Last Updated on November 20, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir
Blood clotting disorders can lead to serious complications if left unnoticed. Abnormalities in the body’s ability to form or dissolve blood clots may result in severe health risks. South Valley Vascular explains that the body naturally forms clots to stop bleeding. But, clots that form without injury can block blood flow and cause harm.Learn signs of a blood clotting disorder and discover the key symptoms that require immediate medical attention.
Recognizing the symptoms early is key. Common signs include unexplained leg swelling, sudden chest pain, and frequent nosebleeds. With Liv Hospital’s trusted care, understanding these symptoms of blood clotting problems can be life-saving.
Blood coagulation is key to stopping bleeding. But, disorders in this process can be very serious. It involves steps that lead to clot formation, which stops bleeding when a vessel is hurt.
The body balances bleeding and clotting well. When a vessel is damaged, platelets stick to it. Then, chemical reactions make fibrin, a protein that traps blood cells and platelets, forming a clot. This stops too much blood loss.
Key components of the coagulation process include:
Blood clotting disorders can cause too much bleeding or clots in the wrong places. Hemophilia and von Willebrand disease cause too much bleeding. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) are when clots form in the wrong places.
| Condition | Description | Symptoms |
| Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) | Clot formation in deep veins, often in the legs. | Swelling, pain, redness in the affected limb. |
| Pulmonary Embolism (PE) | Blockage of an artery in the lungs by a clot. | Sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, coughing up blood. |
| Hemophilia | Genetic disorder causing a deficiency in clotting factors. | Excessive bleeding, bruising, joint pain. |
Blood clotting disorders can lead to serious health issues if not managed. These include post-thrombotic syndrome after DVT, recurrent pulmonary emboli, and chronic bleeding leading to anemia in hemophilia.
“The risk of developing a blood clotting disorder can be influenced by genetic factors, medical conditions, and lifestyle choices. Understanding these risks is key for prevention and early intervention.”
It’s important to know the signs and symptoms of blood clotting disorders. This way, you can get medical help on time. Knowing about clotting and its complications helps manage health and seek the right care.
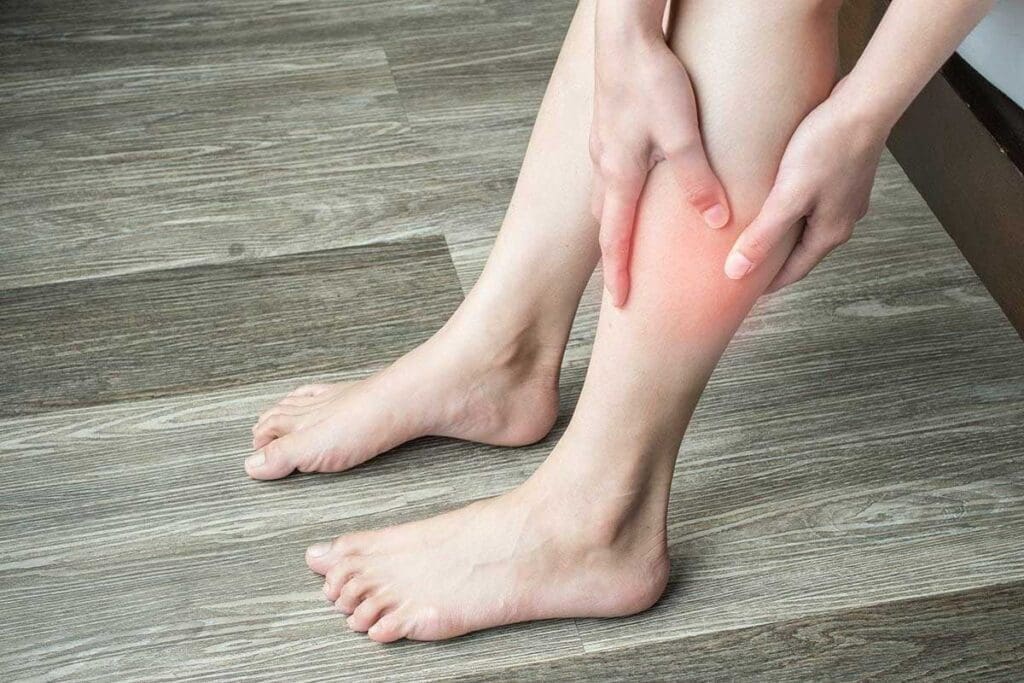
Unexplained swelling and tenderness in the legs could mean you have Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT). This is a serious condition that needs quick medical care.
