Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir

The average adult prostate is about the size of a walnut. As men age, the prostate can change in size.Sex after prostate removal is possible with nerve-sparing surgery. Learn intimacy timeline, erectile aids, and relationship tips.
At 70 years old, the normal prostate size can vary. Knowing the average prostate volume helps spot any issues.
A normal prostate size is usually around 20-30 cubic centimeters in volume. But, health conditions and genetics can change this at 70 years.
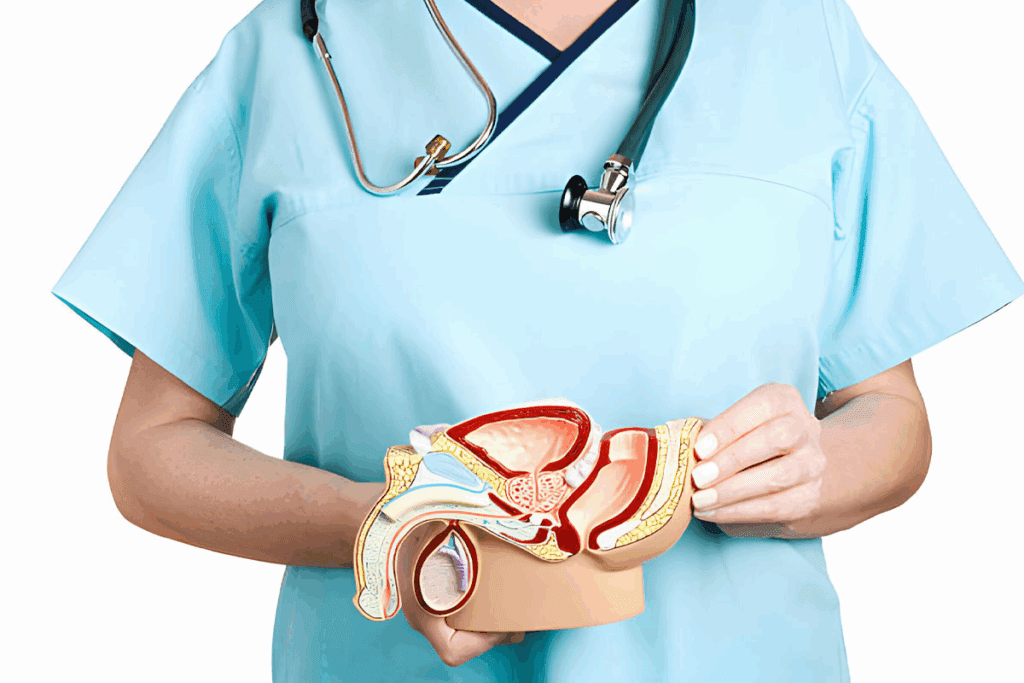
It’s important to understand the prostate gland’s role in male health. This gland is complex, playing a key part in the male reproductive system.
The prostate gland sits in the pelvis, below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It wraps around the urethra, which carries urine out of the body. It’s usually the size of a walnut, but can grow with age.
The prostate gland is vital for male health. It makes seminal fluid, which feeds sperm during ejaculation. This fluid is key for sperm health and movement.
The prostate gland is close to the bladder, urethra, and rectum. Its position around the urethra can impact how well you urinate.
| Characteristics | Description |
| Location | Below the bladder, in front of the rectum |
| Function | Secretes seminal fluid for sperm nourishment |
| Relation to Surrounding Organs | Surrounds the urethra, affecting urinary function |
| Normal Size | Approximately walnut-sized |

The size of the prostate gland changes a lot as men get older. This is due to hormones and other factors. Knowing about these changes helps keep the prostate healthy.
The prostate begins to grow early in life, experiencing significant growth during puberty and continuing to enlarge as men age. In early years, the prostate is small and not very active. At puberty, it starts to grow because of hormones like testosterone.
Growth Patterns: The prostate keeps getting bigger as men age, often a lot after 40. Hormones keep it growing.
From young to old, the prostate goes through many changes. In young men, it’s small and firm. As men get older, it can get bigger and softer because of BPH, a non-cancerous condition.
Hormonal influences are key in prostate growth. Hormones like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) are important. DHT helps prostate cells grow, making the prostate bigger with age.
Hormones, mainly androgens, are vital for prostate growth. The right balance of hormones is important for prostate size and health.
| Hormone | Role in Prostate Growth |
| Testosterone | Primary male sex hormone influencing prostate growth. |
| Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) | A potent derivative of testosterone that promotes prostate cell growth. |
| Estrogen | Though present in smaller amounts in men, estrogen affects prostate health and growth. |
Knowing how hormones affect prostate growth helps manage age-related changes. As men age, it’s important to watch prostate health and deal with problems quickly. This helps keep quality of life good.
