Last Updated on November 26, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
Did you know that prostate issues can start affecting men as early as their 40s? This is a critical health concern because prostate health is closely linked to overall well-being.
As we age, the risk of developing prostate problems increases significantly. In fact, How Quickly Does Prostate Cancer Spread?prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers among older men. Understanding the typical age ranges for these issues is key for early detection and effective management.
We will explore the relationship between age and prostate health. We’ll provide insights into managing and maintaining optimal prostate well-being.
Key Takeaways
- Prostate issues can begin affecting men in their 40s.
- The risk of prostate problems increases with age.
- Understanding typical age ranges is key for early detection.
- Prostate health is closely linked to overall well-being.
- Effective management of prostate health is critical.
The Prostate Gland: Structure and Function
The prostate gland is a key part of men’s health. It’s found below the bladder and wraps around the urethra. This tube carries urine out of the body. The prostate is essential for the male reproductive system.
Anatomy and Location of the Prostate
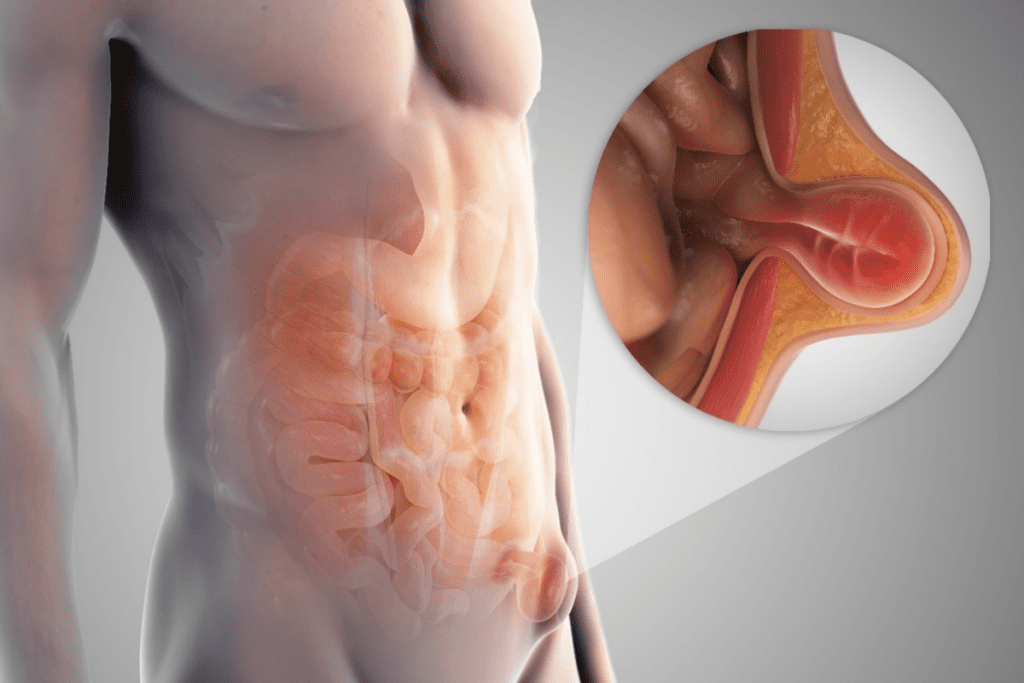
The prostate gland is small, about the size of a walnut. It’s a vital part of the male reproductive system. It makes fluids that are part of semen, which helps sperm during ejaculation.
The prostate is between the bladder and the penis, in front of the rectum. Knowing its anatomy and location helps doctors diagnose and treat prostate problems.
- The prostate gland is situated just below the bladder.
- It surrounds the urethra, affecting urine flow.
- Its location between the bladder and penis makes it a critical part of the reproductive system.
Physiological Role Throughout a Man’s Life

The prostate gland’s role changes as a man ages. During puberty, it grows under male hormones. In adulthood, it keeps producing seminal fluids, helping with fertility.
As men get older, the prostate can change, leading to health problems.
Some key roles of the prostate include:
- Producing seminal fluid to nourish sperm.
- Supporting the urethra, which carries urine and semen out of the body.
- Responding to hormonal changes throughout a man’s life.
We know that keeping the prostate healthy is important, more so as men get older. Understanding the prostate gland’s role helps us see its importance in men’s health. This knowledge encourages us to take steps to support it.
Normal Age-Related Changes in the Prostate
It’s important to know about normal changes in the prostate as men age. The prostate gland is key to the male reproductive system. Its growth and changes are tied to a man’s age.
Prostate Development from Birth to Adulthood
The prostate gland starts growing during fetal development. But it really grows a lot during puberty. This growth is due to androgens, like testosterone. By adulthood, the prostate usually reaches its normal size.
Natural Growth Patterns with Aging
As men get older, the prostate gland changes. It often gets bigger due to benign growth. This natural growth can sometimes cause urinary problems.
We have a table to show how prostate size changes with age:
| Age Group | Typical Prostate Size | Common Changes |
| 20-30 years | Average size, around 20-25 grams | Minimal changes |
| 40-50 years | Gradual increase in size | Possible onset of BPH symptoms |
| 60+ years | Often enlarged, potentially over 40 grams | Higher likelihood of BPH and other prostate issues |
Hormonal Influences on Prostate Size
Hormones, like androgens like testosterone, are very important for the prostate. The conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is key. DHT makes prostate cells grow a lot. Knowing about these hormones helps with prostate health.
Hormonal changes can really affect prostate health. It’s important to manage these changes for overall health.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): The Most Common Prostate Condition
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is a common issue for men as they get older. It’s when the prostate gland grows too big, causing urinary problems.
Typical Age of Onset
The usual time BPH starts is around 40 years old. But, symptoms might show up much later.
Prevalence Rates
BPH gets more common with age. Here’s what studies found:
- By 60, about 50% of men have BPH.
- By 80, this number jumps to 80%.
- Men under 40 rarely have it.
Impact on Quality of Life
BPH can really affect a man’s life, making it hard to use the bathroom. Its impact changes with age:
- Men in their 50s and 60s might have annoying bathroom issues.
- Older men might have worse symptoms, making other health problems harder.
- Managing BPH well can improve life quality at any age.
Prostatitis: Age Distribution and Risk Factors
Prostatitis is when the prostate gland gets inflamed. It can cause pain, trouble urinating, and sex problems. Knowing who gets it and why is key.