DVT happens when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs. Look out for these signs:
Not everyone with DVT shows symptoms. This makes it a silent danger.
Swelling can happen in one leg (unilateral) or both (bilateral). Unilateral swelling often points to DVT. Bilateral swelling might mean heart or kidney issues.
Leg pain with swelling, redness, or warmth needs quick doctor visits. Waiting too long can cause serious problems, like pulmonary embolism.
If you notice these symptoms of blood clotting disorder, get medical help fast. Quick action can help a lot and prevent long-term harm.
Sudden chest pain and trouble breathing are warning signs of a serious issue. A blood clotting disorder can lead to a life-threatening condition called pulmonary embolism (PE). This happens when a blood clot travels to the lungs and blocks blood flow.
Pulmonary embolism is a medical emergency that needs quick action. Symptoms include sudden shortness of breath and sharp chest pain that gets worse with deep breaths. Other signs are a fast heartbeat and coughing up blood.
Recognizing the symptoms of PE is key for getting help fast. If you or someone you know has these symptoms, call for emergency help right away.
Chest pain can have many causes, from minor to serious. It’s important to know the difference to get the right treatment.
Pulmonary embolism symptoms often start suddenly. The pain from PE gets worse with deep breathing, known as pleuritic chest pain.
If you think someone has a pulmonary embolism, call emergency services right away. Keep the person calm and comfortable while waiting. Loosen tight clothes around their neck, chest, and arms to help them breathe better.
When you get to the hospital, tell the medical team everything you know. This includes any recent blood clots, travel, or being immobile.
Bruising without a clear reason might mean there’s a problem with blood clotting. Bruising happens when blood vessels get damaged, letting blood spill into the tissue. While some bruising is normal, too much or unusual bruising could mean a clotting disorder.
Spontaneous bruising, or bruising without injury, is a big warning sign. It can show up anywhere and in different sizes. Watching how often and where these bruises appear is key.
The size, where, and how long bruises last can tell us a lot. Big or long-lasting bruises might mean a problem with platelets. Unusual or frequent bruises need a closer look.
Bruising with symptoms like bleeding gums or heavy periods is a strong clue. It’s important to look at all symptoms together when checking for bruising.
Here’s a table that helps understand bruising signs of clotting disorders:
| Characteristic | Normal Bruising | Potential Clotting Disorder |
| Frequency | Occasional | Frequent or spontaneous |
| Size | Small to moderate | Large or increasing in size |
| Location | Typically on extremities | Can appear anywhere, including unusual locations |
| Duration | Resolves within a few days | Persists or recurs frequently |
| Associated Symptoms | None or minimal | May be accompanied by other bleeding symptoms |
Knowing these signs can help spot clotting disorders early. This makes it easier to get the right treatment and care.
Recurring nosebleeds and bleeding gums might signal a clotting problem. These symptoms show when blood can’t clot right. This leads to ongoing or frequent bleeding.
Clotting disorders can cause different bleeding patterns. Some people get nosebleeds often, while others have bleeding gums. How often and how bad these episodes are can tell us a lot.
Common mucosal bleeding patterns include:
It’s important to check how long and how bad mucosal bleeding is. We look at how often it happens, how much blood is lost, and any other symptoms.
| Symptom | Mild | Moderate | Severe |
| Nosebleeds | Occasional, self-limiting | Frequent, may require intervention | Recurrent, significant blood loss |
| Gum Bleeding | Minimal, occasional | Noticeable, frequent | Persistent, significant |
People with clotting disorders face more oral health problems because they bleed easily. Regular dental visits and care are key to avoiding and managing these issues.
