Last Updated on November 4, 2025 by mcelik
About 20% of people with shoulder bursitis feel pain that goes down their arm. This pain can really affect their daily life and how well they feel.Learn how shoulder bursitis and arm pain are connected and when radiating pain could indicate a more serious issue.
Looking into this condition more, it’s key to know that bursitis and nerve irritation are often connected. This makes figuring out what’s wrong a bit tricky.
Shoulder bursitis happens when the bursae in the shoulder joint get inflamed. Bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs that cushion bones, tendons, and muscles. They help reduce friction and allow for smooth movement.
Bursae are key to the shoulder joint’s function. They act as shock absorbers, reducing the impact between bones and soft tissues. This is vital for the shoulder’s wide range of motions, like rotation and abduction.
In a healthy shoulder, bursae help movement by reducing friction. But, when they get inflamed, it can cause pain and make moving harder.
Inflammation, or bursitis, can come from many things like repetitive motion or direct trauma. When bursae get inflamed, they swell. This leads to more friction and irritation in the shoulder joint.
Shoulder bursitis is a condition that affects the bursae in the shoulder joint, leading to pain and reduced mobility. Understanding the function of bursae and the process of inflammation is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment of this condition.
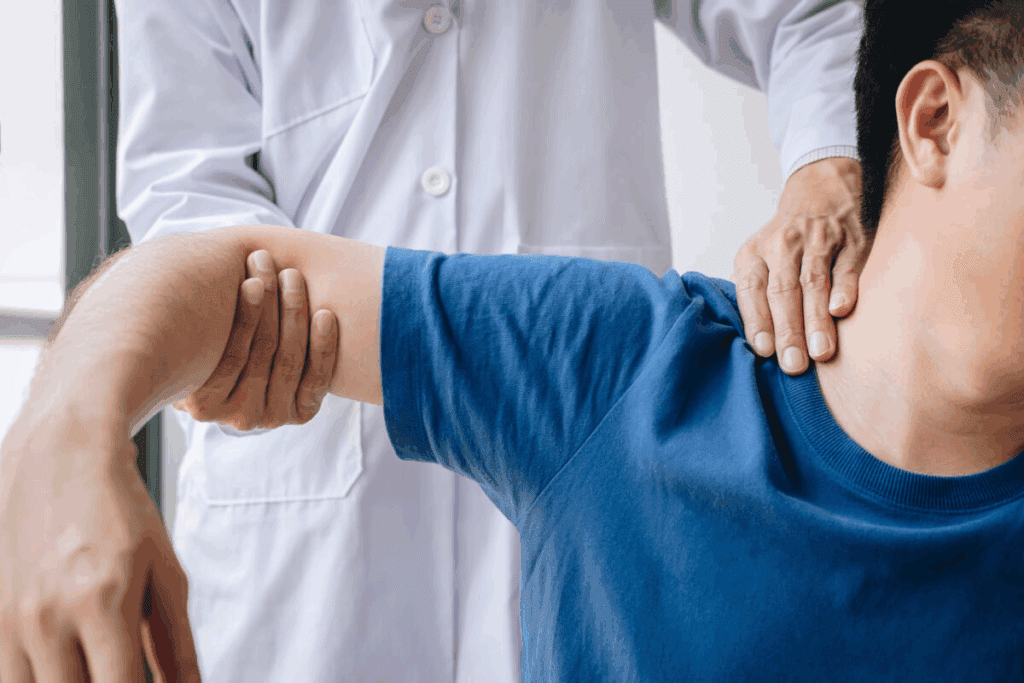

The shoulder joint’s complex anatomy is key to understanding bursitis. It includes bones, tendons, ligaments, and bursae. These work together to allow for a wide range of motion.
The shoulder joint, also known as the glenohumeral joint, is a ball-and-socket joint. It consists of the humerus (upper arm bone), scapula (shoulder blade), and clavicle (collarbone). The rotator cuff, a group of muscles and tendons, surrounds the joint. It provides stability and helps with movement.
