Rheumatology treats musculoskeletal and autoimmune diseases, including arthritis, lupus, gout, and vasculitis.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Overview and definition
Rheumatology is a branch of internal medicine focused on diagnosing and treating rheumatic diseases. These illnesses often cause inflammation, swelling, and pain in the joints or muscles. Today, rheumatology covers much more than just common aches. It mainly addresses autoimmune diseases, where the immune system attacks healthy tissues. This can affect not only bones, joints, and muscles, but also organs like the kidneys, lungs, heart, and skin. There are over 200 different diseases in this field, such as Rheumatoid Arthritis, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), Ankylosing Spondylitis, Gout, and Sjogren’s Syndrome. Since these conditions are usually long-term and affect the whole body, rheumatologists use advanced treatments to slow disease progress and help prevent lasting damage.
Rheumatic diseases are autoimmune and inflammatory conditions where the immune system attacks the lining of joints and other tissues. They usually cause pain, swelling, and stiffness. Without treatment, these diseases can lead to serious joint damage and loss of movement.
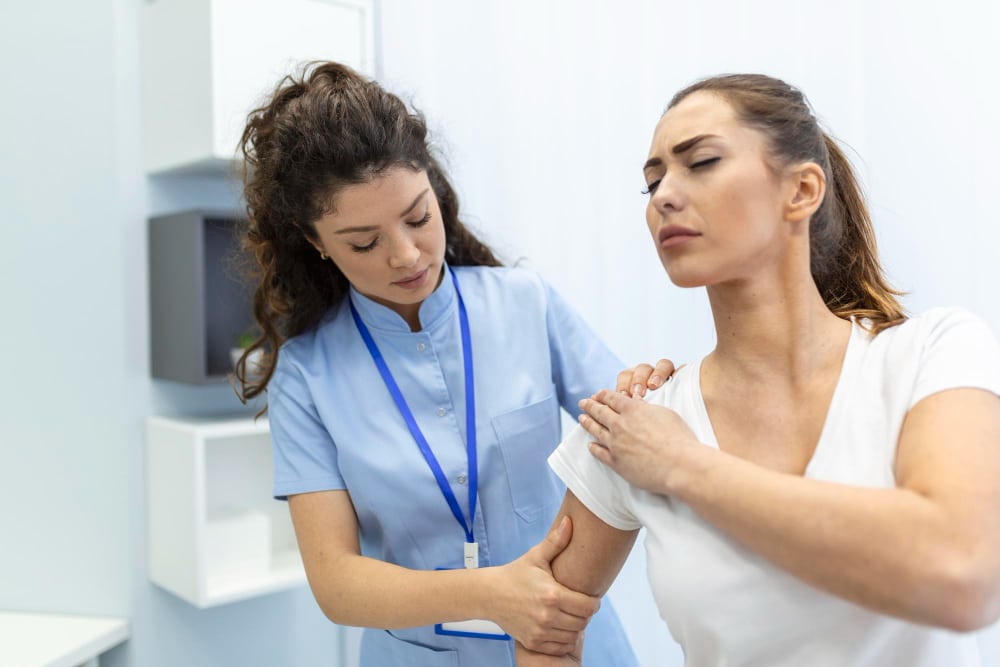

Our specialized Early Arthritis Clinic is set up to diagnose patients as soon as symptoms begin, which is a crucial time for treatment. We also have an infusion center where patients receive advanced biologic therapies in a comfortable environment. Musculoskeletal Ultrasound (MSUS) is used to see joint inflammation in real time and to guide injections accurately.
An interesting piece of information: Share an interesting fact: A hallmark sign of inflammatory arthritis is “morning stiffness” that lasts longer than 30 minutes. Unlike mechanical back pain, which worsens with activity, inflammatory pain often improves with movement, suggesting a systemic rather than structural issue.
Chronic inflammation from these diseases does more than harm cartilage and bone. It releases chemicals into the blood that can cause deep tiredness, mild fevers, and trouble thinking clearly. It also speeds up hardening of the arteries, raising the risk of heart disease. In illnesses like Lupus or Scleroderma, inflammation can scar the lungs or hurt the kidneys, so regular checks of these organs are very important.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Diagnosing these conditions often feels like detective work. Doctors use blood tests to look for autoantibodies (ANA, Rheumatoid Factor, Anti-CCP) and signs of inflammation (CRP, ESR). They also use advanced imaging, such as MRI, to spot inflammation in the bone before any damage shows up on an X-ray.
