Last Updated on October 31, 2025 by
As men get older, they might notice changes in their urine health. This could be because of an enlarged prostate gland. It’s important to know the signs of this condition, called Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), to get help quickly.
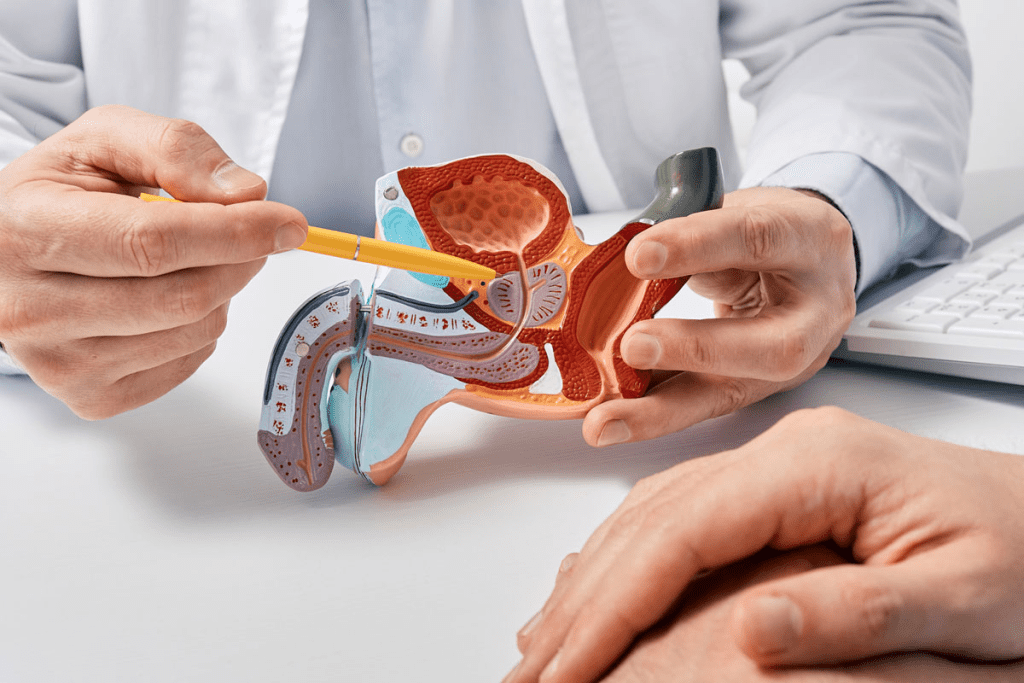
The prostate gland is a small but vital part of the male body. BPH is a common problem that many men face as they age. Knowing the benign prostatic hyperplasia symptoms helps men get the right care.
Understanding what is BPH and how it affects urine health is key. It lets men take steps to stay healthy. Spotting symptoms early is the first step to managing BPH well.
The prostate gland is key to a man’s health, affecting both urine and sex. Knowing how it works and changes is important. This knowledge helps spot problems early.