Many men wonder about the normal prostate size at 70. As men get older, their prostate gland can change size. Knowing what’s normal is key to spotting health issues early.
For men around 70, a normal prostate volume is usually 20 to 50 cubic centimeters (cc). This can vary based on health and genetics.
The weight and size of the prostate are also important. A healthy prostate weighs about 20 grams. It’s often as big as a walnut, but sizes can differ. It’s usually 4 cm wide, 3 cm tall, and 2 cm deep.
An enlarged prostate, or BPH, can really affect a man’s life. If the volume is over 50 cc or the size is bigger than usual, it might be enlarged.
It’s vital for men at 70 to know these measurements. This helps them catch any health problems early.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is a big health issue for men in their seventies. As men get older, the chance of getting BPH goes up. This makes it a common problem for septuagenarians.
Research shows BPH is common among men in their seventies. A big number of men aged 70 and up deal with BPH. The risk of getting BPH grows with age, showing the need for watching and caring.
The exact number of men affected can change due to many things. These include genetics, lifestyle, and health. But, it’s clear BPH is a big problem for many men in this age group.
The growth of BPH in elderly men is linked to hormonal changes. The main change is when testosterone turns into dihydrotestosterone (DHT). This hormone is key in making the prostate bigger. Knowing how this works helps doctors find good treatments.
In older men, the balance of cell growth and death in the prostate gets out of whack. This leads to BPH. Many things, like hormonal shifts and aging, play a part in this.
Telling normal aging from BPH is key for managing BPH right. While some prostate growth is normal with age, big growth that causes pee problems is not. It’s not just a normal part of getting older.
Doctors use tests like digital rectal exam (DRE), prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests, and imaging to tell BPH from normal aging. These tests help figure out the best treatment.
Understanding BPH’s prevalence, how it works, and how to diagnose it helps doctors give better care to men in their seventies. This improves their life quality.
As men age, their prostate size can change. This is due to genetics, lifestyle, and medical factors. Knowing these factors is key to keeping the prostate healthy.
Genetics play a big role in prostate size. Men with a family history of prostate problems are more likely to have an enlarged prostate.
Research has found genetic markers linked to BPH. For example, some genetic changes affect the androgen receptor. This can influence how fast the prostate grows.
What you eat and how you live can affect your prostate. Eating lots of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help prevent prostate enlargement.
Here’s a table showing how different diets affect prostate size:
| Dietary Component | Effect on Prostate Size |
| High Fat Diet | Increased Risk of Enlargement |
| High Fiber Diet | Reduced Risk of Enlargement |
| Antioxidant-Rich Foods | Potential Protective Effects |
Some medical conditions can make the prostate bigger. Diabetes and heart disease, for example, increase the risk of BPH.
It’s important to understand how these factors affect prostate health. This knowledge helps in finding ways to manage prostate issues effectively.
Knowing the size of the prostate is key. Doctors use Digital Rectal Examination (DRE), imaging, and Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) tests. These methods help doctors check the prostate’s health and spot problems early.
A Digital Rectal Examination (DRE) is a basic test for the prostate. A doctor puts a gloved finger in the rectum to feel the prostate. This helps find out if the prostate is too big or has any odd shapes.
Key aspects of DRE include:
Imaging is key for checking prostate size and finding problems. Ultrasound helps measure the prostate and find issues. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) gives detailed pictures of the prostate and nearby areas. It helps find conditions like prostatitis or cancer. Computed Tomography (CT) scans are also used to look at the prostate and pelvic area.
PSA testing checks the Prostate-Specific Antigen in blood. High levels can mean the prostate is too big, has inflammation, or cancer. Even though PSA isn’t a direct size measure, it’s important for checking prostate health. PSA levels can be affected by age, prostate size, and health issues.
Urodynamic studies test how well the bladder and urethra work. They help find urinary problems caused by a big prostate. These studies look at urine flow and pressure to see how prostate size affects urination.
“Urodynamic studies provide important info on how prostate size affects urination. They help doctors decide on the best treatment.”
At 70, men often face prostate enlargement, leading to urinary symptoms. These symptoms can greatly affect daily life and well-being.
Men with an enlarged prostate often have LUTS. Symptoms include weak urine flow, straining, and frequent urination. LUTS can be bothersome and disrupt daily activities. A study found that LUTS are common in elderly men and lower their quality of life.
“The presence of LUTS is a significant predictor of decreased quality of life in older men.”