The bursae in the shoulder are small, fluid-filled sacs. They reduce friction between bones, tendons, and ligaments. There are several bursae in the shoulder region. The subacromial bursa is one of the most significant. Inflammation of these bursae can lead to bursitis, causing pain and discomfort.
The mechanics of the shoulder joint play a key role in bursitis. Repetitive motion, overuse, or direct trauma can irritate and inflame the bursae. When the shoulder joint is subjected to abnormal stress, the bursae can become inflamed. This leads to pain and limited mobility.
| Shoulder Structure | Function | Relation to Bursitis |
| Rotator Cuff | Provides stability and facilitates movement | Inflammation can lead to bursitis |
| Bursae | Reduces friction between bones, tendons, and ligaments | Inflammation causes bursitis |
| Glenohumeral Joint | Ball-and-socket joint allowing wide range of motion | Abnormal stress can lead to bursitis |
Understanding the anatomy and mechanics of the shoulder joint is essential for diagnosing and treating bursitis. By recognizing how different structures interact and impact the bursae, healthcare professionals can develop targeted treatment plans. These plans aim to alleviate symptoms and restore normal shoulder function.
Inflammation from shoulder bursitis can spread due to the musculoskeletal system’s connections. Inflamed bursae irritate nearby tissues like tendons and ligaments. This irritation can cause pain to spread down the arm.
Key factors that contribute to the spread of inflammation include:
The shoulder and arm are connected by a complex network of nerves from the cervical spine. Nerves controlling the shoulder and arm come from the brachial plexus. This network starts in the neck’s spinal cord.
| Nerve Pathway | Function | Relation to Shoulder Bursitis |
| Suprascapular nerve | Controls muscles around the shoulder | Can be irritated by inflammation |
| Axillary nerve | Supplies the deltoid muscle and skin | May be compressed by swollen bursae |
| Radial nerve | Controls muscles and sensation in the arm | Can be affected by referred pain |
Understanding these nerve pathways is key to diagnosing and treating shoulder bursitis. By treating inflammation and its nerve effects, doctors can help manage symptoms.
Shoulder bursitis can show up in different ways, each with its own set of symptoms. Knowing these differences is key for finding the right treatment.
Subacromial bursitis is a common shoulder problem. It happens when the bursa under the acromion gets inflamed. This is often due to repeated actions or direct hits.
This type of bursitis is linked to upper arm pain. The swelling can bother the tissues and nerves around it.
Subdeltoid bursitis affects the bursa under the deltoid muscle. It can cause lateral arm symptoms like pain and weakness. The bursa under the deltoid works with the one under the acromion.
Pain when moving the arm sideways or pressure on the area are signs of subdeltoid bursitis. It can come from repeated strain or a direct injury to the shoulder.
Subscapular bursitis is when the bursa under the subscapularis tendon gets inflamed. It leads to posterior arm discomfort and pain in the front of the shoulder.
The subscapularis tendon is part of the rotator cuff. Bursitis here can mess with the shoulder’s stability and function. Symptoms get worse with arm rotation or lifting heavy things.
Knowing the exact type of shoulder bursitis is vital for the right treatment. Each type needs a specific plan to ease symptoms and improve shoulder function.
Shoulder bursitis is a type of inflammation that affects the shoulder joint. It can cause various symptoms that make daily life harder. Let’s look at these symptoms to understand their impact.
Shoulder bursitis often leads to pain and tenderness in the shoulder. This pain can feel sharp or dull. It usually gets worse when you move your shoulder or arm.
Shoulder bursitis can also cause pain that spreads down the arm. This happens because the inflammation affects nearby nerves.
The pain that spreads can be different in intensity. It might also feel like numbness or tingling.
Key limitations include:
Nerve compression plays a big role in arm pain from bursitis. When the bursae in the shoulder get inflamed, they swell. This swelling puts pressure on nearby nerves.
This pressure can mess up nerve function. It leads to pain that spreads along the nerve paths.
Shoulder bursitis also causes muscle weakness in the arm. The inflammation from bursitis can cause pain. This pain limits movement and strength in the affected shoulder and arm.
Over time, this reduced mobility can lead to muscle atrophy or weakness.