Your rheumatologist is your long-term partner in care. Their main goal is to help you reach remission, meaning no symptoms. They keep track of your immune system and adjust your medications to control inflammation, while also watching for side effects. They can tell the difference between active inflammation and lasting damage.
Treating rheumatic diseases has moved beyond just using painkillers. Now, the standard approach is called “Treat to Target,” which uses DMARDs (Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs) and Biologics. These medicines are designed to block specific parts of the immune system and stop the disease at its source.
Outline the patient’s path. It usually starts with a “bridge therapy” (like steroids) to quickly stop pain, followed by the introduction of long-term maintenance medication. The journey involves regular blood monitoring (every 1-3 months) to ensure the liver and kidneys are handling the medication well.
Rheumatologists work closely with other specialists to give patients the best care. They team up with orthopedic surgeons for joint replacements if needed, physical therapists to help keep patients moving, and nephrologists for kidney problems in conditions like Lupus. Ophthalmologists also play an important role in checking for eye inflammation, which is common in these diseases.
Advise patients on preparation. Because treatments suppress the immune system, patients must screen for latent infections (such as tuberculosis) and update vaccinations before starting treatment. They should know that biologic drugs are powerful and require vigilance—any fever or infection must be reported to the doctor immediately.
While both treat joint and muscle problems, their focus differs.
The key difference often lies in morning stiffness and activity:
This refers to the critical early months of the disease. Identifying and treating Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) aggressively during this early phase can prevent permanent joint damage and deformity. Delaying treatment often results in irreversible destruction of the cartilage and bone.