Nocturia, or frequent nighttime urination, is a symptom of prostate enlargement. It disrupts sleep, affecting health and well-being. Nocturia can be challenging, as it interrupts sleep patterns. Men may wake up many times, feeling tired and unrefreshed.
Urinary retention happens when the prostate blocks urine flow, making it hard to empty the bladder. This can cause overflow incontinence, where urine leaks. Urinary retention is a serious condition that requires medical attention. Men may feel a sudden, urgent need to urinate but can’t.
Prostate enlargement symptoms can greatly impact daily activities. Men may need to plan their day around bathroom breaks. The impact on daily life can be substantial, affecting not just the individual but also their family and friends. Simple tasks, like going for a walk or attending social events, can become challenging due to the need for frequent urination.
Prostate health problems can really change a man’s life. They affect both personal and social life. The effects are wide-ranging, from feeling stressed to having trouble with relationships.
Prostate issues can cause big emotional problems. Men might feel anxious, embarrassed, and frustrated. The emotional toll is real, affecting how they see themselves.
Prostate problems force men to change their lives. They might have to plan their day around bathroom breaks. They also have to limit what they drink and avoid certain activities. These changes can make them feel isolated and lower their quality of life.
Prostate issues can put a lot of strain on relationships. Partners may have to adjust to new intimacy and routines. Talking openly is important to keep the relationship strong.
Prostate problems are linked to depression and anxiety. The ongoing symptoms and possible surgeries can make things worse. Healthcare providers need to tackle these mental health issues too.
It’s important to see how prostate issues affect a man’s life. By treating the physical and emotional sides, doctors can help men live better. This approach improves their overall well-being.
Men with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) have many treatment options. The right choice depends on how bad the symptoms are, overall health, and what the man prefers.
Medicines are often the first treatment for BPH. Alpha-blockers help relax muscles in the prostate and bladder neck. This makes it easier to pee. 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors can also shrink the prostate over time.
For men with more severe symptoms, doctors might suggest taking both types of medicine together.
Men who don’t like taking medicine or don’t see improvement can try less invasive methods. Transurethral microwave therapy (TUMT) and transurethral needle ablation (TUNA) use heat to shrink the prostate.
UroLift is a newer option. It lifts or moves prostate tissue to improve urine flow.
When symptoms are very bad or other treatments fail, surgery might be needed. Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) is a common surgery. It removes tissue blocking urine flow.
Other surgeries include open prostatectomy for bigger prostates and simple prostatectomy, which removes the inner prostate part.
It’s important for men to talk to their doctor about treatment options. This helps find the best choice for their specific situation and health.
Prostate removal surgery can change a man’s sex life. This surgery is often for prostate cancer. It’s important for men to know how it might affect their sex life and what they can do about it.
Men might face changes in their sex life after surgery. These can include trouble getting an erection, changes in orgasm, and lower sex drive. How much these changes affect a man can depend on the surgery and his health.
Surgical Techniques and Sexual Function: The surgery method can affect sex life. Techniques that try to save nerves can help keep erectile function.
Dealing with erectile dysfunction after surgery can involve several steps. This might include:
Men should talk to their doctor to find the best option for them.
Intimacy doesn’t just mean sex. Couples can find other ways to connect, like:
Keeping a strong emotional bond and trying new things can help couples adjust to changes after surgery.
The emotional side of prostate removal is important too. Counseling can help men and their partners. It can address issues like:
Getting professional help is key to dealing with these challenges and improving well-being.
As men turn 70, knowing how prostate size affects cancer risk is key. Prostate cancer is a big worry for older men. Many things can lead to its development.
Studies link bigger prostates to a higher chance of prostate cancer. But, the exact link is not fully understood yet.
Several factors might explain why bigger prostates could lead to cancer. Hormones and genes play a role. Knowing this helps doctors find better ways to screen and diagnose.
Screening for prostate cancer in men over 70 focuses on what’s best for each person.
PSA testing is a common way to check for prostate cancer. But, it’s important to understand PSA results in relation to prostate size. A high PSA level might mean more in men with smaller prostates.
It’s critical to grasp the details of PSA testing. Doctors must look at PSA levels, prostate size, and overall health when figuring out cancer risk.
Choosing between active surveillance and treatment for prostate cancer depends on several things. These include how aggressive the cancer is, prostate size, and the man’s health.
Talking to a doctor about the pros and cons of each option is important. This helps men make informed choices.
As men get older, they can take steps to keep their prostate healthy. What they eat and how much they exercise are key. These choices help a lot in keeping the prostate in good shape.