Acute Bacterial Prostatitis: Age Patterns
Acute bacterial prostatitis is caused by bacteria. It can hit anyone but is more common in young men. It often comes from UTIs or STIs. Seeing a doctor fast is important to avoid serious issues.
Chronic Prostatitis: Who’s Most Vulnerable?
Chronic prostatitis means symptoms keep coming back. It can happen to men of any age but hits middle-aged men more. Things like UTIs, STIs, and lifestyle choices can make you more likely to get it.
Age-Related Differences in Symptoms and Treatment
Prostatitis symptoms and treatments change with age. Younger men might have sudden symptoms from bacteria. Older men might have long-term symptoms from other health problems. Treatments range from antibiotics to therapies to help with symptoms.
Several things can make you more likely to get prostatitis, including:
- Bacterial infections: More common in younger men.
- Urinary tract issues: Can affect men of any age.
- Lifestyle factors: Such as diet, physical activity level, and stress.
Symptoms can be pain in the groin, trouble urinating, and sex problems. How bad these symptoms are can change with age and health.
Treatment for prostatitis depends on the cause and the patient’s age and health. For bacterial prostatitis, antibiotics are the main treatment. For chronic prostatitis, treatment might include medicines, lifestyle changes, and alternative therapies to manage symptoms.
Prostatitis is a complex issue that affects men of all ages. Knowing about its age distribution, risk factors, and how symptoms and treatment vary with age is vital for managing it well.
Prostate Cancer: Understanding Age-Related Risk
Age and prostate cancer risk are closely linked. As we get older, the chance of genetic changes and environmental factors leading to cancer grows. Knowing this risk is key to catching prostate cancer early and managing it well.
Incidence Rates from Age 40 to 80+
Prostate cancer is rare in men under 40. But, it becomes more common after 50. The American Cancer Society says about 1 in 9 men will get prostate cancer in their lifetime. The risk goes up with age:
| Age Group | Incidence Rate per 100,000 |
| 40-49 | 14.2 |
| 50-59 | 134.4 |
| 60-69 | 439.8 |
| 70-79 | 634.9 |
| 80+ | 764.1 |
This shows how much prostate cancer risk increases with age. It’s why we need age-based screening and prevention plans.
Why Cancer Risk Increases with Age
Several things make prostate cancer risk higher with age. Genetic mutations that happen over time can cause cancer in prostate cells. Also, hormonal influences, like testosterone, play a role in prostate cancer growth. Environmental and lifestyle factors also add up with age, raising the risk.
Survival Rates Based on Age at Diagnosis
The age when prostate cancer is diagnosed affects survival rates. Older men often have lower survival rates because of other health issues and more aggressive cancer. The 5-year survival rate for prostate cancer is nearly 100% for early-stage diagnosis. But, this rate changes with age:
- Men diagnosed under 65: 5-year survival rate is about 98%
- Men diagnosed between 65-74: 5-year survival rate is about 95%
- Men diagnosed at 75 or older: 5-year survival rate is about 90%
Knowing these survival rates helps in making better choices about screening and treatment.
Early-Onset Prostate Problems: Under Age 40
Prostate problems in men under 40 are rare but serious. While prostate issues are common in older men, they can also affect younger men. This is often due to genetics or other factors.
Rare but Serious Concerns
Young men can face prostate issues like prostatitis or prostate cancer. These conditions are rare in men under 40 but can have big health effects.
Some important stats show why we need to be aware:
- Prostate cancer in men under 40 is rare, making up less than 1% of all cases.
- Prostatitis, or inflammation of the prostate, can affect men of any age, including those under 40.
Genetic Predisposition Factors
Genetics are key in early-onset prostate problems. Men with a family history of prostate cancer or issues are at higher risk. This is true even if they’re younger.
Important genetic factors include:
- Having a father or brother with prostate cancer, even if they were young when diagnosed.
- Genetic mutations, like those in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, which are linked to breast and ovarian cancer but also prostate cancer risk.
Warning Signs Young Men Shouldn’t Ignore
While prostate problems are rare in young men, knowing the signs is important. Symptoms that need medical attention include:
- Painful urination or trouble urinating.
- Pain in the groin, abdomen, or lower back.
- Frequent urination, often at night.
- Blood in the urine or semen.
Early detection is key to managing prostate problems, no matter your age. Young men, and those with a family history of prostate issues, should watch their prostate health closely. If they notice any concerning symptoms, they should see a doctor.
Prostate Health in Middle Age: 40-59 Years
Middle age, from 40 to 59, is key for keeping the prostate healthy. Men may see changes in their prostate that affect their life quality during this time.
Common Issues During This Critical Period
In their 40s and 50s, men face prostate issues like Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), prostatitis, and a higher risk of prostate cancer. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia is when the prostate gets bigger, leading to trouble with urination.
Prostatitis, or inflammation of the prostate, can also happen. It’s important for men to know the signs of these problems to get help if needed.
The Importance of Baseline Testing
Getting baseline tests is vital for men in their 40s and 50s. A Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) test sets a starting point for PSA levels. This, along with a digital rectal exam, helps find prostate issues early.
Talking to a doctor about PSA tests is a good idea. They can help decide what’s best for you.
Lifestyle Factors That Affect Risk
What you do every day affects your prostate health in middle age. Eating right, staying active, and not smoking are important.
- Eating lots of fruits, veggies, and whole grains is good for your prostate.
- Being active helps lower the risk of prostate problems.
- Not smoking is key, as smoking increases prostate cancer risk.
Choosing healthy habits can help keep your prostate healthy during this important time.
| Lifestyle Factor | Impact on Prostate Health |
| Diet rich in fruits and vegetables | Supports prostate health |
| Regular physical activity | Reduces risk of prostate problems |
| Not smoking | Reduces risk of prostate cancer |
Prostate Concerns for Men 60-75 Years Old
Men aged 60 to 75 often deal with prostate issues. These problems need careful handling. As we get older, our prostate gland changes, leading to both minor and serious conditions.
Expected Changes vs. Warning Signs
Men in this age group may notice various prostate symptoms. It’s important to know the difference between normal aging changes and signs of serious problems. For example, an enlarged prostate is common, but severe urinary issues or pain could mean something serious.
