport Steps:
- Inhalation of air into the lungs
- Oxygen transfer into the bloodstream
- Pumping of oxygen-rich blood by the heart
- Delivery of oxygen to body tissues
Process | Organ Involved | Function |
Inhalation | Lungs | Air intake |
Oxygen Transfer | Lungs | Oxygen into bloodstream |
Pumping Blood | Heart | Pumping oxygen-rich blood |
The Pulmonary Circulation System
The pulmonary circulation system is key to our health. It’s how blood moves between the heart and lungs. Deoxygenated blood goes to the lungs to pick up oxygen and release carbon dioxide.
The importance of the pulmonary circulation system cannot be overstated. It’s vital for keeping oxygen and carbon dioxide levels balanced in our body.
Problems in one organ can affect the other. For example, heart failure can cause lung problems. Lung diseases like COPD can also strain the heart. Knowing how they work together is important for our health.
StatPearls on CPR shows how critical it is to understand the heart and lungs’ teamwork. This is even more important in emergency situations like CPR.
Common Cardiopulmonary Conditions
Cardiopulmonary conditions are a big health issue, affecting millions globally. They involve both heart and lung systems, making treatment hard. We’ll look at common conditions that affect both heart and lungs.
Cardiovascular Diseases Affecting Respiratory Function
Heart problems can really mess with breathing. For example, heart failure can cause lungs to fill with fluid. This makes it hard to breathe. We’ll see how heart diseases like coronary artery disease and cardiomyopathy impact lung function.
The CDC says over 16 million Americans have Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). But heart problems can also cause breathing issues. This makes diagnosing and treating harder.
Respiratory Diseases Affecting Cardiovascular Function
Lung diseases can also harm the heart. Conditions like COPD and pneumonia put extra strain on the heart. We’ll talk about how lung diseases can affect the heart and why treating both is key.
COPD is more than just a lung issue; it affects the heart too. People with COPD are more likely to get heart problems like heart failure. It’s important to understand this connection for better care.
By seeing how heart and lungs work together, we can improve care for these conditions. This approach is vital for better patient outcomes and reducing disease burden.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) and Heart Health
COPD is a big health problem in the U.S., with over 16 million cases. It affects both lung and heart health. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has data on COPD and heart health, showing we need better management.
Prevalence in the United States
More than 16 million Americans have COPD. It’s caused by smoking, pollution, and genetics. The CDC says COPD leads to a lot of sickness and death, costing a lot of money and lost work.
State | COPD Prevalence (%) | Cardiovascular Complications (%) |
Alabama | 8.4 | 12.1 |
California | 6.2 | 9.5 |
New York | 7.1 | 10.8 |
Cardiovascular Complications
People with COPD are more likely to get heart diseases. This includes heart failure and heart rhythm problems. COPD’s inflammation makes heart problems worse.
“The presence of COPD is associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular events, stressing the need for care that covers both lung and heart health.”
Treatment Approaches for Cardiopulmonary COPD
Dealing with COPD and heart issues needs a mix of treatments. This includes medicines, lifestyle changes, and exercise programs. The goal is to help lungs work better, lessen symptoms, and lower heart risks.
- Pharmacological treatments: Bronchodilators, corticosteroids, and phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors.
- Lifestyle modifications: Quitting smoking, exercising, and eating well.
- Pulmonary rehabilitation: Programs with exercise, education, and changing behaviors.
With a complete treatment plan, COPD patients can feel better and have less heart problems.
The Cascade Effect: When One System Affects the Other
The heart and lungs work together closely. If one has a problem, it can affect the other. This means heart or lung issues can lead to serious health problems.
Cardiac Problems Leading to Respiratory Symptoms
Heart failure happens when the heart can’t pump enough blood. This causes fluid to build up in the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath and coughing.