Eating lots of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is good for the prostate. Foods with antioxidants like lycopene in tomatoes and omega-3 fatty acids in fish are extra helpful.
Nutritional Benefits for Prostate Health
| Food | Nutrient | Benefit |
| Tomatoes | Lycopene | Antioxidant properties |
| Fatty Fish | Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Reduces inflammation |
| Green Tea | Catechins | Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects |
Staying active is good for your health and your prostate. It helps keep weight in check and lowers the risk of diseases that can harm the prostate.
Recommended Activities:
Even with a good diet, some supplements can help the prostate. But, always talk to a doctor before taking any supplements.
Seeing your doctor regularly is key for prostate health. Screenings and exams can catch problems early. This makes treatments work better.
Key Takeaways for Prostate Health
The size of the prostate gland can vary a lot among men from different ethnic backgrounds. This is due to genetics and the environment. Knowing these differences helps doctors diagnose and treat prostate issues better.
Studies show that prostate size changes a lot among different racial and ethnic groups. For example, men of African descent often have bigger prostates than Caucasians or Asians. This is because of genetics, lifestyle, and the environment.
These ethnic differences are key for diagnosing and treating prostate issues like BPH and prostate cancer.
Where you live and your environment also affect prostate size. For instance, men in cities might have different prostate sizes than those in the countryside. This could be because of lifestyle, diet, and toxins.
Doctors need to understand prostate size variations to provide better care. This means adjusting how they diagnose and treat patients. For example, a bigger prostate in an African man might be normal, but the same size in an Asian man could be a sign of a problem.
By recognizing and addressing these differences, doctors can give more personalized care to men with prostate issues.
Knowing when to see a doctor for prostate health is key. As men get older, it’s important to know the signs that mean you need to see a doctor. This is true, more so after the age of 70.
Some symptoms mean you need to see a doctor right away. These include:
If you have any of these symptoms, go see a doctor fast.
Regular checks are important for catching prostate problems early. Men over 70 should talk to their doctor about:
Being ready for your urologist visit helps you get the most out of it. Think about asking:
Finding your way through the healthcare system for prostate problems can be tough. It’s important to:
New paths for treating prostate health are being found. The field is growing fast, thanks to medical research and tech advances.
Studies have uncovered the genetic and molecular causes of prostate diseases. Genomic research found markers for aggressive prostate cancer, leading to early treatment.
Imaging technologies like MRI have made diagnosis more accurate. This helps in planning treatments better.
New treatments for prostate conditions are being developed. Minimally invasive procedures are becoming common. They aim to cut down recovery times and boost patient results.
Research on novel therapeutic agents is showing promise. These new treatments could lead to better prostate health management.
Precision medicine is changing prostate health by tailoring treatments. It looks at genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors for personalized care.
Using genomic data in treatment planning is key. It makes treatments more targeted and effective.
PSA testing is important for prostate cancer screening. But, researchers are looking into additional biomarkers for better diagnosis and disease prediction.
New biomarkers could help tell apart slow-growing and aggressive cancers. This could reduce unnecessary treatments and improve patient results.
Keeping prostate health in check is vital for a good quality of life as we age. When men reach their 70s, knowing the normal prostate size and watching for problems is more critical.
Good prostate health comes from being aware, getting regular check-ups, and getting the right medical care. By knowing what affects prostate size and watching for symptoms, men can stay healthy.
Regular health screenings can spot problems early. This means doctors can treat them quickly. This helps men keep doing what they love without interruptions.
By staying informed and working with doctors, men can manage their prostate health well. This lowers the chance of serious issues and boosts their overall health.
At age 70, a normal prostate size is about 20-50cc. This can vary from person to person.
Prostate size often grows with age, starting after 40. Hormones like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone play a role.
Symptoms include lower urinary tract issues, trouble sleeping, and trouble starting to urinate. These can really affect daily life.
Doctors use digital rectal exams, ultrasound, MRI, CT scans, and urodynamic studies to measure prostate size.
Treatments include medicines, minimally invasive procedures, and surgery. The choice depends on symptoms and what the doctor thinks is best.
Yes, removing the prostate can lead to erectile dysfunction. But, there are ways to manage and support this.
Some studies suggest a link between prostate size and cancer risk. More research is needed to confirm this.
To keep your prostate healthy, eat right, exercise, and consider supplements. Regular check-ups are also key.
See a doctor if you have severe urinary issues or pain. Also, get screened after age 70 if recommended.
New research includes treatments, precision medicine, and biomarkers. These aim to improve prostate health outcomes.
Yes, prostate size varies by race, ethnicity, and environment. This affects how doctors diagnose and treat.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!