Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
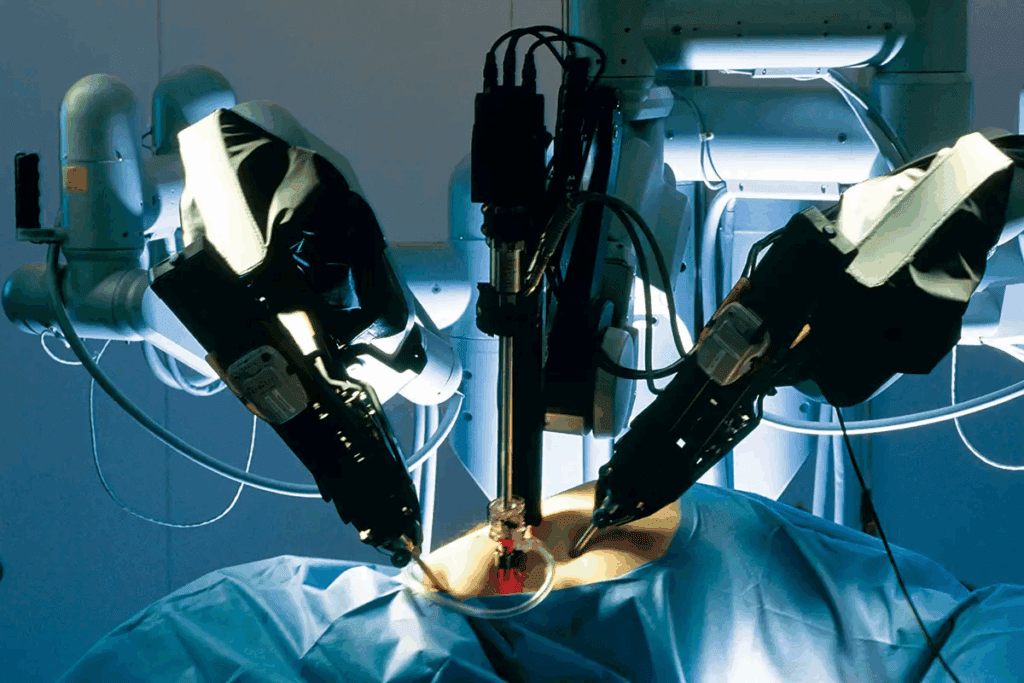
While robotic hysterectomy offers many benefits, it’s not suitable for every patient. Understanding robotic hysterectomy contraindications is crucial to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Every patient is unique, and a thorough evaluation is essential to determine the best treatment approach. Factors such as previous surgeries, adhesions, or certain medical conditions can influence whether robotic surgery is appropriate.
At Liv Hospital, our medical team carefully assesses each patient’s health. We identify any robotic hysterectomy contraindications to ensure that the procedure is both safe and successful, providing personalized care tailored to each individual.