Common symptoms to watch for include:
- Frequent urination
- Weak urine flow
- Difficulty starting urination
- Painful urination
Managing Multiple Prostate Conditions
Men in this age group often face multiple prostate issues at once. These can include BPH, prostatitis, and prostate cancer. A detailed treatment plan is key to handling these conditions well.
| Condition | Common Symptoms | Management Strategies |
| BPH | Urinary frequency, weak flow | Medications, lifestyle changes |
| Prostatitis | Pain, urinary issues | Antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs |
| Prostate Cancer | Often asymptomatic in early stages | Surgery, radiation, active surveillance |
Quality of Life Considerations
Keeping a good quality of life is vital for men dealing with prostate issues. Treatment choices should aim to improve prostate health without harming daily life.
Key considerations include:
- Minimizing urinary symptoms
- Preserving sexual function
- Maintaining overall physical and mental health
Understanding prostate changes and warning signs, managing multiple conditions, and focusing on quality of life helps men aged 60 to 75 manage prostate concerns confidently.
Prostate Health Beyond Age 75
Managing prostate health after 75 is complex. It involves looking at the risks and benefits of treatments and other health issues that come with age.
Risk-Benefit Analysis of Treatment
For men over 75, it’s key to carefully weigh treatment options. We look at the good and bad sides of each treatment. This helps us decide what’s best for the patient’s health and life expectancy.
Younger men might get treatments that aren’t right for older men. This is because older men might face more side effects or drug interactions. We aim to choose treatments that keep the patient comfortable and functional.
Key Considerations for Risk-Benefit Analysis:
- Life expectancy and overall health status
- Potential side effects of treatments
- Impact on quality of life
- Patient preferences and values
Managing Prostate Health with Other Age-Related Conditions
Men over 75 often face many health issues at once. This means we need a team effort to care for them. Healthcare professionals work together to avoid problems with treatments.
For example, a man with prostate and heart disease needs a special care plan. We adjust medications and watch health closely. We also make lifestyle changes to help manage both conditions.
| Condition | Considerations for Prostate Health Management |
| Heart Disease | Monitor interactions between prostate medications and heart medications. |
| Diabetes | Manage blood sugar levels to minimize complications. |
| Chronic Kidney Disease | Adjust medication dosages according to kidney function. |
When caring for prostate health in the elderly, we must think about more than just the physical. Family, caregivers, and healthcare support are vital. They help patients stick to treatment plans and live well.
“The goal of managing prostate health in older men is not just to extend life, but to ensure that the years they have left are lived with dignity and minimal discomfort.”
Racial and Ethnic Variations in Age of Onset
It’s important to know how race and ethnicity affect when prostate problems start. Prostate health varies a lot between different groups. This means some groups face prostate issues earlier or more severely.
African American Men: Earlier Onset and Greater Severity
African American men face a big challenge with prostate cancer. They often get it younger and it’s more aggressive. This is different from other groups.
Genetics, lifestyle, and healthcare access all play a part in this issue. These factors help explain why African American men are hit harder by prostate cancer.
Asian and Hispanic Populations: Different Risk Patterns
Men from Asian and Hispanic backgrounds have lower prostate cancer rates than African American men. But, they have higher rates than some other groups. The age when they get prostate cancer can also vary.
It’s key to understand these patterns. This helps us create better screening and prevention plans for different groups.
Genetic vs. Environmental Factors
Genetics and environment both affect when and how prostate cancer starts. While genetics are important, lifestyle and environment also matter. Things like diet, exercise, and chemical exposure can impact prostate health.
| Ethnic Group | Average Age of Onset | Incidence Rate |
| African American | Earlier than 65 | Higher |
| Asian | 65 and above | Lower |
| Hispanic | 65 | Moderate |
By looking into these factors, we can make prostate health better for everyone. This means improving outcomes for men from all backgrounds.
Age-Specific Prostate Screening Guidelines
Knowing when to get a prostate screening is key for men’s health. These tests help find prostate problems early, like cancer. As men get older, the chance of prostate issues grows, so it’s important to follow the right screening age.
Recommendations for Men Under 50
Men under 50 usually don’t need routine prostate tests unless they’re at high risk. High-risk factors include a family history of prostate cancer or being African American. It’s best for these men to talk to their doctor about their risk to decide on early screening.
Screening Protocols for Ages 50-70
Men aged 50 to 70 should get regular prostate tests. How often depends on their PSA levels and other risks. If the PSA is low, tests every two years might be okay. But if it’s higher, annual tests might be needed. It’s important for these men to talk to their doctor about the pros and cons of screening.
Approaches for Men Over 70
For men over 70, screening decisions get more complex. Those with a short life expectancy might not need tests. But if they’re healthy and expect to live longer, screening could be beneficial. Men in this age group should discuss their health, life expectancy, and screening wishes with their doctor.
| Age Group | Screening Recommendation | Considerations |
| Under 50 | Not recommended unless high risk | Family history, African American descent |
| 50-70 | Regular screening | PSA level, risk factors, health status |
| Over 70 | Individualized based on health and life expectancy | Life expectancy, overall health, personal preference |
By following these guidelines, men can make smart health choices with their doctors. It’s important to think about the benefits of early detection and the risks of screening and tests.
Recognizing Symptoms at Different Life Stages
It’s important to know the signs of prostate problems early. As men get older, their prostate gland changes. These changes can cause different health issues.
Age-Specific Warning Signs
Symptoms of prostate problems vary with age. Younger men might feel pain or discomfort when they pee or ejaculate. Older men often have to pee a lot, have a weak flow, or pee at night.
Men under 40 rarely face prostate issues. But, when they do, it’s often due to prostatitis or other infections. Men between 40 and 59 often deal with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). This can make peeing hard and affect their daily life.
How Symptoms Progress Over Time
Prostate symptoms can get worse over time. They might start with mild pee problems. For example, a man with BPH might first notice his pee flow is weaker. This can get worse if not treated.
It’s key to watch for these changes and talk to a doctor. Early treatment can greatly improve health and prevent serious problems.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Some symptoms need quick medical help. Look out for severe pain, trouble peeing, or blood in pee or semen. If you see these signs, get help right away. They can mean serious health issues.
It’s smart to be proactive about prostate health. Knowing when to see a doctor can help prevent big problems. This way, men can stay healthy and catch issues early.
Diagnostic Approaches Based on Patient Age
Age is key in finding the best ways to check prostate health. As men age, they face more prostate problems. So, doctors use different methods to diagnose them.
PSA Interpretation Across Age Groups
PSA testing is vital for prostate health checks. But, what’s considered normal changes with age. Younger men have a lower PSA threshold, while older men’s thresholds are higher.
