Last Updated on November 26, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
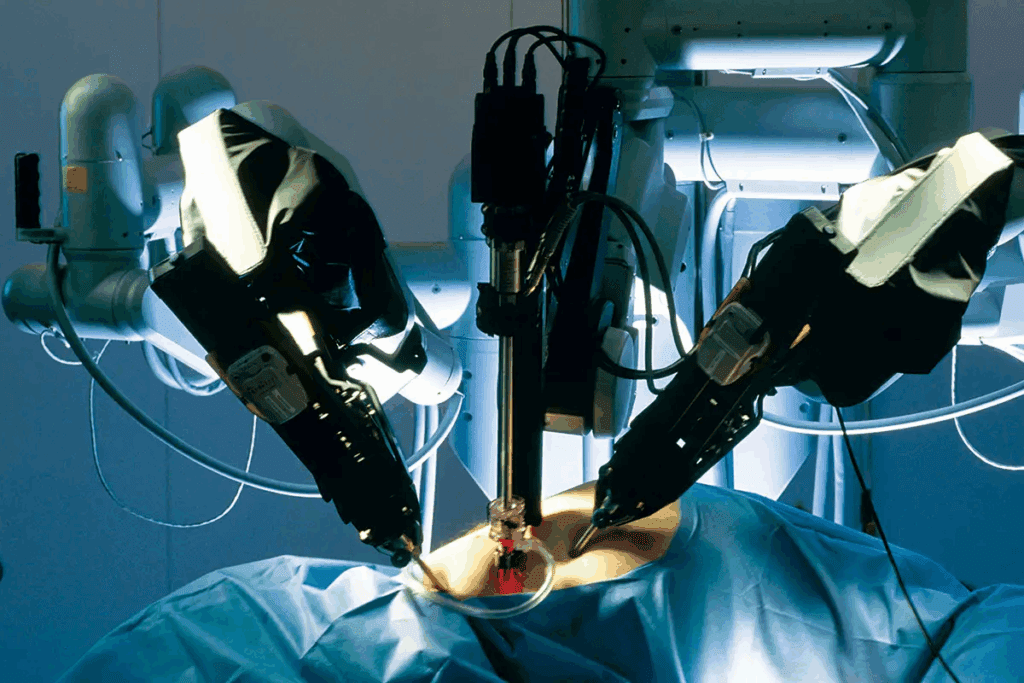
The history of medical innovation is filled with key moments. One of these is the start of robot assisted surgery. This journey began with a major procedure that opened the door to today’s surgical methods.
In 1983, a major event happened in Vancouver, Canada. The Arthrobot, a leading robotic system, was used for the first time. This event started a new chapter in surgery, leading to more advanced systems like the FDA-approved da Vinci surgical system.
The growth of robotic surgery has been amazing. It has changed how we do surgery. Knowing how it started helps us see its current uses and what it might do in the future.
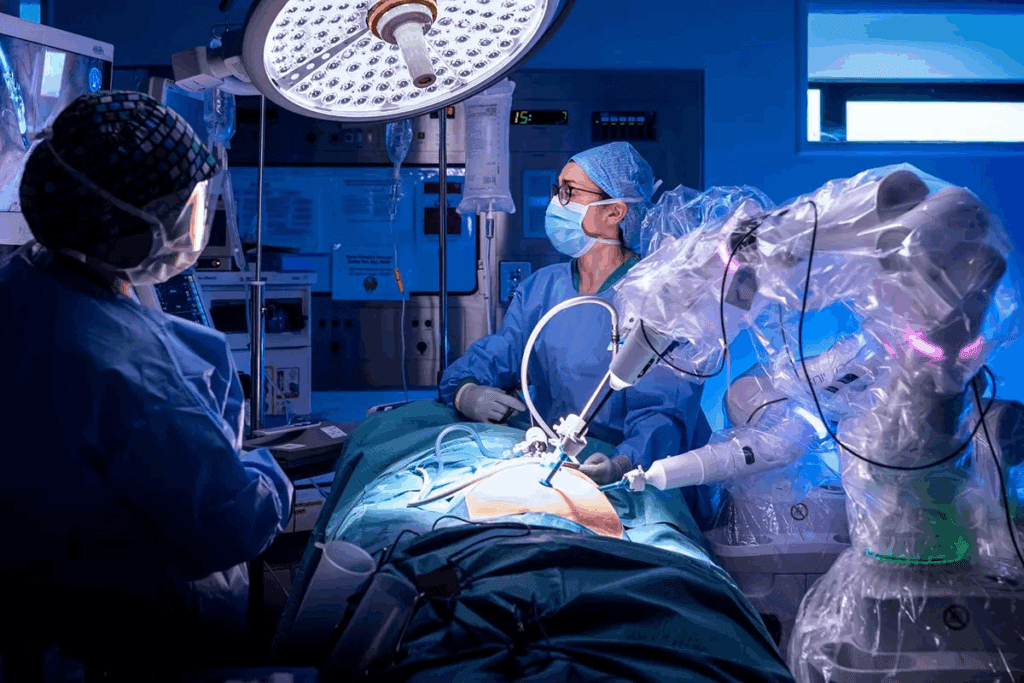
Surgical technology has changed a lot, from simple tools to advanced robots. This change aims for better precision, shorter recovery times, and better patient results.