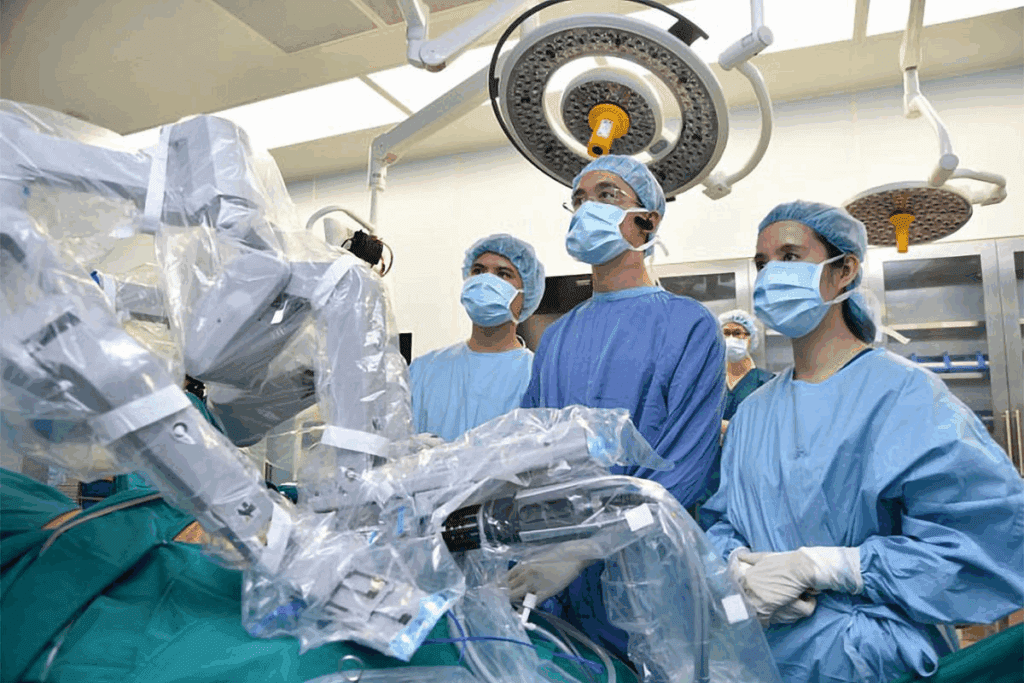
Robotic-assisted hysterectomy is a new way to treat gynecologic issues. It combines the skill of surgeons with robotic technology. This makes the surgery better for patients. Let’s look at what robotic hysterectomy is and the tech behind it.
Robotic-assisted hysterectomy is an advanced minimally invasive surgical option.It lets surgeons remove the uterus with small cuts. This method has advantages like less blood loss and shorter stays in the hospital.
The robotic system gives a clear 3D view of the area being operated on. This helps the surgeon work more precisely and see better.
The main parts of robotic-assisted hysterectomy are:
The Da Vinci Surgical System is used for many surgeries, including hysterectomies. It helps surgeons do complex tasks with enhanced precision. The system has a surgeon’s console, robotic arms, and a vision system.
Using the Da Vinci System in gynecologic surgery has many benefits. These include:
Robotic-assisted hysterectomy has many good points. But, it’s important to know the risks and when it’s not a good choice. This helps doctors decide if it’s right for each patient.
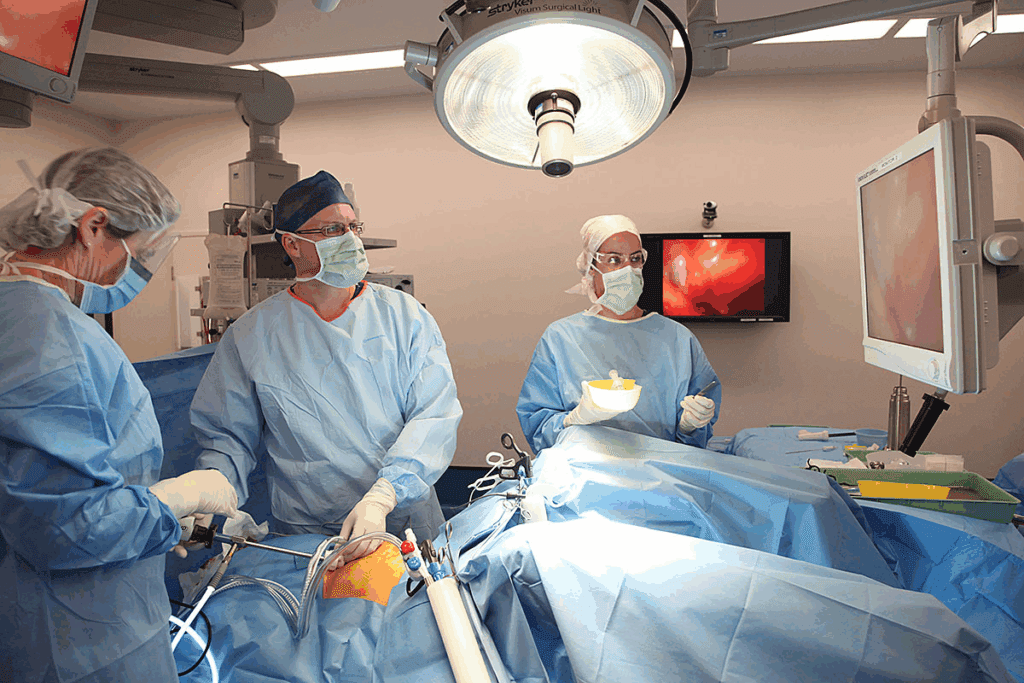
Robotic hysterectomy has its limits. These can be divided into two main types: absolute and relative contraindications. Knowing the difference is key to choosing the right patient and achieving the best results.