A PSA level that’s okay for a 70-year-old might be high for a 40-year-old. This helps spot who’s at risk and avoid too many biopsies in older men with BPH.
Imaging and Biopsy Considerations
Imaging and biopsies also depend on age. Younger men might get more detailed tests, like MRI-guided biopsies, for a precise diagnosis.
Older men might start with simpler tests. They’ll only get biopsies if their PSA levels or other signs suggest cancer. The choice to use imaging or biopsy depends on the patient’s health and life expectancy.
Risk Calculators and Age Factors
Risk calculators use age, PSA levels, family history, and ethnicity to predict prostate cancer. They help decide if more tests are needed.
These calculators help doctors sort men by risk. This way, they can focus on the most at-risk for early checks. It means less testing for those at lower risk.
We make sure each patient gets a unique approach. By considering age and other factors, we aim for accurate diagnoses and effective treatments.
Treatment Options Across the Age Spectrum
Prostate treatment options change with age. A personalized approach is needed. Health, prostate condition, and personal preferences are key in choosing the right treatment.
Conservative Management in Younger Patients
Younger men, usually under 50, often start with conservative management. This includes active surveillance. It means watching the condition closely with tests and exams.
Lifestyle changes are also suggested. These can be diet or exercise. The aim is to avoid harsh treatments that might harm quality of life.
“Active surveillance is a good choice for many young men with low-risk prostate cancer,” a study says. “It helps them keep their quality of life without the side effects of aggressive treatments.”
Balancing Aggression and Quality of Life in Middle Age
Men in their 50s and 60s have a harder decision to make. It’s important to find the right balance between treatment and quality of life. Options include surgery, radiation, or both.
The choice depends on the prostate condition, health, and personal wishes.
- Surgery: Removing the prostate gland (prostatectomy)
- Radiation Therapy: Targeted radiation to kill cancer cells
- Hormone Therapy: Reducing testosterone levels to slow cancer growth
Treatment Considerations for Elderly Men
Elderly men, over 75, focus on symptom management and quality of life. Treatment choices are made with their health and life expectancy in mind. Sometimes, palliative care is best. It aims to improve life quality without aggressive cancer treatment.
Age-Specific Prevention Strategies
We suggest specific ways to keep the prostate healthy at different ages. Knowing what each age needs helps men stay proactive about their prostate health.
Proactive Measures for Men Under 40
Men under 40 should focus on a healthy lifestyle. Eating well and staying active are key. Avoiding too much alcohol and not smoking is also important. Starting healthy habits early can greatly benefit prostate health later on.
Risk Reduction for Men 40-60
Men aged 40 to 60 should aim to reduce their risk. Regular health check-ups and talking to a doctor about prostate health are vital. Eating foods good for the prostate, like those with omega-3s and antioxidants, is also beneficial. Staying fit and at a healthy weight can lower the risk of prostate problems.
| Age Group | Prevention Strategies | Key Actions |
| Under 40 | Healthy Lifestyle | Balanced diet, regular exercise, avoid smoking and excessive alcohol |
| 40-60 | Risk Reduction | Regular check-ups, prostate-friendly diet, maintain healthy weight |
| Over 60 | Maintenance Approaches | Regular PSA testing, manage chronic conditions, stay informed about treatment options |
Maintenance Approaches for Men Over 60
For men over 60, the goal is to maintain and catch problems early. PSA testing and DREs are key for early detection. Managing health conditions and knowing about new treatments are also important. Men in this age group should work with their doctors to create a care plan.
Conclusion
Managing prostate health well means understanding how age affects it. The prostate gland changes a lot as men get older. These changes can raise the risk of different prostate problems.
We’ve looked at how age impacts BPH, prostatitis, and prostate cancer. It’s clear that age-specific prevention and treatment are key. Knowing about these changes helps men stay healthy.
Prevention and catching problems early are key to prostate health. Men should talk to their doctors about their risk and screening options. This includes their age, family history, and health.
By being proactive about prostate health, men can lower their risk of prostate issues. This improves their life quality as they get older. We urge men to focus on their prostate health and seek medical help if they have symptoms or worries.
FAQ
What is the typical age range for developing prostate problems?
Prostate problems can happen at any age. But, they are more common in men over 50. The risk of issues like BPH and prostate cancer goes up with age.
What are the common prostate issues that men face as they age?
Men often face BPH, prostatitis, and prostate cancer as they age. BPH is a non-cancerous enlargement. Prostatitis is inflammation, and prostate cancer is a tumor.
How does the prostate gland change throughout a man’s life?
The prostate gland grows and changes with age. Hormonal changes influence it. It starts growing from birth, grows more during puberty, and can change more with age.
What are the symptoms of BPH, and how do they impact quality of life?
Symptoms of BPH include frequent urination, urgency, weak flow, and waking up to urinate. These symptoms can really affect a man’s life, impacting sleep and daily activities.
Can young men develop prostate problems, and what are the warning signs?
Yes, young men can get prostate problems, though it’s rare. Look out for urinary issues, pain, or unusual symptoms. If you have a family history, be extra careful.
How does age affect the risk of prostate cancer?
Age is a big risk factor for prostate cancer, with most cases found in men over 65. The risk goes up after 50.
What are the age-specific guidelines for prostate screening?
Screening guidelines change with age. Men under 50 should talk to their doctor if they have risk factors. Men 50-70 should consider regular screening. For men over 70, it depends on their health.
How do diagnostic approaches differ based on patient age?
Diagnosing prostate issues depends on age, health, and other factors. Younger men might need different tests than older men.
What are the treatment options for prostate problems across different age groups?
Treatment options vary by age and health. Younger patients might get conservative treatments. Older men might need more aggressive treatments, balancing treatment with quality of life.
How can men prevent or reduce the risk of prostate problems?
Preventing prostate problems includes a healthy lifestyle, avoiding smoking, and managing stress. Regular check-ups and screenings can also help.
Are there racial or ethnic differences in the age of onset for prostate problems?
Yes, there are racial and ethnic differences. For example, African American men get prostate cancer younger and more severely.
What are the key considerations for managing prostate health beyond age 75?
Managing prostate health over 75 involves weighing treatment risks and benefits. Consider overall health, life expectancy, and quality of life. Coordinating care with other health issues is also key.
References
Gupta, S., et al. (2016). Prostate cancer: How young is too young? Journal of Urology, 195(6), 1231-1237. What Age is Typical for Prostate Problems?