Oral health complications may include:
It’s vital to recognize the signs of blood clotting disorders, like mucosal bleeding. Don’t ignore frequent nosebleeds and bleeding gums, even if they’re not the only symptoms.
It’s important for women to know the signs of blood clotting disorders. These symptoms can mean serious health issues if not treated right away.
Heavy menstrual bleeding, or menorrhagia, is a common sign. It means bleeding too much or for too long. This can cause anemia and other problems.
Key indicators of menorrhagia include:
Women who keep having miscarriages or pregnancy problems might have a clotting disorder. They should get checked for it.
Common pregnancy-related complications associated with blood clotting disorders include:
Hormonal birth control can raise the risk of blood clots in some women. This is more likely with birth control that has estrogen.
Women using hormonal contraception should be aware of the following risks:
It’s important to know the signs of blood clotting disorders. These disorders can show up in many ways, including neurological symptoms. These symptoms can be a sign of a serious problem.
Cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT) is when a blood clot forms in the brain’s sinuses. It can cause severe headaches, symptoms like a stroke, and changes in thinking. It’s key to recognize CVT symptoms because they need quick medical help.
Symptoms of CVT include:
Stroke-like symptoms, like sudden weakness or vision problems, can mean a blood clot disorder. Seeking immediate medical care is vital. Quick action can greatly improve outcomes.
Watch for these stroke-like symptoms:
Cognitive and vision problems can also be signs of a blood clot disorder. These can be from mild confusion to severe thinking issues and from blurry vision to total loss of sight. Seeing a healthcare professional quickly is important to find the cause and treatment.
Some cognitive and visual issues linked to blood clotting disorders include:
Noticing skin discoloration or unusual temperature changes in your extremities is key. These signs can point to blood clotting disorders. They show poor circulation or clot formation, which need quick attention.
Red or bluish discoloration in your extremities is a clear sign of blood clotting disorder. It happens when blood builds up or blood flow is blocked. You might also see swelling and tenderness.
The discoloration might not look the same everywhere. It can change in color. Watching for any changes and seeing a doctor is important if it lasts or comes with other symptoms.
Skin ulcers or wounds that won’t heal can show clotting issues. These ulcers happen when blood flow is too low to heal the tissue.
Poor circulation can damage tissue, making wounds hard to heal. If wounds aren’t healing, getting medical help is key to check for clotting disorders.
Pain and temperature changes in one area can also be signs. The area might feel warmer or cooler than the rest. This is due to inflammation or less blood flow.
These symptoms are important to watch for. They might mean there’s a clot. If you have ongoing or severe pain, and temperature changes, get medical help right away.
Abdominal pain can be a sign of a blood clotting disorder. These diseases can show up in different ways. It’s important to know the symptoms early for treatment.
Mesenteric venous thrombosis is when a blood clot blocks the veins draining the intestine. Symptoms include:
It’s key to spot these symptoms early. Mesenteric venous thrombosis can cause serious problems like intestinal ischemia.
Portal vein thrombosis is when a blood clot blocks the vein carrying blood from the intestines to the liver. Warning signs include:
Seek medical help quickly if you notice these signs. Portal vein thrombosis can harm the liver and cause serious issues.
Diagnosing blood clotting disorders that cause abdominal pain and digestive issues needs a detailed look. Doctors must think of other possible causes, like:
| Condition | Symptoms | Differential Diagnostic Features |
| Mesenteric Venous Thrombosis | Severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting | Acute onset, risk factors like clotting disorders |
| Portal Vein Thrombosis | Abdominal pain, splenomegaly, ascites | Chronic liver disease, clotting disorders |
| Gastroenteritis | Diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal cramps | Infectious etiology, often self-limiting |
For a correct diagnosis, a detailed evaluation is needed. This includes imaging and lab tests.
Prolonged bleeding after injuries or surgeries might show a clotting disorder. Clotting disorders make it hard for the body to form blood clots. This can cause too much or too long bleeding.