Absolute contraindications mean robotic hysterectomy is too risky or not possible. This includes severe heart or lung problems, lots of adhesions in the pelvis, and advanced gynecologic cancers. Relative contraindications, on the other hand, might make the surgery harder but don’t rule it out. These include past surgeries in the belly, being overweight, or having a big uterus.
Let’s look at these contraindications in a clear way:
| Contraindication Type | Examples | Implications |
| Absolute | Severe cardiopulmonary disease, extensive pelvic adhesions, advanced gynecologic cancers | Procedure is unsafe or impossible |
| Relative | Previous abdominal surgeries, obesity, large uterine size | Procedure may be complicated but not necessarily precluded |
Choosing the right patient for robotic hysterectomy is essential. This means looking closely at the patient’s medical history, current health, and the details of their condition. By doing this, doctors can decide if robotic surgery is the best choice.
It’s important to have a team approach to picking patients. This team includes gynecologists, anesthesiologists, and other experts. Working together helps make sure the patient’s health is fully considered. This reduces risks and improves results.
Some medical conditions can make robotic hysterectomy risky. It’s important to choose the right patients for this surgery. While robotic surgery has many benefits, it also comes with its own set of risks.
People with severe heart and lung problems face higher risks during robotic surgery. The Trendelenburg position and pneumoperitoneum can cause complications. It’s essential to carefully check if these patients can safely undergo robotic hysterectomy.
The Trendelenburg position can make breathing harder for those with heart and lung issues. Pneumoperitoneum also puts extra pressure on the diaphragm, making breathing even more challenging.
Bleeding disorders and anticoagulation therapy are big concerns for robotic surgery. Patients on blood thinners might bleed more during and after surgery. Those with bleeding disorders need special care to avoid heavy bleeding.
We thoroughly review patients with these conditions. We might adjust their blood thinners or take extra steps to manage bleeding risks during robotic hysterectomy.
Patients with weak immune systems, like those with immunodeficiency disorders or on immunosuppressive therapy, are at higher risk of infections and complications. We take extra steps to prevent these risks, including detailed preoperative checks and postoperative care.
Managing patients with weak immune systems requires a team effort. This ensures their safety and the success of the robotic hysterectomy procedure.
When deciding if a patient is right for robotic hysterectomy, looking at their anatomy is key. The shape and size of a patient’s body can affect how well the surgery can be done.
Pelvic adhesions are a big challenge. These can come from old surgeries, infections, or conditions like endometriosis. Adhesions can make it hard to see and reach the uterus during surgery. Sometimes, they can make robotic surgery too risky or hard.
“Adhesions are a big deal for surgeons thinking about robotic hysterectomy,” experts say. Whether to use robotic surgery depends on the surgeon’s skill and how bad the adhesions are.
Big uteruses, often because of fibroids, can also be a problem. Big fibroids can make it tough to use the robotic tools and see what’s going on. Even though robotic surgery is precise and helps with recovery, very big fibroids might need a different, more open surgery.
Some people have unique body shapes or pelvic changes that make robotic surgery tricky. These need a surgeon who can be flexible and experienced. Sometimes, these differences mean switching to a different surgery method is needed.