Understanding these mechanisms is key for effective treatment. By addressing nerve compression and muscle weakness, healthcare providers can help patients regain full function. They can also reduce pain.
Healthcare professionals use many ways to find out why your shoulder and arm hurt. Finding out if it’s shoulder bursitis is key to fixing the problem.
A detailed check-up is the first step to find shoulder bursitis. We look at how well your shoulder moves and where it hurts. We use special tests like the Neer and Hawkins-Kennedy tests to spot bursitis.
Touching the bursa area can show if it’s sore. This helps us know for sure if you have bursitis.
Imaging tests are vital to confirm shoulder bursitis. X-rays first check for other issues like broken bones or tendon calcification. Ultrasound is great for seeing bursae and swelling.
MRI gives us detailed views of soft tissues. It shows how bad the inflammation is and if there are other injuries.
When looking at shoulder bursitis and arm pain, we must think of other possible causes. Issues like rotator cuff tendinitis, frozen shoulder, and neck nerve problems can feel similar. A full check-up, including tests and imaging, helps us tell them apart.
We also look at diseases like rheumatoid arthritis that can cause bursitis. By using what we find in the exam and tests, we can pinpoint the problem. Then, we can make a plan to fix the pain in your shoulder and arm.
Knowing why shoulder bursitis happens is key to preventing and treating it. Shoulder bursitis can come from many sources. Understanding these causes helps manage the condition better.
Overusing your shoulder or doing the same motion over and over can cause bursitis. Athletes and people with jobs that need repetitive motions are at high risk. It’s important to see how repetitive strain can lead to bursitis.
Doing the same motion can irritate and inflame the bursae. This leads to pain and less mobility. Changing how you do things and taking breaks can help avoid this.
Getting hurt in the shoulder can also cause bursitis. A hard hit or falling on the shoulder can inflame the bursae. Trauma can cause sudden bursitis, which might get better with treatment. But sometimes, it can last a long time.
The impact of trauma on the shoulder and bursae can vary. But it usually causes pain and swelling. Knowing the injury’s details is key to treating it right.
As we get older, our bursae can get more inflamed. Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis also raise the risk of bursitis.
Systemic factors, like inflammatory diseases, can also affect the shoulder and bursae. Managing these conditions is vital to lower bursitis risk.
Anti-inflammatory drugs are often the first choice for treating shoulder bursitis. Ibuprofen or naproxen can reduce swelling and ease pain. Always talk to a doctor to find the right medicine and dose for you.
Corticosteroid injections can also help by reducing inflammation in the bursae. Injecting these steroids directly into the bursa can greatly lessen pain and swelling. This method is good for those who don’t get better with pills.
If other treatments don’t work, surgery might be needed. There are two main surgeries: bursectomy, which removes the inflamed bursa, and arthroscopic surgery to clean out the area. We’ll go into more detail about these options next.
| Treatment Option | Description | Recovery Time |
| Anti-inflammatory Medications | Oral medications to reduce inflammation and pain | Immediate relief, with full effect in a few days |
| Corticosteroid Injections | Direct injection of corticosteroids into the bursa | Relief within a few days, lasting several weeks |
| Surgical Interventions | Removal of the inflamed bursa or arthroscopic surgery | Several weeks to a few months |
It’s important to know about the medical treatments for shoulder bursitis and arm pain. Talking to a healthcare professional can help you choose the best treatment for your needs.
Shoulder pain can really get in the way of your daily life. But, there are some great home remedies that can help. By adding these to your daily routine, you can feel better and take care of your shoulder.
One of the best ways to handle shoulder pain at home is to give your shoulder a break. Resting the affected area and avoiding activities that make the pain worse can help a lot. Also, changing your daily activities to avoid heavy lifting and repetitive motions can aid in healing.
For instance, if your job involves lifting heavy things, taking regular breaks can help your shoulder. Making these small changes can really help your recovery.
Ice and heat therapy are simple but effective for shoulder pain. Ice therapy helps reduce swelling and numb the pain. Wrap an ice pack in a cloth and apply it to the area for 15-20 minutes, several times a day.