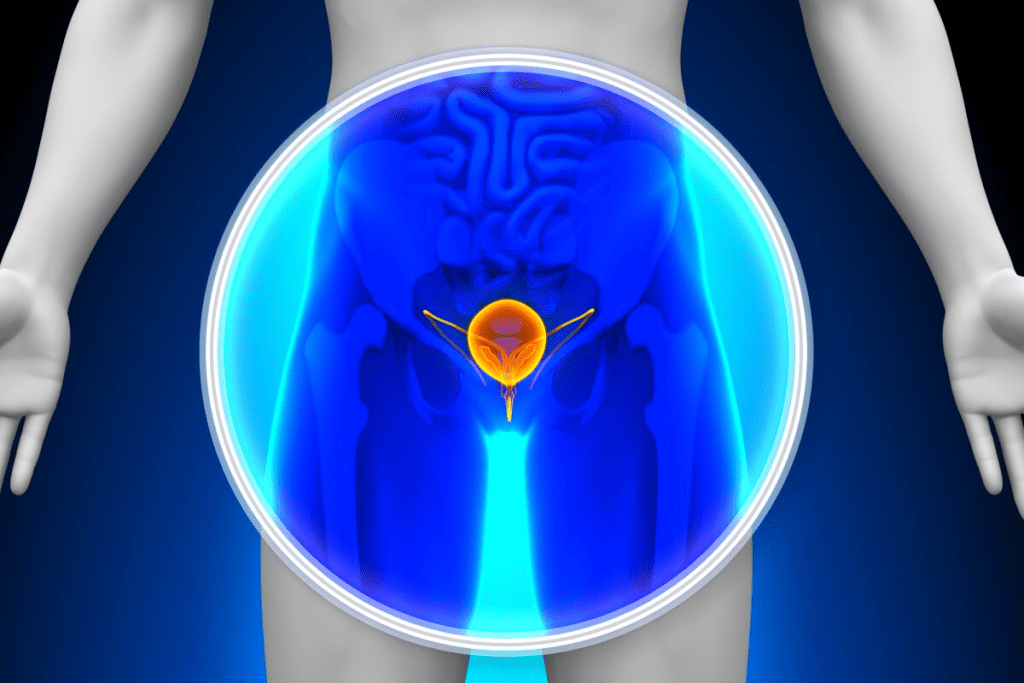
The prostate is a small, walnut-sized organ below the bladder in men. It wraps around the urethra, the tube that carries urine. This location is why prostate issues can affect urination.
The American Urological Association says the prostate makes fluids for semen. Knowing its role in health is vital for men’s well-being.
In healthy men, the prostate is about the size of a walnut. It makes seminal fluid to nourish sperm. A normal prostate doesn’t usually block the urethra, so it doesn’t cause urinary problems.
“A healthy prostate is essential for normal urinary and sexual function,” highlights its importance. A healthy prostate is linked to good reproductive health.
As men get older, their prostate often gets bigger. This can start in the late 40s. The bigger prostate can press on the urethra, causing urine issues.
According to
“The aging male’s prostate health is a critical aspect of his overall quality of life.”
It’s important to watch for these changes and understand their impact. This helps keep men healthy.
Knowing how the prostate works and changes helps men spot problems. It encourages them to get medical help when needed.
BPH, or Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia, is a non-cancerous growth of the prostate gland. It can cause urinary symptoms. As men get older, the prostate gland may grow, pressing on the urethra and affecting urine flow.
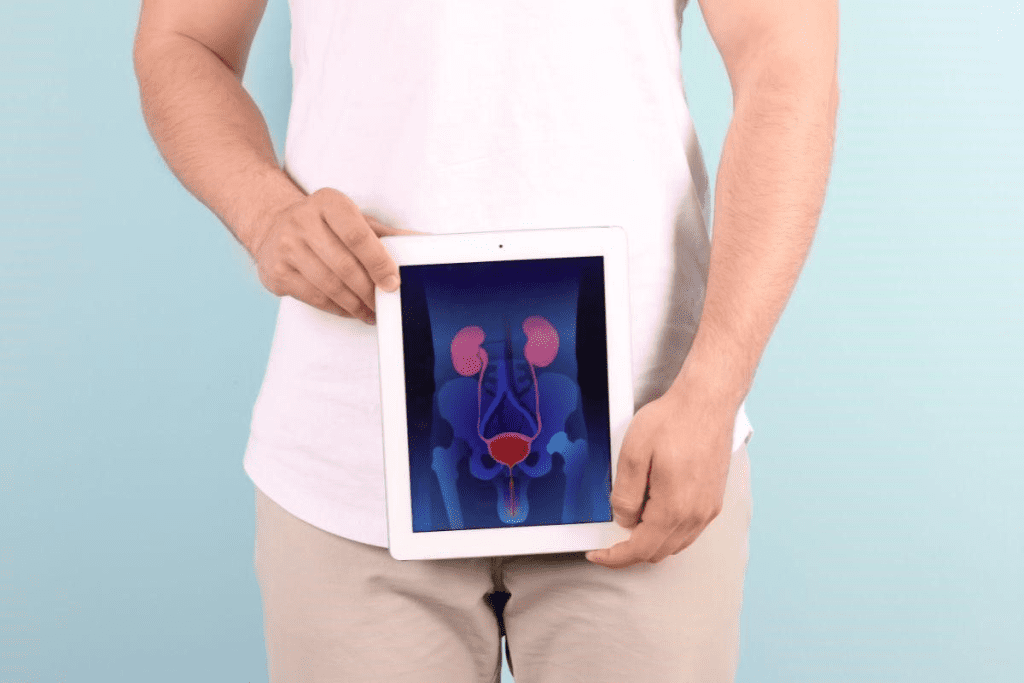

BPH is common in older men. It makes the prostate gland bigger, leading to urinary symptoms. More men over 50 are affected by BPH.