Looking at the limits of robotic hysterectomy shows us how important a good check-up before surgery is. This check-up should look closely at the patient’s body to pick the best surgery.
Robotic hysterectomy candidates with a history of abdominal surgery need careful evaluation. Previous surgeries can make the procedure harder due to adhesions and changed anatomy.
Patients with multiple laparotomies face challenges in robotic hysterectomy. The risk of adhesions grows with each surgery, making the robotic approach harder. “The presence of adhesions can significantly impact the safety and efficacy of robotic surgery,” experts say.
Multiple prior laparotomies can lead to:
Extensive adhesions from previous surgeries can limit the success of robotic hysterectomy. Adhesions can block the surgeon’s view, making it hard to find important structures. In such cases, the risks of minimally invasive surgery risks might be too high.
Surgeons must carefully consider the benefits and risks of robotic hysterectomy for patients with complex abdominal surgery history. Other methods, like open or conventional laparoscopic hysterectomy, might be better.
When looking at the impact of previous surgeries on robotic hysterectomy, a detailed preoperative assessment is key. This includes reviewing the patient’s surgery history, assessing adhesion risk, and discussing robotic hysterectomy side effects with the patient.
By understanding these factors, we can choose the best surgical method for each patient. This helps minimize risks and improve outcomes.
Patients with a high body mass index (BMI) face special challenges during robotic hysterectomy. Obesity can make both the surgery and anesthesia harder.
A high BMI can make robotic hysterectomy less effective. It can lead to less precise surgery and more complications. Studies show that a BMI over 40 makes the surgery much harder.
“The technical challenges with robotic surgery in obese patients are big. Choosing the right patients is key,” says a top expert in robotic gynecologic surgery.
Obese patients taking robotic hysterectomy face higher risks with anesthesia. The Trendelenburg position, needed for robotic surgery, can worsen breathing problems in obese people.
Patients with high BMI face technical hurdles. These include hard port placement and instrument maneuverability. The thick abdominal wall also affects the robotic instruments’ precision.
To tackle these issues, surgeons might adjust their methods. This could include placing more ports or using longer instruments.
In advanced gynecologic malignancies, the use of robotic hysterectomy needs careful thought. These cases pose unique challenges that might make robotic surgery less suitable or even not recommended.
Patients with advanced gynecologic cancers often need more extensive surgeries than robotic hysterectomy can offer. The complexity of these cases may include large tumors, significant local invasion, or other factors that require open surgery.
A study in a reputable medical journal found that stage III or IV cervical cancer patients do better with open surgery. This is because their disease is more extensive. Below is a table comparing robotic and open surgery for advanced gynecologic cancers.
| Surgical Approach | Advantages | Limitations |
| Robotic Surgery | Less invasive, quicker recovery | Limited by tumor size and complexity |
| Open Surgery | Better for extensive disease, more lymph nodes can be removed | More invasive, longer recovery time |
Advanced gynecologic cancers often need extensive lymph node dissection. While robotic surgery can do lymphadenectomy, complex cases may require more thorough lymph node removal. This can be hard to do robotically.
Extensive lymph node dissection is key for accurate staging and better outcomes in advanced cancer. The choice between robotic surgery and open surgery depends on the need for thorough lymph node removal.
When there’s metastatic disease, the role of robotic hysterectomy is more complex. Metastases indicate a more advanced cancer stage, often needing a treatment plan that includes chemotherapy, radiation, and surgery.
Robotic surgery might be part of the treatment plan, but it’s not the only treatment for metastatic disease. The main concern is whether the patient’s condition and disease extent make them a good candidate for robotic surgery.
We must evaluate each patient’s condition carefully. We consider factors like the extent of metastatic disease, overall health, and previous treatments to decide the best surgical approach.
Exploring robotic hysterectomy reveals important cardiovascular and respiratory issues. This surgery offers many benefits but also has challenges. Surgeons and anesthesiologists must be careful to keep patients safe.