Examples of cardiac conditions that can lead to respiratory symptoms include:
- Heart failure
- Coronary artery disease
- Cardiac arrhythmias
Respiratory Problems Leading to Cardiac Symptoms
Chronic respiratory diseases, like COPD, can harm the heart. COPD can cause high blood pressure in the lungs. This puts extra strain on the heart, leading to right-sided heart failure.
The mechanisms by which respiratory problems affect the heart include:
- Increased strain due to pulmonary hypertension
- Hypoxia (low oxygen levels) affecting cardiac function
- Inflammation and oxidative stress impacting cardiac health
The following table summarizes the cascade effect between cardiac and respiratory systems:
Primary System Affected | Condition | Secondary Symptoms |
Cardiac | Heart Failure | Shortness of breath, pulmonary congestion |
Respiratory | COPD | Pulmonary hypertension, right-sided heart failure |
The connection between the heart and lungs is key. Doctors must look at both systems when treating related conditions. This understanding is vital for managing heart and lung diseases well.
Cardiopulmonary Arrest: Understanding a Critical Emergency
Cardiopulmonary arrest happens when the heart and lungs stop working. It’s a serious condition that needs quick action to avoid death.
Definition and Pathophysiology
Cardiopulmonary arrest, or cardiac arrest, is when the heart stops beating. This stops blood and air from moving. It’s a life-threatening emergency that needs fast medical help.
The American Heart Association says it can be caused by heart attacks, drowning, electrocution, and severe injuries. Knowing these causes helps prevent and treat it quickly.
Warning Signs and Risk Factors
It’s important to know the signs and risks of cardiopulmonary arrest. Signs include chest pain, trouble breathing, feeling dizzy, and irregular heartbeats. Risks include heart disease, heart failure, and severe lung diseases.
“Early recognition of these signs and symptoms can significantly improve outcomes,” a study says. Being alert to these signs helps get medical care fast.
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Palpitations or irregular heartbeat
Immediate Response Protocols
The first step in treating cardiopulmonary arrest is Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR). CPR keeps blood flowing and oxygen to organs until help arrives. If there’s an Automated External Defibrillator (AED), it should be used too.
“CPR is a lifesaving technique that is useful in many emergencies, including heart attacks and near drowning, in which someone’s breathing or heartbeat has stopped,” according to the American Heart Association. Quick action can greatly improve survival chances.
We must act fast and follow the right steps to handle cardiopulmonary arrest. This includes calling for help, doing CPR, and using an AED if there is one.
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR): Saving Lives
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation, or CPR, is a lifesaving method used in emergencies. It’s key when someone’s heart stops or doesn’t work right. CPR helps restart the heart and keeps blood flowing to important organs.
Evolution of CPR Techniques
CPR has changed a lot over time. At first, it was just mouth-to-mouth resuscitation. Now, it includes chest compressions, thanks to medical progress. The American Heart Association gives clear guidelines on CPR, focusing on good chest compressions and breaths.
Automated external defibrillators (AEDs) have also been added. They check the heart’s rhythm and give shocks when needed. This has greatly helped CPR, improving chances of survival in cardiac arrest cases.
Current CPR Guidelines and Methods
Today, CPR starts with chest compressions, then breaths. Adults get 30 compressions followed by 2 breaths. The American Heart Association suggests bystanders do Hands-Only CPR for adults who suddenly collapse.
Healthcare workers follow more detailed guidelines. This includes using AEDs, bag-mask ventilation, and advanced airway management. The goal is to do CPR well, without stopping, and get medical help fast.
Survival Rates and Outcomes
Survival rates after CPR depend on many things. These include the cause of cardiac arrest, where it happens, and how well CPR is done. Early CPR can greatly increase chances of survival and better outcomes.
The American Heart Association says out-of-hospital cardiac arrest survival rates are about 10%. But, some places have rates up to 30% or more with good CPR. To improve survival, we need more people to do CPR, do it well, and get help quickly.
In summary, CPR is a critical emergency method that can save lives. Knowing about CPR’s history, current rules, and how it affects survival is important. By teaching CPR and encouraging people to act, we can help more people survive cardiac arrest.