Did you know that prostate issues can start affecting men as early as their 40s? This is a critical health concern because prostate health is closely linked to overall well-being.
As we age, the risk of developing prostate problems increases significantly. In fact, prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers among older men. Understanding the typical age ranges for these issues is key for early detection and effective management.
We will explore the relationship between age and prostate health. We’ll provide insights into managing and maintaining optimal prostate well-being.
Key Takeaways
- Prostate issues can begin affecting men in their 40s.
- The risk of prostate problems increases with age.
- Understanding typical age ranges is key for early detection.
- Prostate health is closely linked to overall well-being.
- Effective management of prostate health is critical.
The Prostate Gland: Structure and Function
The prostate gland is a key part of men’s health. It’s found below the bladder and wraps around the urethra. This tube carries urine out of the body. The prostate is essential for the male reproductive system.
Anatomy and Location of the Prostate
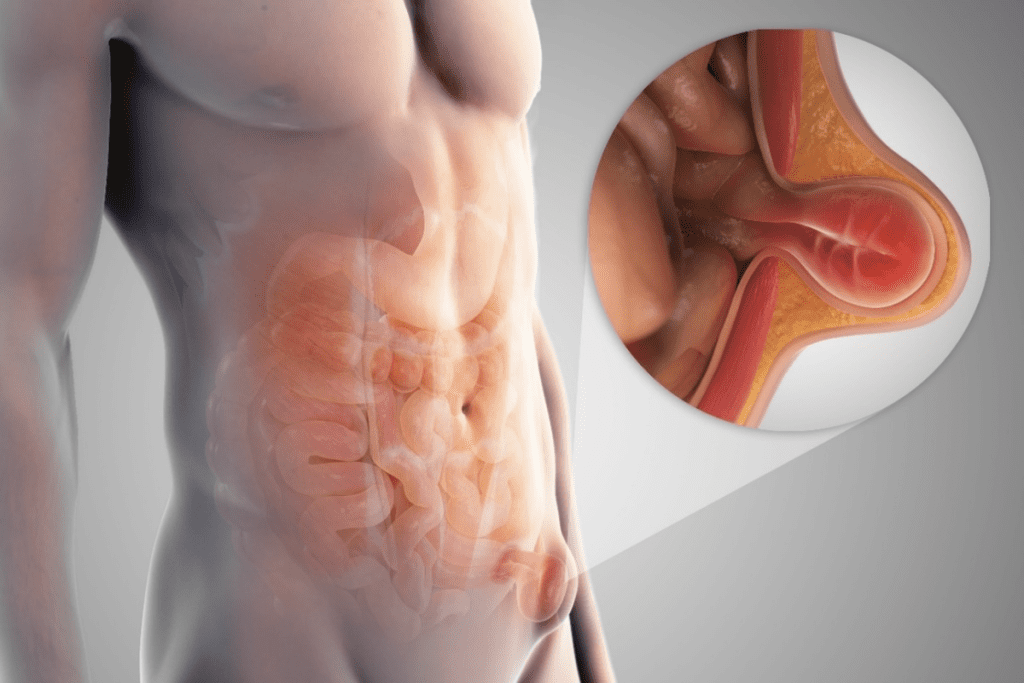
The prostate gland is small, about the size of a walnut. It’s a vital part of the male reproductive system. It makes fluids that are part of semen, which helps sperm during ejaculation.
The prostate is between the bladder and the penis, in front of the rectum. Knowing its anatomy and location helps doctors diagnose and treat prostate problems.
- The prostate gland is situated just below the bladder.
- It surrounds the urethra, affecting urine flow.
- Its location between the bladder and penis makes it a critical part of the reproductive system.
Physiological Role Throughout a Man’s Life

The prostate gland’s role changes as a man ages. During puberty, it grows under male hormones. In adulthood, it keeps producing seminal fluids, helping with fertility.
As men get older, the prostate can change, leading to health problems.
Some key roles of the prostate include:
- Producing seminal fluid to nourish sperm.
- Supporting the urethra, which carries urine and semen out of the body.
- Responding to hormonal changes throughout a man’s life.
We know that keeping the prostate healthy is important, more so as men get older. Understanding the prostate gland’s role helps us see its importance in men’s health. This knowledge encourages us to take steps to support it.
Normal Age-Related Changes in the Prostate
It’s important to know about normal changes in the prostate as men age. The prostate gland is key to the male reproductive system. Its growth and changes are tied to a man’s age.
Prostate Development from Birth to Adulthood
The prostate gland starts growing during fetal development. But it really grows a lot during puberty. This growth is due to androgens, like testosterone. By adulthood, the prostate usually reaches its normal size.
Natural Growth Patterns with Aging
As men get older, the prostate gland changes. It often gets bigger due to benign growth. This natural growth can sometimes cause urinary problems.
We have a table to show how prostate size changes with age:
| Age Group | Typical Prostate Size | Common Changes |
| 20-30 years | Average size, around 20-25 grams | Minimal changes |
| 40-50 years | Gradual increase in size | Possible onset of BPH symptoms |
| 60+ years | Often enlarged, potentially over 40 grams | Higher likelihood of BPH and other prostate issues |
Hormonal Influences on Prostate Size
Hormones, like androgens like testosterone, are very important for the prostate. The conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is key. DHT makes prostate cells grow a lot. Knowing about these hormones helps with prostate health.
Hormonal changes can really affect prostate health. It’s important to manage these changes for overall health.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): The Most Common Prostate Condition
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is a common issue for men as they get older. It’s when the prostate gland grows too big, causing urinary problems.
Typical Age of Onset
The usual time BPH starts is around 40 years old. But, symptoms might show up much later.
Prevalence Rates
BPH gets more common with age. Here’s what studies found:
- By 60, about 50% of men have BPH.
- By 80, this number jumps to 80%.
- Men under 40 rarely have it.
Impact on Quality of Life
BPH can really affect a man’s life, making it hard to use the bathroom. Its impact changes with age:
- Men in their 50s and 60s might have annoying bathroom issues.
- Older men might have worse symptoms, making other health problems harder.
- Managing BPH well can improve life quality at any age.
Prostatitis: Age Distribution and Risk Factors
Prostatitis is when the prostate gland gets inflamed. It can cause pain, trouble urinating, and sex problems. Knowing who gets it and why is key.