At first, surgeries were done by hand, depending on the surgeon’s skill. Then, mechanical tools were introduced, like mechanical retractors and stabilizing devices. These tools were the start of more advanced surgical tools.
The idea of automated surgery started in the early 1900s. A 1942 story called ‘Waldo’ by Robert Heinlein showed a character controlling tools with his hands, predicting today’s robotic surgery. This idea helped create more advanced surgical robots.
“The future of surgery will be shaped by the integration of technology and surgical skill, making surgeons better and helping patients more.”
— Dr. [Name], Surgeon
Before today’s robots, many important technologies came up. These included:
These early steps were key to making robotic-assisted surgery possible. They let surgeons do complex tasks with better accuracy and control.
The Arthrobot was the world’s first surgical robot, developed in 1983 for orthopedic surgeries. It was a major step in combining technology and medicine.
Dr. James McEwen and his bioengineering team in Vancouver, Canada, created the Arthrobot. They made a robotic system for orthopedic surgeries with unmatched precision.
Dr. McEwen’s vision was to improve surgeons’ abilities. He wanted to make complex surgeries more accurate. The team overcame many hurdles, from designing the robotic arm to ensuring it was safe in surgery.
The Arthrobot was designed to help surgeons in orthopedic procedures. It had technical capabilities like precise movement and surgeon control during operations.
Its architecture was groundbreaking, featuring a robotic arm for specific tasks. This precision was a big step up from manual methods.
“The introduction of robotic systems like the Arthrobot into surgical practice represented a major leap forward, combining the dexterity of human surgeons with the precision of machines.”
The Arthrobot’s first use was in orthopedic surgery. It showed its ability to improve surgical results. It allowed for more complex surgeries with less risk to patients.
The success of the Arthrobot led to more robotic systems for different surgeries. Its impact is seen in today’s robotic-assisted surgeries, which are now common.
In 1985, a major breakthrough happened in neurosurgery with the PUMA 560 robotic system. It was a big step forward in robotic-assisted surgery.
The PUMA 560 was made for precision and flexibility. It allowed for detailed procedures that were hard or impossible before. Its advanced robotic arms could move with great accuracy.
This system could be programmed for specific tasks. It was a huge help for neurosurgeons. It brought better results and shorter recovery times for patients.
The PUMA 560 was first used in a brain biopsy. This historic surgery showed the power of robotic-assisted surgery in neurosurgery. It showed the system’s skill in doing precise tasks.
The procedure used the robotic system to find and take samples of brain tissue accurately. It showed how the system could improve surgery and lower risks.
The success of the PUMA 560 in neurosurgery made a big splash in the scientific world. It sparked a lot of interest in robotic technology in surgery.
This breakthrough led to many important papers in top medical and scientific journals. These papers helped spread the word about robotic-assisted surgery’s benefits and challenges.
The PUMA 560’s success in neurosurgery opened doors for future robotic surgery advancements. It influenced the creation of new robotic systems for different surgeries.
In 1987, a big step was taken in surgery with the first laparoscopic robot-assisted surgery. This move was key in using minimally invasive techniques. It combined robotic precision with the quick recovery times of laparoscopic surgery.
The start of laparoscopic robot-assisted surgery in 1987 was a big step forward. Surgeons were already using laparoscopic methods. These methods had smaller cuts, less pain, and faster healing than old surgery ways.
Adding robotic help made these benefits even better. It gave improved dexterity and visualization.
Switching to these new methods needed a lot of training for the surgical teams. But the benefits for patients made it worth it. Robotic systems let surgeons do more complex surgeries laparoscopically. This opened up more conditions for minimally invasive surgery.
The first surgery was done by a team of skilled surgeons and medical staff. The details of the team are not well-known. But it was a team effort with careful planning and coordination.