Research shows that over half of men in their 60s have BPH. Up to 90% of men in their 70s and 80s also have it. It’s not cancer, but it can really affect a man’s life because of the urinary symptoms.
It’s important to know the difference between BPH and prostate cancer. BPH is not cancerous, but prostate cancer is. Both affect the prostate gland, but in different ways.
Even though BPH and prostate cancer share some symptoms, they need different treatments. If you’re experiencing symptoms, see a doctor for the right diagnosis and treatment.
Many men don’t know about prostate issues like BPH until symptoms appear. This lack of awareness comes from symptoms that start slowly and the idea that urinary problems are just part of aging.
Talking about prostate health and BPH symptoms can help men get checked when needed. Regular visits to the doctor can lead to early detection and better management of prostate problems.
An enlarged prostate can cause many urinary symptoms that affect daily life. As men age, their prostate gland grows. This growth often leads to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), where the prostate gets bigger. Knowing the symptoms of BPH is important.
One key symptom of BPH is needing to urinate often and urgently. Men might go to the bathroom more, even at night. This can mess up sleep and daily activities.
It’s hard to start or stop urinating with BPH. Men might struggle to start or empty their bladder fully. This leads to intermittent urination.
Men with BPH often have a weak or slow urine stream. The stream might start and stop, and some might dribble at the end. This shows the bladder isn’t fully empty.
Many men feel like they haven’t fully emptied their bladder after urinating. This feeling can cause them to urinate again soon. It’s a cycle of frequent urination.
It’s important to recognize these symptoms early. If you’re experiencing them, see a healthcare provider. They can help find the cause and suggest treatments.
Understanding these symptoms helps men manage their prostate health. It improves their quality of life.
Many men know about the common signs of an enlarged prostate. But there are also less common signs that are important to notice. These signs can show problems like urinary tract infections or kidney issues. We’ll look at these signs to help you understand the risks of an enlarged prostate.
Hematuria, or blood in the urine, is a less common but serious sign. It happens when the prostate blocks urine flow, causing bleeding. This is not just a BPH issue but needs a doctor’s check to rule out other serious problems.
An enlarged prostate can raise the risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs). When urine flow is blocked, bacteria can grow. UTIs can cause pain and discomfort, and can get worse if not treated.
Bladder stones are another issue with an enlarged prostate. They form when urine is too concentrated. These stones can cause pain and make it hard to urinate, leading to more UTIs.
In severe cases, an untreated enlarged prostate can harm kidney function. Urine backup can damage kidneys over time. This is why managing BPH symptoms is so important.
It’s key for men to notice these signs and get medical help. If you’re experiencing any symptoms, see a doctor for the right care.
Knowing all symptoms of an enlarged prostate helps men take better care of their health. This way, they can make informed choices about their health.
Several factors can increase the risk of an enlarged prostate. These include age, genetics, hormonal changes, and lifestyle choices. Knowing these risk factors helps men prevent and treat the condition early.