Heat therapy, on the other hand, relaxes muscles and improves blood flow. Use a warm bath, heating pad, or microwaveable heat wrap for this. It’s best to use heat therapy after the swelling goes down.
| Therapy Type | Purpose | Application |
| Ice Therapy | Reduce inflammation and numb pain | 15-20 minutes, several times a day |
| Heat Therapy | Relax muscles and improve blood flow | After initial inflammation subsides |
Over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers can also help with shoulder pain. Common ones include acetaminophen and ibuprofen. Acetaminophen helps with pain, while ibuprofen also reduces inflammation.
It’s important to follow the dosage instructions and talk to a healthcare professional if you’re not sure about the best medication for you.
Managing shoulder bursitis often means doing exercises and going to physical therapy. These steps help improve joint movement, lessen swelling, and make the muscles stronger. We’ll look at different exercises and therapy methods to ease symptoms and aid in recovery.
Doing gentle stretches is key to keeping the shoulder flexible and less stiff. Simple stretches done every day can boost movement and cut down on pain. For example, the pendulum stretch involves holding your arm straight and swinging it in small circles. This helps loosen the shoulder without stressing it too much.
The shoulder flexion stretch is another good one. You lift your arm forward and up, keeping it straight. This stretch works on the front and top of the shoulder, which bursitis often affects. Regular stretching can lessen swelling and improve shoulder function.
It’s important to strengthen the rotator cuff and muscles around it to support the shoulder and prevent more irritation. Resistance band exercises are great for this because they work the muscles without too much strain on the shoulder. For example, the external rotation exercise involves using a resistance band to rotate your arm outward, focusing on the rotator cuff muscles.
The scapular squeeze is another key exercise. It strengthens the muscles between and around the shoulder blades. This improves posture and lowers the chance of shoulder injury. Adding these exercises to your routine can make your shoulder more stable and lower the chance of bursitis coming back.
Good posture is essential for shoulder health, as bad posture can make bursitis worse and lead to more problems. Posture correction exercises help align the shoulder better and reduce strain. For instance, the chest stretch involves standing in a doorway with your arms up and leaning forward to stretch your chest and shoulders.
Being aware of your daily activities and making posture-friendly changes can also help a lot. Simple actions like stretching regularly and adjusting your workspace can prevent bad posture. Combining these with other exercises and therapy can lead to better shoulder health and lower bursitis risk.
Shoulder pain that goes down the arm needs a detailed check to find the cause. When pain spreads from the shoulder, we look at many possible reasons. This helps us give the right care.
The rotator cuff is key to the shoulder’s function. Problems here, like injuries or swelling, can cause arm pain. Rotator cuff tendinitis or tears are common and can lead to this pain. We need to figure out how bad the injury is and plan treatment.
Understanding the function of bursae and the process of inflammation is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment of this condition.
Problems in the cervical spine, like herniated discs or spinal stenosis, can also cause arm pain. This can look like shoulder bursitis. It’s important to tell these apart to treat the right condition.
Shoulder bursitis is a common cause of shoulder pain. But, serious conditions like infections, tumors, or referred pain from other areas can also cause similar symptoms. We must watch for these serious cases when we see patients with shoulder pain.
“It’s essential to consider a broad differential diagnosis when evaluating shoulder pain to avoid missing serious underlying conditions,” according to medical experts.
By looking at the patient’s history, physical exam, and test results, we can find the right diagnosis. Then, we can make a good treatment plan for shoulder pain that goes down the arm.
To avoid upper limb pain, we need to understand the importance of good workplace ergonomics and sports techniques. Making smart changes in our daily activities and exercise can help a lot. This can lower the chance of getting shoulder bursitis and arm pain.
Good ergonomics at work is key to avoiding shoulder strain. We should make sure our workspace supports good posture. For example, the computer monitor should be at eye level, and the keyboard should keep wrists straight.
We also need to take breaks to stretch and move. This helps prevent injuries from repetitive strain.