Acute Bacterial Prostatitis: Age Patterns
Acute bacterial prostatitis is caused by bacteria. It can hit anyone but is more common in young men. It often comes from UTIs or STIs. Seeing a doctor fast is important to avoid serious issues.
Chronic Prostatitis: Who’s Most Vulnerable?
Chronic prostatitis means symptoms keep coming back. It can happen to men of any age but hits middle-aged men more. Things like UTIs, STIs, and lifestyle choices can make you more likely to get it.
Age-Related Differences in Symptoms and Treatment
Prostatitis symptoms and treatments change with age. Younger men might have sudden symptoms from bacteria. Older men might have long-term symptoms from other health problems. Treatments range from antibiotics to therapies to help with symptoms.
Several things can make you more likely to get prostatitis, including:
- Bacterial infections: More common in younger men.
- Urinary tract issues: Can affect men of any age.
- Lifestyle factors: Such as diet, physical activity level, and stress.
Symptoms can be pain in the groin, trouble urinating, and sex problems. How bad these symptoms are can change with age and health.
Treatment for prostatitis depends on the cause and the patient’s age and health. For bacterial prostatitis, antibiotics are the main treatment. For chronic prostatitis, treatment might include medicines, lifestyle changes, and alternative therapies to manage symptoms.
Prostatitis is a complex issue that affects men of all ages. Knowing about its age distribution, risk factors, and how symptoms and treatment vary with age is vital for managing it well.
Prostate Cancer: Understanding Age-Related Risk
Age and prostate cancer risk are closely linked. As we get older, the chance of genetic changes and environmental factors leading to cancer grows. Knowing this risk is key to catching prostate cancer early and managing it well.
Incidence Rates from Age 40 to 80+
Prostate cancer is rare in men under 40. But, it becomes more common after 50. The American Cancer Society says about 1 in 9 men will get prostate cancer in their lifetime. The risk goes up with age:
| Age Group | Incidence Rate per 100,000 |
| 40-49 | 14.2 |
| 50-59 | 134.4 |
| 60-69 | 439.8 |
| 70-79 | 634.9 |
| 80+ | 764.1 |
This shows how much prostate cancer risk increases with age. It’s why we need age-based screening and prevention plans.
Why Cancer Risk Increases with Age
Several things make prostate cancer risk higher with age. Genetic mutations that happen over time can cause cancer in prostate cells. Also, hormonal influences, like testosterone, play a role in prostate cancer growth. Environmental and lifestyle factors also add up with age, raising the risk.
Survival Rates Based on Age at Diagnosis
The age when prostate cancer is diagnosed affects survival rates. Older men often have lower survival rates because of other health issues and more aggressive cancer. The 5-year survival rate for prostate cancer is nearly 100% for early-stage diagnosis. But, this rate changes with age:
- Men diagnosed under 65: 5-year survival rate is about 98%
- Men diagnosed between 65-74: 5-year survival rate is about 95%
- Men diagnosed at 75 or older: 5-year survival rate is about 90%
Knowing these survival rates helps in making better choices about screening and treatment.
Early-Onset Prostate Problems: Under Age 40
Prostate problems in men under 40 are rare but serious. While prostate issues are common in older men, they can also affect younger men. This is often due to genetics or other factors.
Rare but Serious Concerns
Young men can face prostate issues like prostatitis or prostate cancer. These conditions are rare in men under 40 but can have big health effects.
Some important stats show why we need to be aware:
- Prostate cancer in men under 40 is rare, making up less than 1% of all cases.
- Prostatitis, or inflammation of the prostate, can affect men of any age, including those under 40.
Genetic Predisposition Factors
Genetics are key in early-onset prostate problems. Men with a family history of prostate cancer or issues are at higher risk. This is true even if they’re younger.
Important genetic factors include:
- Having a father or brother with prostate cancer, even if they were young when diagnosed.
- Genetic mutations, like those in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, which are linked to breast and ovarian cancer but also prostate cancer risk.
Warning Signs Young Men Shouldn’t Ignore
While prostate problems are rare in young men, knowing the signs is important. Symptoms that need medical attention include:
- Painful urination or trouble urinating.
- Pain in the groin, abdomen, or lower back.
- Frequent urination, often at night.
- Blood in the urine or semen.
Early detection is key to managing prostate problems, no matter your age. Young men, and those with a family history of prostate issues, should watch their prostate health closely. If they notice any concerning symptoms, they should see a doctor.
Prostate Health in Middle Age: 40-59 Years
Middle age, from 40 to 59, is key for keeping the prostate healthy. Men may see changes in their prostate that affect their life quality during this time.
Common Issues During This Critical Period
In their 40s and 50s, men face prostate issues like Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), prostatitis, and a higher risk of prostate cancer. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia is when the prostate gets bigger, leading to trouble with urination.
Prostatitis, or inflammation of the prostate, can also happen. It’s important for men to know the signs of these problems to get help if needed.
The Importance of Baseline Testing
Getting baseline tests is vital for men in their 40s and 50s. A Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) test sets a starting point for PSA levels. This, along with a digital rectal exam, helps find prostate issues early.
Talking to a doctor about PSA tests is a good idea. They can help decide what’s best for you.
Lifestyle Factors That Affect Risk
What you do every day affects your prostate health in middle age. Eating right, staying active, and not smoking are important.
- Eating lots of fruits, veggies, and whole grains is good for your prostate.
- Being active helps lower the risk of prostate problems.
- Not smoking is key, as smoking increases prostate cancer risk.
Choosing healthy habits can help keep your prostate healthy during this important time.
| Lifestyle Factor | Impact on Prostate Health |
| Diet rich in fruits and vegetables | Supports prostate health |
| Regular physical activity | Reduces risk of prostate problems |
| Not smoking | Reduces risk of prostate cancer |
Prostate Concerns for Men 60-75 Years Old
Men aged 60 to 75 often deal with prostate issues. These problems need careful handling. As we get older, our prostate gland changes, leading to both minor and serious conditions.
Expected Changes vs. Warning Signs
Men in this age group may notice various prostate symptoms. It’s important to know the difference between normal aging changes and signs of serious problems. For example, an enlarged prostate is common, but severe urinary issues or pain could mean something serious.