The Trendelenburg position is often used in robotic hysterectomy. It tilts the patient so their feet are higher than their head. This can put pressure on the diaphragm, affecting breathing.
Key risks include:
Pneumoperitoneum, or inflating the abdomen with carbon dioxide, affects heart and lung function. It can decrease blood flow back to the heart, leading to heart problems.
| Effect | Description | Clinical Implication |
| Decreased Venous Return | Reduced blood flow back to the heart | Potential for hypotension |
| Increased Systemic Vascular Resistance | Increased resistance in the vascular system | Potential for hypertension |
| Respiratory Changes | Altered lung mechanics due to pneumoperitoneum | Potential for respiratory acidosis |
Anesthesia time during robotic hysterectomy is a risk factor. Longer times can lead to more complications, like heart and lung problems.
Understanding these risks helps healthcare providers manage them. This ensures a safer surgery for patients.
Certain acute conditions and emergencies make us rethink robotic hysterectomy. We must weigh its safety and effectiveness against other surgical options.
A ruptured ectopic pregnancy is a serious issue that needs quick surgery. The main goal is to stop the bleeding and keep the patient stable. Robotic surgery might not be the first choice because of the urgency and need for fast action.
Severe bleeding during surgery is a big challenge. It requires quick blood transfusions and stopping the bleeding. Even though robotic surgery is precise, it might not be the best for severe hemorrhage. Open surgery might be needed for immediate action.
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is another situation where robotic hysterectomy might not be the best choice. The inflammation and possible adhesions make the surgery harder. Deciding on robotic surgery in these cases needs careful thought, considering the inflammation and the patient’s health.
The following table summarizes key considerations for emergency situations and acute conditions:
| Condition | Robotic Hysterectomy Considerations | Alternative Approaches |
| Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy | May not be suitable due to urgency | Open surgery or laparoscopic surgery |
| Severe Hemorrhage | Limited by need for immediate action | Open surgery |
| Acute Pelvic Inflammatory Disease | Complicated by inflammation and adhesions | Laparoscopic or open surgery, depending on severity |
For patients who can’t have robotic hysterectomy, there are other surgical options. When robotic surgery isn’t possible, doctors look for safe and effective alternatives.
Conventional laparoscopic hysterectomy is a minimally invasive surgical alternative. It’s used when robotic help isn’t needed. This method uses small incisions in the belly for laparoscopic tools.
Benefits of this procedure include:
Vaginal hysterectomy is a minimally invasive approach. It removes the uterus through the vagina. It’s good for patients with certain uterine issues and doesn’t need belly cuts.
Advantages of vaginal hysterectomy include:
In some cases, open abdominal hysterectomy is the best choice. This traditional method uses a bigger cut in the belly to reach the uterus.
Open abdominal hysterectomy is often needed for:
Knowing the alternatives to robotic hysterectomy is key for good patient care. Healthcare providers can pick the best surgery based on each patient’s needs and health.
The success of robotic hysterectomy depends on the decision-making process. This process is influenced by the surgeon’s experience and the hospital’s resources. Both the surgeon’s training and the hospital’s capabilities are key to the procedure’s success.
Surgeon training is vital for robotic hysterectomy success. The learning curve for robotic surgery is steep. Surgeons need extensive training to master the technique.
Studies show that surgeons with more robotic experience have better outcomes. They have fewer complications and shorter hospital stays. The training process includes didactic instruction, simulation, and proctoring by experienced surgeons. This helps surgeons develop the skills needed for robotic surgery.
The hospital’s capabilities and resources are also important. Advanced equipment, like the da Vinci Surgical System, is essential. The hospital must also have trained support staff, including nurses and surgical technicians.
The table below shows key factors for choosing robotic hysterectomy:
| Institutional Factor | Description | Importance Level |
| Advanced Equipment | Availability of da Vinci Surgical System or similar technology | High |
| Trained Support Staff | Nurses and surgical technicians trained in robotic surgery | High |
| Surgical Volume | Number of robotic procedures performed annually | Medium |
| Continuing Education | Ongoing training and professional development for surgical staff | Medium |
Healthcare providers should consider both surgeon experience and hospital resources when deciding on robotic hysterectomy. This approach ensures the best outcomes and minimizes risks.