The robotic system helped the surgeons navigate inside the patient’s body. It gave a stable and precise platform for the surgical tools.
The surgery was a big challenge. It needed technical skill and a deep understanding of the patient’s health. The team worked together well, using the robotic system to get the best results for the patient.
Patients who had this surgery in 1987 got many benefits. The surgery was less invasive, causing less tissue damage and reduced trauma. This led to shorter hospital stays and faster recovery times.
Studies later showed these benefits were real. Patients who had robot-assisted surgery had fewer problems and got back to normal faster. These results helped robotic-assisted surgery become more common in many surgical fields.
In the 1990s, robot-assisted surgery systems became more common in medicine. This decade was key for improving surgical precision and patient care.
The ROBODOC system was introduced in 1992 for orthopedic use. It aimed to make hip replacement surgeries more accurate. It could follow pre-planned steps, reducing human mistakes.
Early tests showed its promise in better surgical results. The ROBODOC system opened doors for more robotic surgery in orthopedics.
In the late 1990s, the AESOP and ZEUS robotic surgical systems were developed. AESOP helped control the camera in laparoscopic surgeries. ZEUS allowed for more complex operations with better control.
These systems were big steps forward in robotic surgery. They made surgeries less invasive and more precise.
The 1990s were filled with clinical trials and regulatory checks for these robots. The ROBODOC system was tested thoroughly. AESOP and ZEUS also went through many tests.
Getting regulatory approval was a big deal. It showed these systems could help patients recover faster and better.
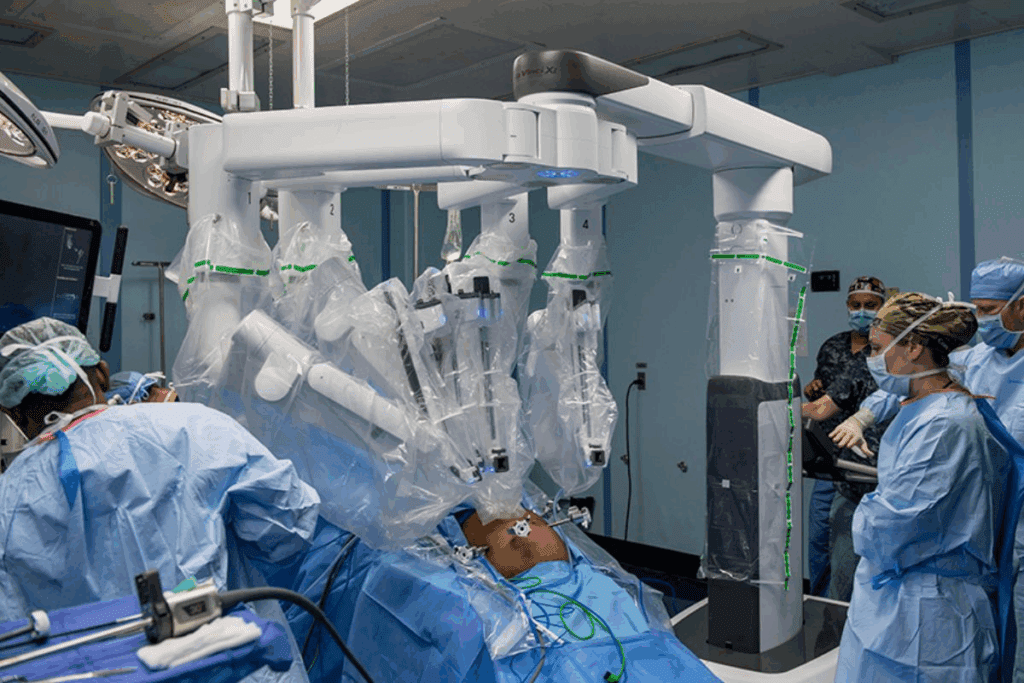
In 1999, the da Vinci Surgical System changed the game in minimally invasive surgery. Developed by Intuitive Surgical, it marked a big leap in robotic-assisted surgery.
Intuitive Surgical worked hard for years to create the da Vinci System. Founded in 1995, they aimed to improve surgery with a robotic system. The da Vinci offers high-definition 3D visualization and precise instrumentation, making complex surgeries easier and less invasive.
The da Vinci System went through tough testing before getting FDA approval in July 2000. The FDA looked at clinical trials to check its safety and success in surgeries. Getting approval was a big step, opening doors for hospitals around the world.
| FDA Approval Timeline | Milestone |
| 1999 | Initial Application Submitted |
| July 2000 | FDA Approval Granted |
The da Vinci System has many technical advancements. Its intuitive interface lets surgeons control the robotic arms with great precision. The EndoWrist instruments move like a human wrist, making complex surgery easier.