ANA (Antinuclear Antibody) is a screening test. A positive result indicates that your immune system is producing antibodies that target your own cells. While it is the hallmark screening test for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), a positive ANA does not automatically mean you have Lupus; further specific testing is required to confirm a diagnosis.
Raynaud’s is a condition where the blood vessels in the fingers or toes overreact to cold or stress. The digits typically turn white (due to lack of blood flow), then blue (due to lack of oxygen), and finally red (as blood rushes back). It is a common early sign of connective tissue diseases like Scleroderma and Lupus.

Listing natural arthritis in the neck remedies, including heat/cold therapy, massage, and gentle stretching. Neck arthritis, also known as cervical spondylosis, affects millions worldwide, mostly

Describing arthritis in wrist symptoms, including grinding (crepitus), deep aching, and pain when gripping objects. Ever felt a constant, sharp pain in your wrists that
Describing what does arthritis feel like in feet, including common sensations like deep aching, grinding, and morning stiffness. Arthritis in the feet and ankles is
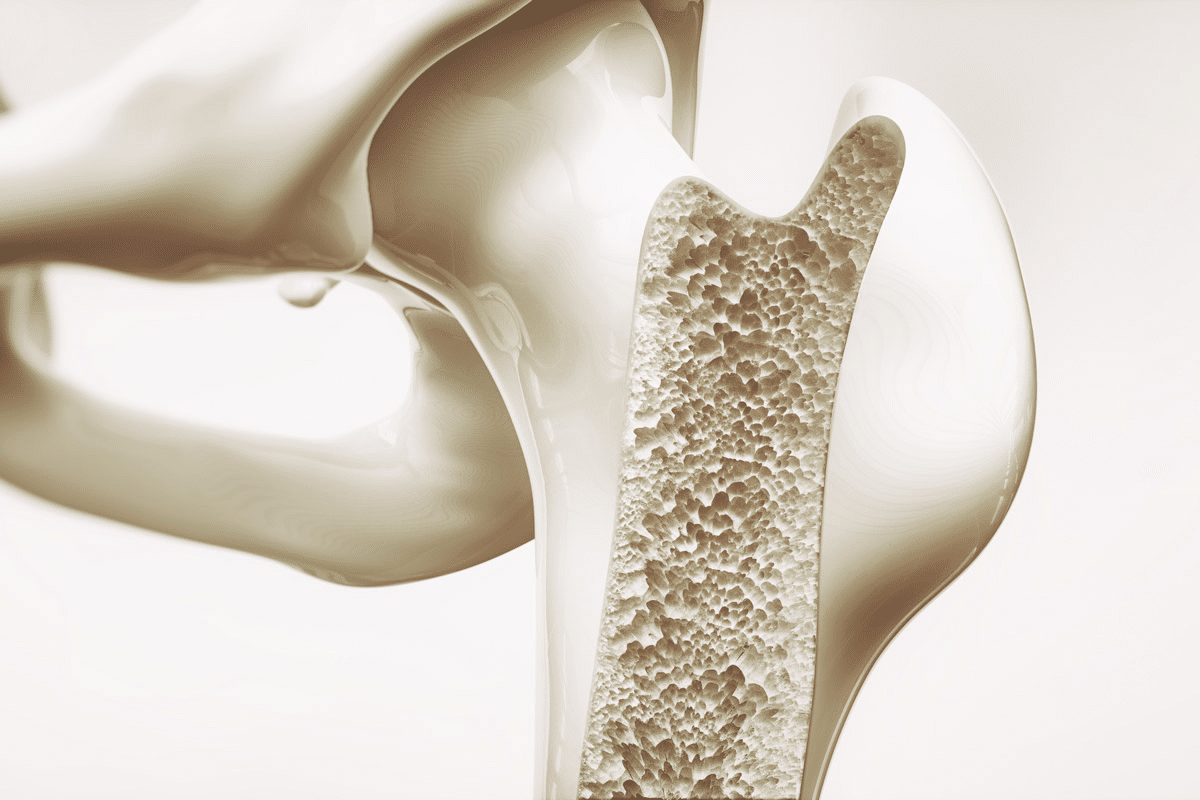
Osteoporosis makes bones thin and fragile, raising the chance of fractures. Bisphosphonates are a key treatment for osteoporosis. They work by stopping bone loss through
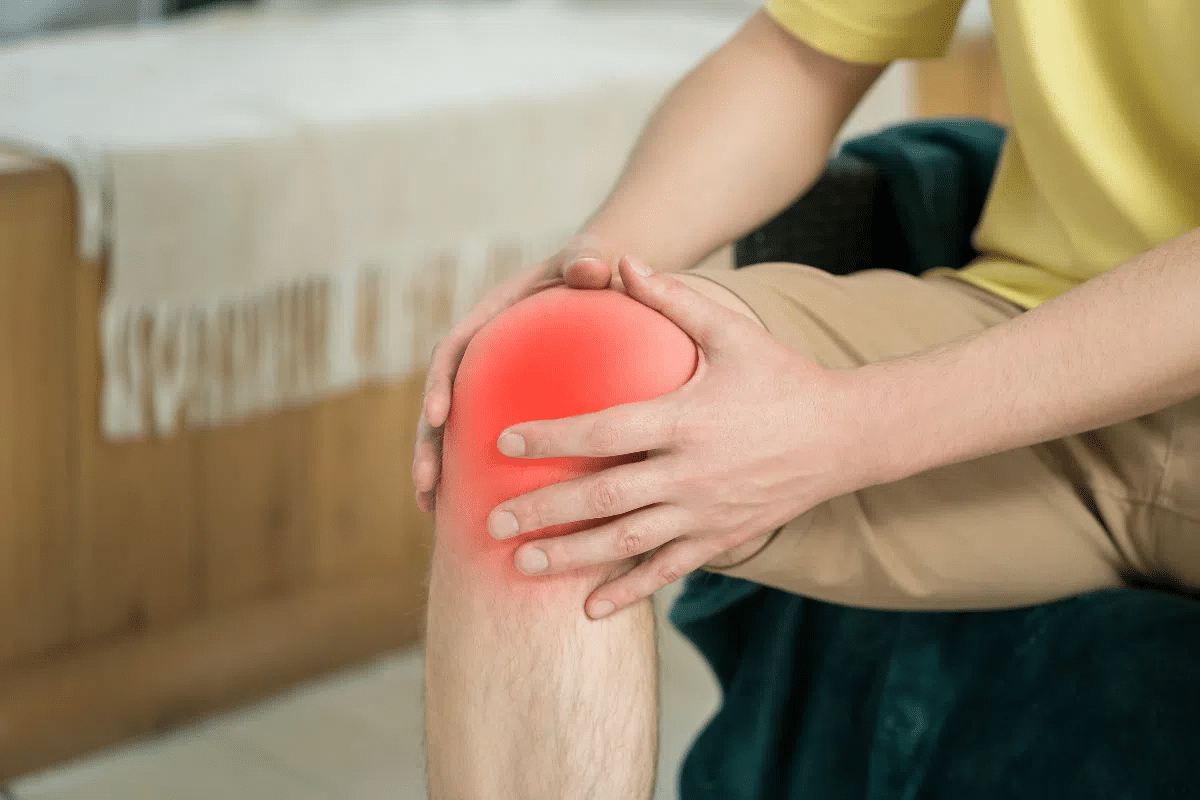
Explaining the aches and pains index and five specific ways local weather conditions affect chronic joint pain levels. Do you wake up with achy joints
Connective tissue is the body’s most common tissue. It has seven main types that help support and protect us. Connective tissue is key to keeping

Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)