Identifying and reducing risks is key for successful robotic surgery, even for borderline patients. Robotic surgery offers many benefits but comes with risks. These risks are higher for patients with certain health or anatomical issues.
Preoperative optimization is vital for borderline candidates. It involves checking the patient’s health thoroughly. This includes managing chronic conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure.
Optimizing nutritional status and correcting anemia are also important. These steps help lower surgical risks.
For those with a high BMI, weight loss counseling is helpful. But, losing weight quickly is often not possible. Quitting smoking is also advised. Smoking can slow down wound healing and increase respiratory risks.
| Preoperative Optimization Strategy | Benefit |
| Management of chronic conditions | Reduces surgical risks by stabilizing health |
| Nutritional optimization | Enhances wound healing and overall recovery |
| Smoking cessation | Decreases risk of respiratory and wound complications |
Intraoperative monitoring and management are critical. They help detect and manage complications during surgery. Advanced hemodynamic monitoring is key for managing fluids and blood pressure, important for patients with heart disease.
Anesthesia should be tailored to the patient’s needs. This includes considering positioning and the risk of pneumoperitoneum-related complications. Proper ventilation strategies are also vital to prevent respiratory issues and ensure enough oxygen.
There may be times during robotic surgery when switching to another approach is needed. This decision should be based on clear criteria, like uncontrollable bleeding or poor visibility.
Surgeons should be ready to switch to laparoscopic or open surgery if needed. Having a predefined plan for these situations is key to minimizing risks and ensuring a good outcome.
It’s important to carefully check if a patient is right for robotic hysterectomy. This helps avoid risks and problems. We talked about when it’s not a good idea, like with severe health issues or past surgeries.
Knowing these details helps doctors decide if robotic surgery is best for each patient. They must think about the risks and possible problems. This ensures the best results for the patient.
Choosing the right patients and knowing the challenges helps surgeons. They can make robotic hysterectomy safer and more effective. Sometimes, other surgeries might be better for some patients.
In the end, a detailed check-up and thinking about each patient’s needs are key. This way, doctors can give the best care and get the best results in gynecologic surgery.
Robotic hysterectomy is a new way to remove the uterus. It uses the Da Vinci Surgical System. This method is different because it offers better vision and control, leading to less blood loss and more precise cuts.
Some conditions make robotic hysterectomy not suitable. These include severe heart or lung problems, bleeding issues, weak immune systems, and big uteruses. Also, those with advanced cancer or needing to remove many lymph nodes might not be good candidates.
Past surgeries can make things harder. But, it doesn’t always mean robotic surgery is out of the question. Doctors will decide based on each case.
Obesity can make things tricky, but it’s not a complete no-go. Yet, people with high BMI might face more challenges during surgery and with anesthesia.
The Trendelenburg position can lead to breathing and heart problems. This is more of a concern for those with heart or lung issues. It’s important to watch patients closely and choose them carefully.
Yes, there are other ways to do a hysterectomy. These include laparoscopic, vaginal, and open surgery. The right choice depends on the patient’s health, body, and the surgeon’s skills.
A skilled surgeon is key for a safe and successful robotic hysterectomy. They need to be well-trained and experienced to avoid problems and get the best results.
To lower risks, doctors can prepare patients before surgery, keep a close eye on them during, and choose them carefully. Having a backup plan for other surgeries can also help.
No, robotic surgery is not the first choice in emergencies. Situations like a ruptured ectopic pregnancy or severe bleeding need quicker action. Other methods might be better for these urgent cases.
The Da Vinci System gives surgeons better vision and control. This means they can do detailed work with less blood loss. It helps patients recover faster and have better results.
Vaginal Hysterectomy – Contraindications and Complications StatPearls, NCBI, 2023
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!