Age is a big risk factor for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH). As men age, the chance of prostate enlargement grows. By 60, over half of men have BPH. It’s rare in men under 40 but becomes more common with age.
Family history is also important. Men with a first-degree relative (father or brother) with BPH are more likely to get it. Genetics can affect prostate size, making some men more at risk.
Hormonal changes, like the balance between testosterone and estrogen, can affect prostate size. As men age, hormone levels change, which can lead to enlargement. Understanding these hormonal changes can help prevent prostate issues.
Lifestyle choices also play a role in BPH risk. These include:
By understanding these risk factors, men can make better lifestyle choices. This may help lower their risk of an enlarged prostate.
Knowing when to see a doctor for prostate symptoms is key to avoiding problems and improving your life. Prostate issues can show up in many ways. It’s important to know when to get medical help.
Some symptoms need quick medical attention. If you notice any of these, get help fast:
Getting ready for your doctor’s visit helps a lot. Here’s what you can do:
Your doctor might suggest several tests to find out what’s wrong with your prostate. These include:
By knowing when to get medical help and being ready for your doctor’s visit, you can get the right care for your prostate symptoms.
Men with an enlarged prostate have many treatment options. Each has its own benefits and drawbacks. The right choice depends on symptoms, health, and personal preferences.
Making lifestyle changes can help with BPH symptoms. Lifestyle modifications are often the first treatment. These include:
These changes can help reduce symptoms and improve life quality.
When lifestyle changes aren’t enough, medication options are considered. There are several types of medications for BPH, including:
These medications can greatly improve BPH symptoms, helping with urination and reducing discomfort.
For those not helped by medication or preferring not to take it long-term, minimally invasive procedures are an option. Some procedures include:
These procedures are less invasive than traditional surgery, with quicker recovery times.
In severe cases or when other treatments fail, surgical interventions may be needed. Surgical options include:
Each surgical intervention has its own benefits and risks. The choice depends on individual circumstances.
Keeping prostate health in check is key to a good quality of life, as men get older. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is a common issue that needs ongoing care and sometimes changes in treatment. We’ve talked about the signs, risks, and ways to treat BPH, stressing the need for medical help when needed.
Long-term care for prostate health includes lifestyle changes, medicines, and sometimes surgery. It’s vital to work with doctors to find the right treatment. Studies show some medicines, like 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, can lead to dementia and depression. This is based on a study on the National Center for Biotechnology Information website.
Men can make smart choices about their prostate health by knowing the pros and cons of treatments. We urge men to focus on their prostate health by staying updated and getting regular check-ups. This ensures the best long-term care.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is a non-cancerous growth of the prostate gland. It can cause urinary symptoms in men. It’s a common issue that many men face as they get older.
Symptoms include needing to urinate often, feeling urgent, and trouble starting or stopping. You might also have a weak stream, dribble, or feel like you didn’t empty your bladder fully.
Factors include age, family history, hormonal changes, and lifestyle. Knowing these risks can help men prevent BPH.
BPH is not cancerous, but prostate cancer is. Both affect the prostate gland but have different causes and treatments.
Options include lifestyle changes, medications, minimally invasive procedures, and surgery. The right treatment depends on symptoms and individual needs.
Changes include dietary adjustments, managing fluids, and bladder training. These can ease symptoms and improve life quality.
Seek help for severe symptoms like urinary retention, blood in urine, or infections. Early treatment can prevent complications.
Tests include digital rectal exam, PSA test, urinalysis, and imaging like ultrasound or MRI. These help diagnose prostate issues.
Yes, BPH can be managed with ongoing care and adjusting treatments as needed. Regular check-ups help maintain quality of life.
The prostate gland is below the bladder and surrounds the urethra. It’s key to the male reproductive system.
The best treatment varies based on symptoms, patient preferences, and health. A healthcare provider can guide the best approach.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!