Risk Factors and Prevention of Cardiopulmonary Diseases
Risk factors for heart and lung diseases are many and varied. They include things we can’t change and things we can. Knowing these factors helps us find ways to stay healthy.
Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Age, Gender, and Genetics
Some risk factors can’t be changed. Getting older increases the chance of heart and lung problems. Being male might also raise the risk for some diseases. And genetics play a big part too, with family history being a clue.
- Getting older raises the risk of heart and lung diseases.
- Men are more likely to get some diseases than women.
- Genetics can greatly increase the risk of these diseases.
Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, Diet, and Exercise
Our lifestyle choices greatly affect our risk of heart and lung diseases. Smoking harms both the lungs and heart, raising the risk of diseases. A bad diet and not enough exercise can also increase risk, leading to obesity and high blood pressure.
- Stopping smoking can greatly lower the risk of heart and lung diseases.
- Eating well, with lots of fruits and veggies, can help.
- Staying active keeps the heart and lungs healthy.
Preventive Strategies and Regular Screening
Preventing heart and lung diseases needs a mix of approaches. Regular check-ups are key, for those at higher risk. Quitting smoking, eating right, and exercising are also important. Managing conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes helps too.
By knowing the risks and taking steps to prevent them, we can lower our chances of getting heart and lung diseases. It’s wise to talk to a doctor about how to keep your heart and lungs healthy.
Conclusion: Maintaining Optimal Cardiopulmonary Health
Keeping our heart and lungs healthy is key to feeling good. We’ve talked about how the heart and lungs work together. This knowledge helps us prevent heart and lung diseases.
Health groups stress the need for lifestyle changes and medical care. Eating right, exercising, and not smoking are important. Also, seeing doctors regularly helps catch problems early.
By teaming up with doctors and making smart choices, we can lower disease risks. This improves our life quality and health.
FAQ
What does cardiopulmonary mean?
“Cardiopulmonary” means the heart and lungs working together. They are key to keeping us healthy.
What is the cardiopulmonary system?
It’s made up of the heart and lungs. They help move oxygen and nutrients to our body’s cells and take away carbon dioxide.
How do the heart and lungs collaborate?
The heart sends blood to the lungs for oxygen. Then, the lungs exchange oxygen for carbon dioxide. This oxygen-rich blood goes to the rest of our body.
What is cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR)?
CPR is an emergency action. It combines chest compressions with breaths to keep blood flowing and breathing going when someone stops breathing or their heart stops.
What are the risk factors for cardiopulmonary diseases?
Risk factors include age, gender, and genetics. Lifestyle choices like smoking, a bad diet, and not exercising also play a part.
How can cardiopulmonary health be maintained?
Keep your heart and lungs healthy by exercising regularly, eating well, not smoking, and managing stress. Also, get regular check-ups.
What is chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)?
COPD is a lung disease that makes it hard to breathe. It often affects the heart too.
What is the cascade effect in cardiopulmonary diseases?
The cascade effect means problems in one system can affect the other. This shows how the heart and lungs depend on each other.
How is cardiopulmonary arrest treated?
Cardiopulmonary arrest is treated with CPR to start blood and breathing again. Then, more advanced medical help is given.
What is the significance of understanding cardiopulmonary medical terms?
Knowing these terms helps us understand heart and lung conditions and treatments. It helps us make better health choices.
What is the definition of cardiopulmonary arrest?
Cardiopulmonary arrest is when the heart stops and breathing stops. It’s a life-threatening emergency that needs quick medical help.
How does COPD affect cardiovascular health?
COPD can harm the heart, causing failure and irregular heartbeats. This is because the heart works harder and there’s inflammation in the body.
What are the warning signs of cardiopulmonary arrest?
Signs include sudden loss of consciousness, no breathing, and no pulse. These need immediate action to save a life.
Reference
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470402/