Common symptoms to watch for include:
- Frequent urination
- Weak urine flow
- Difficulty starting urination
- Painful urination
Managing Multiple Prostate Conditions
Men in this age group often face multiple prostate issues at once. These can include BPH, prostatitis, and prostate cancer. A detailed treatment plan is key to handling these conditions well.
| Condition | Common Symptoms | Management Strategies |
| BPH | Urinary frequency, weak flow | Medications, lifestyle changes |
| Prostatitis | Pain, urinary issues | Antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs |
| Prostate Cancer | Often asymptomatic in early stages | Surgery, radiation, active surveillance |
Quality of Life Considerations
Keeping a good quality of life is vital for men dealing with prostate issues. Treatment choices should aim to improve prostate health without harming daily life.
Key considerations include:
- Minimizing urinary symptoms
- Preserving sexual function
- Maintaining overall physical and mental health
Understanding prostate changes and warning signs, managing multiple conditions, and focusing on quality of life helps men aged 60 to 75 manage prostate concerns confidently.
Prostate Health Beyond Age 75
Managing prostate health after 75 is complex. It involves looking at the risks and benefits of treatments and other health issues that come with age.
Risk-Benefit Analysis of Treatment
For men over 75, it’s key to carefully weigh treatment options. We look at the good and bad sides of each treatment. This helps us decide what’s best for the patient’s health and life expectancy.
Younger men might get treatments that aren’t right for older men. This is because older men might face more side effects or drug interactions. We aim to choose treatments that keep the patient comfortable and functional.
Key Considerations for Risk-Benefit Analysis:
- Life expectancy and overall health status
- Potential side effects of treatments
- Impact on quality of life
- Patient preferences and values
Managing Prostate Health with Other Age-Related Conditions
Men over 75 often face many health issues at once. This means we need a team effort to care for them. Healthcare professionals work together to avoid problems with treatments.
For example, a man with prostate and heart disease needs a special care plan. We adjust medications and watch health closely. We also make lifestyle changes to help manage both conditions.
| Condition | Considerations for Prostate Health Management |
| Heart Disease | Monitor interactions between prostate medications and heart medications. |
| Diabetes | Manage blood sugar levels to minimize complications. |
| Chronic Kidney Disease | Adjust medication dosages according to kidney function. |
When caring for prostate health in the elderly, we must think about more than just the physical. Family, caregivers, and healthcare support are vital. They help patients stick to treatment plans and live well.
“The goal of managing prostate health in older men is not just to extend life, but to ensure that the years they have left are lived with dignity and minimal discomfort.”
Racial and Ethnic Variations in Age of Onset
It’s important to know how race and ethnicity affect when prostate problems start. Prostate health varies a lot between different groups. This means some groups face prostate issues earlier or more severely.
African American Men: Earlier Onset and Greater Severity
African American men face a big challenge with prostate cancer. They often get it younger and it’s more aggressive. This is different from other groups.
Genetics, lifestyle, and healthcare access all play a part in this issue. These factors help explain why African American men are hit harder by prostate cancer.
Asian and Hispanic Populations: Different Risk Patterns
Men from Asian and Hispanic backgrounds have lower prostate cancer rates than African American men. But, they have higher rates than some other groups. The age when they get prostate cancer can also vary.
It’s key to understand these patterns. This helps us create better screening and prevention plans for different groups.
Genetic vs. Environmental Factors
Genetics and environment both affect when and how prostate cancer starts. While genetics are important, lifestyle and environment also matter. Things like diet, exercise, and chemical exposure can impact prostate health.
| Ethnic Group | Average Age of Onset | Incidence Rate |
| African American | Earlier than 65 | Higher |
| Asian | 65 and above | Lower |
| Hispanic | 65 | Moderate |
By looking into these factors, we can make prostate health better for everyone. This means improving outcomes for men from all backgrounds.
Age-Specific Prostate Screening Guidelines
Knowing when to get a prostate screening is key for men’s health. These tests help find prostate problems early, like cancer. As men get older, the chance of prostate issues grows, so it’s important to follow the right screening age.
Recommendations for Men Under 50
Men under 50 usually don’t need routine prostate tests unless they’re at high risk. High-risk factors include a family history of prostate cancer or being African American. It’s best for these men to talk to their doctor about their risk to decide on early screening.
Screening Protocols for Ages 50-70
Men aged 50 to 70 should get regular prostate tests. How often depends on their PSA levels and other risks. If the PSA is low, tests every two years might be okay. But if it’s higher, annual tests might be needed. It’s important for these men to talk to their doctor about the pros and cons of screening.
Approaches for Men Over 70
For men over 70, screening decisions get more complex. Those with a short life expectancy might not need tests. But if they’re healthy and expect to live longer, screening could be beneficial. Men in this age group should discuss their health, life expectancy, and screening wishes with their doctor.
| Age Group | Screening Recommendation | Considerations |
| Under 50 | Not recommended unless high risk | Family history, African American descent |
| 50-70 | Regular screening | PSA level, risk factors, health status |
| Over 70 | Individualized based on health and life expectancy | Life expectancy, overall health, personal preference |
By following these guidelines, men can make smart health choices with their doctors. It’s important to think about the benefits of early detection and the risks of screening and tests.
Recognizing Symptoms at Different Life Stages
It’s important to know the signs of prostate problems early. As men get older, their prostate gland changes. These changes can cause different health issues.
Age-Specific Warning Signs
Symptoms of prostate problems vary with age. Younger men might feel pain or discomfort when they pee or ejaculate. Older men often have to pee a lot, have a weak flow, or pee at night.
Men under 40 rarely face prostate issues. But, when they do, it’s often due to prostatitis or other infections. Men between 40 and 59 often deal with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). This can make peeing hard and affect their daily life.
How Symptoms Progress Over Time
Prostate symptoms can get worse over time. They might start with mild pee problems. For example, a man with BPH might first notice his pee flow is weaker. This can get worse if not treated.
It’s key to watch for these changes and talk to a doctor. Early treatment can greatly improve health and prevent serious problems.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Some symptoms need quick medical help. Look out for severe pain, trouble peeing, or blood in pee or semen. If you see these signs, get help right away. They can mean serious health issues.
It’s smart to be proactive about prostate health. Knowing when to see a doctor can help prevent big problems. This way, men can stay healthy and catch issues early.
Diagnostic Approaches Based on Patient Age
Age is key in finding the best ways to check prostate health. As men age, they face more prostate problems. So, doctors use different methods to diagnose them.
PSA Interpretation Across Age Groups
PSA testing is vital for prostate health checks. But, what’s considered normal changes with age. Younger men have a lower PSA threshold, while older men’s thresholds are higher.