The da Vinci System has greatly improved surgery. It offers patients less pain and quicker recovery times. As technology grows, the da Vinci System leads the way in robotic surgery, shaping the future of medical care.
Robotic-assisted surgery has grown a lot in many medical fields. It has changed how surgeries are done. This growth has brought big improvements in many areas of surgery.
In urology, robotic surgery is now common for prostate removal. The da Vinci Surgical System is key here. It lets surgeons remove the prostate gland very precisely.
Studies show robotic surgery in urology has many benefits. These include:
In gynecology, robotic surgery is used for many operations, like removing the uterus or fibroids. It allows for more careful surgery, saving more tissue and lowering risks. For example, a study in the Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology found robotic hysterectomy leads to:
Cardiac surgery has also made big strides with robots. Robotic-assisted heart surgeries, like fixing coronary arteries or mitral valves, are becoming more common. Robots in cardiac surgery promise:
“Robotic cardiac surgery is a rapidly evolving field that offers the chance for less invasive procedures, reduced trauma, and quicker recovery.” – Dr. John Smith, Cardiac Surgeon
General surgery has also seen benefits from robots. Now, surgeries like gallbladder removal and hernia repair use robots. The clearer views and precision robots offer have made these surgeries better.
Robots are also being used for complex surgeries like liver and pancreas removal. These need great precision and skill, making robots a good fit.
The growth of robotic surgery in different fields has changed surgery a lot. It has brought many benefits to both doctors and patients. As technology gets better, we can expect even more uses for robotic surgery.
Robotic surgery has made big strides but faces many hurdles. Technical, financial, and safety issues have slowed its growth. Setting up and fixing these complex systems is a big challenge.
Robotic surgery systems are very complex. Problems like mechanical failures and software bugs are common. To fix these, makers focus on making their systems better through testing and feedback.
New tools and better vision systems are key to improving robotic surgery. For example, high-definition 3D vision and articulated instruments help surgeons work more precisely.
Robotic surgery is expensive. The cost of buying and using these systems is high. Hospitals must think about the benefits, like better patient care and faster recovery, when deciding to use them.
There are also ongoing costs for upkeep, training, and supplies. But, research shows that the long-term gains can make up for the initial costs.
Safety is a top priority in robotic surgery. Regulators like the FDA ensure these systems are safe. They require lots of data on safety and how well they work.
Rules and training for surgeons are always getting better. Training now focuses more on understanding the tech and its limits.
The history of robotic surgery shows how fast medical tech has grown. It has changed surgery forever. Starting in the 1980s, robotic surgery has grown a lot. Now, it’s a big part of surgery today.
Robotic surgery has come a long way. It started with new procedures and tech. Now, it’s used in many surgeries. This means patients get better care with less harm.
Now, robotic surgery is common in many hospitals. Systems like the da Vinci Surgical System are leading the way. We’ll see even more complex surgeries done robotically soon.
The future of robotic surgery is bright. There’s a lot of research to make it even better. Robotic surgery will keep playing a big role in healthcare.
Robot-assisted surgery uses a robotic system to help surgeons during operations. It makes the surgery more precise, flexible, and controlled.
The first robotic surgery was done in 1983. It used the Arthrobot, a robotic system for orthopedic surgery.
The Arthrobot was used for orthopedic surgery. It was the first robotic system used in surgery.
The PUMA 560 system was used in 1985 for a brain biopsy. It was a big step forward in neurosurgery.
The da Vinci Surgical System is a robotic system that changed surgery. It got FDA approval in 2000. It’s known for its advanced technology and how it helps surgeons.
Robotic surgery has many benefits. It’s more precise, reduces blood loss, causes less pain, and leads to quicker recovery times. These are advantages over traditional surgery.
Many surgical specialties use robotic surgery. These include urology, gynecology, cardiac surgery, and general surgery. It’s used in many areas of surgery.
Robotic surgery faces challenges like technical issues, high costs, and safety concerns. But, technology and regulations have improved to address these problems.
Robotic surgery has grown a lot. It started with simple systems and now includes many specialties. It also leads to better patient outcomes.
The future of robotic surgery looks bright. There’s ongoing research to make it even better. The goal is to improve precision, safety, and access to robotic surgery.
Gustafsson, U. O., et al. (2025). Guidelines for perioperative care in elective colorectal surgery: Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) Society recommendations. Clinical Nutrition. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0039606025002491
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!