Patients with clotting disorders face big risks of bleeding after surgery. Excessive bleeding after surgery can be very dangerous. It might need blood transfusions, longer hospital stays, and more surgeries.
“The risk of bleeding complications after surgery is higher in patients with underlying clotting disorders,” say doctors. It’s key for patients to talk about their health history with their doctor before surgery.
It’s hard to tell if blood loss is normal or not. Normal blood loss after surgery is usually small. Any blood loss that’s more than expected should be checked out.
Things like the surgery type, the patient’s health, and their medical history affect what’s considered abnormal blood loss.
These steps are key to figuring out blood loss.
Delayed bleeding episodes happen after the first bleeding stops. They can occur days or weeks later. They might be triggered by activity or minor injuries.
“Delayed bleeding can be a challenging complication to manage, requiring prompt medical attention to prevent serious outcomes.”
Handling delayed bleeding episodes needs a detailed plan. This includes tests to find the cause and treatment to keep the patient stable.
Diagnosing blood clotting disorders requires both clinical checks and lab tests. Doctors use different tools to find the cause and plan treatment.
A complete blood count (CBC) is key. It shows details about blood, like red and white cells and platelets. Platelet count is very important because it helps prevent bleeding or clotting.
Platelet assessment looks at both count and function. Tests like platelet aggregometry check how platelets work together. This is important for making clots.
Specialized coagulation tests are also vital. They measure clotting factors in the blood. This helps find specific problems.
These tests help diagnose conditions like hemophilia and clotting factor deficiencies.
If tests show a clotting disorder or symptoms don’t go away, see a hematologist. Hematologists know a lot about blood disorders.
A hematologist can do more tests, give a detailed diagnosis, and suggest treatments.
Treatment for blood clotting disorders varies. It might include anticoagulant meds, clotting factor replacement, or other treatments. Anticoagulant therapy stops new clots or makes existing ones smaller.
For bleeding disorders, clotting factor concentrates or other agents might be used. They help with clotting and stopping bleeding.
Managing clotting disorders also means making lifestyle changes and regular check-ups. People with these disorders should work with their doctors to create a good plan.
Blood clotting disorders can cause serious health problems if not treated. It’s important to know the signs early for timely medical help.
We’ve talked about symptoms like unexplained swelling, sudden chest pain, unusual bruising, and frequent nosebleeds. These signs can really affect someone’s life. If ignored, they might lead to serious or even life-threatening conditions.
Getting a diagnosis and treatment early can greatly improve a person’s health. Knowing the signs and acting fast can help avoid serious issues.
If you or someone you know shows these symptoms, see a doctor right away. Getting the right diagnosis and treatment can help manage blood clotting disorders well.
Symptoms include swelling and pain in one leg, sudden chest pain, and trouble breathing. You might also notice unusual bruising, frequent nosebleeds, and heavy menstrual bleeding. Neurological symptoms like severe headaches and stroke-like symptoms are also possible.
If you notice swelling, pain, or bruising, see a doctor. They will check your medical history and do tests like a complete blood count. This helps them figure out if you have a disorder.
DVT is when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs. Doctors use ultrasound and physical exams to diagnose it.
PE is serious and can be life-threatening. It happens when a blood clot travels to the lungs. Look out for sudden chest pain and trouble breathing. Get medical help right away.
Yes, they can be treated. Doctors use medicines, thrombolytic therapy, and lifestyle changes. The treatment depends on the disorder’s type and severity.
Women might have heavy menstrual bleeding, recurrent pregnancy loss, and issues with hormonal contraception. These are signs of blood clotting disorders.
Doctors use physical exams, medical history, and tests like complete blood counts and imaging studies. This helps them diagnose the disorder.
See a hematologist if you suspect or have a blood clotting disorder. Or if you have a family history of it.
Complications include pulmonary embolism, stroke, and organ damage. Getting medical help quickly is key to preventing or reducing these risks.
Some disorders can’t be prevented, but you can lower your risk. Stay healthy, avoid sitting for long, and manage any health conditions you have.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!