A PSA level that’s okay for a 70-year-old might be high for a 40-year-old. This helps spot who’s at risk and avoid too many biopsies in older men with BPH.
Imaging and Biopsy Considerations
Imaging and biopsies also depend on age. Younger men might get more detailed tests, like MRI-guided biopsies, for a precise diagnosis.
Older men might start with simpler tests. They’ll only get biopsies if their PSA levels or other signs suggest cancer. The choice to use imaging or biopsy depends on the patient’s health and life expectancy.
Risk Calculators and Age Factors
Risk calculators use age, PSA levels, family history, and ethnicity to predict prostate cancer. They help decide if more tests are needed.
These calculators help doctors sort men by risk. This way, they can focus on the most at-risk for early checks. It means less testing for those at lower risk.
We make sure each patient gets a unique approach. By considering age and other factors, we aim for accurate diagnoses and effective treatments.
Treatment Options Across the Age Spectrum
Prostate treatment options change with age. A personalized approach is needed. Health, prostate condition, and personal preferences are key in choosing the right treatment.
Conservative Management in Younger Patients
Younger men, usually under 50, often start with conservative management. This includes active surveillance. It means watching the condition closely with tests and exams.
Lifestyle changes are also suggested. These can be diet or exercise. The aim is to avoid harsh treatments that might harm quality of life.
“Active surveillance is a good choice for many young men with low-risk prostate cancer,” a study says. “It helps them keep their quality of life without the side effects of aggressive treatments.”
Balancing Aggression and Quality of Life in Middle Age
Men in their 50s and 60s have a harder decision to make. It’s important to find the right balance between treatment and quality of life. Options include surgery, radiation, or both.
The choice depends on the prostate condition, health, and personal wishes.
- Surgery: Removing the prostate gland (prostatectomy)
- Radiation Therapy: Targeted radiation to kill cancer cells
- Hormone Therapy: Reducing testosterone levels to slow cancer growth
Treatment Considerations for Elderly Men
Elderly men, over 75, focus on symptom management and quality of life. Treatment choices are made with their health and life expectancy in mind. Sometimes, palliative care is best. It aims to improve life quality without aggressive cancer treatment.
Age-Specific Prevention Strategies
We suggest specific ways to keep the prostate healthy at different ages. Knowing what each age needs helps men stay proactive about their prostate health.
Proactive Measures for Men Under 40
Men under 40 should focus on a healthy lifestyle. Eating well and staying active are key. Avoiding too much alcohol and not smoking is also important. Starting healthy habits early can greatly benefit prostate health later on.
Risk Reduction for Men 40-60
Men aged 40 to 60 should aim to reduce their risk. Regular health check-ups and talking to a doctor about prostate health are vital. Eating foods good for the prostate, like those with omega-3s and antioxidants, is also beneficial. Staying fit and at a healthy weight can lower the risk of prostate problems.
| Age Group | Prevention Strategies | Key Actions |
| Under 40 | Healthy Lifestyle | Balanced diet, regular exercise, avoid smoking and excessive alcohol |
| 40-60 | Risk Reduction | Regular check-ups, prostate-friendly diet, maintain healthy weight |
| Over 60 | Maintenance Approaches | Regular PSA testing, manage chronic conditions, stay informed about treatment options |
Maintenance Approaches for Men Over 60
For men over 60, the goal is to maintain and catch problems early. PSA testing and DREs are key for early detection. Managing health conditions and knowing about new treatments are also important. Men in this age group should work with their doctors to create a care plan.
Conclusion
Managing prostate health well means understanding how age affects it. The prostate gland changes a lot as men get older. These changes can raise the risk of different prostate problems.
We’ve looked at how age impacts BPH, prostatitis, and prostate cancer. It’s clear that age-specific prevention and treatment are key. Knowing about these changes helps men stay healthy.
Prevention and catching problems early are key to prostate health. Men should talk to their doctors about their risk and screening options. This includes their age, family history, and health.
By being proactive about prostate health, men can lower their risk of prostate issues. This improves their life quality as they get older. We urge men to focus on their prostate health and seek medical help if they have symptoms or worries.
FAQ
What is the typical age range for developing prostate problems?
Prostate problems can happen at any age. But, they are more common in men over 50. The risk of issues like BPH and prostate cancer goes up with age.
What are the common prostate issues that men face as they age?
Men often face BPH, prostatitis, and prostate cancer as they age. BPH is a non-cancerous enlargement. Prostatitis is inflammation, and prostate cancer is a tumor.
How does the prostate gland change throughout a man’s life?
The prostate gland grows and changes with age. Hormonal changes influence it. It starts growing from birth, grows more during puberty, and can change more with age.
What are the symptoms of BPH, and how do they impact quality of life?
Symptoms of BPH include frequent urination, urgency, weak flow, and waking up to urinate. These symptoms can really affect a man’s life, impacting sleep and daily activities.
Can young men develop prostate problems, and what are the warning signs?
Yes, young men can get prostate problems, though it’s rare. Look out for urinary issues, pain, or unusual symptoms. If you have a family history, be extra careful.
How does age affect the risk of prostate cancer?
Age is a big risk factor for prostate cancer, with most cases found in men over 65. The risk goes up after 50.
What are the age-specific guidelines for prostate screening?
Screening guidelines change with age. Men under 50 should talk to their doctor if they have risk factors. Men 50-70 should consider regular screening. For men over 70, it depends on their health.
How do diagnostic approaches differ based on patient age?
Diagnosing prostate issues depends on age, health, and other factors. Younger men might need different tests than older men.
What are the treatment options for prostate problems across different age groups?
Treatment options vary by age and health. Younger patients might get conservative treatments. Older men might need more aggressive treatments, balancing treatment with quality of life.
How can men prevent or reduce the risk of prostate problems?
Preventing prostate problems includes a healthy lifestyle, avoiding smoking, and managing stress. Regular check-ups and screenings can also help.
Are there racial or ethnic differences in the age of onset for prostate problems?
Yes, there are racial and ethnic differences. For example, African American men get prostate cancer younger and more severely.
What are the key considerations for managing prostate health beyond age 75?
Managing prostate health over 75 involves weighing treatment risks and benefits. Consider overall health, life expectancy, and quality of life. Coordinating care with other health issues is also key.
References
Gupta, S., et al. (2016). Prostate cancer: How young is too young? Journal of Urology, 195(6), 1231-1237.