Ergonomic Adjustments:
For athletes and active people, changing sports techniques can help prevent shoulder bursitis. Working with a coach or trainer to adjust throwing or lifting can help. Also, doing exercises that strengthen the rotator cuff and muscles around the shoulder can support it and prevent injury.
| Sports/Activity | Modification | Benefit |
| Baseball Pitching | Adjust pitching technique to reduce strain on the shoulder | Lessens the risk of bursitis and related arm pain |
| Weightlifting | Use proper form when lifting weights overhead | Reduces stress on the shoulder joint |
| Swimming | Modify stroke technique to minimize shoulder rotation strain | Decreases the likelihood of developing bursitis |
By taking these steps, we can lower our risk of upper limb pain from shoulder problems. It’s about finding a balance. This includes making ergonomic changes and being mindful in sports and physical activities.
Knowing when to see a doctor for shoulder and arm pain is key. Pain can come from many things, like small injuries or serious health issues. It’s important to check your symptoms and decide when to see a doctor.
Some symptoms mean you should see a doctor right away. If you notice any of these, get help fast:
If you see any of these signs, seeing a doctor is important. Quick action can help you heal faster and avoid more problems.
Before your visit, get ready by collecting important info. This includes:
Being ready for your appointment helps your doctor understand your situation better. This way, they can give you the right diagnosis and treatment plan.
By knowing when to get medical help and preparing for your visit, you can tackle your shoulder and arm pain. If you’re not sure about your symptoms or what to do, always talk to a healthcare professional.
Knowing how long it takes to recover from shoulder bursitis is key. It helps set realistic goals and get the best results. We’ll show you the usual healing steps and how to keep your shoulder healthy long-term.
The time it takes to heal from shoulder bursitis depends on how bad it is and the treatment. Here’s what you can generally expect:
Being patient and sticking to your treatment plan is very important for healing right.
To manage chronic shoulder bursitis, you need to keep up with care and watch out for signs of it coming back. Here are some tips for keeping your shoulder healthy for a long time:
| Strategy | Description | Benefits |
| Regular Exercise | Gentle stretching and strengthening exercises | Improves flexibility and reduces stiffness |
| Posture Correction | Maintaining proper posture during daily activities | Reduces strain on the shoulder joint |
| Activity Modification | Avoiding or modifying activities that exacerbate the condition | Prevents flare-ups and promotes healing |
By making these habits part of your daily life, you can greatly improve your shoulder’s health. This will also lower the chance of chronic bursitis.
Shoulder bursitis can lead to pain that spreads down the arm. We’ve covered the different types of bursitis, their signs, and how doctors diagnose them.
There are many ways to treat shoulder bursitis and arm pain. These include medicines, physical therapy, and surgery. It’s important to see a doctor if symptoms don’t go away or get worse.
Preventing shoulder bursitis is also important. This can be done by keeping good posture, changing activities, and doing exercises to strengthen the shoulder. We suggest talking to a healthcare expert for advice on managing shoulder bursitis and arm pain.
Shoulder bursitis is when the bursae in the shoulder joint get inflamed. This can cause pain that spreads down the arm. It happens because of nerve pressure and muscle weakness.
Symptoms include pain and tenderness in the shoulder. You might also feel pain spreading, have trouble moving your arm, and feel numbness or tingling.
Doctors use physical exams and imaging like X-rays or MRI to diagnose it. They also rule out other causes of arm pain.
It’s caused by overuse, repetitive motion injuries, and traumatic injuries. Age and conditions like arthritis also play a role.
Treatments include anti-inflammatory meds, corticosteroid injections, and physical therapy. You might also need exercises or surgery in some cases.
Yes, home remedies like rest, ice and heat, and over-the-counter pain meds can help.
Gentle stretching and strengthening the rotator cuff can improve mobility. It also helps reduce pain.
See a doctor if you have severe pain, numbness, or tingling. Also, if symptoms don’t get better or get worse.
Recovery time varies. But, with the right treatment, most people see big improvements in a few weeks to months.
Yes, if not treated or managed well, it can cause chronic pain and discomfort.
To prevent pain, keep good posture, use proper ergonomics at work, and modify sports or activities to avoid shoulder strain.
Yes, conditions like rotator cuff injuries and cervical spine issues can have similar symptoms. So, getting a proper diagnosis is key.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!